Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms in Biology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is homeostasis?
The relatively constant physiological state of the body despite fluctuations in the environment.
What are the two coordinating systems that maintain homeostasis?
The nervous system and the endocrine (hormonal) system.
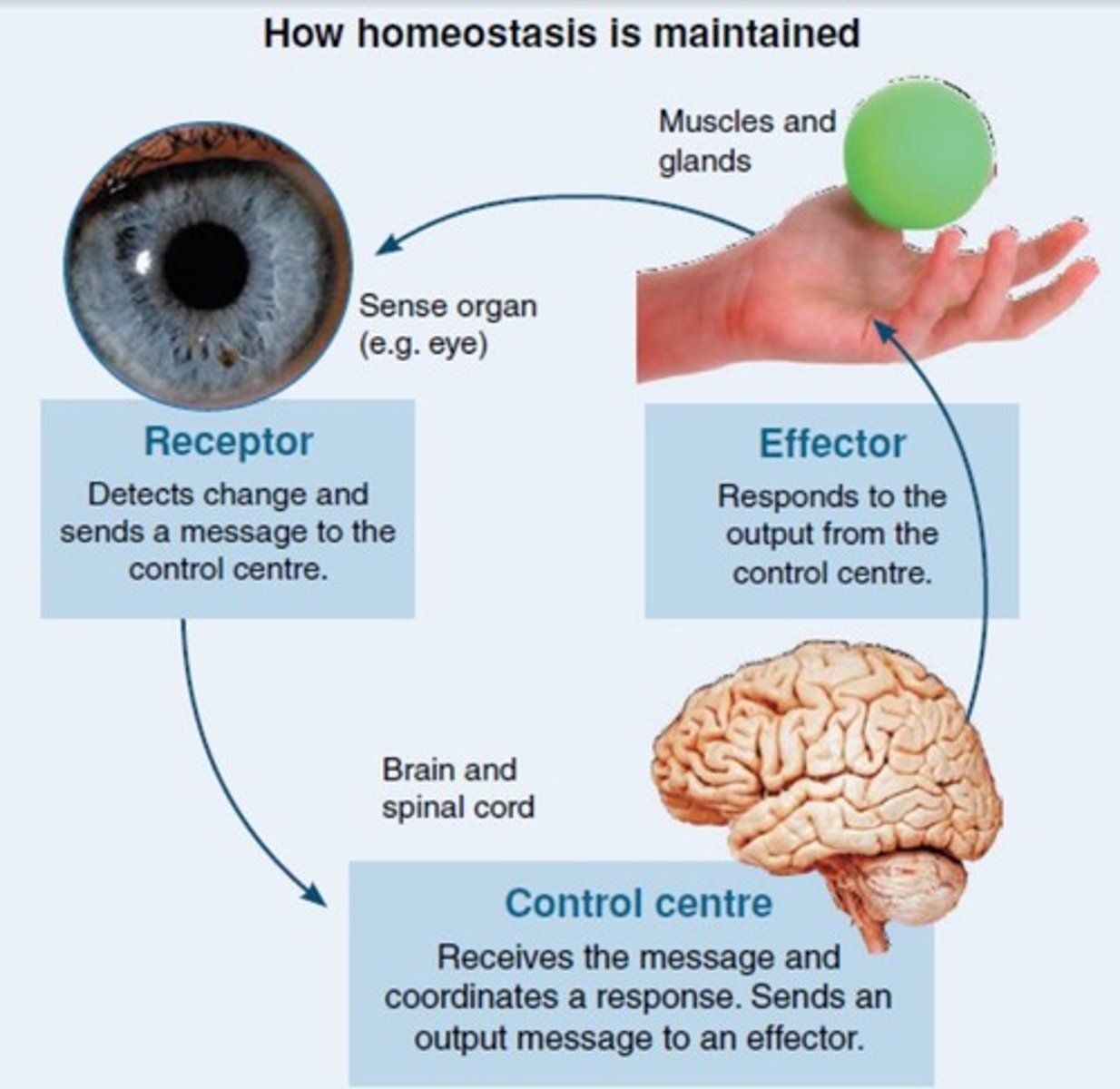
What is the stimulus-response model?
1.Detection of the stimulus/input changes chemical molecules within the cell or animal. In multicellular animals specialised cells are found in a sense organ (receptor).
2.A chemical message is then transmitted to a coordinating centre (regulator: either spinal cord or brain) that determines if a change is required.
3.If so, another chemical message brings about a response (output) within a single cell or effector organ (muscle –movement, or gland – hormone secretion).
What role do sensory receptors play in the body?
They allow the body to respond to a range of stimuli in the internal and external environments.
What do mechanoreceptors respond to?
Physical pressure or distortion. Found throughout the body including skin, muscles, joints and the inner ear.
Where are thermoreceptors primarily found?
