Chap 8C - Chemical equilibria
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Describe (prediction using Le Chateller’s Principle) when temperature decrease for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) (Enthalpy < 0)
By Le Chatelier’s Principle, the system will counteract the decrease in temperature by favouring the forward exothermic reaction to release heat, so position of equilibrium will shift right
In the new equilibrium mixture, the [N2] and [H2] would be lower than the previous one while [NH3] would be higher than the previous one
Kc increase
Describe (Effect on rates of reactions) when temperature decrease for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) (Enthalpy < 0) + draw graph
Since the rates of both forward and backward reactions decrease, equilibrium is reached after a longer time
Draw conc time graph when temperature decrease for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) (Enthalpy < 0)
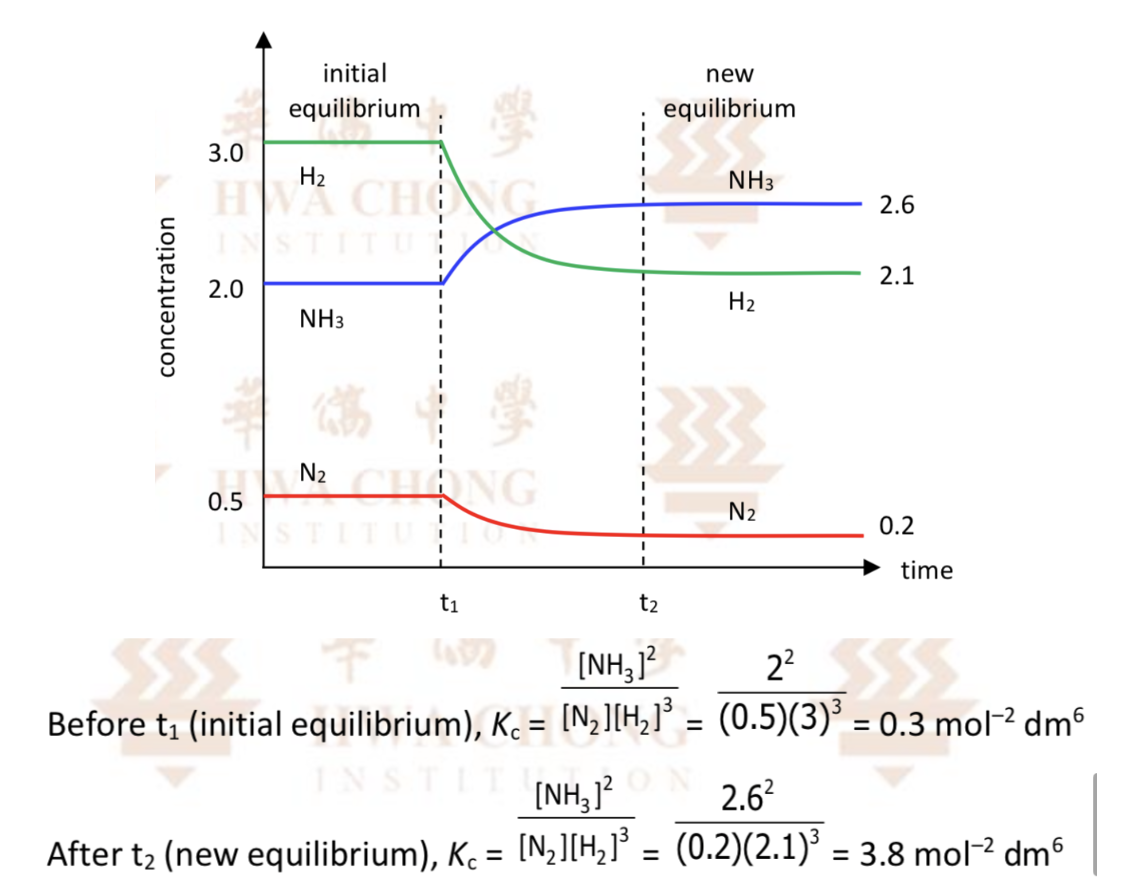
Describe (prediction using Le Chateller’s Principle) when temperature increase for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) (Enthalpy < 0)
By Le Chatelier’s Principle, the system will counteract the increase in temperature by favouring the backward endothermic reaction to absorb the added heat, so position of equilibrium will shift left
High [N2] and [H2] and lower [NH3] at new equilibrium
Kc decreases
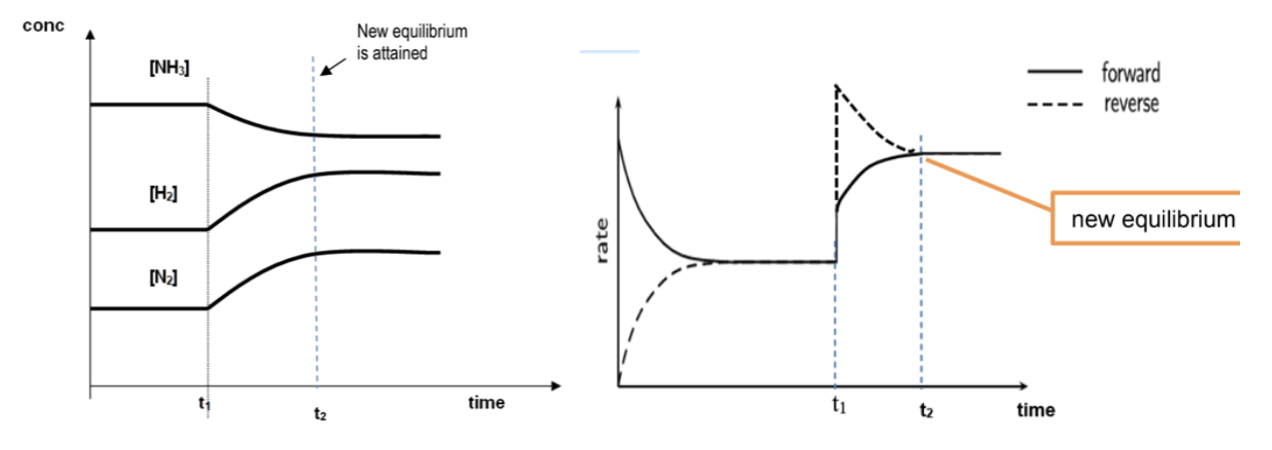
Describe (Effect on rates of reactions) when temperature increase for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) (Enthalpy < 0)
Both forward and backward reactions will become faster as KE of reactants and products increase
Backward rate increases more than forward rate as backward endothermic reaction is favoured in order to remove heat
More H2 and N2 formed and so the forward rate will start to increase while the backward rate will decrease until both rates are the equal
Since the rates of both forward and backward reactions increase, equilibrium is reached faster
Draw conc time and rate time graphs when temperature increase for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) (Enthalpy < 0)
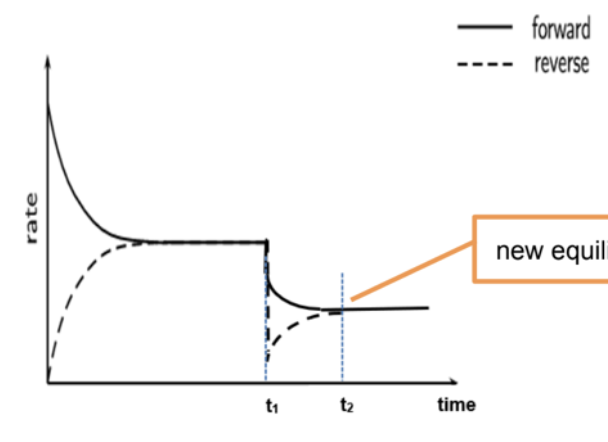
Describe effect of catalyst on POE
