Era 2, 1450 - 1750 CE: The British Empire + Protestant Reformation (Quizlet #13)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1. Era 2 Maritime Based Empires, , 1450 - 1750 CE:
-During Era 2, 1450 - 1750 CE, the Netherlands (Dutch) joined the frenzy of mercantilism and ocean exploration along with the other maritime powers
-these maritime powers now included the Portuguese, British, French, Dutch and Spanish, who all fought for control of the new resource rich territory in the Americas
-These maritime (ocean based) empires held territory in:
-Portuguese (Brazil, Sub-Saharan Africa including Angola from Nzinga, South and Southeast Asia )
-Spanish (South and Central America, Caribbean, Southeast Asia including the Phillipines)
-Dutch (Americas, Caribbean, South Africa, South and Southeast Asia)
-British (North America, Caribbean, Africa, South Asia/India, Southeast Asia and Australia...the sun never sets on the British Empire!)
-Slavery and coerced [forced] labor was a major part of what made these empires profitable
![<p>-During Era 2, 1450 - 1750 CE, the Netherlands (Dutch) joined the frenzy of mercantilism and ocean exploration along with the other maritime powers</p><p>-these maritime powers now included the Portuguese, British, French, Dutch and Spanish, who all fought for control of the new resource rich territory in the Americas</p><p>-These maritime (ocean based) empires held territory in:</p><p>-Portuguese (Brazil, Sub-Saharan Africa including Angola from Nzinga, South and Southeast Asia )</p><p>-Spanish (South and Central America, Caribbean, Southeast Asia including the Phillipines)</p><p>-Dutch (Americas, Caribbean, South Africa, South and Southeast Asia)</p><p>-British (North America, Caribbean, Africa, South Asia/India, Southeast Asia and Australia...the sun never sets on the British Empire!)</p><p>-Slavery and coerced [forced] labor was a major part of what made these empires profitable</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f5bea893-41e5-4967-a830-3b8afeef3ff8.jpg)
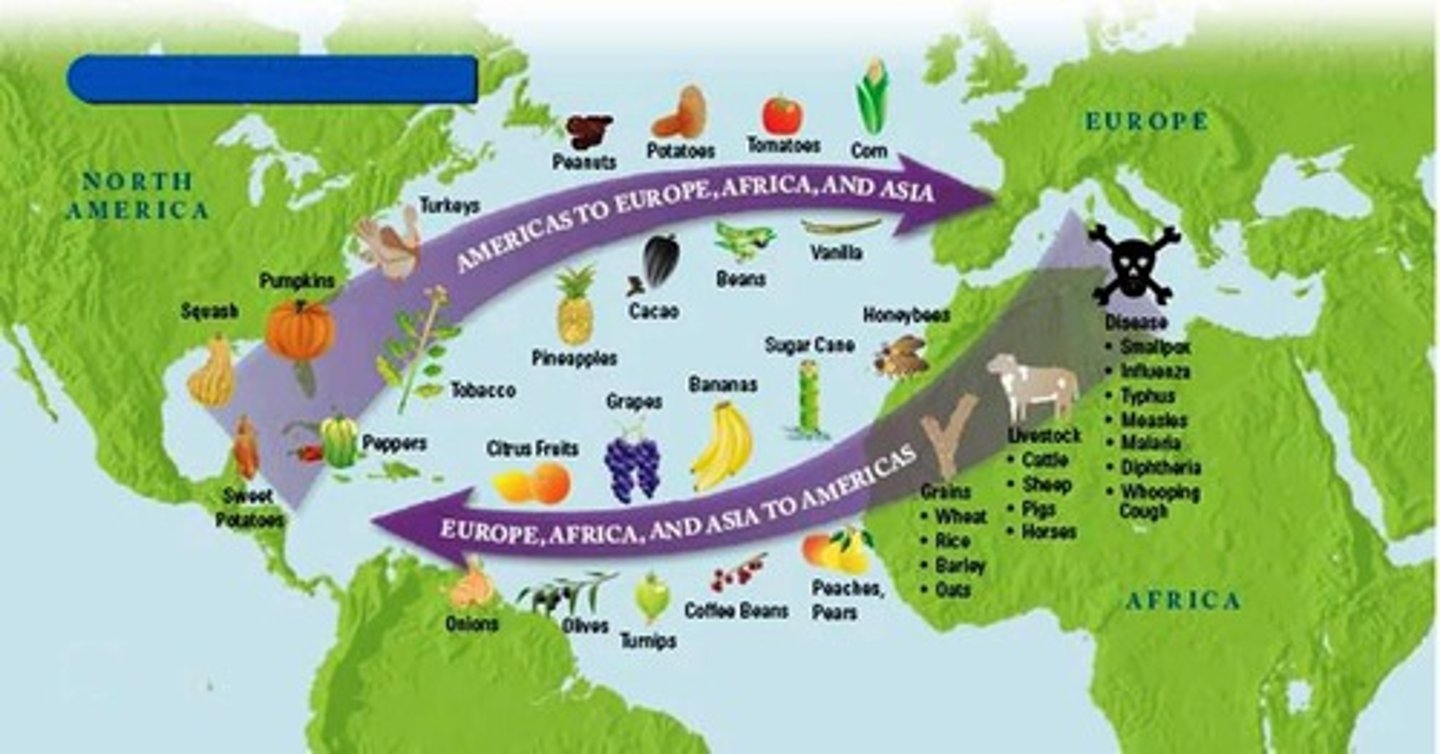
2. Major Event of Era 2: The Columbian Exchange
-After the wild success of the "Travels of Marco Polo," the Europeans were motivated to explore to get to China and the Europeans take to the oceans in order to begin exploration
-Using naval technology such as the magnetic compass, astrolabe, square and lateen sails, and axial rudder, much of which diffused through the Afro-Eurasian trade networks, the Europeans are motivated to take increasingly bigger and biggers risks on the open ocean
-Christopher Columbus, having read Polo's book, "discovers" [accidentally runs into] the New World accidentally; he begins the Trans-Atlantic slave trade and puts the indigenous islanders under a brutal regime of coerced labor; the Spanish conquistadores topple the proud Incan and Aztec Empires in the early 1500's
