Neuro Exam 1
1/368
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
369 Terms
How many drug overdose deaths were there in 2019?
70,630
How many drug overdose deaths were there in the past 12 months? What kind of drug did most involve?
106,584 - most involved opioid
Remember Sheila? She has _____
She has tetanus
What is tetanus?
Tetanospasmin binds irriversibly to membrane at synapse
blocks release of glycine from axon terminals - causes generalized rigidity
What is Opisthotonus?
severe muscle rigidity - dramatic abnormal posture, severe backward arching from toe to heel
symptom of tetanus
Synapse diagram
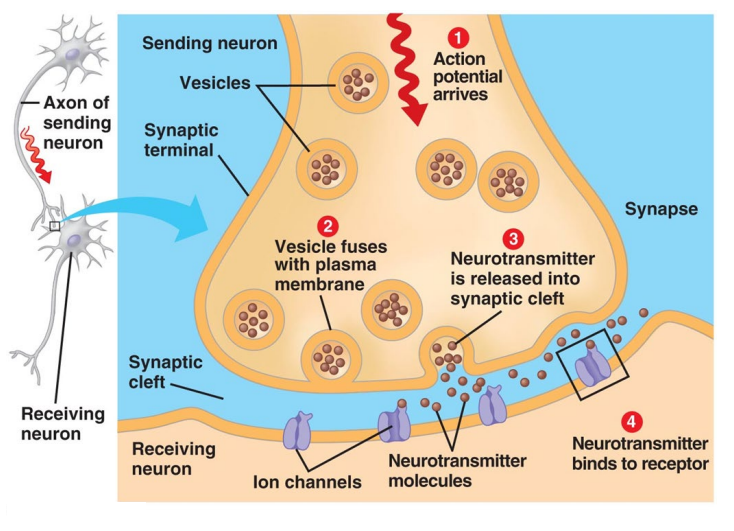
What happened to Don?
Case study:
A retired accountant developed tremor and slowing of movements and was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease at age 67. His neurologist prescribed levodopa to restore dopamine levels. A couple of years later, motor symptoms start to fluctuate and the dopamine receptor agonist ropinirole was added to his treatment.
A few months later, he developed a strong interest in gambling, first buying lottery tickets and then visiting a casino almost every day. He concealed his gambling activity until he has lost more than $100,000. He came for a consultation 5 weeks ago, and ropinirole was replaced with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor drug. He now reports his interest in gambling has disappeared.
What’s going on?
Levodopa increased dopamine levels, which not only improves substantia nigra, but also increases VTA (ventral tegmental area) activity. The VTA is responsible for reward, motivation, and addiction (among other things). The new monoamine oxidase inhibitor drug does not target the VTA, as shown by the decrease in interest towards gambling after changing medication
What are the two receptor subtypes?
Ionotropic and Metabotropic
How do ionotropic receptors work?
open when bound by a transmitter (ligand-gated ion channel)
direct - NT binds to the channel itself
How do metabotropic receptors work?
transmitter binds to receptor, receptor activates G-protein
indirect - NT binds to receptor which signals for the receptor to open
True or false: most drugs act via ionotropic receptors.
False: 75% of all drugs act via metabotropic receptors
good because: the more steps, the more area to intervene
bad because: hard to find one drug that fits all
What does an agonist do?
drug that initiates normal effects of the receptor
pretends to be the neurotransmitter
all agonistic drugs are partial agonists
True or false: agnoists produce the same level of response as a neurotransmitter
False - all agonists are partial agonists
What does an antagonist do?
prevents a receptor from being activated by other ligands
What are the two types of antagonists?
Competitive and Noncompetitive
what is a competitive antagonist
binds directly on the active site - blocks active site, prevents signal transmission
What is a noncompetitive antagonist?
binds to a different site that causes the protein to denature, causing the shape of the binding site to change, reducing the effectiveness of the receptor (partial signal)
True or false: Drugs only have one shot to affect synaptic transmission
False - drugs can affect synaptic transmitssion at many steps
Ionotropic receptors would be most useful in a body system that
A. Needs slow but adaptable output
B. Needs rapid and reliable output
B. Needs rapid and reliable output
What are the classes of neurotransmitters?
Amino acids, Monoamines, Soluble gases, Acetylcholine, Neuropeptide
What are the amino acids?
