Week 1 - Chemistry For Biologists
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Atom
Nucleus = protons (+ve) + neutrons (no charge), electrons (-ve) in cloud around this.
Isotopes
Same number of protons (therefore same element) but different number of neutrons.
Radioactive isotopes
Some isotopes are not stable.
Molecules
Contain two or more elements joined together eg molecular oxygen O2.
Compounds
Molecules made up of different elements eg carbon dioxide CO2.
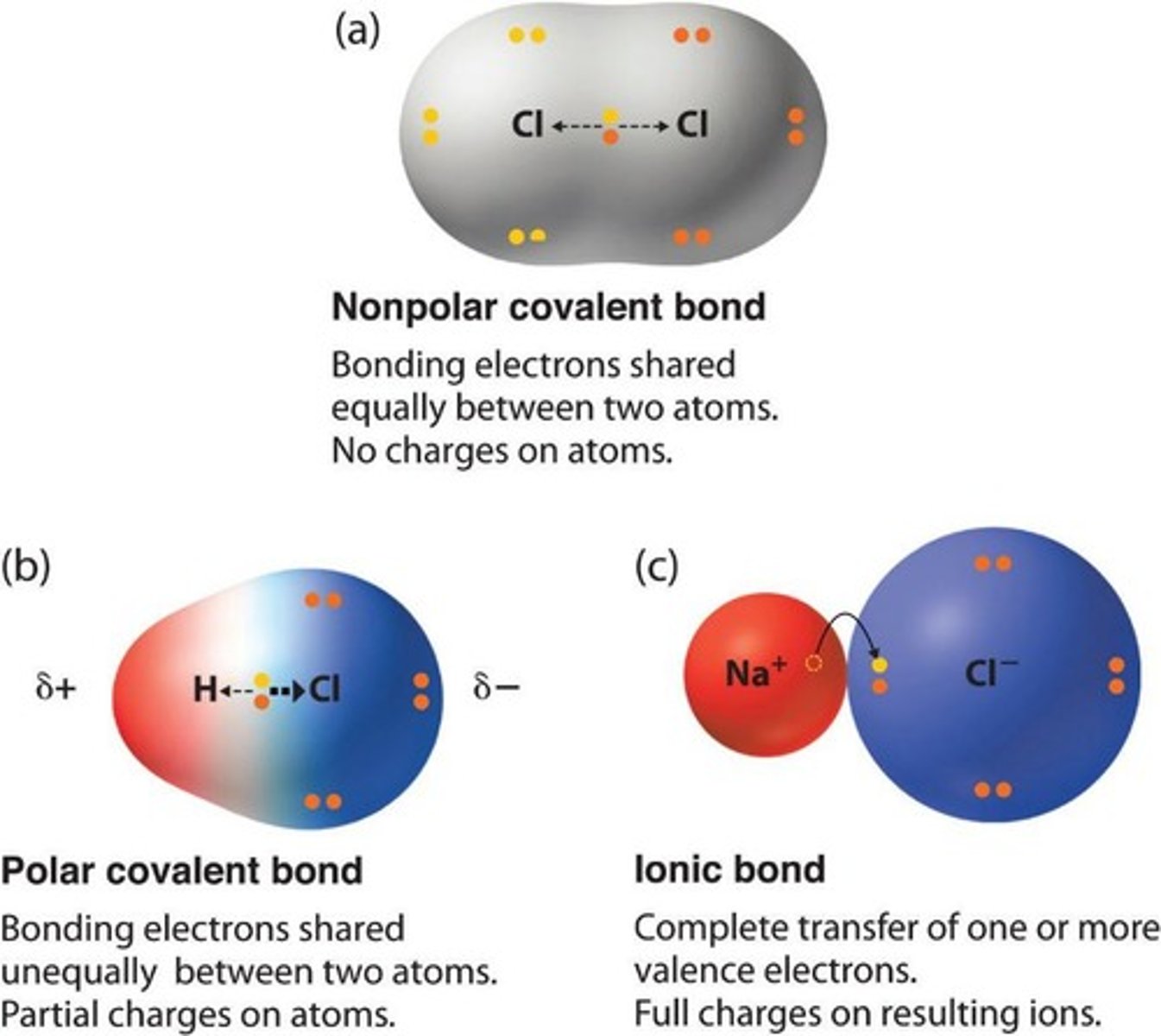
Covalent bond
Electrons are shared (Two non-metals eg. H2O).
Ionic bond
Not shared evenly (between non-metal and metal eg. NaCl).
Metallic bond
Electrons shared (Two metals).
Hydrogen bonds
A special type of dipole dipole bond occurs specifically between a hydrogen atom bonded to either an oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atom.
Dipole dipole bonds
Occur when the partially positively charged part of a molecule interacts with the partially negatively charged part of the neighbouring molecule.
Van der Waal's forces
Also called London dispersion forces; weak in small molecules, but increase in strength in larger molecules.
Organic compounds
Compounds built around carbon which likes to form 4 covalent bonds.
Inorganic compounds
Compounds that do not contain C-H bonds.
Structure = function
The three-dimensional shape of macromolecules is due to the covalent bonds formed by carbon.
Temporary dipole effect
Occurs when electrons collect asymmetrically around the molecule.
Polar covalent bonds
Bonds where there is a difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved, leading to partial charges.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA
Hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Macromolecules
Large molecules that include proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and double stranded DNA.
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Nucleus
The central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons.
Electrons
Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom.
Protons
Positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutrons
Neutral particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Chemical bonds
Forces that hold atoms together in compounds and molecules.