Chapter 2: Organisation of the organism
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
cell membrane
partially permeable to allow certain substances to enter and leave the cell
cytoplasm
where chemical reactions take place
nucleus
contains DNA and controls the cell
mitochondria
where aerobic respiration happens
ribosome
allows protein synthesis
vacoule
cell sap to keep cell turgid
cell wall
rigid to keep shape of cell, strengthens the cell
chloroplast
contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
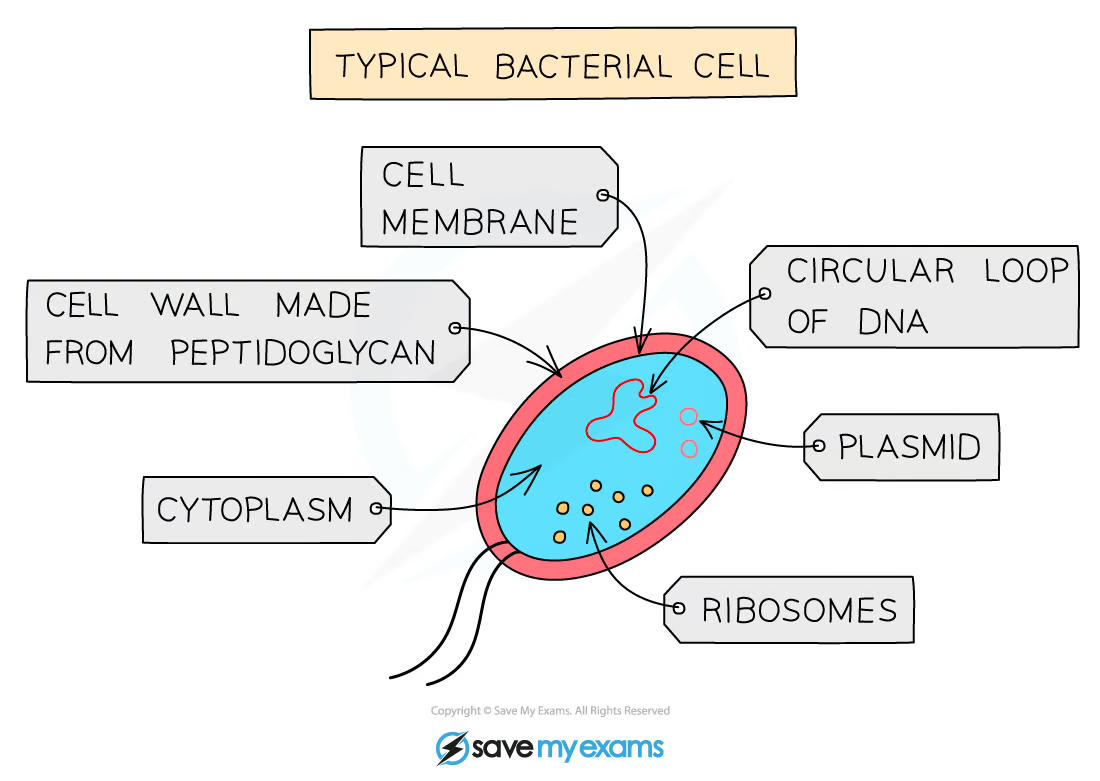
structure of a bacterial cell
cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, circular DNA, plasmids
function of ciliated cells
movement of mucus in the trachea and bronchi
adaptations of ciliated cells
tiny hairs called cillia
function of root hair cells
absorption
adaptations of root hair cells
elongated shape for more surface area
function of palisade mesophyll cells
photosynthesis
adaptations of palisade mesophyll cells
regular shape so it can fit in small spaces
many chloroplasts
function of neurons
conduction of electrical impulses
adaptations of neurons
long, connections on both ends
function of red blood cells
transport of oxygen
adaptations of red blood cells
no nucleus, allows for more O2 transport
large surface area
function of sperm and egg cells (gametes)
reproduction
adaptations of sperm
flagellum to move
adaptations of egg cells
large, bulky
contains egg yolk
formula for magnification
size of drawing / size of specimen
image / actual
cm to mm to micrometer
1 cm = 10 mm
1 mm = 1000 micrometers