Microfinance W3-W4
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MF in PH & Int Setting
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1960
rural banks and cooperatives started the concept and practice of serving small loans. agricultural workers and fisherfolks benefited from this initial access to small credit. banks couldn’t sustain the program because of low repayment rate and some structural problems in their scheme
1970-mid 1980
government mobilized rural banks, development banks, and other government financial institutions to provide highly subsidized credit to the rural poor. through its directed credited programs, they hoped to bring down the cost of credit and help ease poverty
Why does DCPs failed?
didn’t reach the target clientele as subsidies were cornered by big borrowers
bred corruption at different levels as these involved government funds
massive repayment problems resulted in huge fiscal costs for the government
New Approach in Credit Methodology
was develop because of the lesson from the implementation of various government credit programs in the 70s and 80s
Late 80s
NGOs became potent partners of the government against poverty through microfinance. they provided much-needed small loan for small entrepreneurial activities
industry evolved from being in the margins to becoming mainstream with commercial banks eyeing to enter the industry
NGOs
they devised alternative options for non-collateralized loans and savings instruments for the poor
provided individual and group lending but sed group pressure or group accountability as collateral
met the needs of the entrepreneurial poor despite of certain regulatory and prudential issues
Philippine microfinance
began as social development initiative to alleviate poverty
moved from marginal to the mainstream, toward commercialization and microbanking
different from other development approaches
microcredit could be sustained without an endless supply of donor subsidies and resources
a feature that attracted government anti-poverty officials who worked on new legislation and mobilized public resources to bring down barriers to the adoption of microfinance by Philippines semi-formal and formal institutions
1993
formation of a Presidential Task Force on Credit for the Poor
consultative meetings to draw up a Master Plan for Credit for the Poor
Master Plan
identified 3 pronged strategy to alleviate poverty through microfinance
policy reform
financial resource-mobilization
capacity building
1st Thrust
to raise financial resources was embodied in the organization of the People’s Credit and Finance Corporation in 1996
2nd Thrust
area of developing a conducive policy environment, including lobbying for the passage of RA 8425 and the establishment of a government body, the National Anti-Poverty Commission (NAPC)
3rd Thrust
building institutional microfinance capacity through government fund called the People’s Development Trust Fund (PDTF)
1990
microfinance sector has grown dramatically in the PH, characterized by increases in terms of the numbers of borrowers, amount of the loan portfolios, number of areas covered, and number of institutions engaged in microfinance
October 2005
over 2.5 million households had access to financial services with total microfinance loan releases to almost 30 billion pesos since 2001
over 99% women borrowers engaged in some form of economic activity
these entrepreneurial poor comprised the bulk of microfinance clients
most were intro trading and services
some engaged in manufacturing or production-related activities
Classification of the poor as target for microfinance services
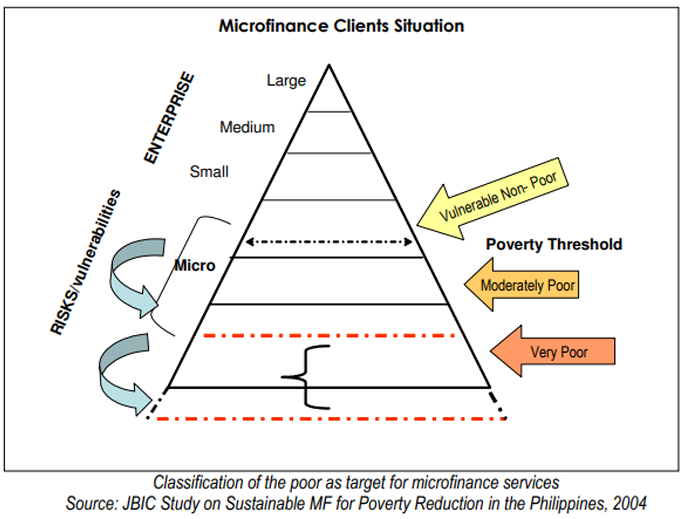
Microfinance Clients
mostly belong to the moderately poor and vulnerable non-poor, which are below the poverty threshold
Common prevailing MF methodologies adopted in the PH
Grameen Bank Approach
the ASA