In the skin, particularly in areas more sensitive to temperature changes. Detect changes in skin temp and provide info to Hypothalamus in the brain
What do nociceptors detect?
Noxious or potentially damaging stimuli, including extremes in temperature, pressure, and toxic chemicals. They are sensory neurons that are external: skin, cornea, mouth and nose and internal receptors in several organs. Experienced as pain.
What is the function of photoreceptors?
They detect color, intensity, and movement of light in the eyes.
What do chemoreceptors detect?
The presence of chemicals, such as smell, taste, and levels of CO2 & O2 in the blood. Breathing and hr increase and decrease to adjust blood composition
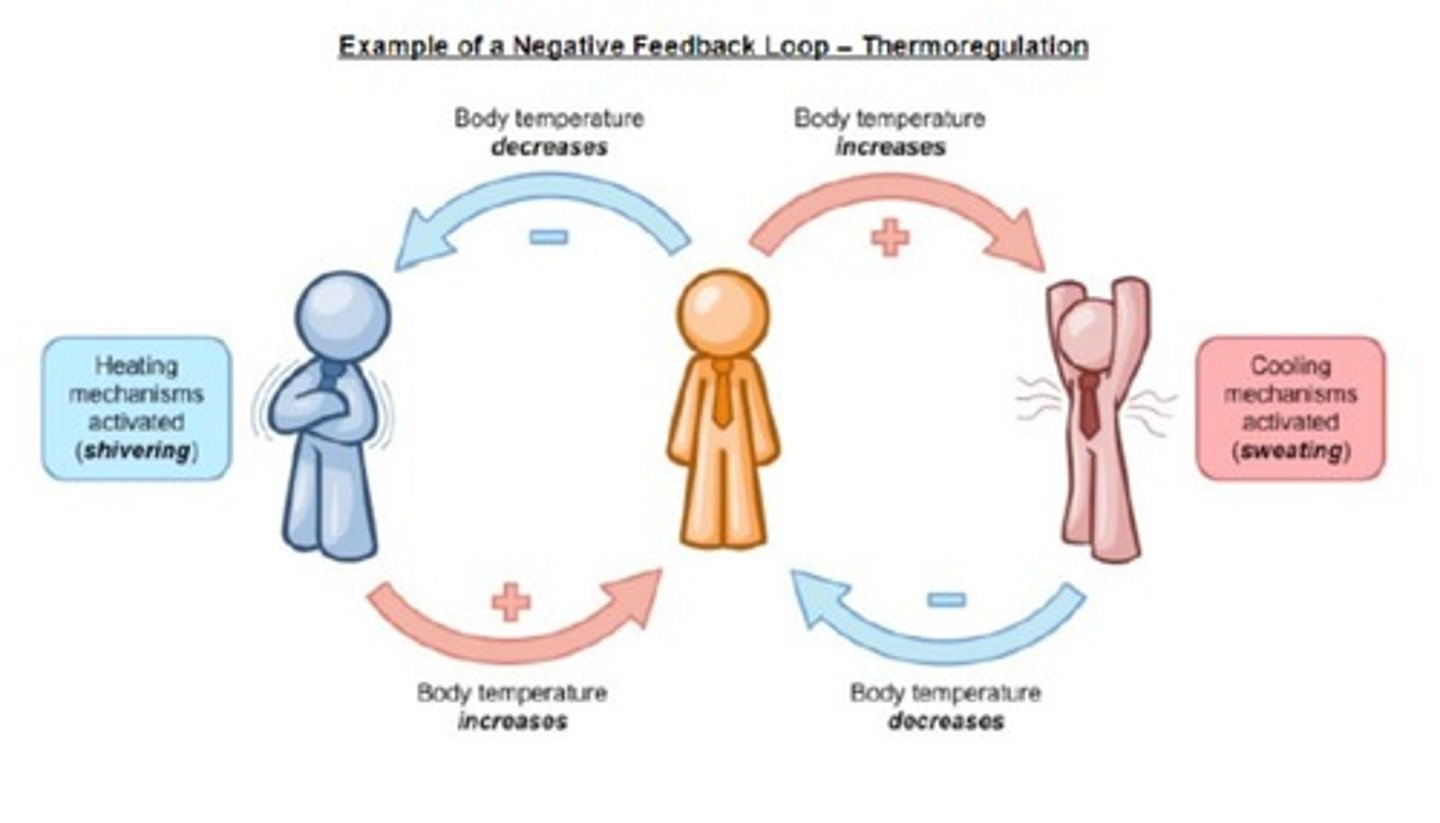
What is negative feedback in homeostasis?
A mechanism that detects departures from a desired set point and acts to restore the steady state. Dampens variations and has a stabilising effect.
What are some examples of negative feedback mechanisms?
Thermoregulation, blood sugar regulation, and osmoregulation.
What is positive feedback?
A response that reinforces and amplifies the change detected until the stimulus is removed.

What are some examples of positive feedback mechanisms?