-Once the Americas are discovered, the Europeans begin to colonize it; this sets off a MASSIVE exchange of goods, foods, diseases, and other things known as the Columbian Exchange
-The Middle Passage and use of enslaved persons formed the backbone of the economy of many of the new European maritime empires in the Americas, as Western Europe's hegemony [power] skyrockets
![<p>-After the wild success of the "Travels of Marco Polo," the Europeans were motivated to explore to get to China and the Europeans take to the oceans in order to begin exploration</p><p>-Using naval technology such as the magnetic compass, astrolabe, square and lateen sails, and axial rudder, much of which diffused through the Afro-Eurasian trade networks, the Europeans are motivated to take increasingly bigger and biggers risks on the open ocean</p><p>-Christopher Columbus, having read Polo's book, "discovers" [accidentally runs into] the New World accidentally; he begins the Trans-Atlantic slave trade and puts the indigenous islanders under a brutal regime of coerced labor; the Spanish conquistadores topple the proud Incan and Aztec Empires in the early 1500's</p><p>-Once the Americas are discovered, the Europeans begin to colonize it; this sets off a MASSIVE exchange of goods, foods, diseases, and other things known as the Columbian Exchange</p><p>-The Middle Passage and use of enslaved persons formed the backbone of the economy of many of the new European maritime empires in the Americas, as Western Europe's hegemony [power] skyrockets </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8e7ad492-c752-4862-a438-e3817975eed7.jpg)
3. Dutch East India Company (VOC) 1602
-The Dutch, like the Portuguese, also established a powerful trading post empire
-They did it in India and Africa with a very powerful JOINT STOCK COMPANY that was started in 1602
-Unlike the Portuguese, this was a private company that required people to buy stock; if the company was successful, they got massive profits
-This company established trading posts and a Trading Post Empire all over the world and the merchants who ran it were very powerful; the VOC held trading posts and colonies in the Americas, the Caribbean, Africa, and Asia
-Dutch merchants used advanced ship design to their advantage, and their "fluyts" which allowed them to build ships that required half the crew and carried double the cargo of European rivals.
-The Dutch Empire became rich based on trade in spices, silks, porcelain, tobacco, sugar, cotton, silver, gold, Asian tea, coffee
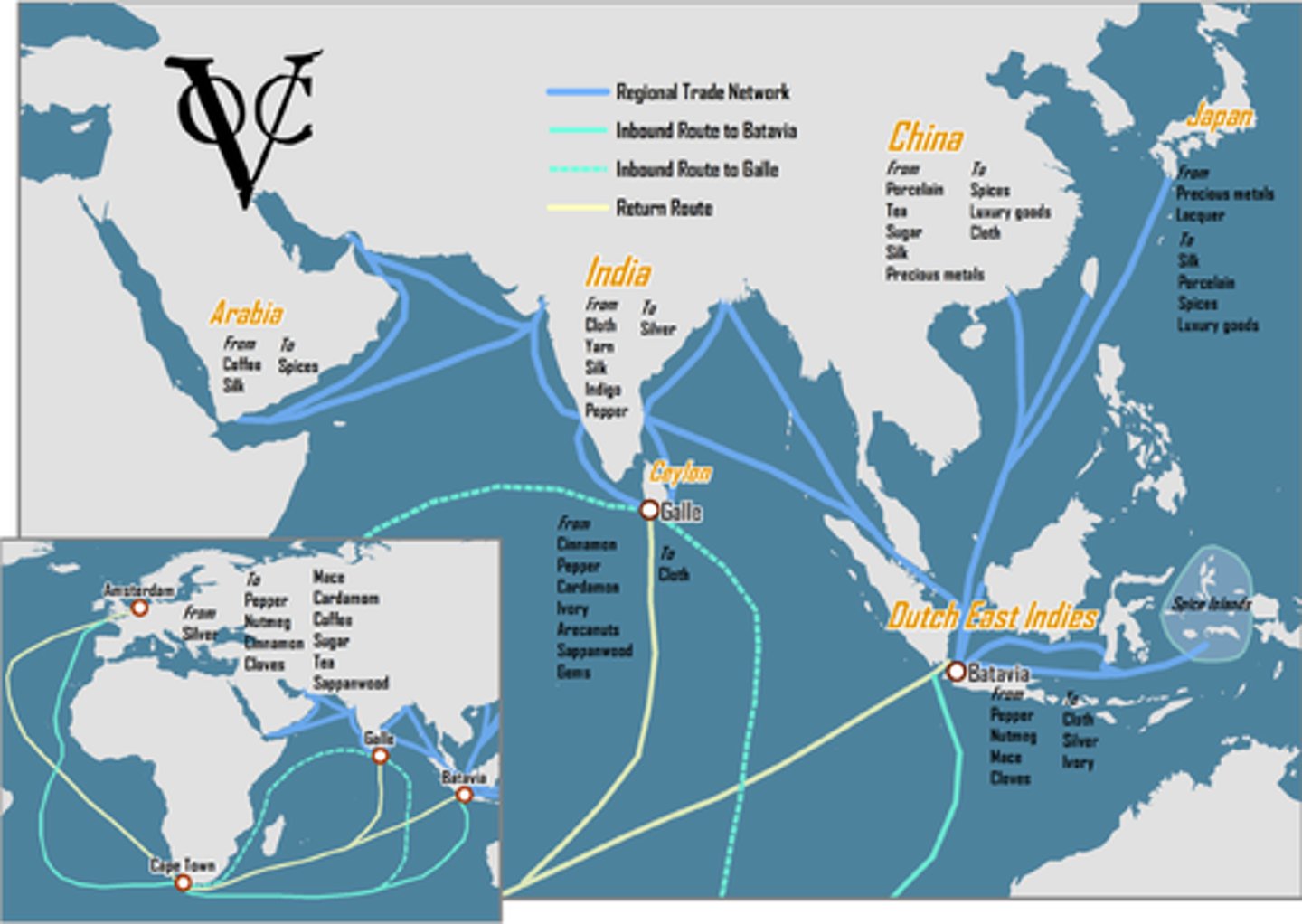
4. The Maritime Dutch Empire, Era 2: 1450 - 1750 CE
-During Era 2, 1450 - 1750 CE, the Netherlands (Dutch) joined the frenzy of mercantilism and ocean exploration along with the other maritime powers
-these maritime powers included the Portuguese, British, French, and Spanish, who all fought for control of the new resource rich territory in the Americas
-The Dutch would establish a foothold in New Netherlands in 1609, which would become New York when the British bought it from the Dutch in 1674
