Chapter 15 - Monopolistic Competition and Product Differentiation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Super Snacking Services is a typical monopolistically competitive firm. Initially, the market is in the long-run equilibrium, and then there is an increase in the market demand for snacks. In the short run, the price of snacks will _________, and the market output of snacks will ________.
(A) fall; fall
(B) remain unchanged; remain unchanged
(C) rise; rise
(D) rise; fall
rise; rise
How could firms in a perfectly competitive market move their market towards a monopolistically competitive market?
(A) Attempt to price fix
(B) Attempt to create a cartel
(C) Attempt to conduct game theory
(D) Attempt to create a brand for their product
Attempt to create a brand for their product
(Figure: Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Designer Clothing) Use Figure: Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Designer Clothing. The figure illustrates a firm in the ______; in the _______, the demand and marginal revenue curves will shift to the _________.
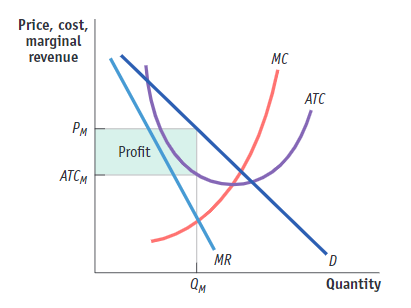
(A) long run; short run; right
(B) short run; long run; left
(C) short run; long run; right
(D) long run, short run; left
short run; long run; left
Which of the following events could possibly shift the supply curve to the left and raise prices in many markets in our economy?
(A) the Eversource rate hikes
(B) All 3 of the possible answers listed here could shift the supply curve to the left
(C) The potential railroad strike
(D) The political unrest in China
All 3 of the possible answers listed here could shift the supply curve to the left
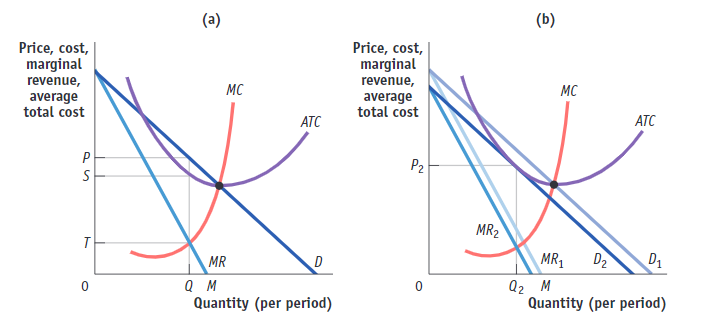
(Figure: The Market for Designer Boots in Monopolistic Competition II). Use Figure: The Market for Designer Boots in Monopolistic Competition II. Which panel(s) in the figure show(s) a monopolistic competitor in the long run equilibrium?
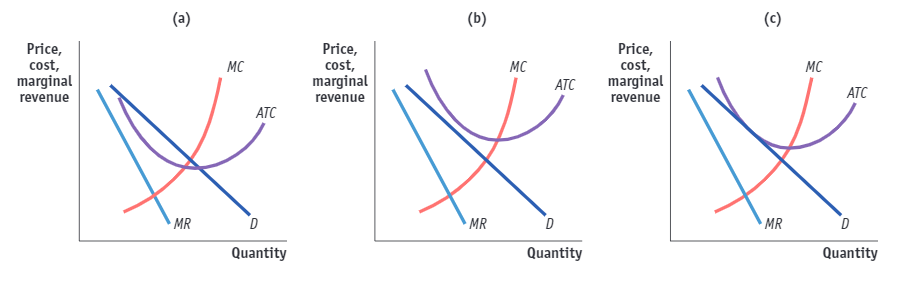
(A) panels (a), (b), and (c)
(B) panel (c) only
(C) panel (b) only
(D) panel (a) only
panel (c) only
When we compare the long run conditions of a Perfectly competitive firm to the long run conditions of a Monopolistically competitive firm we see that the Perfectly competitive firm is
(A) less productive and cost efficient than the Monopolistically Competitive firm
(B) less productively efficient and more cost efficient than the Monopolistically Competitive firm
(C) more productively efficient and less cost efficient than the Monopolistically Competitive firm
(D) more productively efficient and cost efficient than the Monopolistically Competitive firm
more productively efficient and cost efficient than the Monopolistically Competitive firm
Florists in the town of Minerva, Illinois, operate in a monopolistically competitive market. The price in long-run equilibrium for a flower shop is _______, and output is ________, than would be the case for a perfectly competitive firm with an identical production function and cost curves
(A) higher; higher
(B) higher; lower
(C) lower; lower
(D) lower; higher
higher; lower
(Figure: The Market for Designer Boots in Monopolistic Competition). Use Figure: The Market for Designer Boots in Monopolistic Competition. A positive economic profit will be earned if the profit-maximizing price is _____ in panel _________.
