Proximal upper limb
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
3 bones that compose the shoulder girdle
clavicle
scapula
proximal humerus
2 ends of the clavicle
acromial end (attaches at the shoulder)
sternal end (attaches at the sternum)
Jugular notch
jugular (suprasternal) notch is located at the superior end of the sternum
at lateral aspects of jugular notch will feel the medial end of the clavicle, which is bulbous and forms a prominence
Shape of clavicle
S shaped
medial 2/3 convex anteriorly
lateral 1/3 concave anteriorly
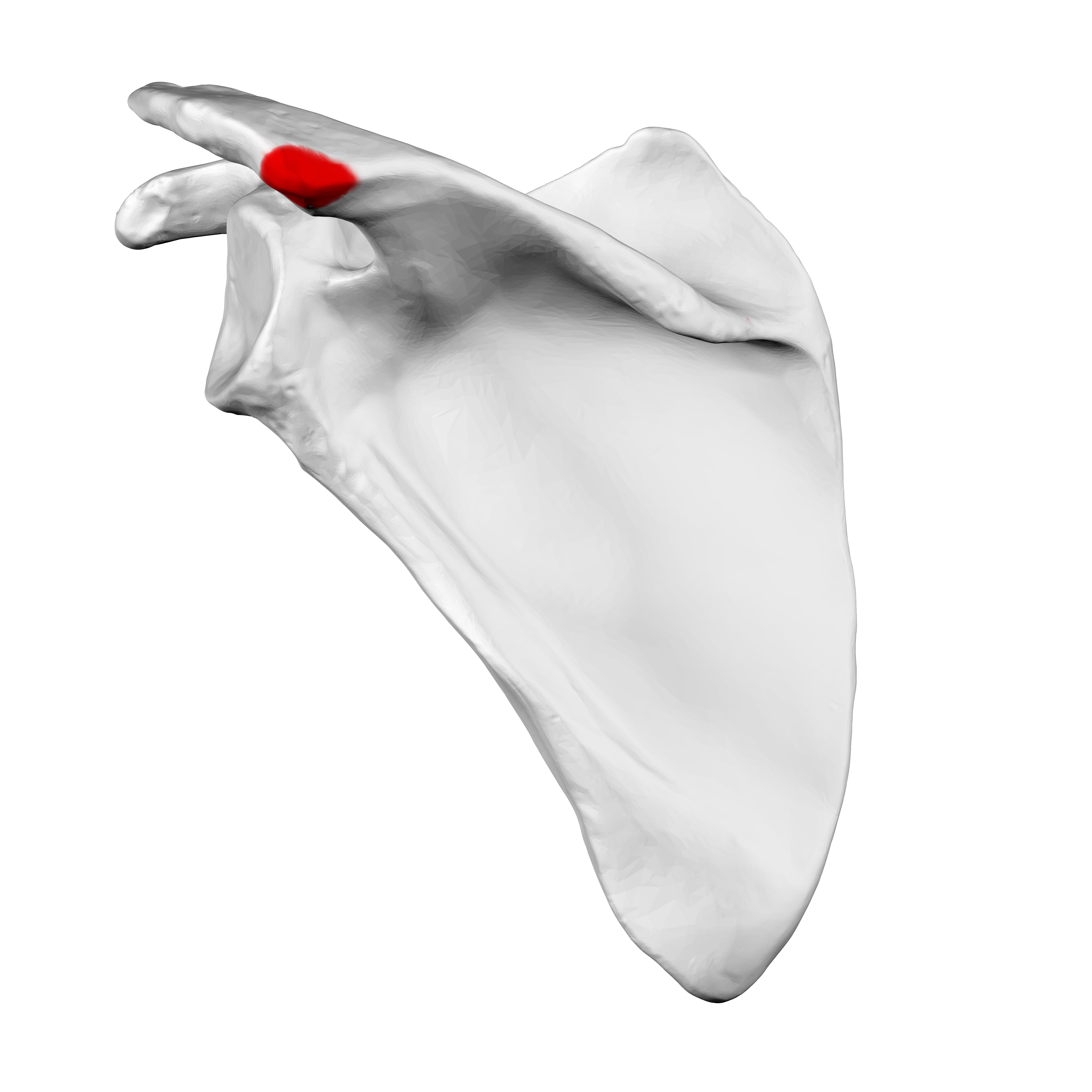
Acromion
will find it when you move laterally from the jugular notch, till the summit of the shoulder
contributes to the contour of the shoulder
is rectangular shape
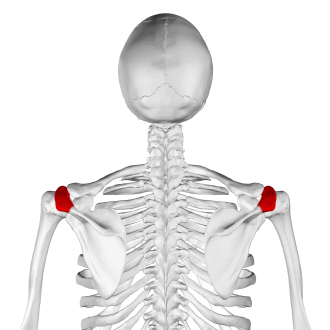
Acromial angle
felt at the point of junction of the lateral border of the acromion, with the inferior border of the crest of the spine of the scapula
angle is used as the proximal point when measuring distances in the upper extremity
What part of the sternum articulates with the clavicle?
