the skull lecture notes
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
what are the two visible junctions and which sutures meet there
bregma - the coronal and saggital sutures meet
lambda - the saggital and lambdoid sutures meet
what does the calvaria consist of?
an external and internal layer of compact bone separated by diploe
what is the diploe what specific bone does it have within it, what is special about it regarding canals?
cancellous bone which contains red bone marrow. The diploe has canals formed from the passing of diploic veins
what bones make up the calvaria
frontal bone
parietal bones
occipital bone
how many sutures does the calvaria have, name them and the bones they connect
3
lamboid suture - connects the occipital bone to the parietal bones
saggital - connects the two parietal bones
coronal - connects the frontal bone to the parietal bones
the frontal crest serves as an attachment for what?
falx cerebri
what is the longitudinal groove found in the anterior cranial fossa called (behind the frontal crest) ?
the groove for the superior saggital sinus
the margins of the superior saggital sinus provide attachment to what?
the falx cerebri
the falx cerebri are attached to what?
the margins of the superior saggittal sinus and the frontal crest
on each side of the superior saggital sinus there are several depressions what are these depressions called and how are they formed?
granular foveolae formed by the arachnoid granulations
what is a sinus?
A space in the dura matter that collects venous blood from the brain and drains it towards the internal jugular vein
what parts make up the superior border of the orbit? (the roof)
the orbital surface of the frontal bone (anterior part)
the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone (the posterior part)
anterolaterally a depression formed by the lacrimal gland
what makes up the medial border of the orbit?
the body of the sphenoid
the frontal process of the maxilla
the lacrimal bone
the orbital plate of the ethmoidal bone
what makes up the lateral border of the orbit?
the greater wing of the sphenoid bone
the orbital surface of the zygomatic bone
what makes up the inferior border of the orbit?
the orbital process of the palatine bone
the orbital surface of the body of the maxilla
what makes up the roof of the maxillary sinus?
the same structures that make up the inferior border (floor) of the orbit
orbital surface of the body of the maxilla
orbital process of the palatine bone
what bones form the orbit
frontal bone
ethmoid bone
lacrimal bone
maxilla
palatine
zygomatic
sphenoid
where is the superior orbital fissure found?
between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone
which bones form the major part of the viscerocranium?
the jaws
what bones make up the jaws?
the mandible
the maxillae - 2 paired bones
which bones form the upper jaw?
the maxillae
which bones form the lower jaw?
the mandible
which bone contains the maxillary sinus?
the maxilla
the maxilla contains which sinus?
the maxillary sinus
the maxilla take part in the formation of which structures?
the orbital cavity, nasal cavity, hard palate
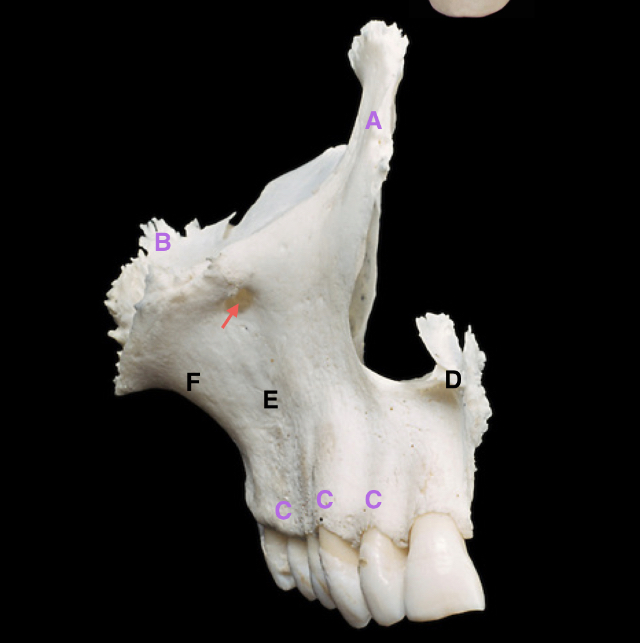
label the parts including the arrow
A - frontal process
B - zygomatic process
C - alveolar process
D - anterior nasal spine
E - canine fossa
J - jugal crest
pointed arrow - infraorbital foramen
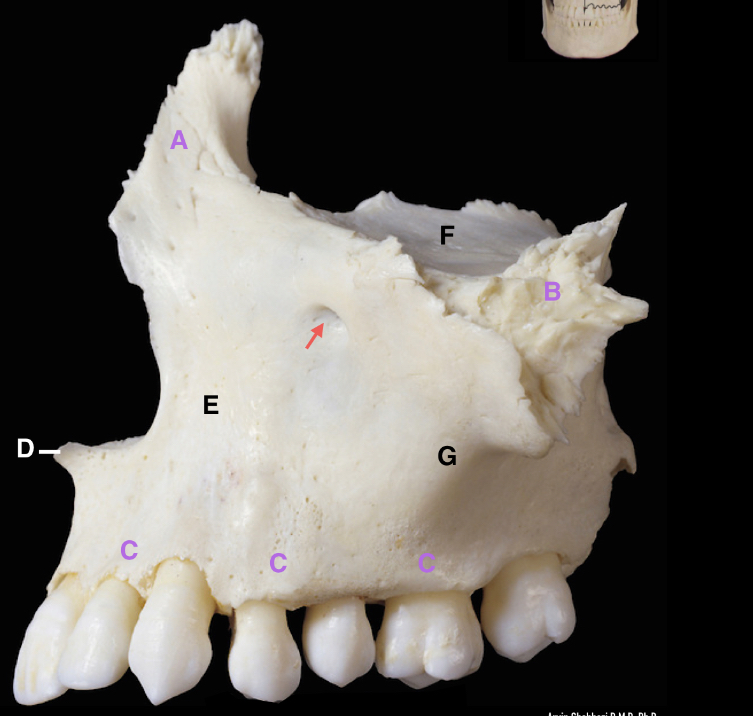
label the parts including the arrow
arrow - infraorbital foramen
A - frontal process of maxilla
B - zygomatic process of maxilla
C - alveolar process
D - anterior nasal spine
E - canine fossa
F - orbital plate of maxilla
G - jugal crest
what is the name of the suture that connects the alveolar processes of the two maxilla? and where is this suture?
The intermaxillary suture, located at the midline of the hard palate.
the two maxillae diverge laterally to form what opening?
the piriform aperture which is the bony edge around the nostrils
at the lower border of the piriform aperture in the midline there lies a bony projection termed as what?
the anterior nasal spine
the malar surface of the maxillae is concave, forming what structure?
the canine fossa
superiorly the malar surface is continuous with what structure?