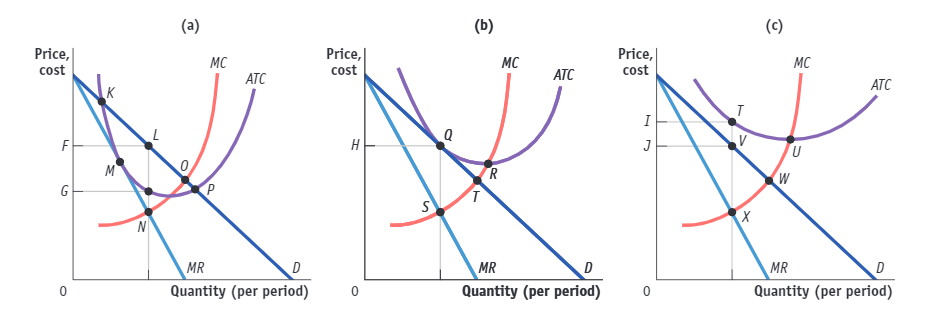
(A) G; (a)
(B) I; (c)
(C) F; (a)
(D) H; (b)
F; (a)
(Figure: Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Couture Clothing). Use Figure: Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Couture Clothing. If the firm shown in the figure maximizes its returns, it will:
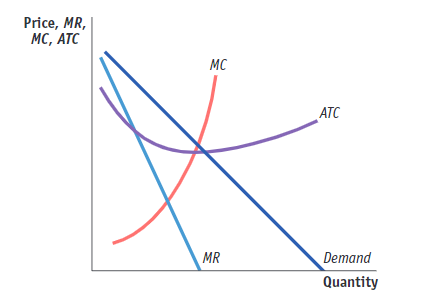
(A) break even
(B) earn a positive economic profit
(C) incur a loss
(D) incur a loss equal to its MR
earn a positive economic profit
(Figure: Short Run and Long Run Profit in Monopolistic Competition). Use Figure: Short Run and Long Run Profit in Monopolistic Competition. In monopolistic competition, long-run equilibrium is characterized by:
(A) profit maximization, which occurs where P = MR = MC
(B) P = MR
(C) P < MR
(D) P > MR
P > MR
For a monopolistically competitive firm, marginal cost is __________ in long run equilibrium.
(A) greater than price
(B) related to price but not in a predictable way
(C) equal to price
(D) less than price
less than price
How could firms in a monopolistically competitive market move their market towards an oligopoly market?
(A) play game theory
(B) Attempt to create a branding for their product
(C) lower prices
(D) attempt to create some barriers to entry
attempt to create some barriers to entry
(Figure: Fast Food Profit in Monopolistic Competition III). Use Figure: Fast Food Profit in Monopolistic Competition III. The profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
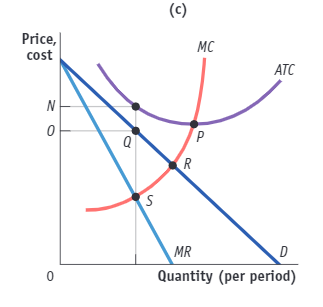
(A) P
(B) R
(C) S
(D) Q
S
(Figure: Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run). Use Figure: Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run. Which statement is False?
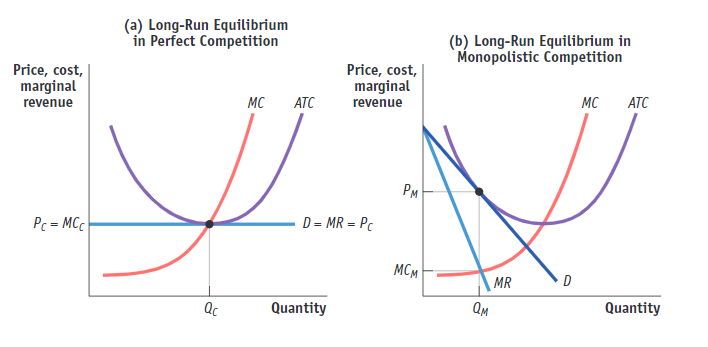
(A) Both panels show markets in which firms cover all of their implicit and explicit costs
(B) Firms in panel (a) cannot have profits in the long run, but those in panel (b) can
(C) Firm in the market shown in panel (a) produce identical products, whereas those in panel (b) produce similar but differentiated products.
(D) Both panels show markets that have many firms
Firms in panel (a) cannot have profits in the long run, but those in panel (b) can
Coors is a widely recognized brand name. During the World Series each year, this beer company has many of the most successful ads. Which statement is TRUE about advertising for Coors?
(A) It decreases the costs of supplying Coors
(B) It is designed to increase the demand for Coors
(C) It is designed to increase excess capacity
(D) It guarantees customers that Coors tastes better than do other beers.
It is designed to increase the demand for Coors