Glutamate, aspartate, glycine, GABA
amino acids make me gagg
What are the two classes of monoamines?
Catecholamines, Indolamines
What are the catecholamines?
Dopamine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine
What are the Indolamines
Serotonin
What are the soluble gases?
Nitric oxide, carbon monoxide
What are the acetylcholines?
acetylcholine
What are the neuropeptides?
Endorphins
What is glutamate?
Main excitatory NT of the CNS, responsible for EPSPs
amino acid NT
most important NT in the cerebral cortex
What are the ionotropic receptors for glutamate?
AMPA, NMDA (Mg2+-blocked), Kainate
How are receptors named?
Named by the first discovered agonist
What are the metabotropic receptors of Glutamate?
mGluRs
How is glutamate removed from the synapse?
reuptake
What is excitotoxicity?
excessive release of glutamate → kills neurons
causes:
neural injury (stroke, head trauma, etc)
abnormalities in glial function
failure to remove glutamate from synapse
What kind of protein channels does glutamate activate?
Na+, K+, Ca2+
Summary of glutamate’s actions diagram
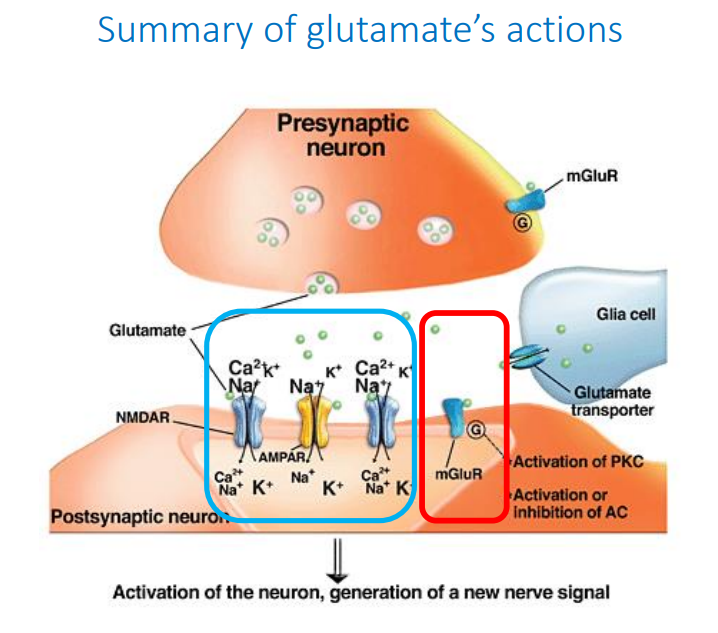
What is GABA?
Ionotropic inhibitory NT (Cl- permable)
produces fast inhibitory effects
amino acid NT
most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain
What do the GABA agonists do?
potent tranquilizers (fast inhibitory effects)
What are the GABA agonists?
Ethanol (alcohol)
Benzodiazepine (for sleep)
Barbiturate (ex: Valium)
Neurosteroids
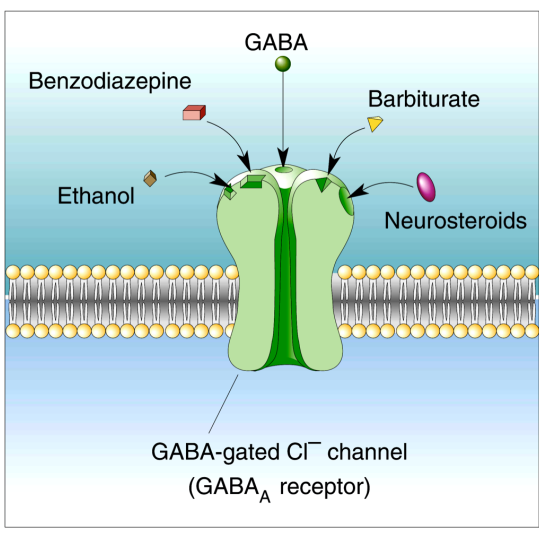
What channels does GABA open?
