Ch 10 Guide
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
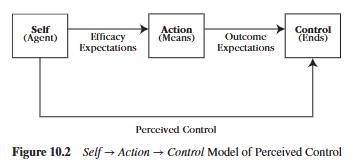
Describe expectancy and its two types.
Expectancy is someone’s personal (subjective) prediction of an event’s likelihood to occur.
An efficacy expectancy is one’s judgment of their own ability to take action (Can I do it?), whereas an outcome expectancy is a judgment about a specific outcome and whether or not their action will cause that outcome (Will my action cause XYZ? Will it work?)
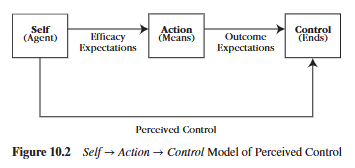
What is an efficacy expectation?
An efficacy expectancy is one’s judgment of their own ability to take action (Can I do it?)
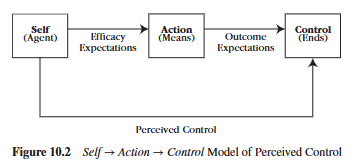
What is an outcome expectation?
Outcome expectancy is a judgment about a specific outcome and whether or not their action will cause that outcome (Will my action cause XYZ? Will it work?)
What is the efficacy expectation and the outcome expectation for a political candidate who wants to win an election, believing that by giving a convention speech she can win?
Efficacy expectation: Pertains to her confidence that she has “what it takes” to deliver a competent speech
Outcome Expectation: Once the speech is given, the speech will produce positive outcomes. People will listen, be persuaded by her oratory, and vote for her in the election.
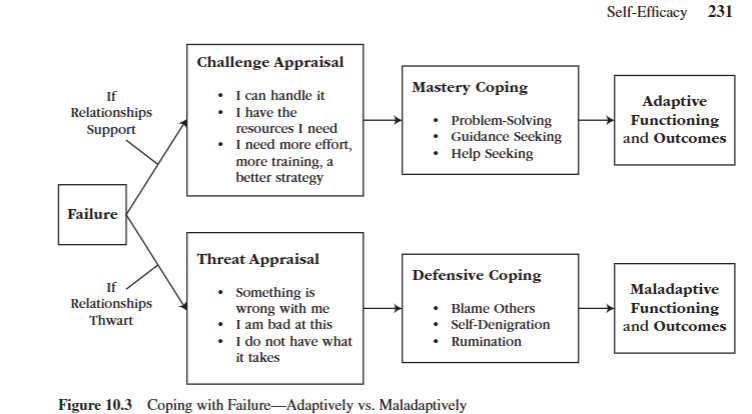
Describe failure feedback and two types of appraisals.
Failure feedback is when we improve on our progress by utilizing failure and its teachings to us. It is a highly social process.
Challenge appraisals are one’s opportunity to grow and learn, leading to mastery oriented coping and adaptive functioning and outcomes, because of this positive thinking. A challenge appraisal is reached if a person’s surrounding relationships support them.
On the other hand, threat appraisal is feedback that signals danger to one’s well being, which leads someone to cope defensively and in self-protective ways. This leads to maladaptive functioning and outcome which can be influenced by thwarted relationships.
What is self-efficacy? What is the opposite of efficacy?
One’s judgement of how well (or poorly) one will cope with a situation, given the skills one possesses and the circumstances one faces.
Self-Doubt
What variables decide the extent to which a performer copes well or poorly when skills and abilities are stressed?
Self-efficacy & self-doubt
What are the main sources of self-efficacy?
The main sources of self efficacy from most to least influential are personal behavior history, vicarious experience, verbal persuasion, and physiological state.
What effects does self-efficacy have on behavior?
Self-efficacy affects our choices, efforts/persistence, thinking/decision-making, and emotionality.
It is what helps us decide whether to approach or avoid activities, whether or not we can cope and recover from setbacks, thinking effectively through problems, and coping successfully with anxiety in reaction to distress and negative emotionality.
Describe the mastery motivational orientation.
Mastery motivational orientation is when one is able to focus on achieving their goals despite setbacks, which can be failure feedback. They would see failure feedback as constructive. Their response to failure turns into how they better themselves.
Describe the helpless motivational orientation.
A helpless motivational orientation stems from having a fragile self-view as failure occurs, leading one to cope ineffectively, withdrawing, and contributing their experiences as out of their control (externally). They would not view failure feedback as constructive. They take it more personally and see it as a sign of personal inadequacy, leading to potential despair spirals. It is giving up and the over justification of why they failed.
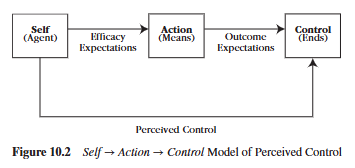
What do we learn from the learned helplessness study (Fig. 10.2)?
The learned helplessness study taught us that when we condition people to believe they have no control over their environment, it will affect their future personal control beliefs and lead them to eventually believe that life’s outcomes are uncontrollable. This was seen with the dogs that received an inescapable shock conditioning, which then led them to not escape from shock when it was completely possible and in their control.
What are the similarities between helplessness and depression?
Helplessness relates to depression in the way that depressed individuals have a skewed perception of personal control. Both possess this powerless belief that can lead to lower self-esteem, fear-mobilized emotionality, simply because they think there is a lack of control. They both believe that their powerlessness is a permanent condition that can lead to deficits in learning, emotions, and motivation.
Describe attribution theory.
Attribution theory attempts to explain why a particular outcome occurred, and asks the “Why” of whether it was successful or a failure. Attribution theory can be split up into a pessimistic or optimistic explanatory style, and these styles relate to attribution theory because they try to causally explain and justify their failure in different ways. In other words, they try to “attribute” their success or failure to some explanation.
Describe reactance theory.
Reactance theory is the motivational state arising when people feel threat in their freedom. People experience reactance only if they expect to have control over what happens to them, which is why if they feel threatened, they react by becoming more active even to the point of aggression. The theory focuses on how people react to outcomes that are uncontrollable to them. It explains how perceived loss of freedom can lead to resistance or aggressive behavior in response to attempts to restrict choices.