-Aided by the efforts of the Dutch East India Company (VOC), the Dutch also built trading posts in Africa and Asia, establishing colonies in South Africa at Cape Town and in India and Southeast Asia
-Dutch merchants used advanced ship design to their advantage, and their "fluyts" which allowed them to build ships that required half the crew and carried double the cargo of European rivals.
-The Dutch Empire became rich based on trade in spices, silks, porcelain, tobacco, sugar, cotton, silver, gold, Asian tea, coffee all around the world
-As with the other European Maritime Empires of Era 2, 1450-1750 CE, the Dutch profited from coerced labor/slavery in all of their colonies
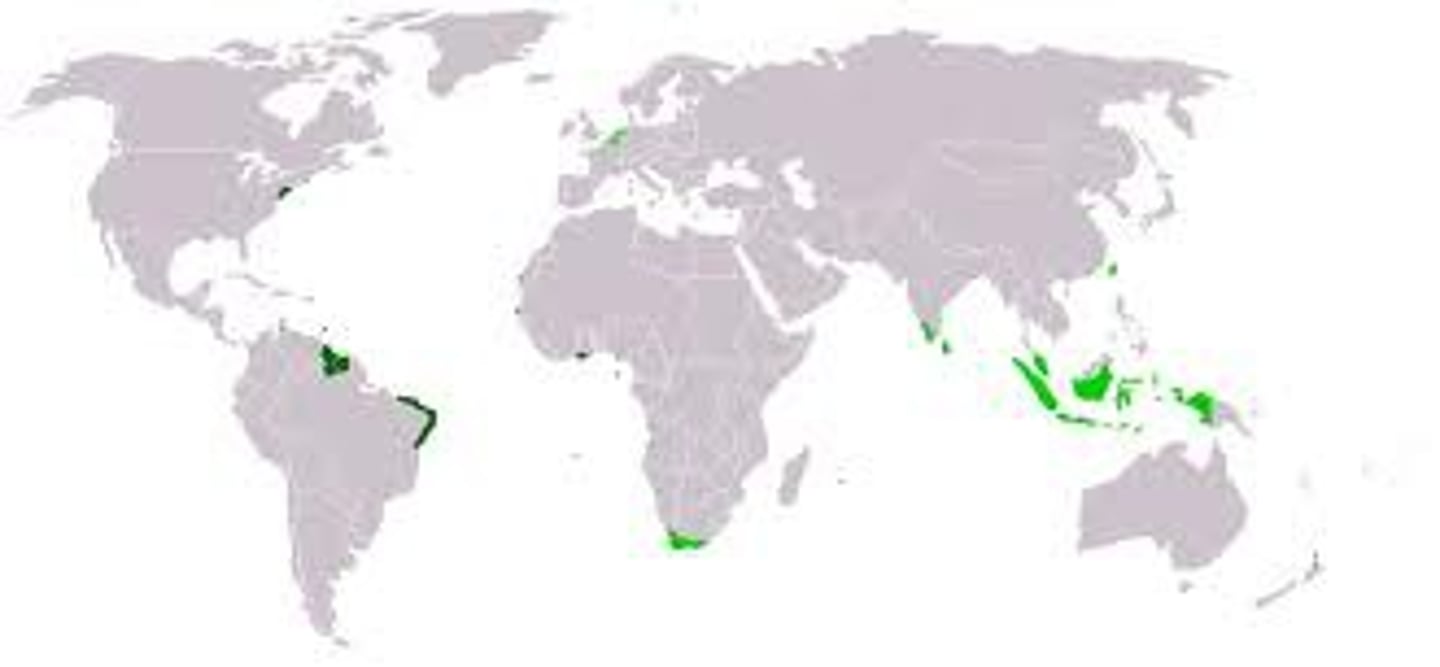
5. 1492 -1800 CE
-Everything having to do with colonization and transAtlantic trade in the Americas happens AFTER Columbus
-The Dates of the Columbian Exchange
6. British Maritime Empire in North America/Caribbean 1450 CE to 1750 CE
-The Europeans took to the seas in a frenzy after Columbus discovered new lands and peoples in the Americas
-This MARITIME empire, meaning an empire that was spread over oceans, was one of the most powerful European empires from 1450 - 1750 CE
-This was a maritime empire that spread from Europe to North America
-This maritime empire consisted of 13 colonies in North America that would eventually rebel against the empire in 1775 in the American Revolution
-This empire also held lots of territory in Canada and the Caribbean
-Later they would hold territory in Africa, Asia, and would colonize India, one of their most profitable colonies
-The British East India company helped make this empire profitable;
-Trade goods included cash crops like tobacco, sugar, and cotton. The British enslaved Africans to provide the labor on many of their plantations
7. Joint Stock Companies
-Much of the British and European ocean exploration from 1450 CE to 1750 CE was driven by private companies and not by governments; a company would raise money by selling stock
-The company would sell stock to people; if you bought stock and the company did well, you would make a lot of money; if the company did not do well, your would lose money
-People would buy stock and the companies would go on journeys to India and China to try to make money
-The British East India Company was an example of this

8. British East India Company 1600 CE
-This was a British joint-stock company that explored much of the world after getting its charter in 1600 CE
-They established important trading posts all over the world in India, Africa, the Caribbean, and the Americas
-People bought stock in the company and then if the company made a lot of profit on a voyage to India or China, the stock holders would get lots of money back in return
-The company traded in many things and many places, but some of its most profitable products were tea, coffee, opium, cotton, and sugar.