Cl-
Summary of GABA’s actions (diagram, not a knowt)
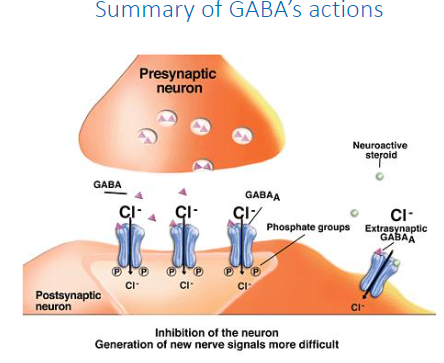
What is Glycine?
Major inhibitory neurotransmitter in spinal cord
amino acid NT
What does Strychnine do?
blocks glycine → opisthotonus
symptoms:
after 20 minutes
neck stiffness
twitching muscles
feeling of suffocation
violent convulsions - body is arched and the head bent backward
After a minute muscles relax, but a touch or noise causes convulsions to recur, or they recur spontaneously, every few min.
What is strychnine used for?
rat poison - suffocation
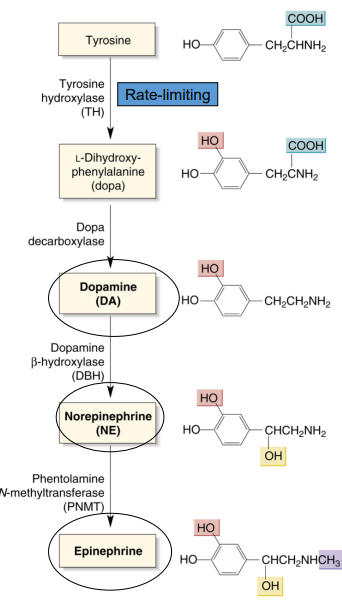
catecholamine synthesis
what is the precursor for dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine?
what is the rate-limiting step for the precursor → catecholamine reaction?
precursor: tyrosine
rate-limiting step: tyrosine hydroxylase (enzyme that breaks down tyrosine)
3-year-old identical twins from London had severely low muscle tone, intellectual disability, and seizures.
What is the cause? What is the treatment, and why does this help?
cause: low activity of tyrosine hydroxylase
treatment: dopamine infusions
helped because tyrosine hydroxylase indirectly stimulates dopamine production - catacholamine synthesis
What is the catecholamine synthesis pathway?
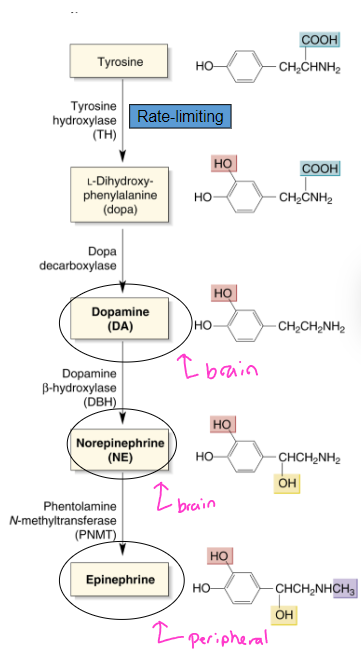
what is the mesolimbocortical pathway of dopamine and its function?
What is the mesostriatal pathway of dopamine and its function?
mesolimbocortical:
VTA → nucleus accumbens, cortex, and hippocampus
function: addiction, learning, schizophrenia
mesostriatal:
substantia nigra → striatum
function: motor control
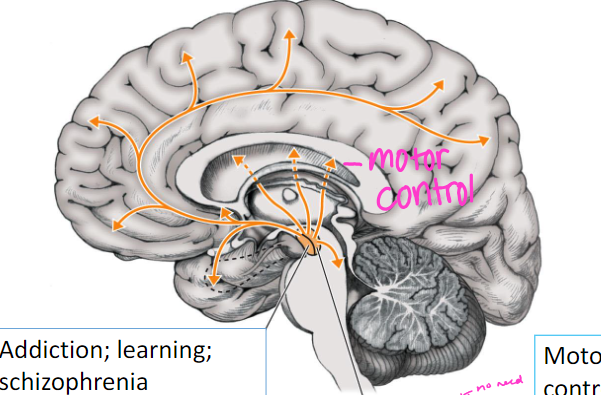
What is the norepinephrine pathway and its function?