Manubrium of sternum
Important features of the proximal humerus
head
shaft
anatomical and surgical necks
greater tubercle (important feature related to shoulder abduction)
lesser tubercle
intertubercular groove
deltoid tuberosity
radial groove
Important features of the sternum
manubrium
jugular (suprasternal) notch
body
xyphoid process
Important features of the scapula include
spine
coracoid process
acromion
acromial angle
medial border
lateral border
superior angle
inferior angle
supraspinous fossa
infraspinous fossa
glenoid cavity
4 joints of the shoulder girdle
sternoclavicular
acromioclavicular
glenohumeral
scapulothoracic
Sternoclavicular joint
between the manubrium of the sternum and the medial end of the clavicle
this joint is the only connection between the axial skeleton and the upper limb
saddle-shaped synovial joint
Acromioclavicular (AC) joint
plane synovial joint
between acromion of scapula and lateral end of clavicle
ligaments include:
acromioclavicular ligament
coracoclavicular ligament
Ligaments of acromioclavicular (AC) joint
acromioclavicular ligament
coracoclavicular ligament
Acromioclavicular ligaments
pair of intrinsic ligaments within the capsule of the joint
Coracoclavicular ligament
extrinsic ligament
is the major stabilizer of the AC joint
2 parts:
conoid ligament
trapezoid ligament
2 parts of coracoclavicular ligament
conoid ligament
trapezoid ligament
Glenohumeral joint
very mobile ball and socket joint
when a limb is raised above the head, ~2/3 of the apparent movement takes place at the glenohumeral joint and ~1/3 of movement is strenoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints
At what degree does the glenohumeral capsule become lax (and why does this happen?)
Capsule becomes lax when the humerus is abducted ~45° from the scapula —> this allows for considerable separation between the scapula and the humerus
What ligament prevents displacement superiorly at the head of the humerus?
Coracoacromial ligament
Scapulohumeral rhythm
refers to the ratio of scapulothoracic and glenohumeral joint movement during shoulder movement
when a limb is raised above the head:
~2/3 of apparent movement is glenohumeral joint
~1/3 of apparent movement is sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joint
scapula and humerus move in 1:2 ratio
i.e. when arm is abducted 180°, 120° is rotation of humerus at glenohumeral joint, 60° is rotation of scapula
can see the medial border and inferior angle of the scapula move during shoulder abduction
Features of the glenohumeral joint
glenoid fossa
glenoid labrum
tendon of long head biceps
coracoid process
acromion
coracoacromial ligament/coracoclavicular ligament
joint capsule
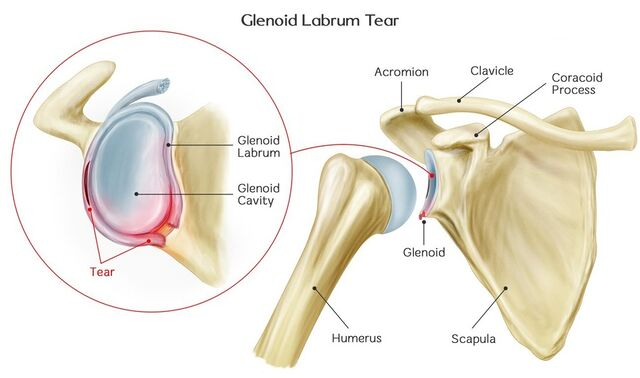
What is the glenoid labrum?