The malar surface of the maxillae is continuous with the orbital plate of the maxilla and forms the floor of the orbit superiorly
what structure of the maxilla is found anteriorly to the orbital plate of the maxilla?
the frontal process of the maxilla
the frontal process of the maxilla extends to where?
the frontal process extends above the piriform aperture and meets the frontal and nasal bones
what are the processes and surfaces that make up the maxillae?
Surfaces;
infratemporal surface
the posterolateral surface of the maxilla (also known as the infratemporal surface) forms the anterior wall of what structure?
the infratemporal fossa
what structure makes up the anterior wall of the infratemporal fossa?
the posterolateral surface of the maxilla
the malar and infratemporal surfaces of the maxilla meet at a bony ridge extending from the zygotmatic process to the alveolus adjacent to the first molar tooth known as?
zygomatico-alveolar crest or the jugal crest
on which process of the maxilla is the jugal crest or the zygomatico-alveolar crest found?
the zygomatic process
the malar and infratemporal surfaces of the maxilla meet adjacent to which alveolus?
the alveolus adjacent to the first molar tooth
the posterior convexity of the infratemporal surface of the maxilla is termed as?
the maxillary tuberosity
the maxillary tuberosity has what on it? / presents what?
alveolar foramina
what is associated with the alveolar foramina? (what does the alveolar foramina transmit?)
posterior superior alveolar nerves
the posterior superior alveolar nerves supply what?
the posterior maxillary teeth
the palatine processes of the maxillae arise as what?
horizontal plates
