1 Biological Classification and Diversity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Carbohydrates
Composed of Carbon atoms (C) , Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O)
Monosaccharides
cannot be broken down into smaller sugars
Polysaccharides
composed many monosaccharides attached by glycosidic bonds
Lipids
group of diverse hydrophobic macromolecules; 3 different types of lipids
Fats and Oils
Important energy source and source of essential fatty acids
Phospholipids
Biological membranes composed of 2 layers of phospholipids
Steroids
Cell communication
Proteins
have a range of function and chemical properties which include structure, enzymes, storage, contractile, and transport
DNA
Carries the genetic information of the cell. Specific portions of DNA (genes) are used as instructions to synthesize proteins
RNA
Most types are involved in protein synthesis
Central Dogma
The process by which genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins, explaining the transfer of sequence information.
Cell/Plasma Membrane
Separate the interior of the cell (cytoplasm) from the external environment
Taxonomy
branch of Biology that names and classifies organisms based on their similarities and differences
Taxon (taxa)
Groups of organisms in a classification system, such as species, genus, family, and higher ranks that share common characteristics
Species
group of living organisms that under normal conditions will breed and have healthy fertile offspring with other individuals within that group. Two organisms of the same species are the most similar to each other
binomial nomenclature
scientific name for an organism consists of 2 words
Genus + Species (Italic)
3 domains
1. Domain Bacteria
2. Domain Archaea
3. Domain Eukarya
Criteria for 3 domains
- Presence or absence of Nucleus and membrane bound Organelles
- Number of Cells
- Metabolism
Systematics
field of Biology that uses comparative anatomy, development and molecular data to determine the evolutionary relationships between species
Phylogenetic Tree
a diagram that depicts the relationship between different species or groups of organisms
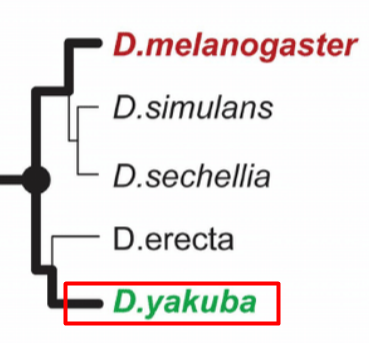
The tip
represents a species or a group of species
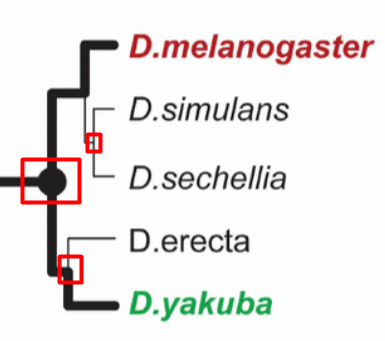
Node
represents a common ancestor
Branching event
represents a point where new a species formed, possibly acquiring new traits, differentiating them from the common ancestor
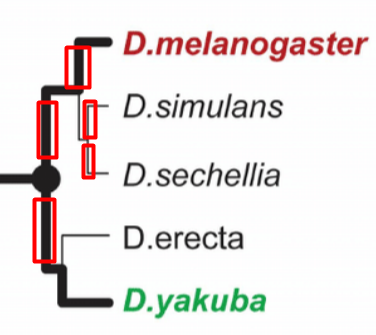
basal taxon
A lineage that evolved early from the root and that remains unbranched
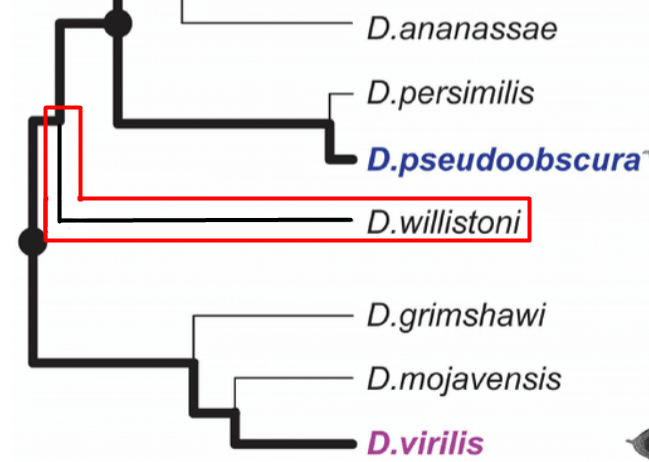
sister taxa
Two groups/species are considered this if they share one node
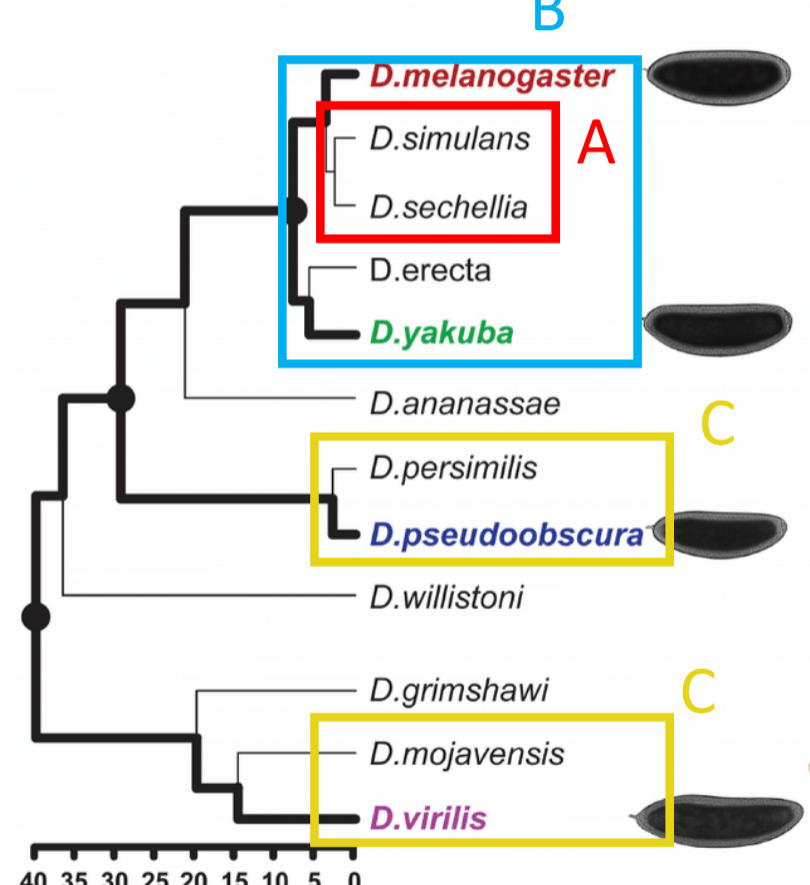
clade (monophyletic group)
group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
In the image, group A and B are a clade while group C is not