Fibrocartilaginous ring that attaches to the rim of the glenoid fossa, to help deepen and stabilize the shoulder joint
3 movements of scapolothoracic articulation
elevation/depression
protraction/retraction
upward rotation/downward rotation
Scapulothoracic joint/articulation: description, movements
not a true anatomical joint (really an articulation)
used to describe basic movements of the scapula
acromioclavicular and strenoclavicular joints are involved
basic movements of the scapula include: protraction/retraction, elevation/depression, rotation
3 anterior axioappendicular muscles
pectoralis major
pectoralis minor
serratus anterior
2 heads of pectoralis major
clavicular head
sternocostal head
Clavicular head of pectoralis major (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
proximal attachment: clavicle
distal attachment: intertubercular groove of humerus
main action: flexes the glenohumeral joint
Sternocostal head of pectoralis major (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
proximal attachment: sternum
distal attachment: intertubercular groove of humerus
main action: extends the glenohumeral joint from the flexed position
Distal attachment and main action of pectoralis major (as a whole)
distal attachment: anterior edge of intertubercular groove
main action: adduction and medial rotation of glenohumeral joint
Anterior axillary fold
Formed by the inferior border of the pectoralis major
(is the anterior aspect of the armpit,, “chicken wing”)
Pectoralis minor (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
proximal attachment: ribs
distal attachment: coracoid process
main action: stabilization of the scapula against the thoracic wall
Serratus anterior (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
proximal attachment: ribs
distal attachment: medial border of scapula
main action: scapular protraction
*important muscle that stabilizes scapula against body
Posterior axioappendicular muscles (4)
Muscles located from the trunk to the scapula on the back:
trapezius
latissimus dorsi
levator scapulae
rhomboids
How are latissimus dorsi and pectoralis major alike?
Both pass directly from the trunk to the humerus
Latissimus dorsi (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
proximal attachment: thoracic vertebrae, ribs and iliac crest
distal attachment: intertubercular (bicipital) groove of humerus
Main action: glenohumeral extension, adduction and internal (medial) rotation
Relationship between lat dorsi and teres major
Lat dorsi wraps around teres major from posterior to anterior and together these muscles form the posterior axillary fold
What muscles is the posterior axillary fold made up of? (2)
Latissimus dorsi and teres major
3 parts of the trapezius
upper (descending/superior)
middle
lower (ascending/inferior)
Trapezius (medial attachment, lateral attachment, main action)
medial attachment: cranium, cervical and thoracic (T1-T3) vertebrae
lateral attachment: clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula
main action:
upper (descending/superior) fibers: shoulder elevation
middle fibres: scapular retraction
lower (ascending/inferior) fibres: shoulder depression
Where are the rhomboids located in relation to the trapezius?
Rhomboids are deep to the trapezius
2 rhomboids
rhomboid major
rhomboid minor
Rhomboid minor
Medial attachment: vertebrae in neck (C7, T1)
Lateral attachment: medial end of the spine of the scapula
Main action: scapular retraction + downward (medial) rotation
Rhomboid major
Medial attachment: thoracic vertebrae (T2-T5)
Lateral attachment: medial border of the scapula
Main action: scapular retraction and downward (medial) rotation
Rotator cuff muscles (4)
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
teres minor
subscapularis
SITS
What are rotator cuff muscles?