locus coeruleus to hippocampus, basal ganglia, and cortex
function: mood, arousal, sexual behavior
(remember: if you see locus coeruleus, always think norepinephrine)
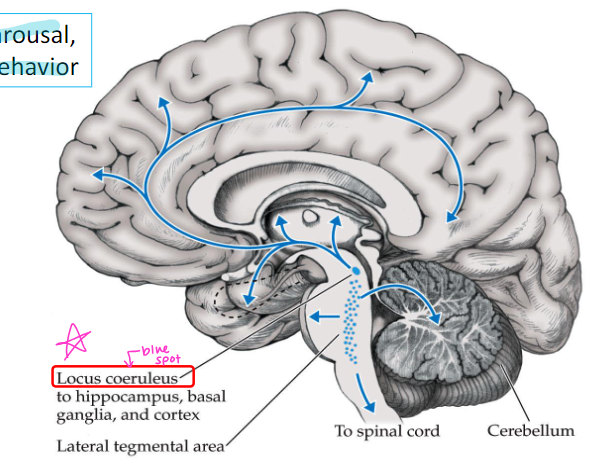
what does ‘locus coeruleus’ mean?
blue spot
Serotonin pathway and function
raphe nuclei - produces serotonin
Mesencephalic serotonergic cells → thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cortex
function: sleep, sexual behavior, anxiety
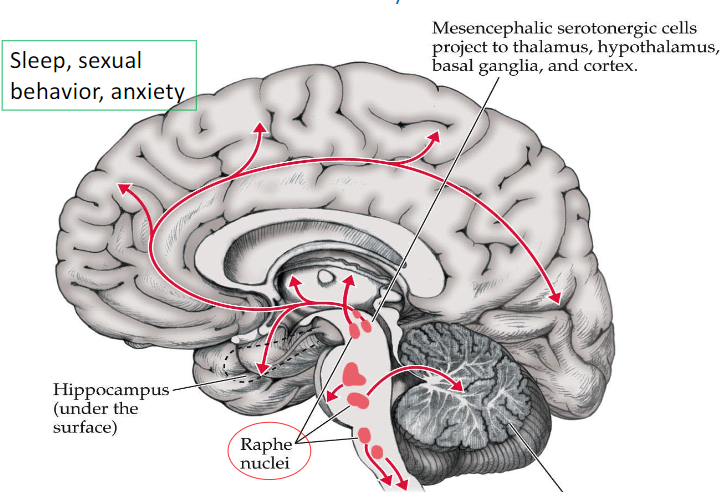
function of the raphe nuclei
produces serotonin
cholinergic pathway
basal forebrain to fornix
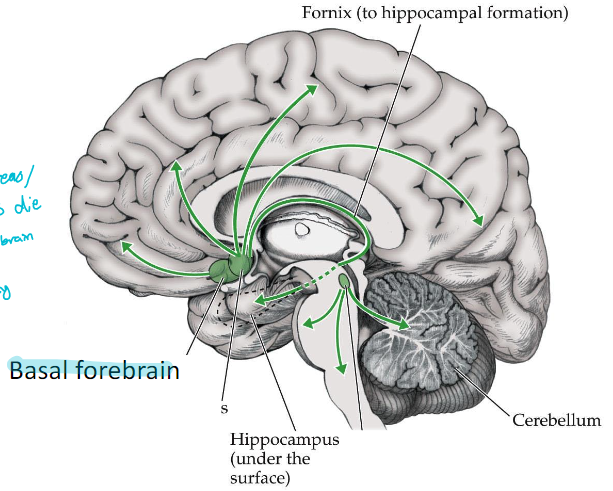
What is the function of the basal forebrain?
Involved in learning and memory
cell death causes Alzheimer’s
True or false: you can easily store gas neurotransmitters
false
Where is nitric oxide produced?
dendrites (produced in the postsynaptic neuron)
NO serves as a(n) ______grade transmitter by diffusing back into the ______________. This _____________ neighboring neurons.
retro, presynaptic neuron, synchronizes
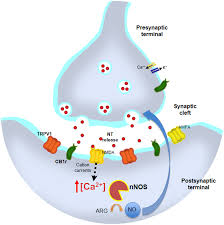
What are the two types of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors?
