Exam 4 Musculoskeletal pathophysiology
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
long bones are usually found where
upper and lower extremities
what happens to long bones after puberty
metaphysis and epiphysis fuse tog
what are short bones
irregularly shaped bones in wrists and ankles
examples of flat bones
skull, rib cage, scapula
flat bones purpose
to protect a cavity and vital rogans and to allows for other things to be attached to them
irregular bones example
vertebrae and ethmoid
where is bone marrow found
in medullary cavities of the long bones throughout the skeleton
also found in the cavities of cancellous bone in the vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and flat bones of the pelvis
red vs yellow bone marrow
red for RBC production
yellow made of adipose tissue
spongey bone
cancellous bone. has lots of bone marrow
Bone cells are nourished by diffusion from
canaliculi
Haversian canals
each canal carries 1 – 2 blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerve fibers
Volkmann canals
contain blood vessels; connect adjacent Haversian canals
The distribution of blood in the cortex occurs through the
Haversian and Volkmann canals
what is an important regulator of calcium and phosphate levels in the blood
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
PTH effect on calcium
Prevents drops in calcium levels
PTH regulation
increased calcium levels inhibits PTH release
PTH maintains serum calcium levels by inhibition of calcium release from bone, conservation by the kidneys, enhanced intestinal absorption through activation of Vit. D, and reduction of phosphate levels
PTH affect on phosphate
Prevents rises in phosphate levels
relationship of calcium and phosphate
calcium and phosphate have an inverse relationship. as one goes up the other goes down. both controlled by PTH
calcitonin actions
Inhibits the release of calcium from the bone
Causes calcium to sequester in bone cells and inhibit osteoclast activity
Reduces renal tubular reabsorption of calcium and phosphate
if someone has high calcium, give
calcitonin
Calcitonin synthesis and release is stimulated by
increase in serum calcium
calcitonin clinical uses
Paget disease
Hypercalcemic crisis
Vit. D2:
ergocalciferol
Vit. D3:
cholecalciferol
Why must Vitamin D must be converted?
Must be converted to be physiologically active and metabolized to compounds that mediate its activity
food with high vitamin D
milk, seafood, liver,
Intestinal absorption of vitamin D occurs mainly in the
jejunum
What can spontaneously convert 7-dehydrocholesterol D3 to Vit. D3
UV radiation from sunlight
The most potent Vit. D metabolite is
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-(OH)2D3)
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-(OH)2D3) actions
Increases intestinal absorption of calcium and promotes the actions of PTH on resorption of calcium and phosphate from bone
Intestinal absorption and bone resorption increase the amount of calcium and phosphorus available to the mineralizing surface of the bone
what hormones stimulate 1,25-(OH)2D3 production by the kidney
PTH and prolactin
What inhibits 1,25-(OH)2D3 production by the kidney
calcitonin
vitamin d affects
mood, depression, anxiety
Joints
are sites where 2+ bones meet
ligaments
attach to the joint capsule and bind the ends of bones together
(bone to bone)
tendons
join muscles to the periosteum of articulating bones
(muscle to bone)
dislocation
The displacement or separation of the bone ends of a point with loss of articulation
Subluxation:
partial dislocation
dislocation is often
result of trauma
seen in the shoulder and acromioclavicular (AC) joints
dislocation manifestations
Pain, deformity, limited movement/range of motion (ROM)
fractures occur when
more stress is placed on the bone than it can absorb
fractures categories (NOT classification)
Sudden injury
Most common
Fatigue or stress
Pathologic
fractures classification according to
Classified according to location, type, and direction or pattern of the fracture line
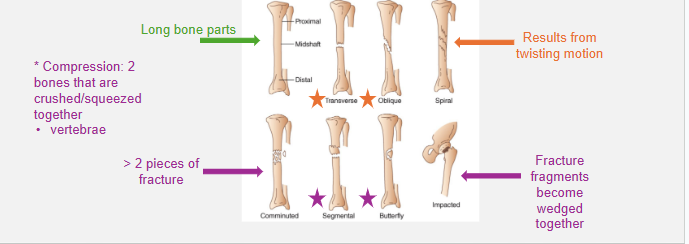
spiral fractures often seen in
domestic abuse or sexual assault
compression fractures often in
vertebrae
manifestations of fractures
Pain, tenderness at the site
Inflammation
Loss of function
Loss of nerve function
Local shock
Abnormal mobility
Deformity
Long bones: angulation, shortening, rotation
compartment syndrome
Condition of increased pressure within a limited space that compromises the circulation and function of the tissues
compartnemnt syndrome clinical manifestations
Severe pain that is out of proportion to the injury
Paresthesias, diminished reflexes, loss of motor function
compartment syndrome treatment
Removal of restrictive devices
Casts, splints, dressings
Elevating extremity to reduce edema
Fasciotomy
Incision of the fascia to separate it to allow for compartment to decompress
Those with a lower extremity fracture are at risk for
VTE
fat embolism syndrome (FES)
life-threatening manifestations resulting from the presence of fat droplets in the small blood vessels of the lung, kidneys, brain after a long bone or pelvic fracture
FES pathogenesis
Unclear mechanism… thought to result from fat droplets that are released from the marrow or adipose tissue at the fracture site into the venous system through a torn vein
FES manifestations
Respiratory failure: chest pain, shortness of breath, tachycardia, cyanosis
Cerebral dysfunction: confusion, change in behaviors, disorientation, seizures
Skin and mucosal petechiae: chest, axillae, neck, shoulders
FES diagnosis
arterial blood gas
FES treatment
Correct hypoxemia, inflammation, maintaining fluid balance
Osteopenia
reduction in bone mass greater than expected for age, race, or sex
occurs due to a decrease in bone formation, inadequate bone mineralization, or excessive bone deossification
major causes of osteopenia
