Classics midterm 2 terms
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
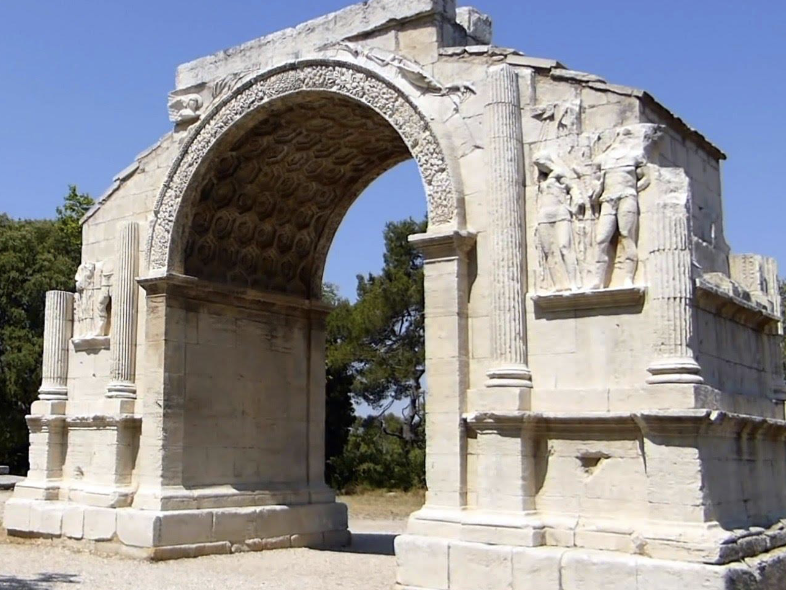

Arch: triumph
Romans build arches to show their dominance or physical control of the place
its possible that the Glanum arch (built in 10-25 BCE) is a triumph arch because its at the city entrance, but its embedded in the city wall so it might not be.
example: glanum arch in this picture, one that is for sure a triumphal arch is the arch of titus
Attic
The flat top part of a triumphal arch (the part that sits on top of the piers
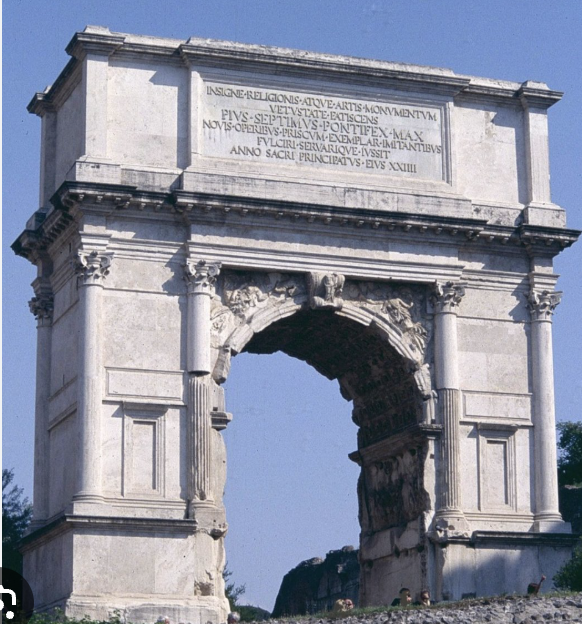

Single bay arch
less common, only one arch window in a triumphal arch
example: the arch of titus
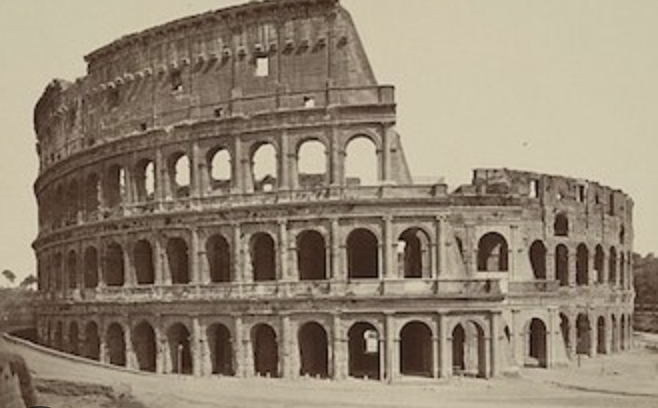

Arcade: running arches over and over next to each other
example: the exterior of the colosseum has three stories of arcades (the fourth story is just windows)
Forum
the place of public meetings, law courts, the main area for Roman activity during the republic.