-By the mid 1700's this was the most powerful corporation in the world, by some claims controlling half of all global trade in the world. The company was so powerful it had its own private army of 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Government's army.
-Their most profitable trade goods included tobacco, sugar, cotton, and tea
-They participated in the African slave trade and carried enslaved persons on their ships
9. Jamestown 1607 CE
-Founded in 1607, this town struggled mightily when it was first founded until the discovery of Tobacco
-This was the first British town in North America in Virginia; initially, the town really struggled with starvation, disease, and Native American attack
-Once tobacco was discovered and grown by John Rolfe, the town was economically successful and the colony of Virginia became one of the first powerful colonies in the British Empire
-Virginia saw the beginning of African slavery in the what would become the United States in 1619 CE
10. 1607 CE
-Date of the founding of Jamestown, the first tobacco growing British colony in North America
11. Virginia 1600 CE to 1750 CE
-Jamestown was in this tobacco growing colony; it was the first major British colony in North America
-Once tobacco was discovered and grown by John Rolfe, the colony was economically successful and it became one of the first powerful colonies in the British Empire
-Initially included indentured servitude; would turn to slavery and import enslaved persons [slaves] throughout the 1600s to provide the labor in the economy
![<p>-Jamestown was in this tobacco growing colony; it was the first major British colony in North America</p><p>-Once tobacco was discovered and grown by John Rolfe, the colony was economically successful and it became one of the first powerful colonies in the British Empire</p><p>-Initially included indentured servitude; would turn to slavery and import enslaved persons [slaves] throughout the 1600s to provide the labor in the economy</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8fbb3ef7-11ac-4235-9177-3b9bd8c839e2.jpg)
12. Massachussetts
-This British North American colony was known for the Puritan religious group that founded it, known as the Pilgrims and founded in the 1600's
-Situated in what became known as New England, its major city was Boston
-Its economy was based off of small farms, fishing, lumber, and lots of merchants who traded in the Triangular Trade with the Caribbean and Europeans

13. Plantation Farming
-In the southern and Caribbean British colonies, the British began to force enslaved Africans [slaves] onto large farms where they grew tobacco, sugar, indigo, rice, and later on, cotton
-These were MASSIVE farms in the South [southern United States today] and Caribbean that used indentured servants and enslaved persons to run for a massive profit
-These type of farms were extremely profitable and increased British economic hegemony [power] and later on, United States hegemony after the American Revolution
-The largest and most profitable plantations were often sugar plantations in the Caribbean and Brazil. Cotton in the Southern United States took off the in the late 1700's and early 1800s.
![<p>-In the southern and Caribbean British colonies, the British began to force enslaved Africans [slaves] onto large farms where they grew tobacco, sugar, indigo, rice, and later on, cotton</p><p>-These were MASSIVE farms in the South [southern United States today] and Caribbean that used indentured servants and enslaved persons to run for a massive profit</p><p>-These type of farms were extremely profitable and increased British economic hegemony [power] and later on, United States hegemony after the American Revolution</p><p>-The largest and most profitable plantations were often sugar plantations in the Caribbean and Brazil. Cotton in the Southern United States took off the in the late 1700's and early 1800s.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/337eb4a2-4c07-4105-bae3-e926a439c033.jpg)
14. Forms of Coerced Labor
-As agriculture began to spread, there was an even bigger increase in coerced [forced] labor as the elite classes did not want to work in agriculture or work in construction building large things. There were several types of forced labor:
-Chattel slavery = total ownership of the enslaved person, who had no human rights (the slavery most American students know the most about-the harshest form of slavery,--used in Southern United States, Caribbean, Latin America, Eurasia)
-Serfdom--not fully enslaved, but tied to the land and owe allegiance, work, and profits to the lord--found in Europe, Russia, and Japan
-Indentured Servitude--5 to 7 years of forced labor--Americas, Europe
-Mit'a System--1/7th of population used to build things under forced labor--The Incan Empire; Spanish Empire in South America
-Encomienda System--forced labor on hacienda plantations in return for "Christianity"-- Spanish Empire in South America
-Hacienda System; forced labor on plantations in Spanish Empire in South America
-Most of these forms of coerced labor died out in Era 3, 1750 - 1900 CE, as the effects of the Enlightenment spread around the world. However, there was still forced labor in many European colonies and there is still child labor and other unfair practices around the world today.