microenterprise access to banking services (MABS)
extension of loans
continues to be the most dominant service provided to the poor by MF institutions across types
Savings
primarily consisted of forced savings and capital build-up, which formed part of the lending methodologies
Microfinance Sector
compromised 1,000 MF institutions including branches (rural, thrift, cooperatives, NGOs)
overall impact had been positive according to impact studies
access to financial services allowed poor household to diversify their sources of income through multiple economic activities
better income, assets, and higher household expenditures were reported for clients
among borrowers there was evidence of movement out of poverty over several loan cycles
Microfinance
its concept came into existence in the 15th century but was put into practice in late 1970s by the Grameen Bank of Bangladesh and it was adopted by the developed and developing countries
process of extending financial services to those people who have low income and it becomes hard for them to get finance from banks and other private money lenders
broad concept to provide financial services to those who are getting finance from a bank
available only to the poorer people
revolutionary concept in an economy, and it helps to meet the basic financial needs of the poor people and save them from all kinds of risks
increases the per national capital income and tries to bring equality in the economy
offers loans, savings, insurance, and much more to the underprivileged
an economic and social tool by which a needy people get to finance to meet their need
Microcredit
aspect of the microfinance which is specifically meant to provide credit to the poor customers
main purpose is to use this finance for those who want to come out of the poverty and be self-sufficient and earning ability is very low
given to those who are unemployed, don’t have property, don’t have a sound credit history
will increase the income level of the poor people along with living standard
poor people will get loan without putting anything as collateral security
Definition: Microfinance VS Microcredit
MF indicates a number of financial services provided to the small entrepreneurs and enterprise who don’t get finance from the banks or any other institutions
MC is a small loan facility provided to the people who have less earning and encourage to become self-employed

Components: Microfinance VS Microcredit
MF is whole concept
MC is an aspect or component of MF, an extended service of MF
Microfinance VS Microcredit
both important factors for the development of an economy as there is a high percentage of the population who live in poor condition, this concept helps to improve the condition of this people
BSP defines MF
provision of a broad range of financial services such as deposits, loans, payment services, money transfers and insurance products to the poor and low-income households, for their microenterprises and small businesses, to enable them to raise their income levels and improve their living standards
provision of financial services to low-income clients, including the self-employed
1980
NGOs adopted practices from Bangladesh’s Grameen Bank and Association for Social Advancement (ASA) to follow suit the credit programs
MF programs
began giving non-collateralized credit to grouped clients, targeting entrepreneurial poor
MFIs
provide financial and social intermediation services such as group formation, development of self-confidence, and training in financial literacy and management capabilities among members of a group.
Current Sector of MF
composed of over 2,000 microfinance institutions including branches (rural, thrift, cooperatives, NGOs)
top 10 players comprise 88% of the market share in terms of number of borrowers
number 1 institution in terms of borrowers is ASA Philippines, with its’ clients amounting to 1 million.