Emblema
Central panel, usually made off site and set into the pavement
example could be in the house of the painters at work, or the paintings of families/imperial people in the forum of trajan
Apotheosis
Deification: glorification of a subject to divine levels. Done to Julius Caesar after his death. Diefied people do not wear shoes.
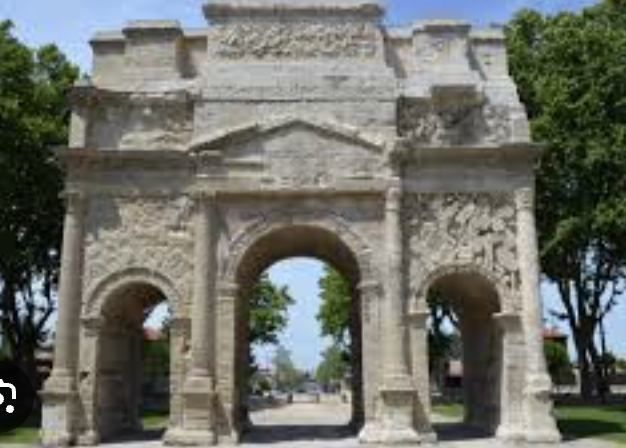

triple bay arch
more common roman arches
three arch categories
example: the glaunum arch
Ashlar masonry
regular cut and quarried stone
no mortar to glue together different pieces of stone
first style of painting is made to look like ashlar masonry. The colosseum uses more of this traditional style by using iron clamps to connect travertine piers rather than using mortar
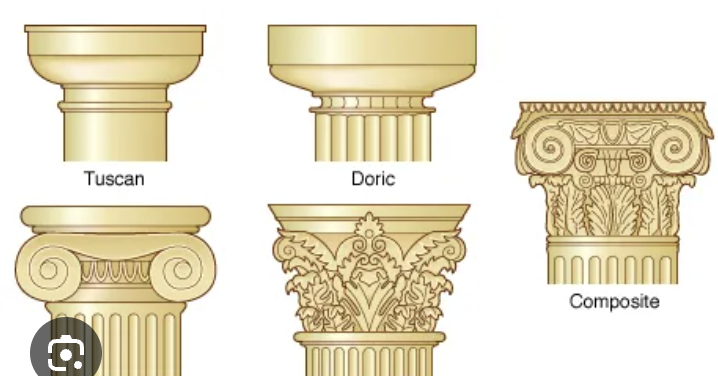
capital
Tuscan: smooth column without volutes
Doric: ribbed column without volutes
Ionic: ribbed column with swirly volutes
Corinthian: heavily decorated top
colisseum used tuscan, ionic, corinthian in that order for the arcades
Cella
cell
the inner area of a temple
usually etruscan temples are tripartite aka three cells
Dromos
passageway in greek (usually entrance to a tomb)
Forum
the roman forum was a large rectangular plaza that had all the buildings necessary for civic functioning. There were other forums (the main was forum boarium) but there was also the forum built by Pompey and Caesar.