A catalyst lowers the activation energy of both forward and backward reactions by the same amount
Hence, both forward and backward reaction rates increase by the same extent.
The time taken to reach equilibrium is shortened.
Position of equilibrium and value of K is not affected
Explain under what conditions can inert gases be added under + its effect
Constant volume
The partial pressure (or concentration) of the reactants and products do not change though there is an increase in total pressure
Reaction is not disturbed, and the equilibrium position is unchanged
Constant total pressure
The volume of the system must increase to keep total pressure constant when an inert gas is added -> partial pressure of the reactants and products will decrease
pT = Preactant + Pproduct + Pinert gas
By Le Chatelier’s Principle, the system will counteract by shifting the position of equilibrium to the side with more gas particles present (left) to raise the partial pressures in order to overcome the disturbance
NOTE: The effect of adding inert gas at constant pressure on the equilibrium position is the
same as increasing the volume of vessel
Describe 450 degree condition for Haber process (effect on ROR at lower temp)
Since the forward reaction is exothermic, a low temperature would result in a higher yield of NH3
Rate of reaction is too slow at low temperature, and it takes a long time to establish equilibrium
High temperature increases the rate of production but results in lower yield and higher production cost
Compromise is needed and a moderately high temperature of 450°C is used to ensure a reasonable rate of production and yield
Describe 200atm of Haber process
The forward reaction takes place with a reduction in the number of gaseous particles
A high pressure will favour the desired reaction (increase yield)
Too high a pressure increases the cost of production (more expensive and stronger equipment that could withstand the high pressure needs to be used)
Describe
Catalyst |
Continuous removal of NH3 |
Molar ratio of N2 : H2 = 1 : 3 |
of haber process
Catalyst |
NOTE: Catalyst does not affect the percentage of NH3 in the equilibrium mixture |
Continuous removal of NH3 |
|
Molar ratio of N2 : H2 = 1 : 3 |
|