![<p>-As agriculture began to spread, there was an even bigger increase in coerced [forced] labor as the elite classes did not want to work in agriculture or work in construction building large things. There were several types of forced labor:</p><p>-Chattel slavery = total ownership of the enslaved person, who had no human rights (the slavery most American students know the most about-the harshest form of slavery,--used in Southern United States, Caribbean, Latin America, Eurasia)</p><p>-Serfdom--not fully enslaved, but tied to the land and owe allegiance, work, and profits to the lord--found in Europe, Russia, and Japan</p><p>-Indentured Servitude--5 to 7 years of forced labor--Americas, Europe</p><p>-Mit'a System--1/7th of population used to build things under forced labor--The Incan Empire; Spanish Empire in South America</p><p>-Encomienda System--forced labor on hacienda plantations in return for "Christianity"-- Spanish Empire in South America</p><p>-Hacienda System; forced labor on plantations in Spanish Empire in South America</p><p>-Most of these forms of coerced labor died out in Era 3, 1750 - 1900 CE, as the effects of the Enlightenment spread around the world. However, there was still forced labor in many European colonies and there is still child labor and other unfair practices around the world today.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9353ebed-43d1-4145-b3a7-12a6e88343c5.jpg)
15. Indentured Servitude
-A type of forced or coerced labor that was limited in time. You basically had to agree to do forced labor for 5 to 7 years
-At the end of the the 5 to 7 years, if you had served well, you were supposed to get free land on the frontier and supplies to start a farm
-Most people who did this in the British colonies initially were white and came from British jails; they often mixed and lived with enslaved persons [slaves], which caused the upper classes to be concerned
-as a result of white indentured servants mixing and allying with African enslaved persons, the upper classes passed new laws to separate and divide lower class whites and African enslaved persons. These were the first laws of segregation in the British colonies
-Later on the British and other Europeans would use Indian and Chinese indentured labor in their African, Caribbean, and Latin American colonies
![<p>-A type of forced or coerced labor that was limited in time. You basically had to agree to do forced labor for 5 to 7 years</p><p>-At the end of the the 5 to 7 years, if you had served well, you were supposed to get free land on the frontier and supplies to start a farm</p><p>-Most people who did this in the British colonies initially were white and came from British jails; they often mixed and lived with enslaved persons [slaves], which caused the upper classes to be concerned</p><p>-as a result of white indentured servants mixing and allying with African enslaved persons, the upper classes passed new laws to separate and divide lower class whites and African enslaved persons. These were the first laws of segregation in the British colonies</p><p>-Later on the British and other Europeans would use Indian and Chinese indentured labor in their African, Caribbean, and Latin American colonies</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5e90ae21-6e6d-43a4-9e73-4ddd545a0c92.jpg)
16. Chattel Slavery
-Once indentured servitude became too expensive, British plantation owners began turning to ___________________________________ for the labor for tobacco, indigo, sugar, rice, and later cotton
-This type of slavery is the most harsh and intense kind of forced labor; it means complete ownership over someone; you can buy and sell them, you own them from birth to death, and could punish them violently even to the point of death. They had no human rights