Nicotinic and Muscarinic
What are the characteristics of a Nicotonic ACh receptor?
ionotropic
excitatory
PNS
Muscles use nicotinic ACh receptors
______ is an antagonist that causes paralysis when binding to _______ ACh receptors.
curare, nicotinic
What are the characteristics of a Muscarinic ACh receptor?
Metabotropic
Excitatory or inhibitory
CNS
When _________ binds to muscarinic ACh receptors, it ________
scopolamine, alters cognition
main agonists for nicotinic and muscarinic receptors (hint: what were they named after?)
nicotinic: nicotine
muscarinic: muscarine
When are endorphins produced?
During:
exersise
excitement
pain
eating spicy food
love
orgasm
endorphins are the body’s natural ____
painkillers
What are endogenous opiates? Are they addictive?
Peptide NTs that bind to opioid receptors
naturally made in the body
relieve pain (analgesics) and produce a feeling of well-being
Yes, they are addictive.
What are the three endogenous opiates?
Enkephalins
Endorphins
Dynorphins
What are neuromodulators?
indirectly affect transmitter release or receptor response
ex: adenosine
What is adenosine? How does caffeine relate to adenosine?
neuromodulator - inhibits catecholamine release via presynaptic autoreceptors
during wakefulness, adenosine builds up, making you sleepy
caffeine blocks adenosine → catacholamine release → arousal
notes about coffee
FYI: Mayo Clinic Proceed Aug. 2013: A study of 40,000 individuals found greater than 50% increased mortality in young men and women who drank more than 4 cups a day
But moderate coffee intake LOWERS all-cause mortality
What are antipsychotic (neuroleptic) drugs? What are the typical neuroleptics?
used for schizophrenia and aggressive behavior
typical neuroleptics - dopamine antagonists
schizophrenia could be caused by increase in dopamine
What do monoamine oxidase inhibitors do?
prevent breakdown of monoamines at synapse
What is the main antidepressant?
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
What is the major action of antidepressants?
accumulation of monoamines
What are the two classes of antidepressants?
