M3L1 - Protein Purification
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Why purify proteins
Study the folded 3D structures (xray crystallography)
Identify protein function
What the substrates are
What binding to substrate does
Identify proteins amino acid sequence
Predict the seuqnece of gene encoding the protein
Develope antibodies specific to protein
Can be used in immunoflourescence microscopy to detect protein location in cell/tissue
7 Steps to isolate protein
Identify unique assay/experiment for protein (how to detect it)
Select protein source
Extract proteins from cell
Solubilize protein
stabilize protein
fractionate (seperate) your protein
Evaluate purity
Protein Assay
Way of detecting protein
Ex. measuring enzymatic activity if it’s an enzyme by looking for release of a product or use of substrate
Ex. Use antibody to moniter the presence/conc of protein
Ex. if binds to unique substrate like RNA or actin, moniter biological activity to see presence
Protein Source and Extraction
Should be easily obtained in large amounts
Studying muscle protein? Get it from muscle cells
Studying Hemoglobin? Use RBC
Choose a cell low in similar proteins which may co-purify with your target
Protein source must be low in proteases that may destroy target
You could add protease inhibitors during purificaiton steps
You could also express the rpotein in alternative cell types (like mouse protein in bactera)
Ensures you extract the greatest amount of protein
Lysing Cells:
Chemical lysis
physical grinding
ultrasonic sonicators
Protein Solubilization
Soluble Proteins:
Cytosolic proteins
secreted proteins
Insoluble Proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Membrane-associated Proteins
Factors affecting protein solubility:
Ph of Solution
Salt conc
Presence of detergents (in more insoluble proteins)
Detergents:
Help stabilize molecular interactions in a protein
increases solubility of insoluble proteins in solution
Protein Stabilization
Maintains native structure and prevents degredation
You should maintain non-covalent interactions stabilizing the folded protein
Parameters:
Temp
Protease inhibitors
Ligands
Salts
Metal ions
Concentration of target protein (may aggregate at high conc)
pH
Protein Fractionation
Seperating proteins into different groups
Many techniques are present to take advantage of a chemical/physical property
Proteins vary in
charge
size
polarity
solubility
shape
Protein Fractionation Techniques
Ion Exchange Chromatography (charge)
Gel Filteration Chromatography (Size)
Adsorption Chromatography (Polarity)
Affinity Chromatography (Specificity in Binding)
Protein Fractionation: Charge
Ion exchange chromatography
gel electrophoresis
Protein Fractionation: Size
Gel electrophoresis
gel filteration chromatography
ultracentrifugation
Protein Fractionation: Polarity
Adsorption chromatography
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography
Protein Fractionation: Specificity in Binding
Affinity chromatography
Seperates proteins from a protein-protein or protein-substrate binding
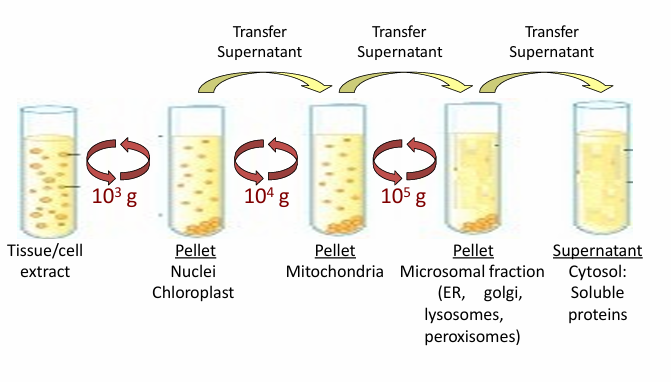
Differential Centrifugation
Commonly begins protein irolation
Isolates a subset of proteins based on size or subcellular localization