the horizontal plates of the palatine processes of the maxillae is located where?
in the junction between the body of the maxillae and the alveolar processes of the maxillae
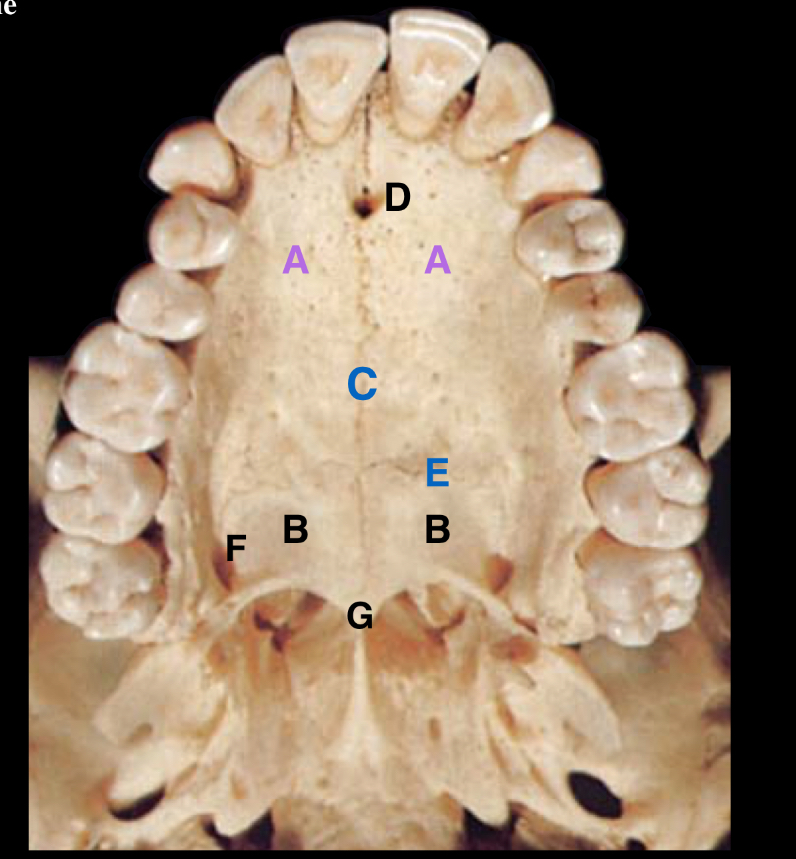
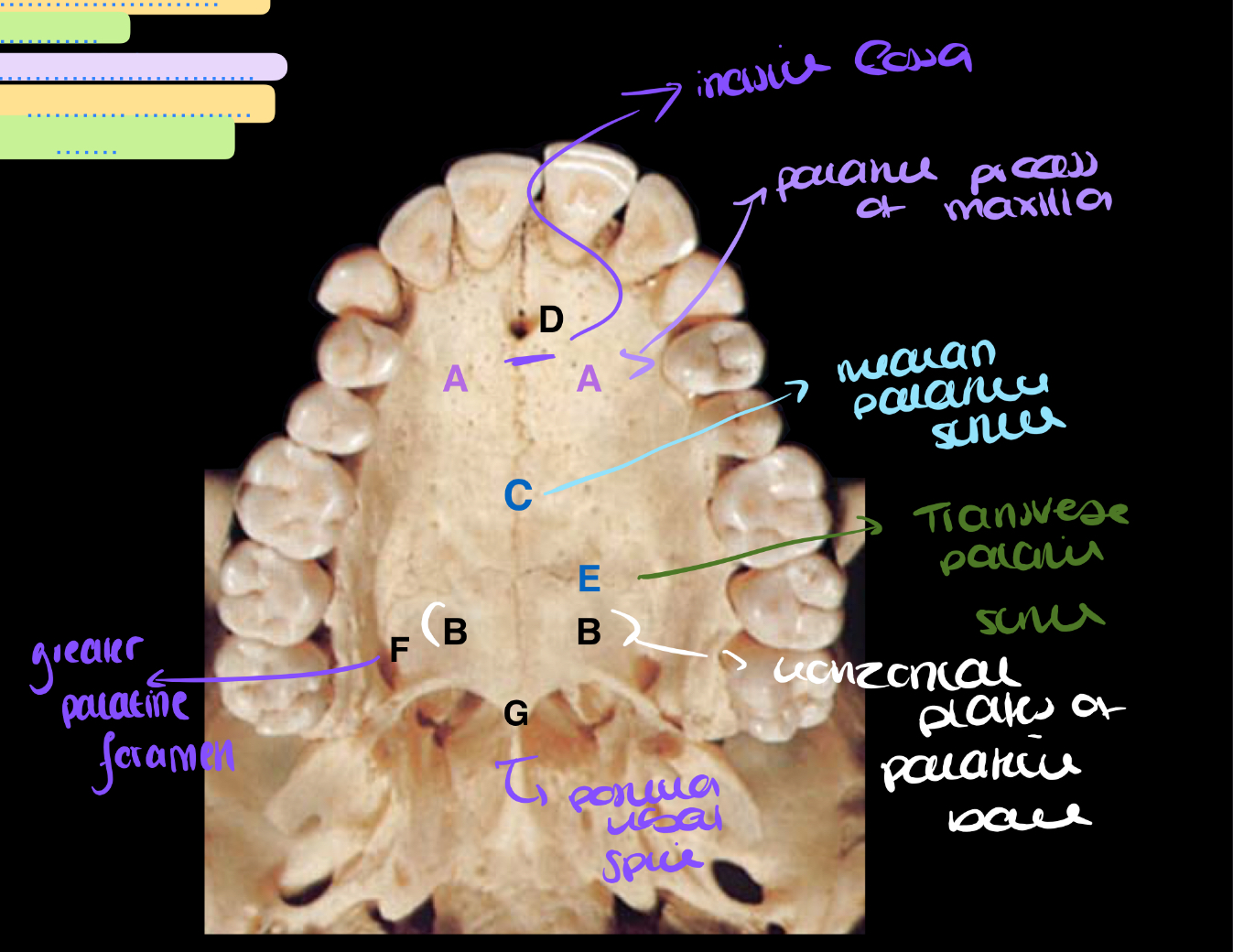
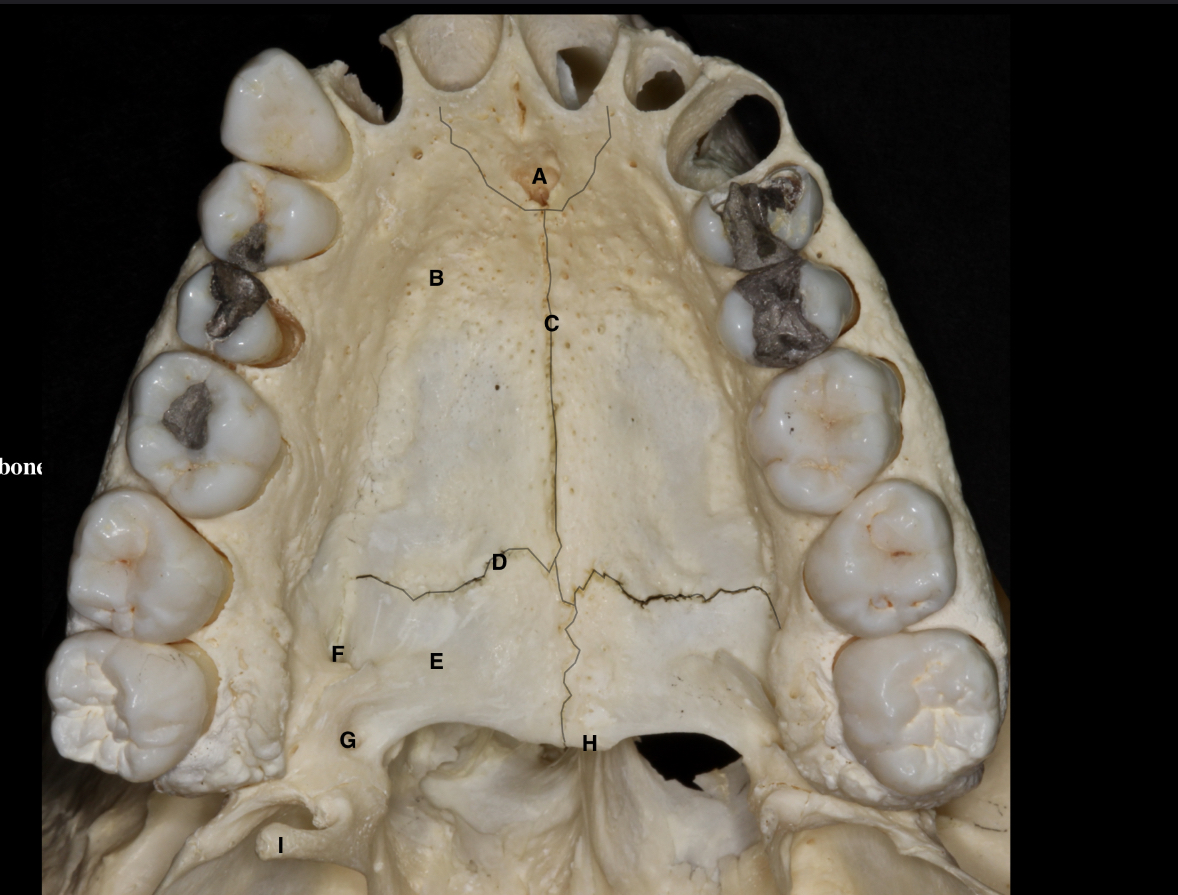
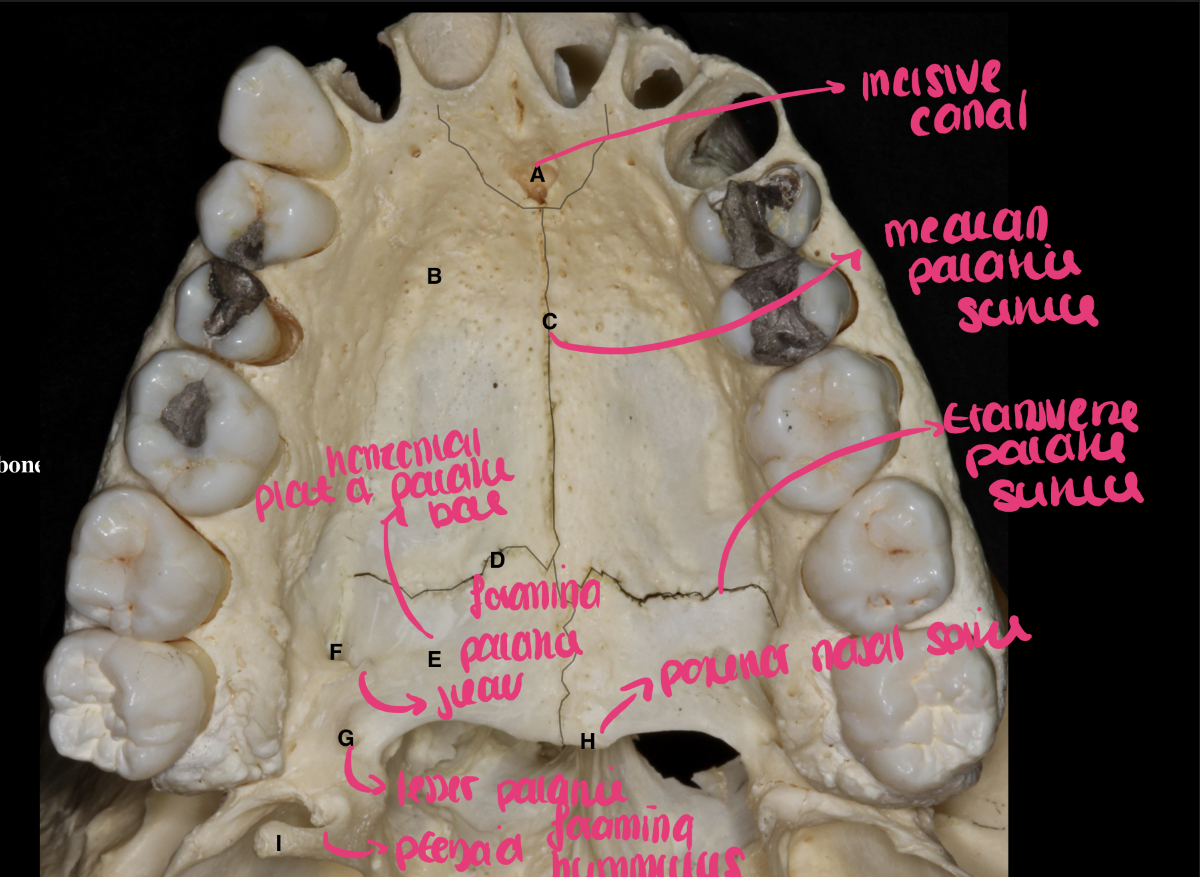
label the parts of the hard palate
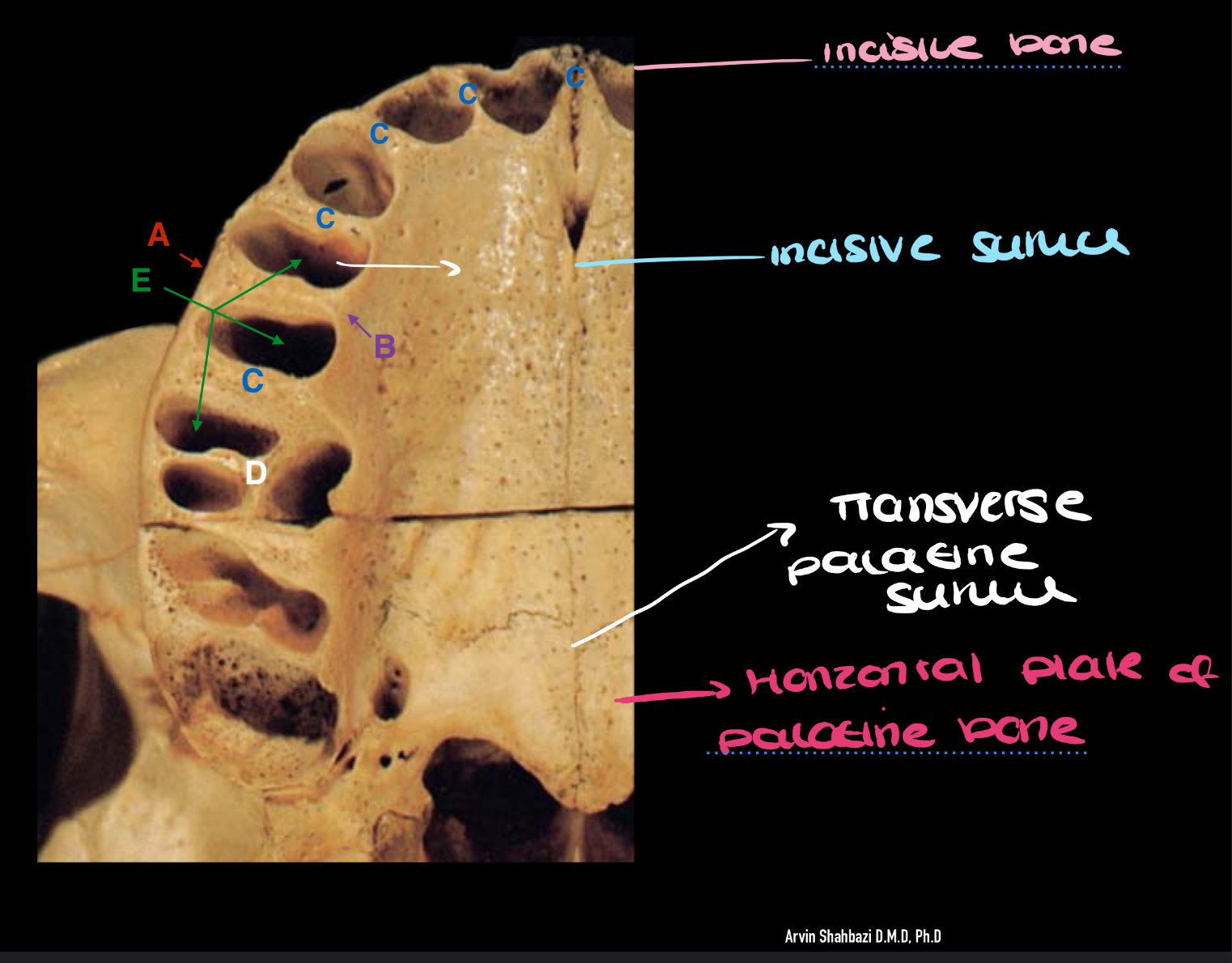
label the diagram + what is the role of the interdental bony septa ?
A - buccal alveolar plate
B - palatal alveolar plate
C - interdental bony septa - separates the alveolar sockets
D - inter-radicular septum between the buccal roots of the 1st permanent molar
E - alveolar socket or dental alveolus
the medial wall of the maxilla forms the border of which structure?
lateral wall of the nose
how is the nasolacimal canal formed?