these muscles attach to the scapula
is separated from the coracoacromial arch by the subacromial bursa
inflammation of this bursa is clinically termed subacromial bursitis
Subscapularis (origin, insertion, main action and where it is found)
Origin: subscapular fossa on the anterior surface of the scapula
Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
Main action: strong internal rotator of the shoulder + adducts the glenohumeral joint
Is on the anterior surface of the scapula
Supraspinatus (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: supraspinatus fossa of the scapula
Distal attachment: greater tubercle of the humerus
Main action:
initiation of the first 15° of glenohumeral abduction and assisting the deltoid
from a fully adducted position, glenohumeral abduction MUST be initiated by the supraspinatus
Infraspinatus (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: infraspinatus fossa of the scapula
Distal attachment: greater tubercle of humerus
Main action: external (lateral) rotation of glenohumeral joint
Teres minor (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: lateral border of scapula
Distal attachment: greater tubercle of humerus
Main action: external (lateral) rotation of glenohumeral joint
Parts of deltoid muscle (3)
anterior (clavicular)
middle (acromial)
posterior (spinal)
Deltoid (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula
Distal attachment: deltoid tuberosity
Main actions:
Anterior (clavicular): glenohumeral flexion and internal (medial) rotation
Middle (acromial): glenohumeral (shoulder abduction) —> BUT does not become a fully effective abductor until 15 degrees of abduction
Posterior (spinal): part of glenohumeral extension and external (lateral) rotation
What muscles contribute to glenohumeral flexion? (4)
anterior deltoid
coracobrachialis
pectoralis major (clavicular head)
biceps brachii (long head)
What muscles contribute to glenohumeral extension? (6)
posterior deltoid
latissimus dorsi
teres major
teres minor
triceps (long head)
pectoralis major (sternocostal head)
What muscles contribute to glenohumeral abduction? (2)
middle deltoid
supraspinatus
What muscles contribute to glenohumeral adduction? (6)
latissimus dorsi
pectoralis major
teres major
coracobrachialis
anterior deltoid (if GH is flexed)
posterior deltoid (if GH is extended)
What muscles contribute to glenohumeral external rotation? (3)
infraspinatus
teres minor
posterior deltoid
What muscles contribute to glenohumeral internal rotation? (5)
subscapularis
pectoralis major
latissimus dorsi
teres major
anterior deltoid
serratus anterior
What muscles contribute to scapulothoracic retraction? (3)
rhomboids
trapezius (middle fibers)
latissimus dorsi
What muscles contribute to scapulothoracic elevation? (3)
trapezius (upper fibers)
levator scapulae
rhomboids
What muscles contribute to scapulothoracic depression? (5)
trapezius (lower fibers)
serratus anterior
lat dorsi
pectoralis major (sternocostal head)
pectoralis minor
What muscles contribute to scapulothoracic upward rotation? (2)
trapezius (upper and middle fibers)
serratus anterior
What muscles contribute to scapulothoracic downward rotation? (5)
rhomboids
lat dorsi
levator scapulae
pectoralis major (sternocostal head)
pectoralis minor
Key features of the distal humerus (6)
medial epicondyle (important structure related to tendonitis and fractures)
lateral epicondyle (important structure related to tendonitis and fractures)
trochlea
capitulum
coronoid fossa
olecranon fossa
Olecranon process
Olecranon process forms a prominence on the dorsum of the elbow between the 2 epicondyles
Plane of olecranon process and medial/lateral epicondyles
When elbow extended: olecranon process and medial/lateral epicondyles lie upon the same horizontal plane
When elbow flexed: 3 bony points mark the positions of the angles of an equilateral triangle
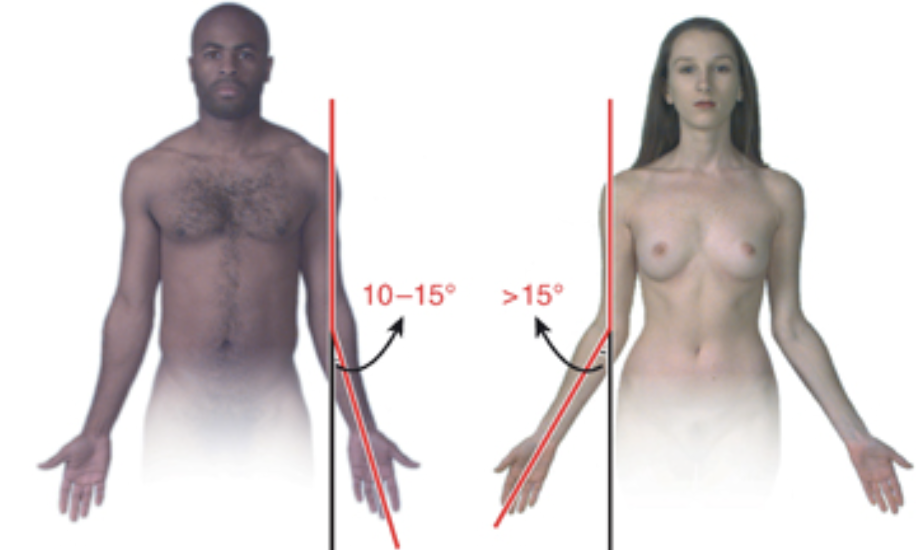
Carrying angle
When elbow is extended, the humerus and ulna do not lie with each other but meet at an angle (carrying angle) of ~10-15°
This is the natural resting posture of these structures
Note that the angle is greater in women
Important features on proximal ulna (4)
olecranon process
coronoid process
trochlear notch
radial notch
Important features on the proximal radius (2)
radial head
neck
3 articulations of the elbow joint
humeroulnar
proximal radioulnar
humeroradial
What type of joint is the elbow joint?
