8 Reactivity trends
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what do grp2 metals react w water to form
an alkaline hydroxide and hydrogen gas
how does reactivity change down grp2
reactivity increases down grp2
(Be least reactive
Ra most reactive)
what is produced when a metal reacts w a dilute acid
salt and hydrogen gas
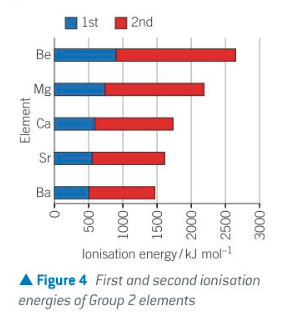
why does reactivity increase down grp2
the atoms of grp2 elements react by losing their 2 valence electrons to form +2 ions
the formation of +2 ions from gaseous atoms requires the input of two ionisation energies
ionisation energies decrease down the group because the nuclear attraction of the outer electrons decreases
this is due to increasing atomic radius and increasing electron shielding down the group
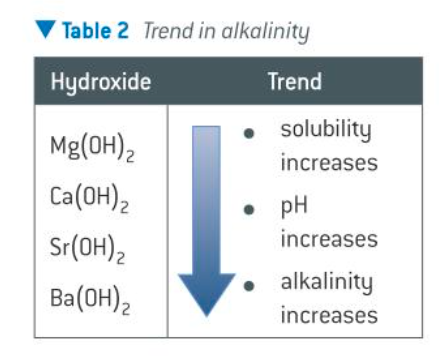
how does solubility change down grp2 hydroxides
solubility of the hydroxides in water increases down the group therefore the resulting solutions contain more OH-(aq) ions and are more alkaline
what grp2 compound is used in agriculture and what for
calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
increase the pH of acidic soils (neutralises acid in soil forming water)
what are grp2 compounds used for in medicine
antacids, treating acid indigestion
what is ‘milk of magnesia’ and the benefits
a suspension of white magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 in water
no gas produced
mostly insoluble (won’t harm body on way down)

reaction of grp2 metal + water(g)
produces metal oxide and hydrogen gas

what else can be used as an antacid and why isn’t it used as often
calcium carbonate CaCO3 but it produces carbon dioxide :(
what structure do halogens have in their solid state
they form lattices with simple molecular structures
trend in bpt down grp7 and why
bpt increases down grp
more electrons
stronger London forces
more energy required to break IMF
bpt increases
trend in reactivity down grp7 and why
reactivity decreases down grp
atomic radius increases
more electron shielding
less nuclear attraction to attract an electron from another species
reactivity decreases
what does fluorine look like at rtp
pale yellow gas
what does chlorine look like at rtp
pale green gas
what does bromine look like at rtp
red-brown liquid
what does iodine look like at rtp
shiny grey-black solid
what does chlorine solution in water and cyclohexane look like
in water: pale green
in cyclohexane: pale green

what does bromine solution look like in water and in cyclohexane
in water: orange
in cyclohexane: orange

what does iodine solution look like in water and cyclohexane
in water: brown
in cyclohexane: violet

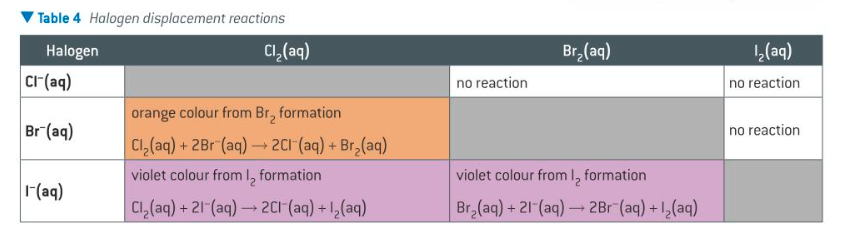
halogen-halide displacement reactions
a solution of each halogen is added to aqueous solutions of the other halides
a reaction takes place, the halogen displacing the halide from solution if more reactive
solution changes colour
what needs to be added to halogen-halide displacement reactions to distinguish the results and why
solutions of iodine and bromine in water appear a similar orange-brown colour depending on conc
add an organic non-polar solvent e.g. cyclohexane and shake
non-polar halogens dissolve more readily in cyclohexane than in water
in cyclohexane the colours are much easier to tell apart - iodine being a violet

what are the results of the halogen displacement reactions
chlorine has reacted with both Br- and I-
bromine has reacted with I- only
iodine has not reacted at all (least reactive)
which is the strongest oxidising agent in the halogens
fluorine
oxidising agent def
a reagent that oxidises (takes electrons from) another species
disproportionation
a redox reaction in which the same element is both oxidised and reduced
what is chlorine used for
water purification
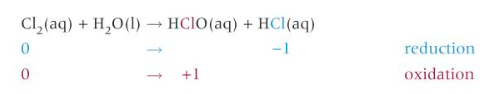
formula for chloric (I) acid
HClO
formula for chlorate (I) ions
ClO-
reaction of chlorine with cold, dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide
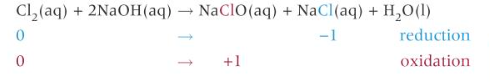
what is NaClO used for
household bleach
benefits and risks of chlorine use
kills bacteria, water safe to drink
chlorine extremely toxic gas
is a respiratory irritant in small concs., large concs. can be fatal
how are chlorinated hydrocarbons formed and what’s their risk
when chlorine in drinking water reacts with organic hydrocarbons e.g. methane formed from decaying vegetation
suspected to cause cancer
carbonate test
Add HNO3 until bubbles stop
Removes CO32- ions
Gas turns lime water cloudy
sulphate test
Add Ba(NO3)2
White ppt formed in SO42- present
Filter to remove BaSO4 ppt
halide test
Add AgNO3
Confirm with aqueous ammonia
White Cl- dissolves in dilute NH3
Cream Br- dissolves in concentrated NH3
Yellow I- doesn't dissolve
test for ammonium ion NH4+
Add NaOH(aq)
Ammonia gas NH3 released
No bubbles as very soluble in water
Warm the mixture
Test with damp (so NH3 can dissolve) red litmus paper -> goes blue
If there's ammonia given off, there are ammonium ions.
what order should you test
carbonate
sulphate
halides