the lacrimal groove meets the lower edge of the lacrimal bone and with the maxilla form the nasolacrimal canal
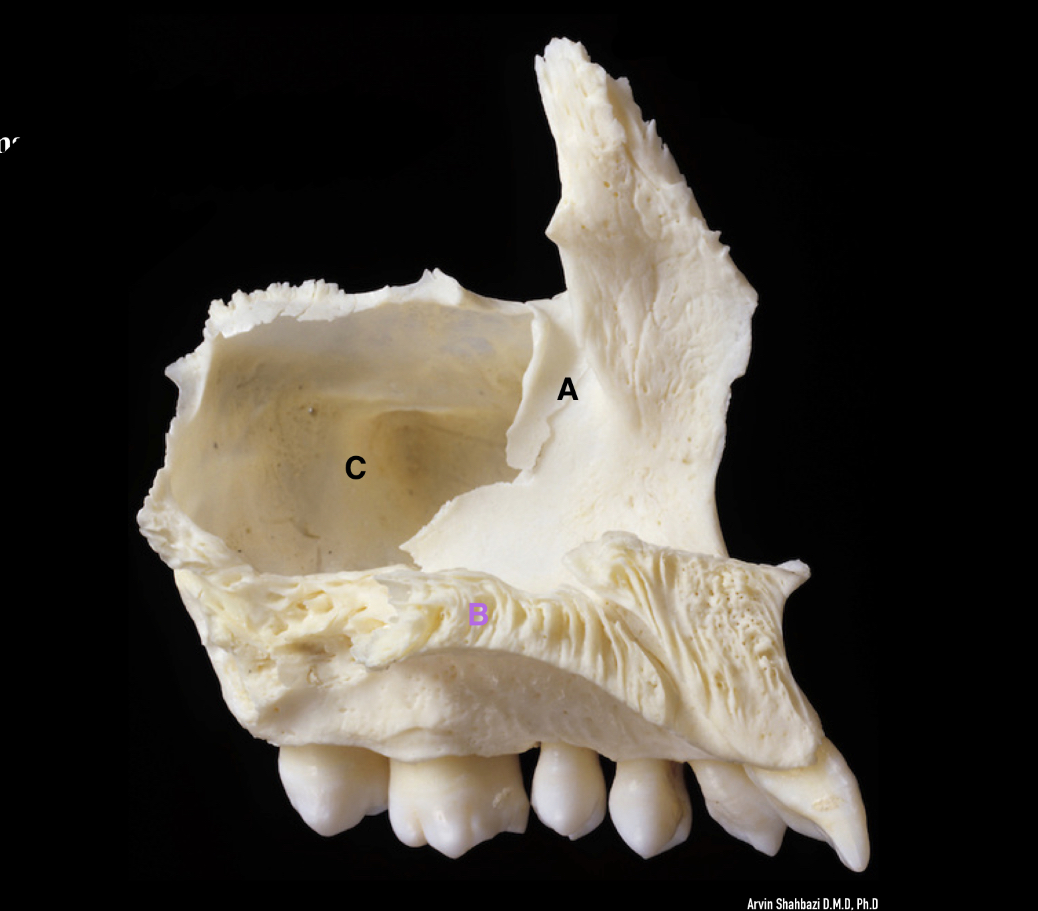
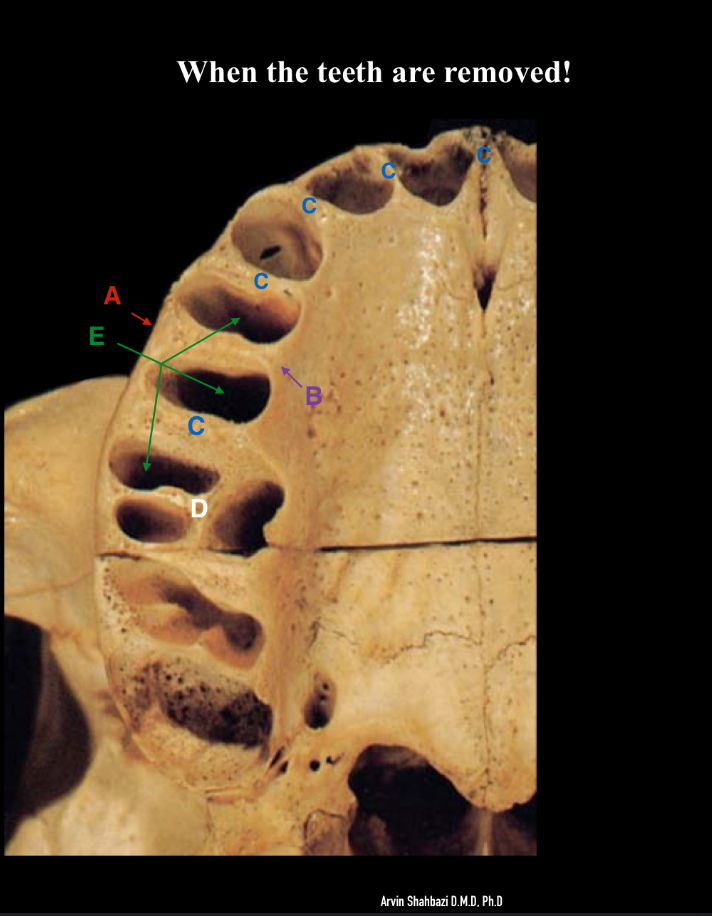
name the labelled parts
A - lacrimal groove
B - palatine process of maxilla
C - maxillary sinus
name the surfaces of the maxilla
nasal surface
orbital surface
facial surface
infratemporal surface
name the processes of the maxilla
the frontal process
the zygomatic process
the palatine process
alveolar process
what two fossae are formed by the maxilla?
the infratemporal fossa
pterygopalatine fossa
what is the shape of the maxillary sinus?
pyramidal shaped
what is the largest paranasal sinus?
the maxillary sinus
what fills the maxillary?
air, its an air filled sinus
what lines the maxillary sinus?
mucusa - the tissue lining that lines organs and body cavities and produces mucus
what cavity does the maxillary sinus connect to?
the nasal cavity
where is the maxillary sinus located? which part of which bone?
the body of the maxilla
the medial wall of the maxillary sinus forms what?
the lateral wall of the nasal cavity
the apex of the maxillary sinus extends into what process of the maxilla?
the zygomatic process of maxilla
the roof of the maxillary sinus forms what structure partly?
the floor of the orbit
the floor of the maxillary sinus is formed by what structures?
the alveolar processes and partly the palatine process of the maxilla
the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus makes up what surface?
the fascial surface of the maxilla
the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus forms which surface?
the infratemporal surface of the maxilla
the ostium (opening) of the maxillary sinus is located on which wall?
the medial wall of the maxillary sinus
the ostium of the maxillary sinus allows the maxillary sinus to open up into which meatus?
the middle nasal meatus
the maxillary sinus drains in which meatus?
the middle nasal meatus
the position of the ostium lies well above the floor of the sinus, what is wrong with this position? and what does this mean for infections?
it makes it unfavourable for drainage, which may require surgical intervention
in the maxillary sinus the roots of which teeth are found?
the pre-molars and molars
which of the teeth is the closest to the maxillary sinus?
the 2nd molar specifically the apex of its palatal root (one of the 2nd molar’s roots)
what can sometimes separate the maxillary sinus and the teeth instead of bone?
mucosa
when extracting teeth in this region why should you be careful?