Manubial temple
temple dedicated by a general to a god before going to battle to celebrate their eventual conquest
most built in campus martius
example: temple of portunus, temple of herculus victor, temple in the forum of trajan was built from the spoils of Trajan’s victory over Dacia
Necropolis
city of the dead, lots of earthen burial mounds. This was common in Etruscan culture seen in cerveteri
example: cerveteri
Travertine
local stone in Rome that looks and acts like marble, but is local rather than the greek marble
most of the colosseum used travertine, very little of it used concrete (more for decor)
Tumulus
above ground earthen burial mounds
tombs
seein cerveteri and tarquinia
Axial orientation
direction of entrance for a building/temple
etruscan temples have frontal axial orientation
greek temples have access on all sides
the pantheon has a frontal axial orientation which makes you see a very ancient approach (triangular pediment, corinthian columns, marcus Agrippa’s name) and it confuses you when you walk into the dome
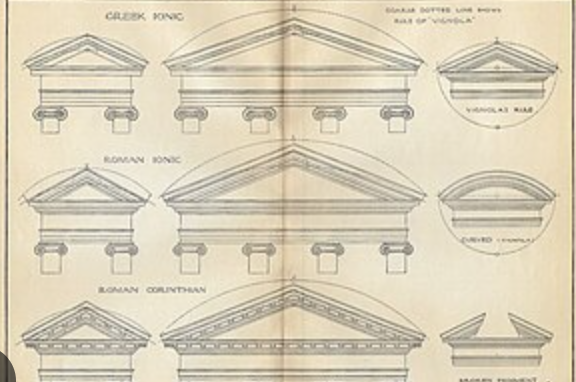
Pediment
top of the temple (the triangular part)
traditional pediment on pantheon, but there is a second one as well
peripteral
having columns all around a building
greek style
temple to augustus and roma in Judea has peripteral columns (very much influenced by hellenistic styles)
pseudoperipteral
having columns just in the front of the temple that are freestanding and the others are engaged in the back
roman style mimicking a greek style but slightly different
podium
lifted platform that the temple sits on
common for roman/etruscan temples
porch
deep porch is common for etruscan temples
where the columns stand
Tholos
round building
more common for greek architecture
example: temple of herculus victor, monument of Julii (the top of it)
Tripartite architecture
three part architecture
common in etruscan culture
seen in the triple bay arches (the triumphal arch of tiberius at orange)
arena
the main stage area in an amphitheater
the arena in the colosseum used to be sand previously, and then was filled in later
Cavea
seating area in an amphitheater
Atrium
the entrance foyer type of area
house of the vetti atrium has lockboxes
Fauces
entryway into the roman domus (the roman house)
fauces have apotropaic images
impluvium
the sunken basin in the peristyle garden that catches rainwater or has a fountain
tablinum
area for the client patron meetings (salutatio)
house of vetti has this removed and has a peristyle garden instead
triclinium
the dining room in a roman domus
likely the unfinished room in the house of the painters at work
dado
bottom strip in a fresco painting
usually has a different pattern or color
left unfinished in the triclinium in the house of the painters at work
fresco painting
using pigment on wet plaster to seal in a water based color painting onto the wall
acroterion
a sculpture that is placed on the top of a pedestal or building
the acroterion of minerva and hercules was the only surviving part of the archaic temple on the tiber
historical relief
common in roman art
displays a roman historical retelling in sculptures
imago
likeness, word for portrait
roman domus has imago showing the comparison or similarities to their ancestors
register
division of a sculpture into horizontal bands or rows
ara pacis has two registers
terra cotta
baked earth
a lot of terracotta used in etruscan culture (cerveteri)
sarcophagus of the spouses
Verism
showing age and wisdom through wrinkles on the face
example: veristic portrait of a mid first century BCE male (head covered)
claudius goes back to this veristic idea because he comes to power at a later age and wants to connect himself with his legacy
Emblema
central panel usually made off site and later set into the pavement
??? example
Opus vermiculatum
worm like mosaic work
in the house of the faun (the alexander the great and theater mask mosaics)
opus sectile
more geometric cut mosaic work
in the tablinum of the house of faun
tessera
small regular cut stones used in mosaics
obverse
head side of a coin
reverse
tails of a coin
Apotropaic
wards off evil
the fauces image of priapus in the house of the vetti is an apotropaic
apotheosis
deification: turning a mortal into a god like divine figure
the arch of titus “apotheosis of Titus” shows this
decursio
roman military parade in honor of the deceased
damnatio memoriae
public condemnation of a person’s memory
this is a modern term for the common roman practice at this time
seen in the cancelleria relief where domitian is removed and repalced with nerva’s head
paludamentum
military cloak worn by a general
seen in the portrait of the Tivoli general
profectio
a ritual before a departure for war
this is seen in the cancelleria relief
princeps
means “first”, the title given to Augustus in 27 BCE when he didn’t want to come to power as “emperor” but the people named him princeps or first citizen
pater patriae
father of the fatherland
name given to augustus in 2 BCE
fibula
pin
granulation
covering a surface with tiny granules of precious metals or gold
this is seen in the fibula found in the regolini galassi tomb
spolia
war booty
often displayed in different sculptures or reliefs showing victory
seen in the arch of titus (the side showing Spoils from the sack of jerusalem, the menorah is a spoil of that war)
souvetaurilia
sacrifice of a bull
seen in the altar of domitius ahenobarbus
trophy
captures arms of the enemy are built to look like a scarecrow on a wooden post
shows victory sign
iconography
interpretation of visual symbols or images