Tricyclics
block reputake of norepinephrine and serotonin
high BP + adrenaline = higher BP → death
older, not used as often because of the risks
SSRIs
serotonin acccumulates in synapses
fewer side effects
prozac, zoloft
Anxiolytics (tranquilizers)
reduce nervous system activity
Types of anxiolytics
Benzodiazepine
GABA agonists
endogenous agonists:
Allopregnanolone
Diazepam-binding inhibitor (released by astrocytes)
Barbiturates are ___________
depressing
What do Barbiturates do? What are their clinical uses?
block sodium channels
increase flow of chloride ions (GABA agonist)
it was used to execute people…main medical use now is for anesthesia and epilepsy
In _____ doses, alcohol is a stimulant, turning off ________, and reducing _________ and ________.
low
cortical inhibition
social constraints
anxiety
At ______ doses, alcohol is a sedative
high
What does alcohol markedly do?
reduces brain metabolism
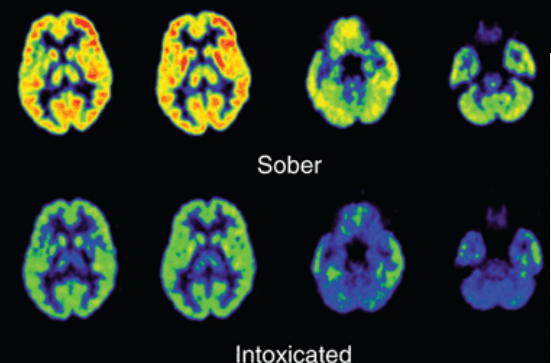
alcohol’s effects are ____
biphasic (initial stimulant phase followed by a depressant phase)
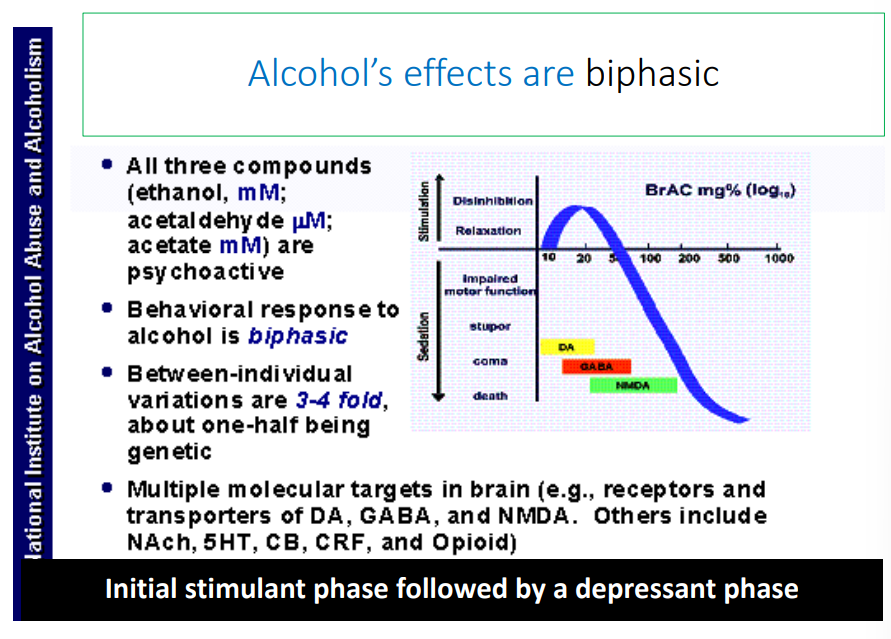
What neurotransmitter systems does alcohol affect
glutamate, GABA
inhibits glutamate at low doses
acts as GABA receptor to increase binding of GABA
effects:
sedation
anxiety reduction
muscle relaxation
inhibitired cognitive and motor skills
What are the pleasurable effects of alcohol
stimulation of dopamine, serotonin, opiates, and cannabinoid
Cause of alcohol-related seizures
compensatory increase in glutamate receptors over time
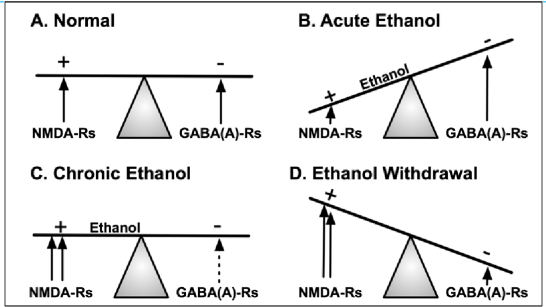
OJ is a 45 yo man who presents to the ED after a seizure during his first day at a local alcohol/drug rehab center. He was ordered by the court to attend this center after his second drunk driving violation in one year.
It has been about 60 hours since his last drink. What is happening to him?
tonic-clonic seizures
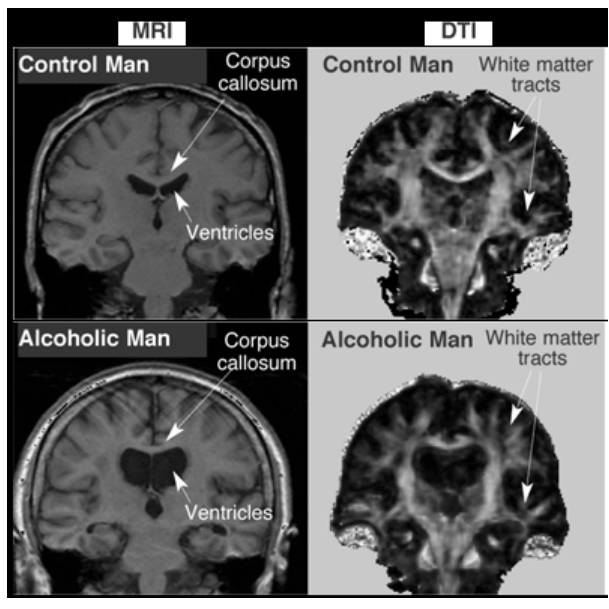
What does alcohol do to your brain?
drink shrinks your brain - damages cerebellum and frontal lobe
note: neurons and glia can recover!!