Because an oro-antral fistula can form
what is an oro-antral fistula?
a pathological opening between the maxillary sinus and the oral cavity
what is the strongest bone of the face and bears the lower teeth?
the mandible
which part of the mandible carries the lower teeth and the alveolar processes?
the body of the mandible
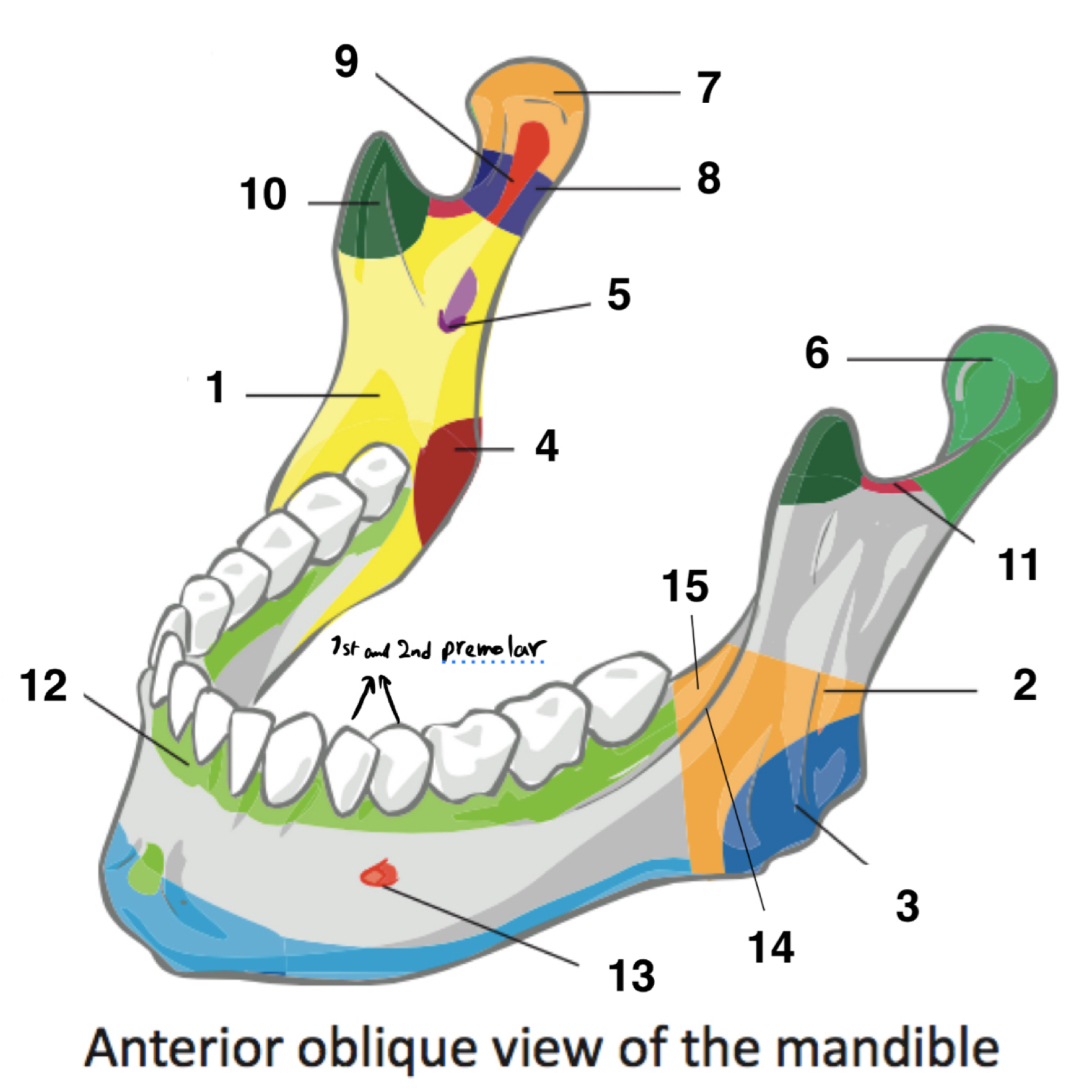
name the parts of the mandible
1 - ramus of mandible
2- angle of mandible
3 - masseteric tuberosity of mandible
4 - pterygoid tuberosity of mandible
5 - mandibular foramen
6 - condylar process of mandible
7 - head of mandible
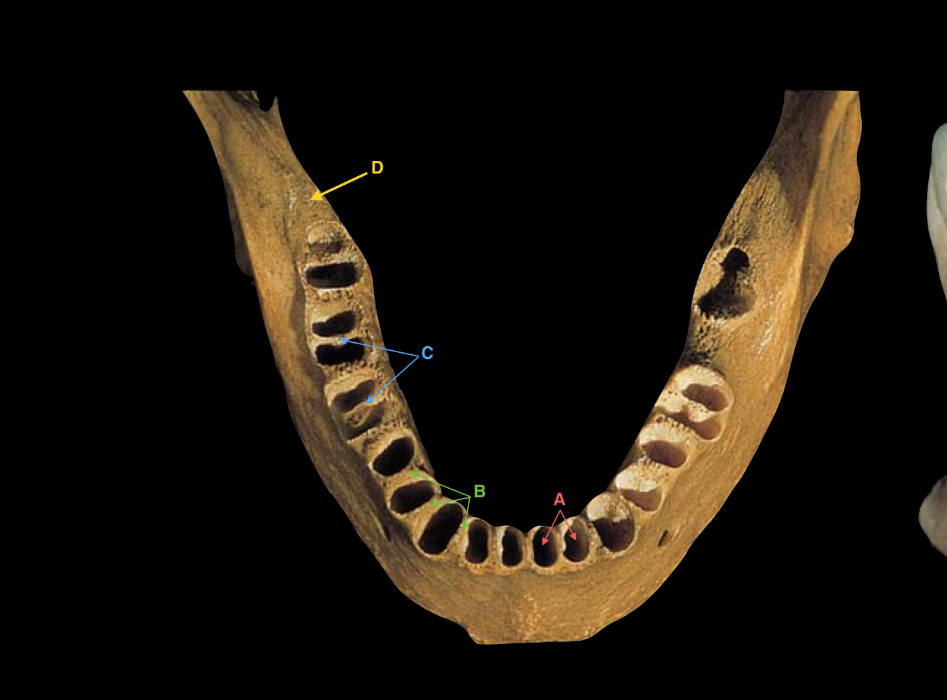
name the labelled parts of the diagram
D - retro-molar fossa (behind 3rd molar tooth)
C - inter-radicular septum
B - interdental (bony) septum
A - alveolar socket
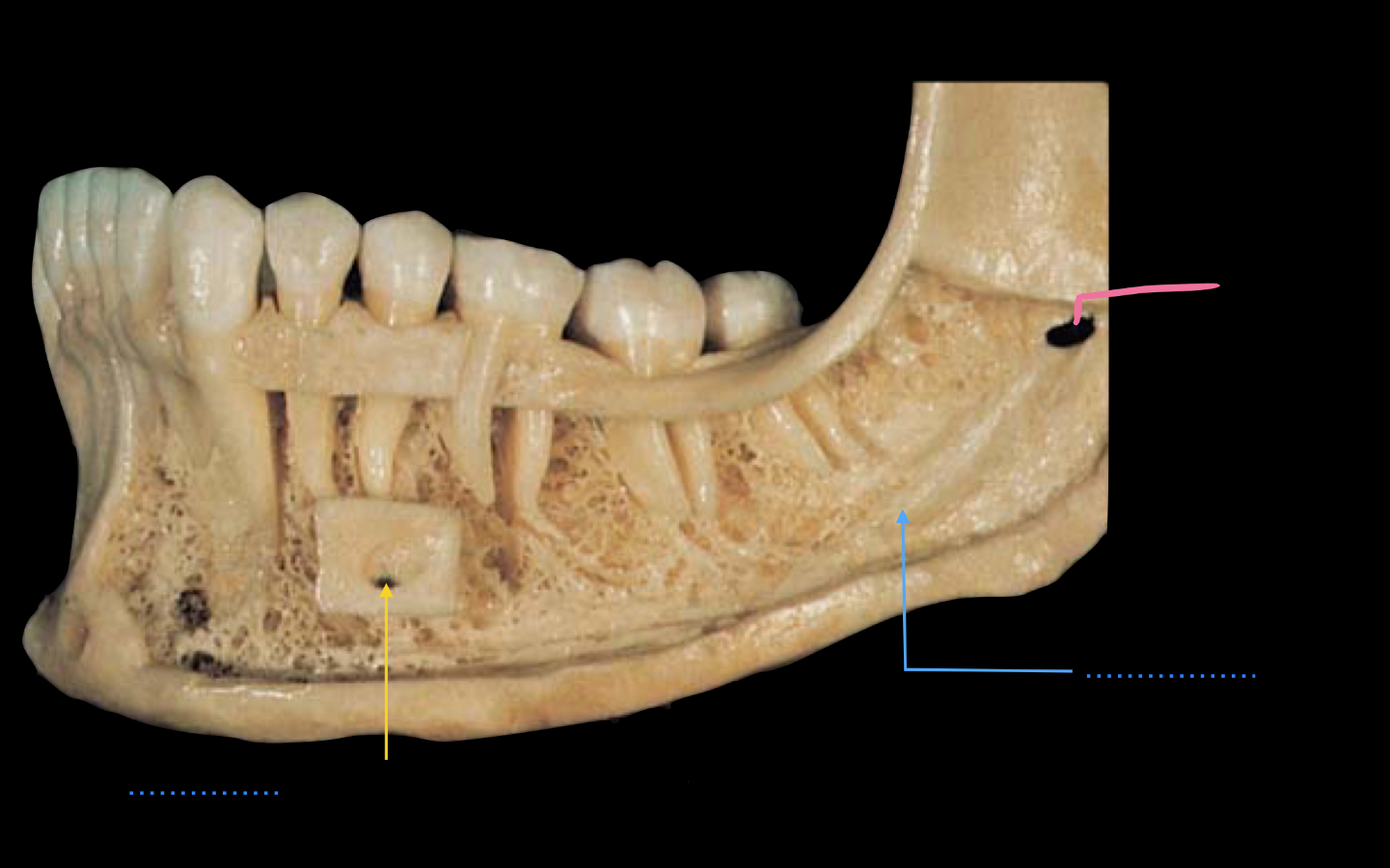
name the parts
yellow line - mental foramen (located between first and second pre-molars)
blue line - mandibular canal
pink line - mandibular foramen
the roof of the oral cavity is formed by which (two) structures?
the hard and soft palate
what is the hard palate composed of?
the incisive bone (premaxilla)
the palatine processes of the maxillae
the horizontal plates of the palatine bone
the incisive bone is what part of the maxilla and holds what sort of teeth?
the incisive bone is the ventral part of the maxilla and houses the incisor teeth
does the incisive bone develop as an independent bone or part of the maxilla completely?
it develops as an independent bone
what suture separates the maxilla from the incisive bone?
the incisive suture
the palatine process of the maxilla connects to the contralateral palatine process of maxilla through which suture?
