Theoretical Emulsification
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is an emulsion?
→ A metastable dispersion of liquid droplets in an immiscible liquid.
What is a single emulsion
A 2-component system with liquid droplets dispersed in another liquid.
What is a double emulsion?
A 3-component system with primary emulsion droplets in another liquid.
What is the droplet diameter range for pharmaceutical emulsions?
100 nm – 25 µm.
What are the common routes of administration for pharmaceutical emulsions?
Topical, parenteral, oral.
What are colloids in emulsions?
Multi-component dispersed phase systems where the disperse phase is within the size range of 1–1000 nm.
Which type of emulsion is most common in pharmaceuticals?
Oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions.
What are the characteristics of separate phases in emulsification?
Low energy
Thermodynamically favourable
Stable
What are the characteristics of an unstable dispersion in emulsification?
High interfacial energy
Thermodynamically unfavourable
Unstable
What are the characteristics of phase separation in emulsification?
Low energy
Thermodynamically favourable
Stable

How to Make Droplets Last?
🟢 Q: How does an emulsifier help stabilize droplets?
Forms an interfacial film around droplets
by Lowers interfacial energy
How to Make Droplets Last? How does a viscosity enhancer help stabilize droplets?
Inhibits droplet diffusion
Prevents droplet merging togather
Mechanisms of Emulsification
🟢 Q: How do emulsifiers aid emulsification? 3
Most emulsifiers are amphiphilic (e.g. surfactants).
Mediate molecular interactions at the phase boundary.
Lower droplet interfacial energy (γ).
Emulsion Stability
🟢 Q: What is the stability nature of emulsions?
droplets undego
Emulsions are metastable.
Droplets undergo Brownian motion and may interact with each other.
factors Affecting Emulsion Stability
🟢 Q: How do droplet interactions affect emulsion stability?
Attraction → Promotes droplet consolidation → Leads to instability.
Repulsion → Promotes droplet separation → Enhances stability.
What are the main forces in DLVO theory?
Electrical repulsion: Due to the electrical double layer.
Van der Waals attraction: Induced dipole-induced dipole interactions.
What is the key assumption of DLVO theory?
No other interaction forces exist between the particles/droplets.
How do attractive and repulsive energies behave in DLVO theory?
what do the sum of these forces detrmines ?
Attractive energy (VA) and repulsive energy (VR) change at different rates with particle distance.
The sum of these energies (VT) determines whether particles disperse or flocculate.
What happens at the primary minimum?
Net attraction occurs.
Leads to irreversible coagulation
What happens at the primary maximum?
Net repulsion occurs.
Leads to a stable dispersion.
What happens at the secondary minimum?
Net attraction occurs.
Leads to reversible flocculation.
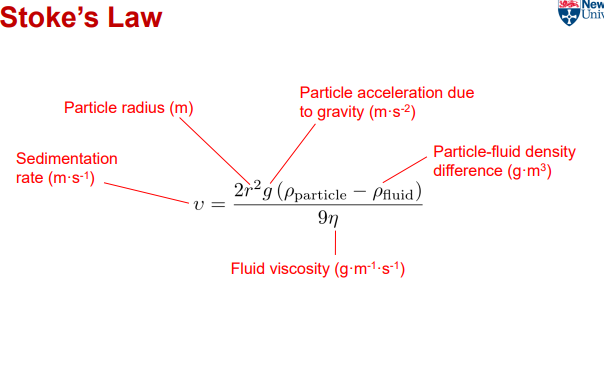
What is sedimentation in emulsions?
Particles (droplets) sink in the continuous phase due to opposing forces.
What factors promote sedimentation?
Larger droplet size=Bigger particles settle faster due to greater gravitational force overcoming fluid resistance.
Greater density difference between droplet and continuous phase
Lower fluid viscosity=less resistance, allowing particles to settle more easily.
What determines emulsion type? 2 things
1. Phase volume ratio: disperse phase typically <70%.
2. Bancroft rule: “The phase in which the emulsifier is more soluble is the continuous phase.” – Hydrophilic emulsifier → O/W emulsion. – Lipophilic emulsifier → W/O emulsion
Bancroft rule 2
1. Like associate with like.
2. Close the gap
What is the rationale behind Bancroft’s rule?
The bulkier portion of the emulsifier, whether hydrophilic or hydrophobic, tends to face outwards, determining the continuous phase.
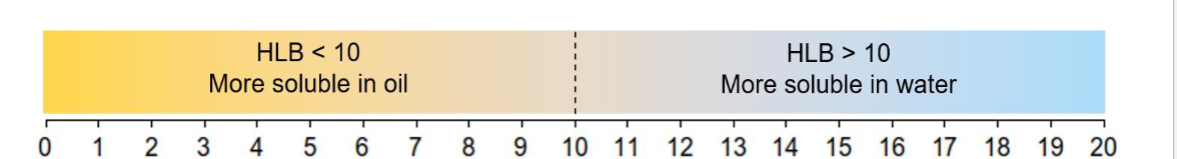
What does the Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance (HLB) indicate?
It determines whether an emulsifier is predominantly hydrophilic or lipophilic.
What does the HLB scale indicate?
It is a numerical scale indicating the overall hydrophilicity/lipophilicity of an emulsifier.
How does the HLB scale function as an ordinal scale?
if the hlb is less than 10 it is more soluble in?
if the hlb is greater than 10 it is more soluble in?
Doubling the HLB value does not necessarily make an emulsifier twice as hydrophilic.
less=oil
more=water