1.6 muscle & tendon
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:50 AM on 12/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
aponeurosis of muscle
connects muscle to bone or tendon
2
New cards
epimysium
binds the muscle belly together
3
New cards
sarcolemma
specialised cell membrane on muscle cells
4
New cards
fascicles
bundles of muscle fibres/cells, forming the muscle belly
5
New cards
perimysium
binds each fascicle into bundles
6
New cards
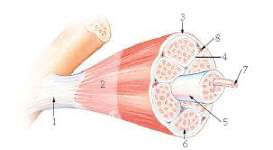
1?
tendon
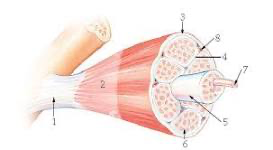
7
New cards
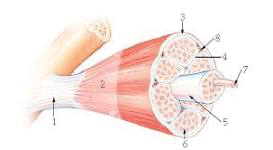
2?
aponeurosis
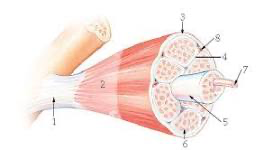
8
New cards
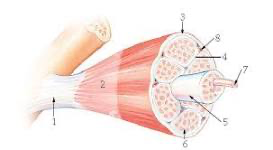
3?
epimysium
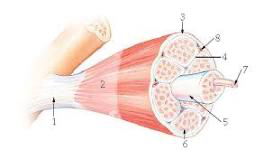
9
New cards
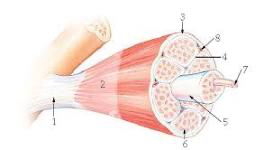
4?
perimysium
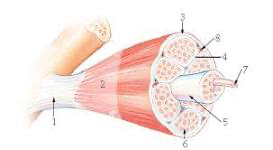
10
New cards
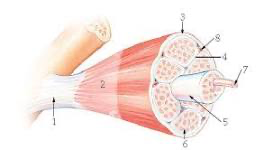
5?
structure = fascicle
membrane = sarcolemma
membrane = sarcolemma
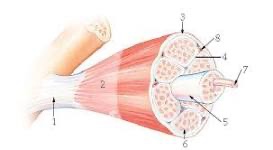
11
New cards
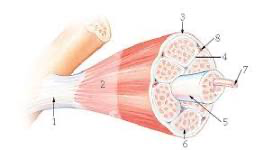
6?
endomysium
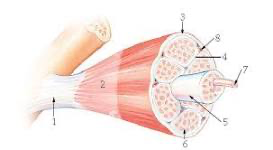
12
New cards
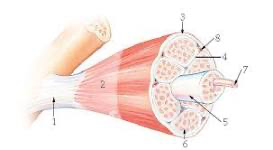
7?
myofibril
13
New cards
sarcomere
basic contractile unit of a myocyte (muscle fibre)
14
New cards
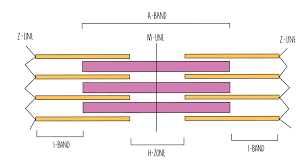
what is this structure? what is the pink? what is the yellow?
pink = myosin
yellow = actin
yellow = actin
15
New cards
cardiac muscle structure
striated
single central nucleus
involuntary
irregular arrangement with intercalated disks
single central nucleus
involuntary
irregular arrangement with intercalated disks
16
New cards
smooth muscle structure
no striations
single nucleus
involuntary
longer contractions
single nucleus
involuntary
longer contractions
17
New cards
"force"
push or pull on an object, causing it to change velocity
18
New cards
formula for 'work done'
force x Δdistance
*Δ = change in
*Δ = change in
19
New cards
formula for 'power'
Δwork/Δtime
20
New cards
pennate muscle
muscle fibres at an angle to internal tendon/aponeurosis
increases physiological cross sectional area (which is proportional to force)
increases physiological cross sectional area (which is proportional to force)
21
New cards
parallel muscle
fibres run parallel to line of pull
more sarcomeres in series
potential for increased velocity of contraction (speed = distance/time)
found where a limb needs movement
more sarcomeres in series
potential for increased velocity of contraction (speed = distance/time)
found where a limb needs movement
22
New cards
tenocytes
tendon cells
look like lines (histology)
look like lines (histology)
23
New cards
tendon hierarchy
fascicles -> sub fascicles -> collagen fibres -> collagen fibrils
24
New cards
roles of tendon (5)
- minimising distal limb mass (e.g. horse)
- joins muscle to bone (transmitting muscle fore to skeleton)
- elastic energy storage
- energy conservation
- power amplification
- joins muscle to bone (transmitting muscle fore to skeleton)
- elastic energy storage
- energy conservation
- power amplification
25
New cards
long tendons are often coupled with pennate muscles for better power amplification (t/f)
true
26
New cards
stretched tendons recoil faster than a muscle shortens (t/f)
true