-These type of enslaved persons in the British colonies received the harshest treatment of any forced laborers and were often brought in from Africa via the Caribbean and the Middle Passage
-Despite facing violent threats every day, chattel slaves resisted on a daily basis, ran away from enslavers [masters] and organized several rebellions throughout the Americas
![<p>-Once indentured servitude became too expensive, British plantation owners began turning to ___________________________________ for the labor for tobacco, indigo, sugar, rice, and later cotton</p><p>-This type of slavery is the most harsh and intense kind of forced labor; it means complete ownership over someone; you can buy and sell them, you own them from birth to death, and could punish them violently even to the point of death. They had no human rights</p><p>-These type of enslaved persons in the British colonies received the harshest treatment of any forced laborers and were often brought in from Africa via the Caribbean and the Middle Passage</p><p>-Despite facing violent threats every day, chattel slaves resisted on a daily basis, ran away from enslavers [masters] and organized several rebellions throughout the Americas</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a0c66c02-1412-4201-9ecd-d1af5d0956e0.jpg)
17. Mulatto
-Once the British began bringing over slaves, there was mixing between the white and black populations
-This was the term for someone who was mixed race, black and white. These people were still considered "black" still and were not given political or economic privileges or opportunities in society
-in its original meaning, translates into "mule." Dehumanization was a consistent part of racism and white supremacy, as calling non-white and mixed-race people animal names dehumanized them and helped justify social class hierarchies [rankings] based on skin color
![<p>-Once the British began bringing over slaves, there was mixing between the white and black populations</p><p>-This was the term for someone who was mixed race, black and white. These people were still considered "black" still and were not given political or economic privileges or opportunities in society</p><p>-in its original meaning, translates into "mule." Dehumanization was a consistent part of racism and white supremacy, as calling non-white and mixed-race people animal names dehumanized them and helped justify social class hierarchies [rankings] based on skin color</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6a58566b-f47d-4842-8ff3-ec6d70c90af6.jpg)
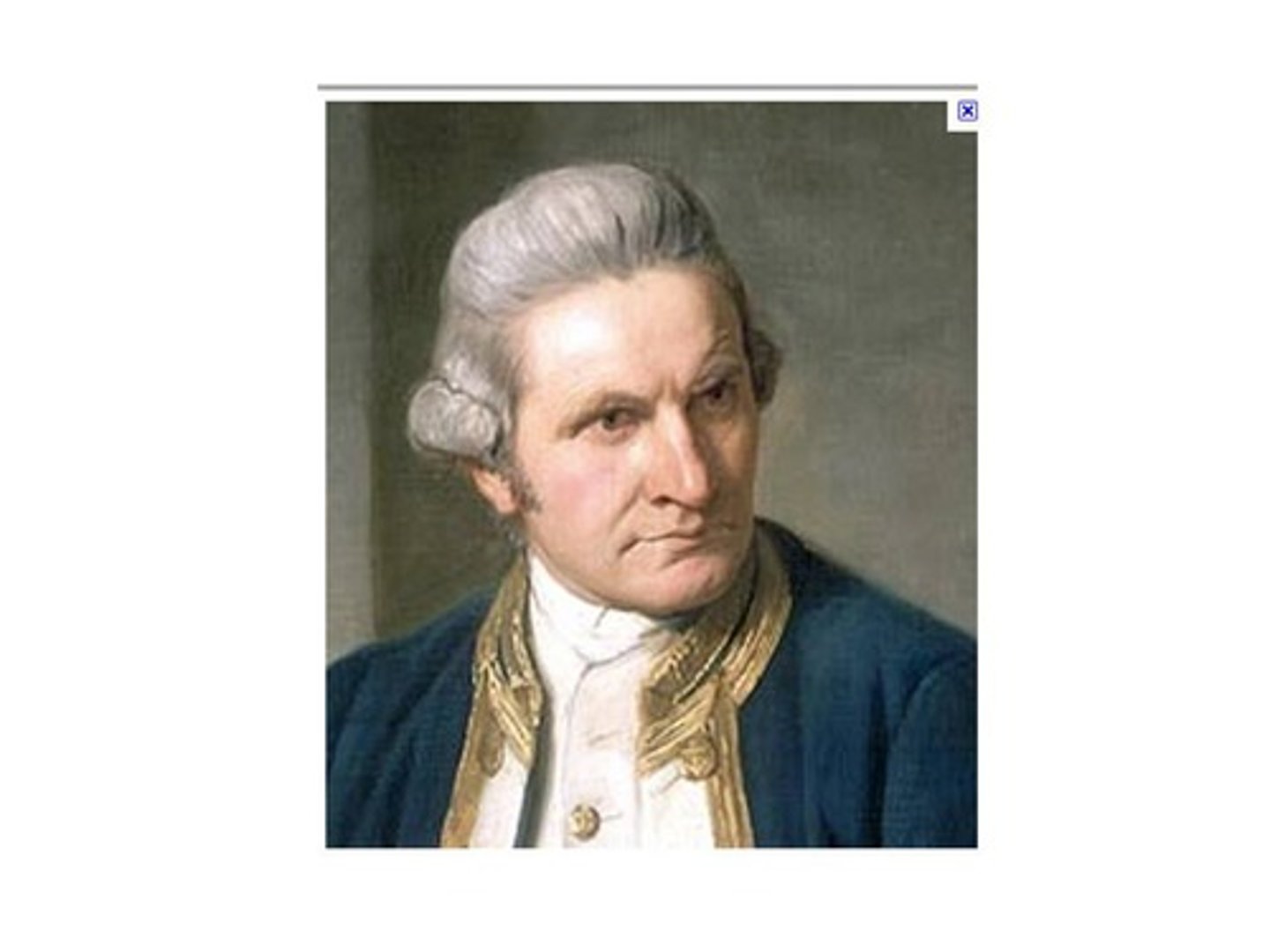
18. James Cook
-A British sea explorer who explored the Pacific and claimed Australia for the British in 1770 CE
-Visited Hawaii and many of the other Pacific and South Pacific Islands; one of the first Europeans to visit many parts of the world; created many maps and made many scientific discoveries along the way
-killed and clashed with many indigenous peoples in places that he discovered, using the advantage of guns, germs, and steel to defeat native peoples
-He himself was killed in a fight with the Hawaiians in 1779 while attempting to kidnap the Queen of Hawaii

19. Squanto
-He was a member of the Patuxet tribe born around 1585 in North America in modern day Massachusetts. It is hard to verify [know the exact truth] all the details of his story
-Most likely, he was lured on board a ship by a man named Thomas Hunt with the promise of trade and then was kidnapped, enslaved, brought across the Atlantic Ocean and forced to work in Spanish mines
-He was bought by Spanish friars [monks] and brought to England, where he learned English. Eventually, after many years, he made it back across the Atlantic Ocean to North America, only to find his entire village, family, and friends killed and wiped out by disease.