median palatine suture
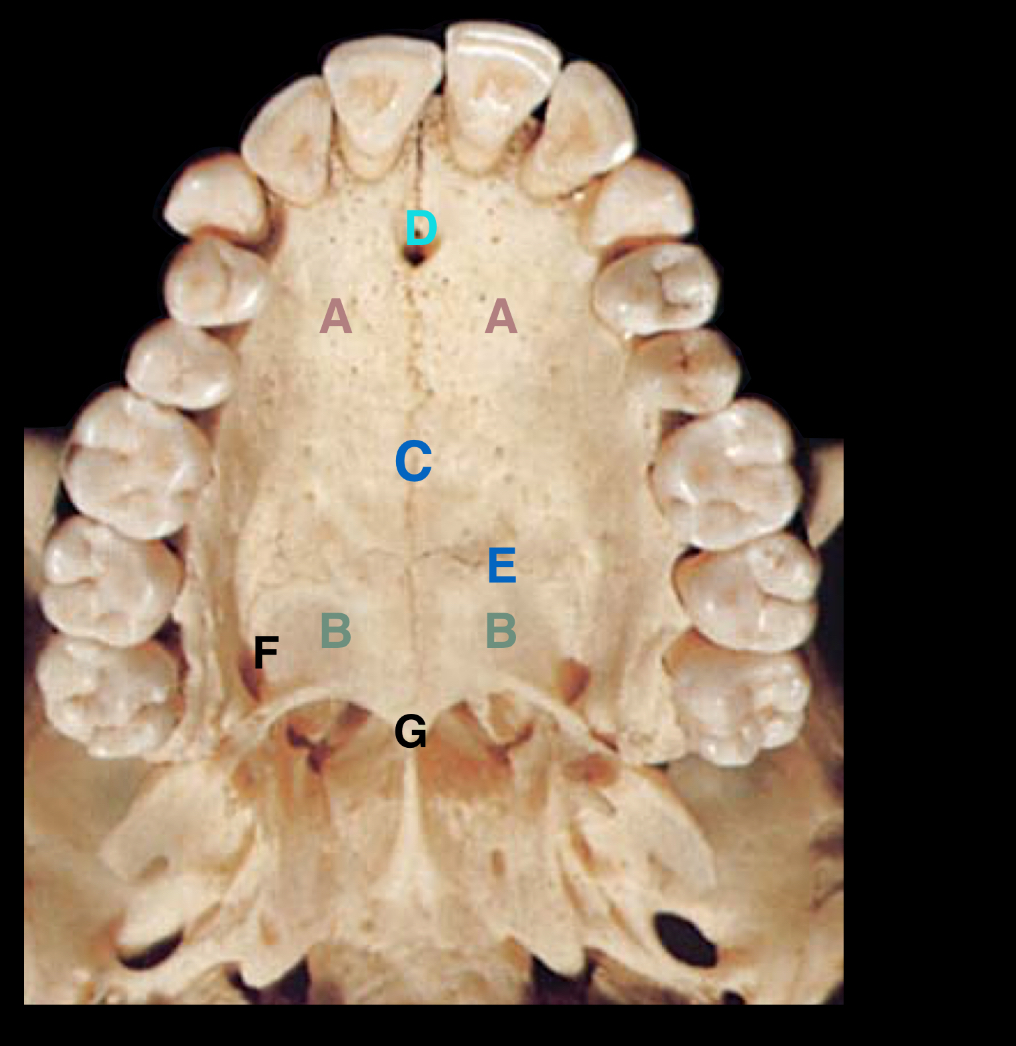
Label the parts

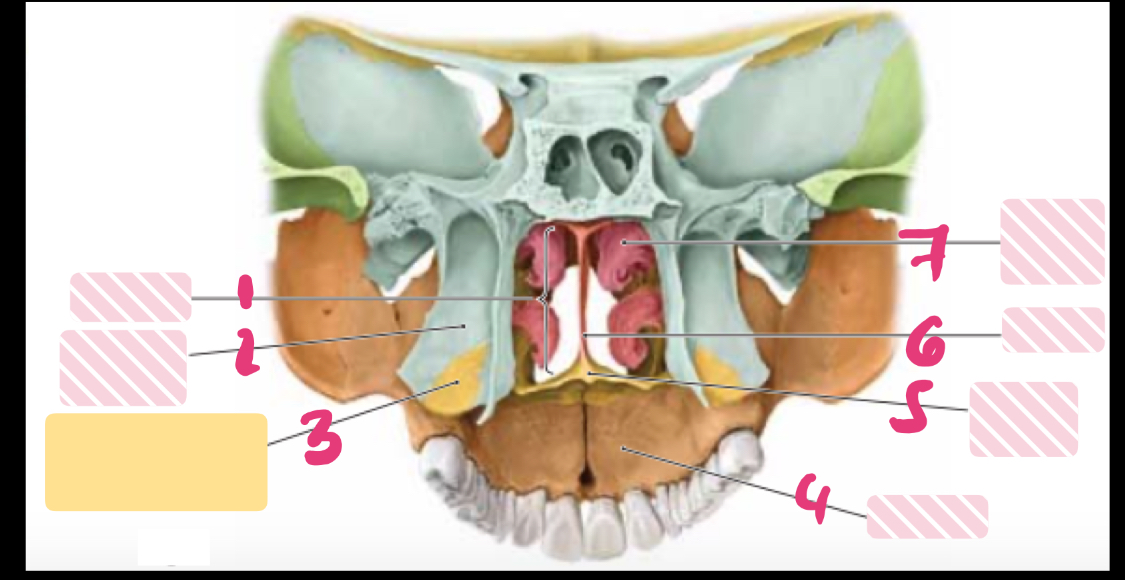
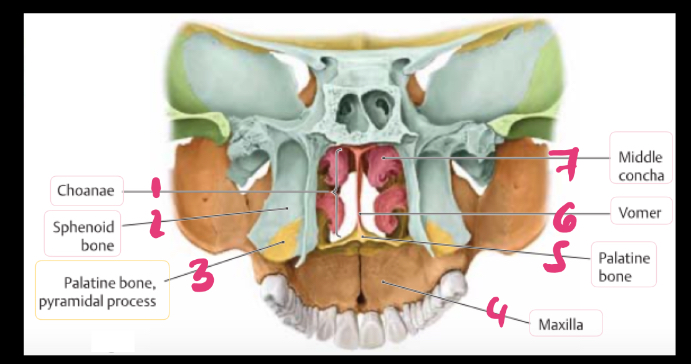
label the parts
label the parts of the hard palate
label the letters

what shape is the pterygopalatine fossa?
inverted tear drop or pyramid shaped
where is the pterygopalatine fossa?
located between the lateral the bones on the lateral side of the skull, posterior to the maxilla
what are the seven connections of the pterygopalatine fossa?
middle cranial fossa
infratemporal fossa
oral cavity (roof)
orbit cavity (floor)
nasal cavity (lateral wall)
nasopharynx
what are the walls of the pterygopalatine fossa?
anterior wall
posterior wall
medial wall
superior wall
name the bones that make up the walls for the pterygopalatine fossa
superior wall; greater wing of sphenoid bone (infratemporal surface), body of sphenoid bone
medial wall; perpendicular plate of palatine bone
posterior wall; medial and lateral pterygoid plates of sphenoid bone
anterior wall; posterior wall of maxilla (infratemporal surface of maxilla, maxillary tuber, body of maxilla)
lateral wall; pterygomaxillary fissure
inferior wall; pyramidal process of palatine bone
state the first connection of the pterygopalatine fossa
foramen rotundum connects the middle cranial fossa to the pterygopalatine fossa, contains the maxillary nerve (5.2 cranial nerve)
state the second connection of the perygopalatine fossa
Pterygoid’s canal (vidian’s canal) connects the external base of the skull to the pterygopalatine fossa
state the third connection of the pterygopalatine fossa
the palatovaginal canal /pharyngeal canal connects the pterygopalatine fossa to the external base of the skull (nasopharynx)
between which structures does the palatovaginal canal (pharyngeal canal) sits? and in reference to the pterygopalatine fossa, where is the palatovaginal canal?
the palatovaginal canal sits between the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone and the vaginal process of the sphenoid bone
The palatovaginal canal is located inferoposteriorly to the pterygopalatine fossa
the inferior orbital fissure is divided into two parts, name them
anterolateral part
posteromedial part