Rabbits
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What are some key features of a rabbits head
Large erect or floppy pinnae
Large protuberant eyes
Cleft lip
Twitchy nose
Vibrissae
Specialised dentition
What are the main features of rabbits ears
Used for thermoregulation
Funnel sound by rotating 270 degrees
Used for administering medications and blood sampling
Lots of blood vessels that are fragile and easily damaged
What are the main features of rabbits eyes
Positioned laterally for a wide field of view
Have a third eyelid
Harderian gland which produces very stable tear film
Single ventral lacrimal punctum draining into nasolacrimal duct
What are the most common causes of eye problems in rabbits
Protuberant eyes mean higher risk of trauma
Underlying dental disease
What will be noticed in an ophthalamic exam
Merangiotic retina
No tapetum
What is exopthalmos
When eyes become more protuberant looking
What causes exopthalmos
Fright causing increase in blood pressure
Diseased venous plexus
What ocular muscles are in their eyes
Additional extraocular muscle the depressor palpabrae
Rectus dorsalis
Large retrobulbar venous sinus outside the extraocular muscles
What drains rabbits eyes
The external jugular
What are the features of rabbit dentition
Hypsodont teeth
Reserve crown
Enamel extens below the gumline
Aradicular and elodont so have open root or no true root
Peg teeth
What is their dental formula
I 2/1 C0/0 P3/2 M 3/3
What is the sequence of events which leads to the development of chronic dental disease in rabbits
Dietary cause such as low fibre causing reduced tooth wear
Inadequate occlusal wear causes overgrowth of incisors, premolars and molars
Maloclussion develops which alters the bite and spurs form
Progressive elongation of teeth causes roots to elongate intp jaw bones
Causes pain and anorexia
Which features makes it difficult to examine the mouth of a conscious rabbit
Small oral cavity
Large tongue
Narrow oropharynx
Cheek folds
Strong jaw muscles
Stress and fragility
Why is it sensitive to touch a rabbits nose
They have a blind spot so adaptations to compensate it
Sensitive pads on nares
Presence of vibrissae
What are the main features of a rabbits respiratory system
Obligate nasal breathers
Epiglottis rostral to soft pallate
Nose twitches rapidly unless very relaxed
30-60 bpm respiratory rate
Small thoracic cavity
High chest wall compliance
Low functional residual capacity
Diaphragmatic contraction drives breathing
Very sensitive to respiratory irritants
What is the structure of their lungs
Right lobe has cranial, middle, causal and accessory lobes
Left lung as cranial, middle and caudal lobes
Thymus persists in the adult rabbit found in the cranial mediastinum
Why is intubating a rabbit challenging
Long tongue
Small glottis
Narrow oropharynx
Laryngospasm
What are the key cardiovascular parameters of rabbits
Heart rate is 150-300 bpm
Systolic blood pressure is 90-135 mmHg
Total blood volume is 50-75 ml/kg
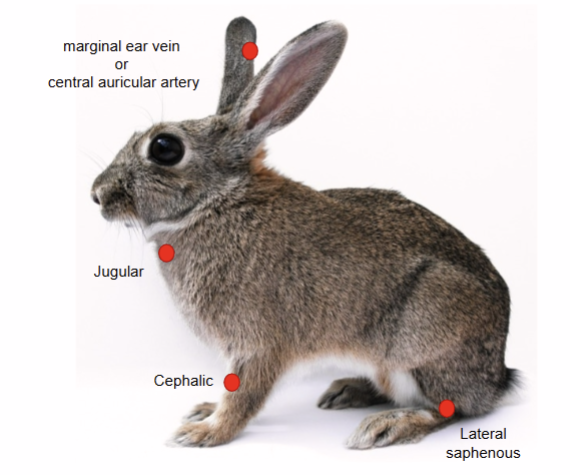
What are the venupuncture sites on rabbits
Jugular
Lateral saphenous
Cephalic
Marginal ear vein
What are the main features of their digestive system
Hind gut fermenters
Large stomach and huge caecum
Highly efficient food converters
WIll select concentrates over fibre
Fibre essential for gut health
Do have a gall bladder
What happens at the first stage of rabbit digestion
Starts at the mouth
Grinding action of the cheek teeth
Strong tongue ensures all food is masticated prior to swallowing
What are the salivary glands
Parotid
Sublingual
Zygomatic
Mandibular
What is the oesophagus like
Three layers of striated muscle extending all the way to the cardia of the stomach
What is the stomach like
Lies to left of midline
Thin walled and J shaped
Well developed cardiac sphincter prevents vomiting
What is the pH of rabbits stomach
1-2 so stomach and SI are practically sterile
Neonates is 5-6.5
What is the small intestine like
Accounts for 12% of digestive tract volume
Secretes an enzyme called moltin
Moltin stimulates motility in SI, colon and rectum but no effect on caesum
Moltin is released in response to fat and inhibited by carbohydrate
What is the sacculus rotundus
Where the terminal ileum ends at the junction with the colon and caecum
What does the hindgut consist of
Caecum
Promimal colon
Distal colon
What is the caecum like
40% of GI volume
Ends in vermiform appendix
What is the proximal colon like
50cm
Split into haustra sacculations, single haustra and fusus coli
Terminal portion is fusus coli
What does the fusus coli do
Regulated passage of ingesta into distal colon
Seperates hard from soft faeces
What is the distal colon like
90 cm
No sacculations
Very long
What happens in hindgut fermentation