Osteoporosis
Osteomalacia
Malignancy (multiple myeloma)
Endocrine disorders (hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism)
osteoporosis
Characterized by a loss of mineralized bone mass causing increased porosity of the skeleton and susceptibility to fractures
Often associated with the aging process
osteoporosis Imbalance between bone resorption and formation
Resorption > formation
Some things that my contribute to osteoporisis
Poor nutrition and decreased physical activity
Age-related decrease in intestinal absorption of calcium due to deficient activation of Vit. D
Postmenopausal osteoporosis
Estrogen deficiency… loss of cancellous bone and predisposition to fractures of the vertebrae and distal radius
Secondary osteoporosis risk factors
Endocrine disorders: hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, Cushing syndrome, DM
Malignancies: multiple myeloma
Alcohol use disorder
Alcohol is a direct inhibitor of osteoblasts and inhibits calcium absorption
Medication use: corticosteroids (prednisone), aluminum-containing antacids, anticonvulsants
when do people usually recognize they have osteoporosis
The first manifestations of the disease typically accompany a fracture. It is often a silent disorder
clinical manifestations of osteoproriss
Loss of height
Kyphosis
Systemic symptoms (weakness, fatigue, pain) are suggestive that osteoporosis is caused by an underlying disease process
more common in Secondary osteoporosis
best way to diagnose osteoporosis
Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
osteoporosis treatment
Regular exercise
Calcium supplementation
Vit. D supplementation
Antiresorptive agents
Estrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
Bisphosphonates
Calcitonin
Anabolic agents
is pain a normal part of the aging process?
pain is NOT part of natural aging process. pain means something is wrong. never write off pain because someone is old
Osteomalacia and Rickets are characterized by
softening of bone but not loss of bone
who is affected by Osteomalacia and Rickets
Osteomalacia - adults
Rickets- children
Osteomalacia 2 main causes
Insufficient calcium absorption from the intestine due to lack of dietary calcium or deficiency of or resistance to the action of Vit. D
Phosphate deficiency due to increased renal losses or decreased intestinal absorption
Osteomalacia can lead to
chronic renal failure called renal rickets
Osteomalacia clinical manifestations
Bone pain and tenderness
Fractures (with disease progression)
Muscle weakness
Severe cases
Slightly reduced serum calcium levels
what is the best way to treat osteomalacia
Treat the cause…
Nutrition
Sun exposure
rickets etiology
Kidney failure
Malabsorptive syndromes (celiac disease, cystic fibrosis)
Medications (anticonvulsants, aluminum-containing antacids)
Nutritional rickets
Results from inadequate sunlight exposure or inadequate intake of Vit. D, calcium, phosphate
clinical manifestations of rickets
Bone deformities
Unmineralization
Enlarged and soft skull
Delayed closure of fontanels
Deformities are likely to affect the spine, pelvis, and long bones
Lumbar lordosis and bowing of the legs
rickets treatment
Nutrition
Diet with calcium, phosphorus, and Vit. D
Supplementation
Sunlight exposure
Paget Disease progression
onset - marked by regions of rapidly occurring osteoclastic bone resorption
later progresses to period of hectic bone formation with increased osteoblasts rapidly depositing bone in a chaotic manner
leads to poor quality bones… bowing and fractures
Localized to the spine, skull, hips, pelvis
pagat disease etiology
Genetic and environmental influences
big genetic component!! if first degree relative has it your chances go way up
Paget Disease: Clinical Manifestations
often asymptomatic but can have many manifestations
Paget Disease: Clinical Manifestations head
Headache, intermittent tinnitus, vertigo, eventual hearing loss
Paget Disease: Clinical Manifestations spine
Kyphosis of the thoracic spine
Paget Disease: Clinical Manifestations femur and tibia
Bowing
Coxa vara
Reduced angle of the femoral neck due to softening
Waddling gait
Paget Disease: Clinical Manifestations neurocognitive
Nerve palsy syndromes
Mental decline
Paget Disease: Clinical Manifestations cardiovascular
High-output heart failure
Calcific aortic stenosis
Most common cause of death…
order of pagets disease osteogenic carcinomas
Femur 🡪 pelvis 🡪 humerus 🡪 tibia
Paget disease diagnosis
Based upon bone deformity characteristics and XR changes
Bone scans
Bone biopsy
paget disease treatment
Pain: NSAIDs, anti-inflammatory agents
Suppressive agents: bisphosphonates, calcitonin
Prevent further spread and neurologic deficits
paresthesia
the sensation of tingling, burning, pricking or prickling, skin-crawling, itching, “pins and needles” or numbness on or just underneath your skin.
should you elevate or lower a limb with compartment syndrome
elevate (reduces edema)
what does vitamin d do
help the body absorb and retain calcium and phosphorus
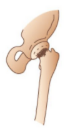
what kind of fracture is this
impacted
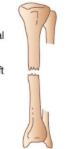
what kind of fracture is this
transverse
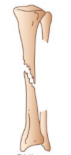
what kind of fracture is this
oblique

what kind of fracture is this
spiral
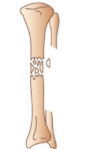
what kind of fracture is this
communited

what kind of fracture is this
segmental

what kind of fracture is this
butterfly
A client with a closed reduction of a wrist fracture has a plaster cast applied. Which nursing intervention is the highest priority immediately after the procedure?
Performing a peripheral circulation assessment
The nurse caring for a child with a deficiency in vitamin D knows that the deficiency places the child at risk for:
rickets
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Systemic iimmune mediated joint inflammatory disease