-He went to live with a nearby tribe. Later, British colonists named the Pilgrims arrived. They were struggling to feed themselves and were dying. Squanto, who spoke English, helped them learn agricultural techniques like using fish as fertilizer, provided them with good seeds, taught them how to fish and hunt. He also acted as translator for them
-With Squanto's help they got on their feet; that fall, they shared food together in the first "Thanksgiving"
-He died of a disease known as "Indian fever" in 1622
![<p>-He was a member of the Patuxet tribe born around 1585 in North America in modern day Massachusetts. It is hard to verify [know the exact truth] all the details of his story</p><p>-Most likely, he was lured on board a ship by a man named Thomas Hunt with the promise of trade and then was kidnapped, enslaved, brought across the Atlantic Ocean and forced to work in Spanish mines</p><p>-He was bought by Spanish friars [monks] and brought to England, where he learned English. Eventually, after many years, he made it back across the Atlantic Ocean to North America, only to find his entire village, family, and friends killed and wiped out by disease.</p><p>-He went to live with a nearby tribe. Later, British colonists named the Pilgrims arrived. They were struggling to feed themselves and were dying. Squanto, who spoke English, helped them learn agricultural techniques like using fish as fertilizer, provided them with good seeds, taught them how to fish and hunt. He also acted as translator for them</p><p>-With Squanto's help they got on their feet; that fall, they shared food together in the first "Thanksgiving"</p><p>-He died of a disease known as "Indian fever" in 1622</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5d66f3d-ea13-494d-9f5a-4f7d1ac1e56d.jpg)
20. The Protestant Reformation 1500's
-During the Middle Ages, the Catholic church started to become corrupt. If you sinned, you were able to "buy forgiveness" from the church; you could pay for "Indulgences" which forgave your sin
-A man named Martin Luther believed that you could not buy your way into heaven. He wrote a rant about it called the "95 Theses" and the printing press helped spread it all over Europe
-Luther and others began protesting against the Catholic church. Many new Christian churches formed and broke off and away from the Catholic Church. This movement spread like wildfire across Europe and millions joined the new churches and left the Catholic church.
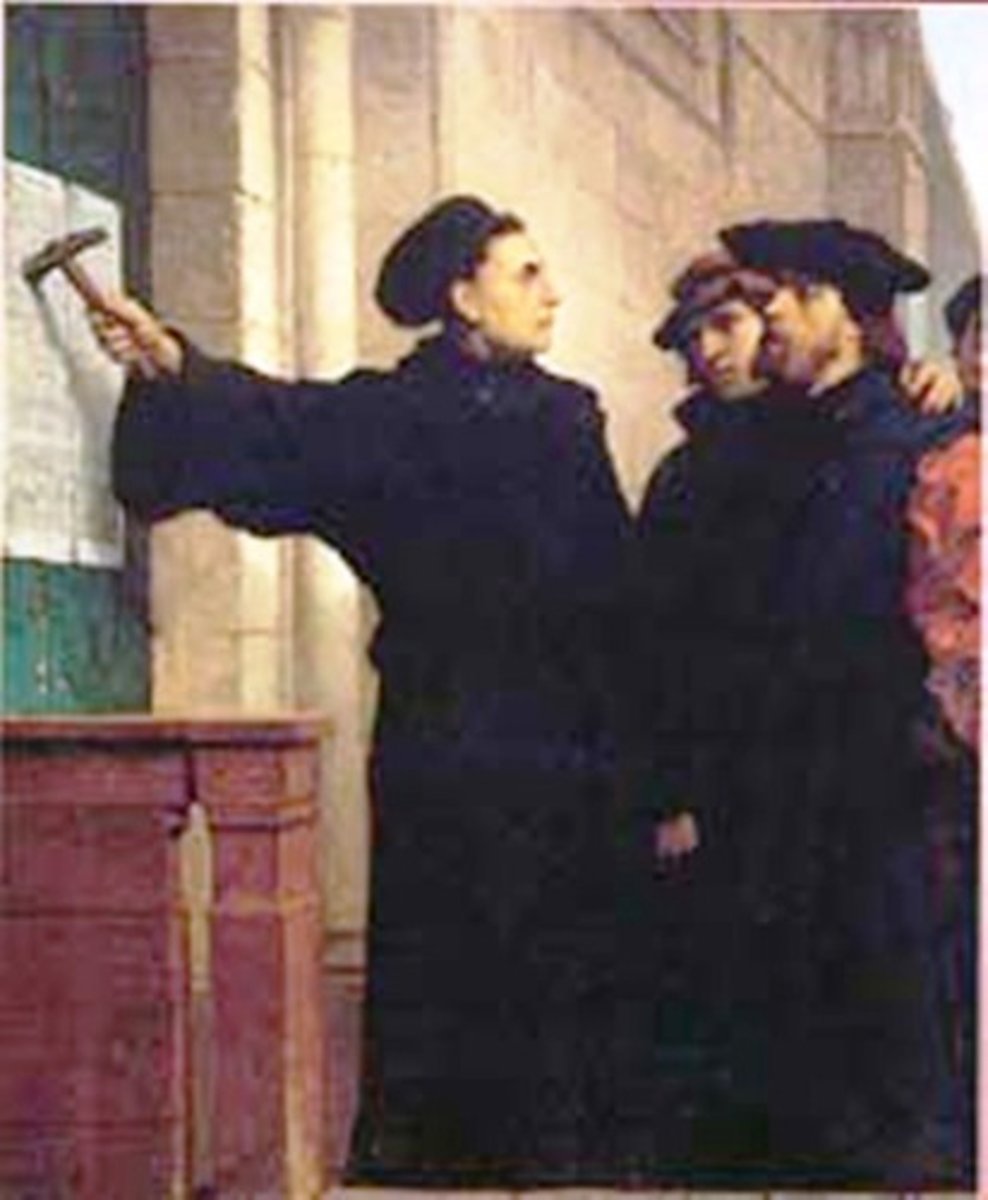

21. Martin Luther
--During the Middle Ages, the Catholic church started to become corrupt. If you sinned, you were able to "buy forgiveness" from the church; you could pay for "Indulgences" which forgave your sin
-A man named _______________ _______________ believed that you could not buy your way into heaven. He wrote a rant about it called the "95 Theses" and the printing press helped spread it all over Europe
-_______________ and others began protesting against the Catholic church. Many new Christian churches formed and broke off and away from the Catholic Church. This movement spread like wildfire across Europe and millions joined the new churches and left the Catholic church.