Microorganisms in the caecum perform fermentation producing VFA which absorb across the caecal wall
The bacteria replicate in the caecum forming a vital source of protein
Caecal contents are expelles as caecotrophs which are eaten from the anus
Caecal pellet protected from stomach by by mucus covering and bacterial replication continues
Digestion of caecel pellet delivers protein to animal
What controls gut motility
ANS controls GI tract motility particularu the fusus coli
Hormonal control by motilin and prostaglandin
Presence of indigestible fibre in gut encourages motility and reduces caecal retention time
How are hard pellets produced
Contractions in proximal colon separate indigestable particles from liquid component
Indigestable contents move to centre of lumen and further water is absorbed
Hard pellets are produced
What are soft faeces formed
Smaller particles and liquid content move into peripheral lumen
Antiperistalysis returns them to caecum for further fermentation
Caecum contracts to expel soft contents into proximal colon which then move rapidly through distal colon with no further absorption
What are caecotrophs
Produced about 8 hours post feeding
Eaten directly from anus
Provide source of protein, vitamin B and K
What discourages consumption of caecotrophs
High protein and low fibre
What encourages consumption of caecotrophs
High fibre and low protein
What is the reproductive capacity of rabbits
Around 60 kits per year
Can rebreed immediately after giving birth
What are the features of rabbits reproductive cycle
Induced ovulators
Ovulations occurs 10-13 hours after coitus
Gestation length of 30-33 days
Parturition lasts 30 minutes
What do kits eat
Feed once or twice a day for 3-5 minutes at a time
Maternal immunity is placental
Start to take solid food around 18-21 days
What is the nutritional value of rabbit milk
13% Protein
9% fat
1% lactose
2.3% minerals
How are rabbits sexed
Best sexed at weaning or later
Should be double checked
Males have no nipples
Men have sccrotal sac and prepuce
What are the features of a rabbits penis
Sits within rounded penile sheath
Can be extruded using gentle digital pressure from 2 months old
No os penis
What are the features of the scent glands
Two hairless pockets seen either side of the urogenital area
Often have hard and crusty material within
What are the features of the scrotal sacs
Cranial to penis
Large epidydimal fat pads
Open inguinal canal meaning testes can be easily retracted into abdomen
What accessory sex glands do male rabbits have
Seminal vesicles
Prostate
Paired bulbourethral glands
What are the features of the female reproductive system
Duplex uterus
Large saccular vagina
Two cervices
Long convuleted oviducts
Mesometrium stores fat
Uterus and ovarian pedicle
What happens in pseudopregnancy
Caused by infertile mating or presence of a male
Caused by secretion of progesterone from CL
See enlarged mammary glands and abdomen
May pluck belly and make a nest
Regresses naturally but can reoccur multiple times
What are the features of their red blood cells
HCT 33-35%
RBC smaller then canine but larger then feline
Anisocytosis and polychromasia and normal on a smear
Lifespan of 57 days
What are the features of their white blood cells
Lymphocyte is the most common circulating leucocyte
Neutrophils called heterophils as cytoplasm stains pink-red
Eosinophils have a bilobed nucleus and birght pink staining granuals
What is the rabbits vertebral formula
C7, T12, L7, S4, Cd16
WHat are the features of their musculoskeletal system
Light and flexible
Powerful epaxial and hindlimb muscles
Tibail and fibula partially fused
5 digits of forelimb
4 digits on hindlimb
No footpads
What are the three hair types
Long guard hairs
Short guard hairs
Undercoat
What are the different fur types
Satin
Rex
Wool
Normal
What causes ulcerative pododermatitis
No footpads
Exacerbated by hard cage surfaces and unhygienic conditions
More common in overweight animals or those with thin coat
Where are the scent glands
Chin glands
Inguinal glands
Anal glands
What are the features of the kidneys
Unipapillate
Single medullary pyramid
How does rabbit calcium absorption differ from that of most other mammals
It is passive and unregulated
Absorb calcium directly in proportion to how much is in the diet
Excess calcium is not blocked at the gut but instead excreted through the kidneys into urine as calcium carbonate crystals
This is why rabbit urine can appear thick
What does normal urine look like
From pale yellow to dark red
Cloudy
Colour is dietary dependent
What causes urolithiasis
Excessive prolonged dietary calcium intake
What is the normal pH of rabbits urine
8-9
Because of insoluble calcium precipitates
Can cause bladder and urinary stones