Childbirth, lactation, ovulation, blood clotting, and fever.
What is the effect of unresolved positive feedback?
It can be fatal, as seen in cases like fever.
How do sensory receptors contribute to homeostasis?
They detect changes in the environment and send signals to coordinating centers to initiate appropriate responses.
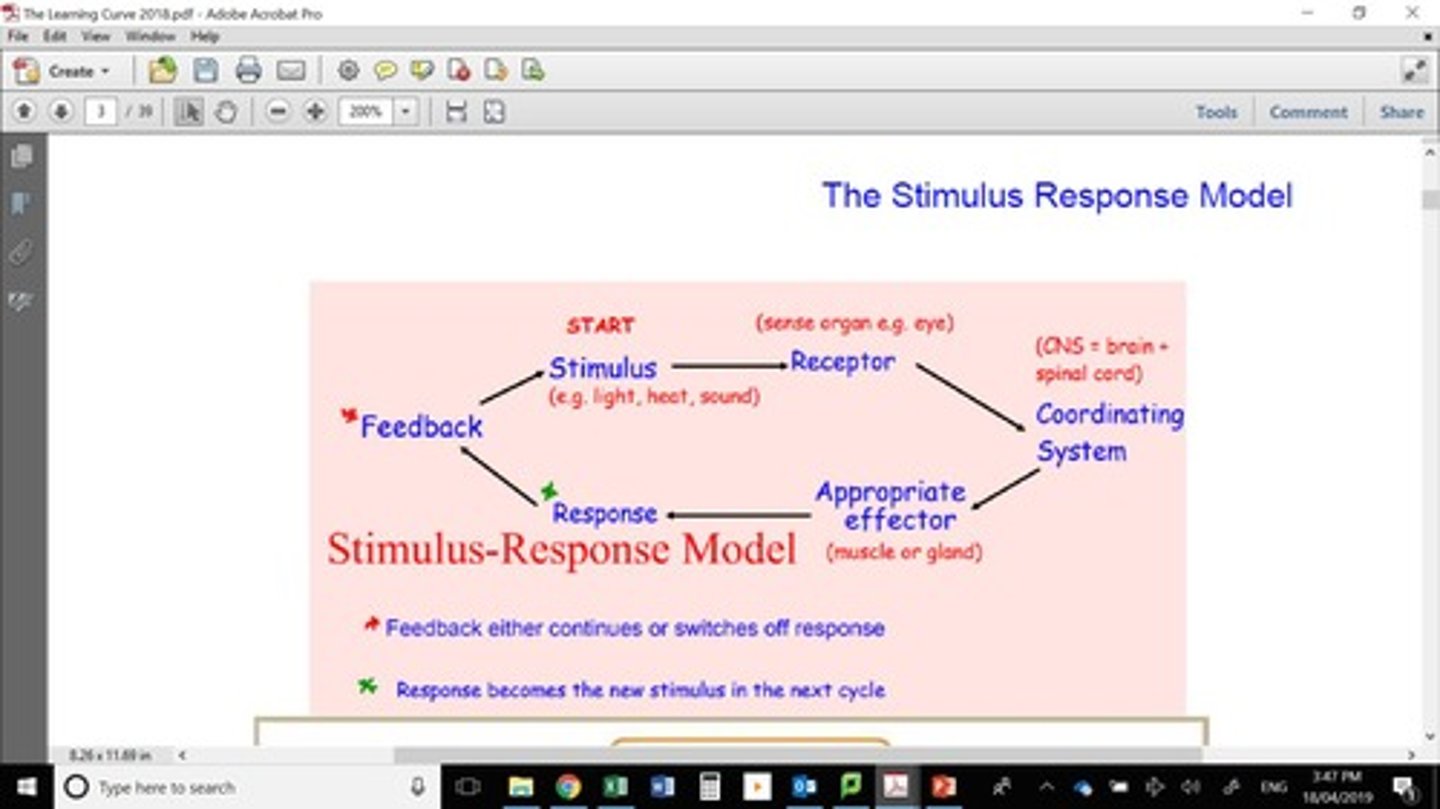
What is the role of the coordinating center in the stimulus-response model?
It determines if a change is required based on the received stimulus.
What happens after the coordinating center decides a response is needed?
Another chemical message is sent to an effector organ to bring about a response.
What is the significance of the steady internal state maintained by homeostasis?
It allows the body to function optimally despite external changes.
What is the relationship between homeostasis and feedback mechanisms?
Homeostatic processes are primarily controlled by negative feedback, while positive feedback amplifies changes.
What is the impact of sensory receptors on physiological responses?
They enable the body to react appropriately to stimuli, ensuring homeostasis is maintained.
What is feedback?
A reaction that may act as a stimulus to either stop (negative feedback) or maintain (positive feedback) the behavior/process.
Homeostatic processes are controlled by negative feedback and hence these systems occur more commonly in the body.