Steps:
Spin tubes at 1000g
Produces a pellet at the bottom with nuclei/chloroplasts while fluid has other cellular components
Split those based on the protein you’re studying
Spin supernatant fluid (if that’s where ur protein is) at 10,000g
Produces a pellet with mitochondria
Split those based on the protein ur studying
Spin supernatant fluid (if that’s where ur protein is) at 100,000g
Produces a pellet with ER, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes
Supernatant fluid is just cytosole for cytosolic proteins
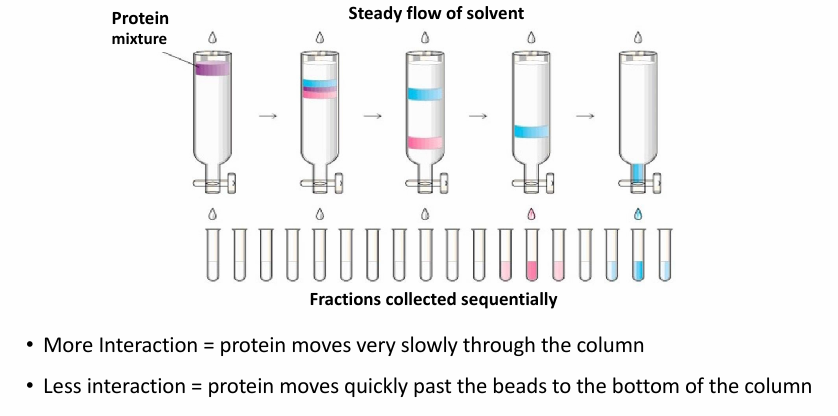
Chromatography
Commonly second step of protein fractionation
(aq) extract is poured down column with matrix to help sort proteins based on different properties
If there’s interaction between protein and beads, it wil be slow to move (blue)
Lower interactions means faster to move (pink)
thus Pink proteins will come out first
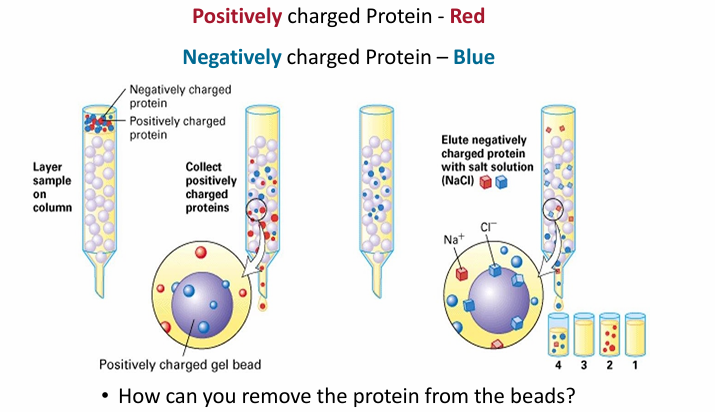
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Beads in the column are charged, usually positive
Example:
Protein extracts are loaded at top (red and blue)
Red = +
Blue = -
Red will flow by faster as + repels +
Blue will be attracted and move slow
To elute blue, the column must be washed
Washing column
Main basis: Interfere with ionis interactions
Way 1: Adding salt solution (NaCl)
Cl- will disrupt the interaction of blue and the beads by interacting with the beads
Way 2: Warm wash solution
Way 3: change in pH of wash solution
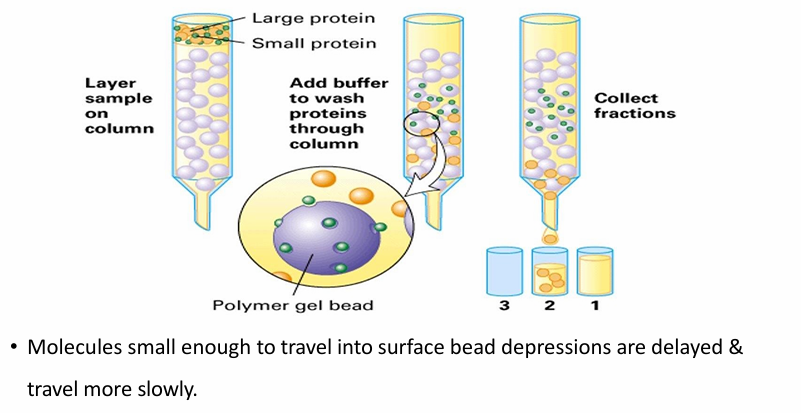
Gel Filteration Chromatography
Seperates protein by size
Beads have small holes in them
Small proteins get trapped while larger ones flow past
Fraction 2 will have all the larger proteins
Removing the beads and washing them/spinning on low speed dislodges small proteins from the beads
Beads can vary in size depending on protein of interest
Bead sizes are defined upon threshold size (the largest protein that could fit)
Affinity Chromatography
Seperates proteins based on specificity of binding to another molecule
Beads are covalently attached to antibody
The antibody will associate with a single protein (the antigen)
target protein will stay in the column due to non-covalent interactions with the antibody
The other proteins elute straight in fraction 1
To remove the target, pH / temp / [salt] can be changed
Ex. a GTP-binding protein can be isolated by attaching GTP to the beads
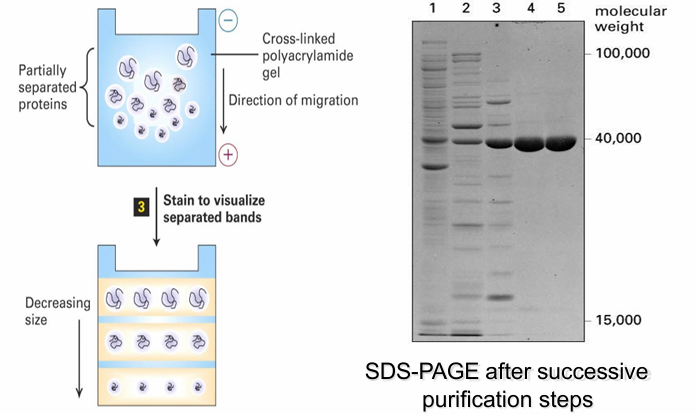
SDS-PAGE electrophoresis
intentionally denatures protein
Denature with SDS and then coat them so all proteins have (-) charge
Eliminates the effect of shape/charge density
Load onto polyacrylamide gel
Apply current through get (all (-) proteins move towards the positive end based on their molecular weight
Small proteins move quick, large move slow
SDS-PAGE electrophoresis: Western Blot
Comding SDS-PAGE electrophoresis with protein-specific antibodies in western blot results in directly detecting the target proteins
Proteins are seperates from polyacrylaminde gel then transferred to membrane
The membrane is incubated with the antibody sollution for target protein so it can be detected
Even if similar structures, it will only identify the target protein