Hinge (flexion/extension)
Ligaments in the elbow joint (3)
ulnar collateral ligament
radial collateral ligament
annular ligament
Movement of humeroradial articulation?
Radius pivots in the annular ligament at the humeroradial articulation and the proximal radioulnar joint
Muscles of the arm (4)
triceps brachii
biceps brachii
corachobrachialis
brachialis
What is the primary component of arm extensor group of muscles?
Triceps brachii
3 heads of triceps brachii
long
lateral
medial
Positioning of long, lateral and medial heads of the triceps brachii
Long and lateral heads lie side by side superficially to the medial head that lies alone on a deeper plane
Triceps brachii long head (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
Distal attachment: olecranon
Main action: elbow extension
*crosses over the shoulder and elbow joints —> extends the elbow as well as the shoulder joint
Triceps brachii lateral head (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: posterior humerus
Distal attachment: olecranon
Main action: elbow extension
Triceps brachii medial head (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: posterior humerus
Distal attachment: olecranon
Main action: elbow extension
When is triceps brachii activated?
Triceps brachii is activated with elbow extension against resistance
3 flexor muscles in the arm
coracobrachialis
biceps brachii
brachialis
Coracobrachialis (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: coracoid process
Distal attachment: humerus
Main action: flexion and adduction of the arm at the glenohumeral joint
Biceps brachii long head (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action + extra info)
Proximal attachment : supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
Distal attachment: tuberosity of radius
Main action: forearm supination and elbow flexion
originates inside the shoulder joint and inserts onto the radius and indirectly to the ulna via the bicipital aponeurosis
crosses the shoulder and elbow —> flexes the elbow and shoulder
Biceps brachii short head (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: coracoid process
Distal attachment: tuberosity of radius
Main action: forearm supination and elbow flexion
Brachialis (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: humerus
Distal attachment: coronoid process
Main action: flexes the elbow joint in all positions
What connects the radius and ulna?
Radius and ulna are connected by the interosseus membrane
Anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm
Anterior compartment: contains flexors and pronators of the forearm
Posterior compartment: contains the extensors and supinators of the forearm
Muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm (8)
supinator
brachioradialis
extensor carpi radialis longus
extensor carpi radialis brevis
extensor carpi ulnaris
extensor digitorum
extensor digiti indicis
extensor digiti minimi
Where are the supinator and brachioradialis found?
Along with the wrist and digital (finger and thumb) extensor muscles in the posterior compartment of forearm
Supinator muscle (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: lateral epicondyle of the humerus and posterior ulna
Distal attachment: radius
Main action: rotates the radius to turn the palm anteriorly (up)
Brachioradialis (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: supraepicondylar ridge of humerus
Distal attachment: radius
Main action: elbow flexion when forearm is in neutral position
Is apparent when the elbow is flexed 90° against resistance with the forearm in the middle position between supination and pronation
Is referred to as the drinking muscle
What 2 muscles contribute to supination of the forearm?
Biceps brachii
Supinator
What are the wrist extensors? (3)
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Where do extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi attach proximally?
They form a common extensor tendon and attach to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Where is extensor digiti indicis found?
In the posterior compartment of the forearm
Originates from the distal 2/3 of the ulna
Extensor carpi radialis longus (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: supracondylar ridge of humerus
Distal attachment: base of 2nd metacarpal
Main action: wrist extension and abduction (radial deviation)
Extensor carpi radialis brevis (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: forms common extensor tendon and attaches to lateral epicondyle of humerus
Distal attachment: base of 3rd metacarpal
Main action: wrist extension and abduction (radial deviation)
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Proximal attachment: forms common extensor tendon and attaches to lateral epicondyle of humerus
Distal attachment: base of 5th metacarpal
Main action: wrist extension and adduction (ulnar deviation)
Extensor digitorum (proximal attachment, distal attachment, main action)
Proximal attachment: forms common extensor tendon and attaches to lateral epicondyle of humerus
Distal attachment: extensor expansions of fingers
Main action: extends fingers primarily at metacarpophalangeal joint (secondarily at the interphalangeal joint)