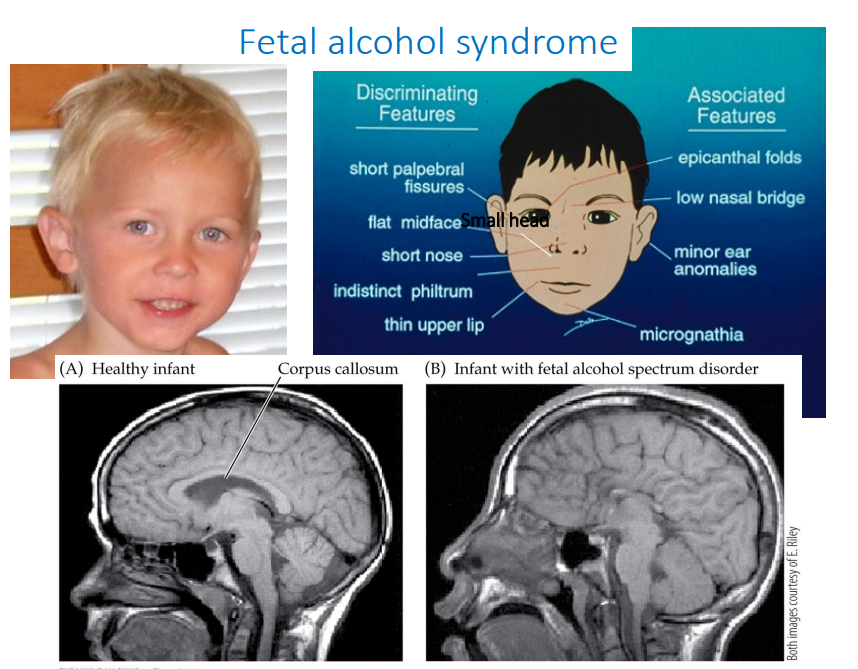
A child has a small head with a flat face, short nose with a low nasal bridge, and thin upper lip. What is the diagnosis?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
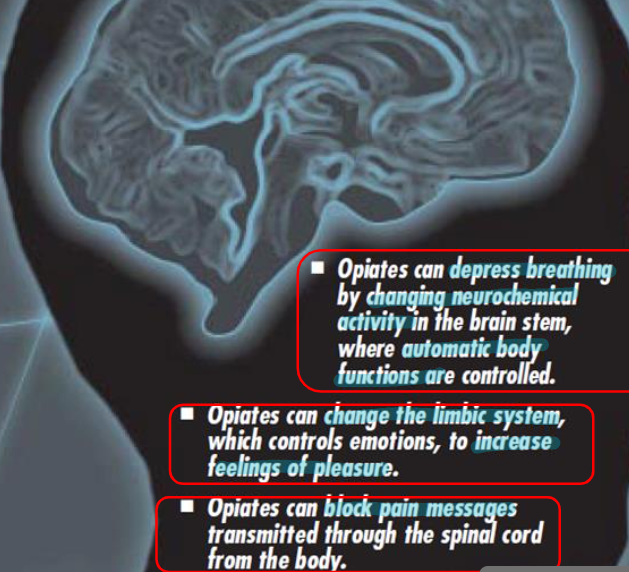
What do opiates do?
What is the treatment for an opoid overdose?
narcan (naloxone)
What is morphine, where is it found, and what does it do?
potent analgesic
found in opium
binds to opoid receptors in the brainstem (locus coeruleus, periaqueductal gray)
What is the origin of the name of heroin?
named for “heroic” - initially marketed as a cure for codeine addiction
metabolizes into morphine, addictive - not a great cure!
What company made heroin in the beginning?
Bayer company
53 y/o man is found down in the driveway of a house. EMS arrives and on exam he is comatose, and his pupils are tiny (2mm) and barely react to light. An IV is inserted and he is given naloxone. Within a minute he arouses and opens his eyes.
What is the diagnosis?
opiate/fentanyl overdose
What is the active ligand in marijuana?
THC (tetrahydrocannabinoid)
What do cannabinoid receptors bind? (marijuana)
anandamide
2-AG
(endocannabinoids)
What are endocannabinoids
hydrophobic (lipophilic) molecules - can’t store in vesicles, thus exist as part of the membrane
synthesized on demand
retrograde signaling - activate cannabinoid receptors on nearby neurons
True or false: in 3000 BC, Indian medical practice used marijuana to treat appetite loss
True
What are the effects of marijuana?
impairs short-term memory
slow reaction time
altered judgement/decision making
alters mood - calmness; in high doses, paranoia
What does nicotine do?
primary psychoactive and addictive drug in tobacco
activates ACh receptors in VTA
periphery - muscle twitching
centrally - increased alertness