Stage 2 Navigation and human factors
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What is pilotage
Understanding where you are at using visual points or charts
what is dead reckoning
is navigation solely by means of calculations based on time, airspeed, distance, and direction.
what is pressure altitude
the height above the standard atmosphere level of 29.92 inches of mercury (inHg).
what is true altitude
The height above mean sea level.
what is indicated altitude
the reading on the altimeter when the altimeter setting is set to the local barometric pressure.
what is density altitude
Pressure altitude corrected for variations from standard temperature.
what is absolute altitude
The vertical distance of the aircraft above ground level.
when does density altitude equal pressure altitude
when atmospheric conditions are standard.
which altitude directly relates to aircraft performance
density altitude
when is pressure altitude equal to indicated altitude
when the altimeter setting is set to 29.92 Hg.
which altitude is used mainly for calculations and fight level computations
pressure altitude
which altitude is crucial during approach and landing
absolute altitude
if the air has more pressure what does that do to density
density will increase
if temperature is higher what will happen to density and why?
density will decrease because particles to move faster and spread out
why does air density decrease with increasing pressure altitude
there's less air above to compress the air at higher altitudes.
what is the difference between density and density altitude
Density refers to the mass of air per unit volume, while density altitude is a measure of air density expressed as an altitude in the International Standard Atmosphere
If flying in low air density weather what will that do to the aircrafts performance
makes the aircraft perform as if it were flying at a higher pressure altitude
what does VOR stand for
very high frequency (VHF) Omni-directional Range.
what is the frequency range of the VOR
between 108.0 MHz and 117.95 MHz
where is the VOR antenna located in the DA-40
in the tail
What does DME stand for
Distance Measuring Equipment
how does a DME work and what is the purpose
measure distance by timing the interval between the "interrogation pulse" from the transmitter and the "reply pulse" from the receiver. (works like Sonar)
what are the 2 VHF Signals that a VOR sends out
reference and variable phase
what is a reference phase
A constant signal sent in all directions from the VOR station.
what is a variable phase
A rotating signal that varies based on direction from the station.
How does a VOR work
VOR sends out a reference signal (360 degrees).
It also sends a rotating signal (like a spinning light).
Your aircraft compares the two signals to figure out your bearing (radial) from the station.
what are the diversion procedures
(ABCDEFG)
Airport
Best heading
Course
Distance
Estimate time enroute
Fuel req.
Groundspeed
what is an instrument that helps pilots determine whether they’re on course. shows you if you’re to the left or right of that line
CDI

what is an advanced navigation unit that shows your current heading and how much you need to turn to get on the course.
HSI
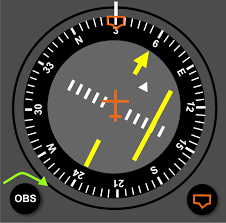
What are some VOR limitations
Line-of-sight: signal blocked by terrain or obstacles
Cone of confusion: signal becomes unreliable directly over the station
Reverse sensing: when the VOR needle gives opposite indications. (DA40 does not get this)
What does GPS stand for
Global Positioning System
How many GPS satellites does the USA have
31 satellites
What does GNSS stand for
Global Navigation Satellite System
what satellite systems are included in GNSS
includes GPS and other global or regional systems
what is trilateration
A method used by GNSS to determine your position by measures distance from at least 3 satellites to find a 2D location.(4 for 3D)
what is RAIM and what does it do. how many satellites does it need?
Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring.
It checks GPS signal accuracy and integrity and alerts the pilot if GPS data is unreliable.
Needs signals from at least 5 satellites
what is WAAS and what does it do
Wide Area Augmentation System
Uses ground stations and geostationary satellites to correct GPS errors.
What is the difference between RAIM and WAAS?
RAIM only checks GPS signal integrity.
WAAS both checks and corrects GPS signals
What is FDE and what does it do. how many satellites does it require to work?
Fault Detection and Exclusion
Not only detects a faulty satellite signal, but also excludes it from navigation solutions
Requires signals from at least 6 satellites
what are the different types of Notams
FDC (airspace)
D (ground)
TFR (Temporary Flight Restriction)
what are the lost procedures ( 5 C’s)
Climb
Communicate
Confess
Comply
Conserve
what is hypoxic hypoxia caused by
high altitude
what is hypemic hypoxia caused by
carbon monoxide
what is stagnant hypoxia caused by
G force
what is histotoxic hypoxia caused by
alcohol
what part of your eyes are used during the day
cones
what part of the eyes are used during the night
rods
what is hypoxia caused by
reduced oxygen to the brain
Why is it dangerous to fly too soon after scuba diving?
can cause decompression sickness (bends). This happens because nitrogen absorbed into the body tissues under high pressure during a dive can form bubbles in the bloodstream
What are the FAA's recommended wait times between scuba diving in controlled conditions and flying?