ASA Philippines
comprises 25% of the entire market
operates nationwide, providing both financial and non-financial services to its clients
ASA in Ortigas
have branches all over the country
1,073,580 active borrowers
P5,790,323,880 gross loan portfolio
1,073,580 depositors
P3,206,703,390 deposits
CARD NGO
market share of 19%
operates nationwide
CARD situated in Laguna
have branches all over the country
816,620 active borrowers
P5,028,134,100 gross loan portfolio
- depositors
P2,339,217,430 deposits
CARD Bank
16% market share
666,570 active borrowers
P5,537,709,650 gross loan portfolio
1,657,250 depositors
P4,644,624,160 deposits
Pagasa
5% market share
209,110 active borrowers
P1,208,491,020 gross loan portfolio
228,970 depositors
P455,961,440 deposits
NWTF
207,170 active borrowers
P1,313,304,190 gross loan portfolio
216,820 depositors
P468,519,700 deposits
TSKI
176,590 active borrowers
P968,435,050 gross loan portfolio
319,780 depositors
P470,451,740 deposits
TSPI
176,220 active borrowers
P1,670,731,590 gross loan portfolio
180,800 depositors
P781,027,170 deposits
PR Bank
134,900 active borrowers
P9,335,617,280 gross loan portfolio
99,620 depositors
P3,144,878,110 deposits
KMBI
125,850 active borrowers
P652,546,510 gross loan portfolio
136,670 depositors
P311,541,450 deposits
ASKI
102,300 active borrowers
P1,573,646,580 gross loan portfolio
96,670 depositors
P270,772,020 deposits
Variety of MF in the PH
credit unions
commercial banks
NGOs (Non-governmental Organizations)
cooperatives
sectors of government banks
for-profit MFIs
growing
in India, referred as Non-Banking Financial Companies
Credit Unions
member-owned financial cooperative that is created and operated by members and shares profits with owners
a type of financial institution, is a member-owned financial cooperative, controlled by its members and operated on the principle of people helping people, providing its members credit at competitive rates as well as other financial services
financial institutions, like banks, except the members own the credit union
nonprofit entities that aim to serve their members rather than seeking to earn a profit
often offer better savings rates, lower loan rates and reduced fees
Commercial Banks
type of bank that provides services such as accepting deposits, making business loans, and offering basic investment products that are operated as a business for profit
refers to a financial institution that accepts deposits, offers checking account services, makes various loans, and offers basic financial products like certificates of deposit (CDs) and savings accounts to individuals and small businesses
NGOs
microfinance Non-Government Organization (MF-NGO)
non-stock, non-profit organization duly registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) with the 30 primary purpose of implementing a microenterprise development strategy and providing microfinance programs, products and services such as microcredit
can get, organize and raise funds from various methods, processes, programs, projects and activities
Getting grants from Funding agencies through Projects
Funding from International Funding Agencies
Funding from Government Schemes
Fund Raising from Corporate under CSR
Student and Child Sponsorship program
Cooperatives
autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned enterprise
democratically owned by their members, with each member having one vote in electing the board of director
people-centered enterprises owned, controlled and run by and for their members to realize their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations
bring people together in a democratic and equal way
purpose is to realize the economic, cultural and social needs of the organization's members and its surrounding community
often have a strong commitment to their community and a focus on strengthening the community they exist in or serve
Group Lending
allows a group of individuals - often called a solidarity group to provide collateral or loan guarantee through a group repayment pledge
incentive to repay the loan is based on peer pressure, if one group member defaults, the other group members make up the payment amount
Flexible Payment Schedule
on-the-spot loans that don't come from a traditional lender, like a bank or credit union
loan is typically paid back in monthly installments, depending on the agreement
in some cases, payment plans may help consumers budget their purchases better or provide a lifeline in an emergency
they can come in handy for those with irregular incomes
but like with any loan, flexible payment plans can snowball into debt.
Flexible Payment Plans Example
affirm allows users to shop at select stores online and select them as a payment option upon checkout
buyers can then select the length of their payment schedule and confirm the loan with Affirm
interest rates on Affirm loans range from 10% to 30%, and repayment periods can be three months, six months or 12 months
both Affirm and Afterpay did not respond to requests for comment
Bi-weekly
a payment with principal and interest payments due every two weeks
instead of making 12 monthly payments, a borrower with a biweekly payment will be required to make 26 half-month payments
Monthly
payment with principal and interest payments due every month
Limited Liability
type of legal structure for an organization where a corporate loss will not exceed the amount invested in a partnership or limited liability company (LLC)
investors' and owners' private assets are not at risk if the company fails.
Rural Banks
designed to provide financial services to rural and agricultural communities
MF Products and Services
Microcredit
Microsavings
Microinsurance
Payment and Remittance Services
Role of MF in Agricultural Development
access to capital
financial inclusion
risk management
knowledge and capacity building
sustainable agricultural practices
market linkages
social and gender impact (women empowerment)
Challenges in Farmers’ Access to MF
limited financial literacy
land tenure issues
high interest rates and transaction costs
vulnerability to climate change
limited access to physical banking infrastructure
trust and awareness
Innovative MF Products for Farmers
crop loan with buy-back agreement
mobile-based agri-financing
weather-indexed microinsurance
warehouse receipt financing
cooperative-based microfinance
agri-enterprise financing
livestock and poultry financing