-This movement was called the Protestant Reformation; the answer to this question is the name of the Monk

22. The 95 Theses, 1517 CE DATE REQUIRED FOR CREDIT
--During the Middle Ages, the Catholic church started to become corrupt. If you sinned, you were able to "buy forgiveness" from the church; you could pay for "Indulgences" which forgave your sin
-A man named Martin Luther believed that you could not buy your way into heaven. He wrote a rant about it called the _______________ _____________ and the printing press helped spread it all over Europe
-Luther and others began protesting against the Catholic church. Many new Christian churches formed and broke off and away from the Catholic Church. This movement spread like wildfire across Europe and millions joined the new churches and left the Catholic church.
-This movement was called the Protestant Reformation; the answer to this question is the name of the document the monk published
-THIS IS THE TERM FOR WHAT HE WROTE
-DATE REQUIRED FOR CREDIT HERE, THIS

23. The Catholic Reformation or Counter Reformation
-Once Martin Luther published the "95 Theses", millions around Europe started leaving the Catholic Church
-The Catholic Church realized it had to make some changes to keep people in the church; it began its own series of reforms and corrections
-They created a new group of missionaries called the Jesuits who went to the Americas and elsewhere to convert people to Catholicism
-They built Catholic schools to get kids dedicated to Catholicism early on
-There was also lots of Witch Hunting and Religious Wars in Europe; thousands were burned at the stake or killed over religion

24. The Thirty Years War 1618 - 1648
-After the Protestant Reformation, there was a lot of religious conflict in Europe as the Reformation spread
-In Italy, the Holy Roman Emperor tried to force people to stay Catholic, although many tried to leave Catholicism
-This started one of the most brutal wars in European history; almost every European country got involved
-It was incredibly brutal and destructive; fought in the 1600's, it was the most brutal war in Europe until the World Wars
-Hundreds of thousands died; many were massacred or hung from trees outside of towns

The Renaissance 1300's 1600's
-After the Bubonic Plague, the Europeans were devastated until they experienced this period of "Rebirth"
-Art, painting, and architecture all grew and blossomed. Some of the most famous works of art in European history were created
-Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael, and Donatello (the Ninja Turtles!) were some of the most famous artists
-Many of these artists admired the Ancient Romans and Ancient Greeks and much of the work created around this time was about Ancient Rome and Greece
-Center of the ___________________ was in the Italian City-States
-The "Mona Lisa," "The Sistine Chapel" and the "School of Athens" were created as famous paintings
-Techniques like vanishing point, chiaroscuro, and repeated sketching revolutionized art and allowed artists to draw "realistic" examples of the human body and human scenes
26. Leonardo DaVinci, Michelangelo, Raphael (1500's)
-These are three of the most famous Renaissance painters from 1450 - 1750 CE. We will examine their work in class. They are all Italian
-Le___________________ created "The Mona Lisa" and other famous works of art
-Le____________________was also a scientist and an inventor; created early versions of the parachute, tank, and helicopter; was famous for being multi-talented and a brilliant genius who could do tons of different things
-Mi___________________ painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, where God was about to touch Adam and give him life
-Ra___________________ painted the "School of Athens" and other very famous works
-They all used the techniques of vanishing point, chiaroscuro, and repeated sketching to create realistic art that brought the human body to life on canvas

27. Demographics in the Americas 1450 - 1750 CE
-Demographics = population statistics
-Initially after the Columbian Exchange, the population of the Americas plummeted due to smallpox and measles that the Europeans brought, in addition to death from wars and conquest
-As many as 90% of native American populations were killed by disease, and some by conquest and war in what many historians consider a genocide
- European colonization and forced migration the Middle Passage brought the population of the Americas back up.
-By 1750, the population of the Americas had gone back up due to Colonization and the new food crops of the Columbian Exchange
-Native American populations never fully recovered and never got economic and political power back
28. North Atlantic Fishing Trips
-Many Europeans were still taking trips across the _____________________________ in order to fish for cod
-This led to the settlement of Iceland, Greenland, and Nova Scotia
-Once the Americas were discovered, fishermen in the North Atlantic continued to look for a water route to Asia
-Some people tried to go through North American rivers; others, like Vitus Bering, searched for routes through the Arctic and over the top of North America
-The Three European countries that led the way in Ocean Exploration in the North Atlantic were the British, Dutch, and French
29. American Silver for Asian Luxury Goods
-Above all else, as part of mercantilism, the Spanish wanted silver and gold so they could use it to increase their power and wealth
-Once they mined it, they sent most of it on ships back to Spain; some of it traveled on the Manila Galleon boats to the Philippines so it could be used to trade with China
-They had mines at Potosi and in Mexico where they used the Mit'a System to force the natives to work to get this
-As it spread around the world, this was critical for increasing trade and allowing countries to create money and currency; European Maritime Empires started to use more silver in currency, and this made international trade easier
-The Ming Dynasty in China required payment in silver for a time; this drove Chinese demand for silver up
-the Spanish and other Europeans became immensely wealthy trading American Silver for Asian luxury goods like silk, Spices, and Porcelain
-The silver was mined using forced labor and contributed to the rise of the Trans Atlantic Slave Trade, as historians estimate that millions of native laborers died at mines like Potosi