24 hour wait for all altitudes
What are the FAA's recommended wait times between scuba diving in uncontrolled and flying?
12 hours below 8000ft
24 hours above 8000ft
What is spatial disorientation?
When a pilot's sense of direction conflicts with reality due to lack of visual reference
What are the three types of spatial disorientation illusions?
Vestibular (inner ear)
Visual (eyes)
Postural (muscle/joint)
What is the leans?
Illusion that you need to lean in opposite direction
What is the Coriolis illusion?
the illusion that you feel your in a constant turn
What is the graveyard spiral?
the illusion that once aircraft is level they need to spin again
What is the somatogravic illusion?
the illusion that you feel as you are rapidly accelerating
What is an inversion illusion?
the illusion that a sudden climb to level flight creates the sensation of tumbling backward
What is an elevator illusion?
the illusion that you are climbing
What is false horizon illusion?
the illusion that the horizon is slanted
What is autokinesis?
the illusion that a stationary light appears to move when stared at in the dark
What should you consider before flying? PAVE
pilot - fit to fly
aircraft- airworthy
environment- weather
External pressure- expectations or time risk
What is the difference between a hazard and a risk in aviation?
Hazard- A real or potential condition that can lead to injury, illness, or damage
Risk- The chance or probability that a hazard will cause a loss or negative outcome
what is IMSAFE
Illness
Medication
Stress
Alcohol
Fatigue
Emotion
what are some things you should consider before flight (5 P’s)
Plan
Plane
Pilot
Passengers
Programming
what is the decide model
Detect a change
Estimate the need to counter it
Choose a desirable outcome
Identify actions
Do the actions
Evaluate the results
what are the types of VOR’s
VORCAN
VOR
VOR/DME
What do you do if the engine fails in flight?(ABCDE)
Airspeed – Best glide
Best landing spot – Pick a field, road, etc.
Checklist – Fuel selector, mixture
Declare – 121.5, squawk 7700
Evacuate/Execute – prepare for landing
If wing catches on fire what do you do?
throttle idle
bank to 30-45 degrees opposite direction of fire
pitch down to between 119 to 129 knots
What should you do if you fly into IMC accidentally?
AVIATE
NAVIGATE
COMMUNICATE
symptoms of hypoxia
increased breathing rate
headache
lightheadedness
dizziness
tingling or warm sensations
sweating
poor coordination
impaired judgment
tunnel vision
euphoria.
What is always needed when a mode c transponder is needed
ADS-B out
Whats information is included with the HSI
Heading, CDI, and OBS
When is LAHSO used at airport
Used for intersecting runways.(students cannot use this)
What does hypoxia do
Reduces the oxygen in the body. Effects the brain
why does hypoxic hypoxia occur
there isn't enough oxygen in the air (high altitudes)
How does hypemic hypoxia occur
when the blood's capacity to carry oxygen is reduced (carbon monoxide)
why does stagnant hypoxia occur
there's a reduction in blood flow, leading to insufficient oxygen delivery to the body's tissues (g force)
Why does histotoxic hypoxia occur
cells are unable to utilize oxygen (alcohol)
What is hyperventilation and how can you help it
when you breathe in a way that is faster and deeper than your body needs, causing a drop in carbon dioxide levels in your blood.
Can help by breathing into bag or talking.
What are some symptoms of hyperventilation
Lightheadiness
Dizziness
Shortness of breath
What is the somatosensory system and how can it affect pilots during flight?
senses position, pressure, and motion through nerves in muscles and joints.
In flight can cause spatial disorientation.
Why shouldnt you fly while congested
can cause ear pain, sinus pain, vertigo, and eardrum rupture
What are some vestibular illusions
Leans
Coriolis illusion
Graveyard spiral
Inversion
Elevator
What are some somatosensor illusions
somatogravic illusion
What are some visual illusions
Autokinesis
False horizon
Runway width illusion(narrow feels like flying high, wide feels like flying low)
What are the hazardous attitudes and their antidotes (AIM IR)
Anti-authority: "Don't tell me what to do"
- Antidote: follow the rules
Impulsivity: "Do something quickly"
- Antidote: Not so fast. Think first
Invulnerability: "It won't happen to me"
- Antidote: It could happen to me
Macho: "I can do it"
- Antidote: Taking chances is foolish
Resignation: "Whats the use"
- Antidote: I can make a difference and I am not helpless