Unit 2 - Spotting a Business Opportunity
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is internal (organic) growth + its methods
when a business expands by growing its own activities -new products (innovation, research and development) -new markets (through changing the marketing mix or taking advantage of technology and/or expanding overseas)
advantages and disadvantages of organic growth
less risky as the business grows by doing what it is already good at so retains its culture, economies of scale, higher market share and sales
growth is slower
what does external (inorganic) growth usually involve?
merger takeover
advantages and disadvantages of external growth
economies of scale. increased revenue and market share
clash of cultures, diseconomies of scale (communication problems), lack of trust
type of business ownership for growing businesses + advs & disadvs
public limited company
lots of finance raised, expand and diversify, limited liability
disagreements between shareholders, someone could take over the company, accounts must be made public
internal sources of finance for established businesses
retained profit selling assets
external sources of finance for established businesses
loan capital share capital, including stock market flotation
why do business aims and objectives change as a business evolves?
in response to: market conditions technology performance legislation internal reasons
how do business aims and objectives change as a business evolves?
-focus on survival or growth -entering or exiting markets -growing or reducing the workforce -increasing or decreasing the product range
impact of globalization on business
-imports: competition from overseas, buying from overseas -exports: selling to overseas markets -changing business locations -multinationals: businesses that operate in more than one country
barriers to international trade
tariffs trade blocs
how do businesses compete internationally?
-using e-commerce and the internet -changing the marketing mix to fit that country's culture
examples of ethical issues for businesses
exploiting workers, Fair Trade, comfortable working environment, animal testing ...
advs and disadvs of acting ethically
customer satisfaction, staff is more motivated
costly (higher labour costs and ethically sourced materials), may lead to higher prices and so lower sales. Trade-off between ethics and profit
examples of environmental issues for businesses
packaging, recycling, renewable energy resources, sustainability...
advs and disadvs of being environmentally friendly
competitive advantage, attract customers
expensive, trade-off between being sustainable and making a profit
potential impact of pressure group activity on the marketing mix
e.g change products by using ethically sources raw materials or promotional campaigns to repair negative publicity pressure group has caused
design mix
function, aesthetics, cost
product life cycle
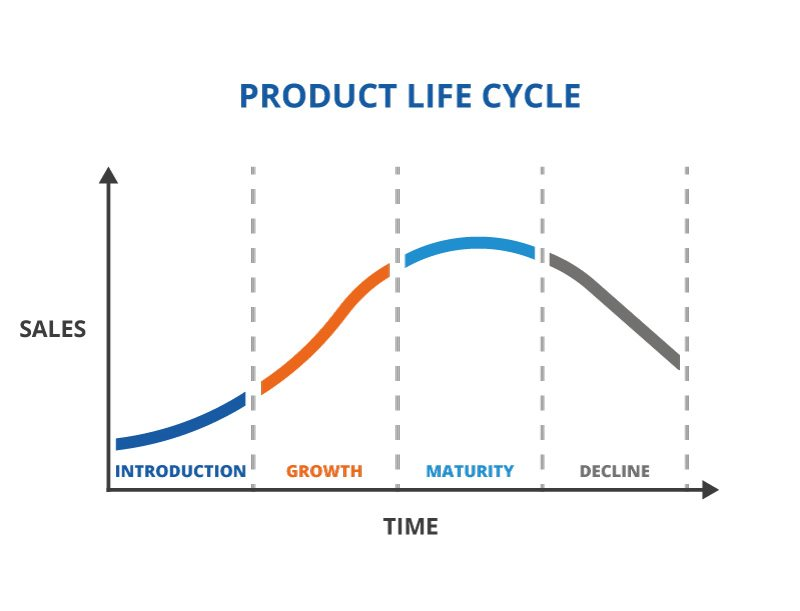
extension strategies
Methods used to prolong the life of a product: -adding more or different features -using new packaging -targeting new markets -changing advertisements -lowering price
importance of differentiating a product/service
competitive advantage
pricing strategies
price penetration: low to high -loss leader pricing: price is set below cost so no profit is made but customer will buy other products as well -price skimming: high to low -competitive pricing: charge similar prices to competitors -cost-plus pricing: add a certain amount to costs depending on how much profit they want to make
influences on pricing startegies
technology competition market segments product life cycle
promotion strategies
advertising sponsorship product trials special offers branding
use of technology in promotion
targeted advertising online viral advertising via social media e-newletters
methods of distribution
retailers e-tailers
purpose of business operations
produce goods provide services
Job Production
Producing a one-off item specially designed for the customer
unique, high quality products, customer satisfaction, added value
requires skilled labour, low productivity as it is slow
Batch Production
certain quantities of identical products are made
flexible, machinery lowers costs, economies of scale
time needed to change between batches lowers productivity
Flow Production
producing items in a continually moving process
fast, economies of scale
capital-intensive, needs lots of space for product storage
advantages of using technology
-quick and accurate e.g CAD Design -increases productivity -more consistent quality -continuous 24/7 -cheaper is the long term
disadvantages of using technology
-expensive: regular maintenance and staff training -staff may be worried they will lose jobs, demotivates them -inflexible as machines are suited to one task
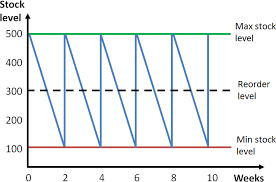
Bar Gate Stock Graph
Just In Time stock control
A system where stock is delivered only when it is needed
no warehouse for stock means lower rent, stock less likely to go out of date
requires lots of coordination between firm and suppliers, could run out if there is a mistake in delivery/order, losing out on economies of scale
Procurement
finding and buying things that a business needs from suppliers outside the business
Logistics
getting goods and services from one part of the supply chain to another
To choose a supplier, a business must consider
quality trust availability cost delivery (cost, speed, reliability)
impact of logistics and supply decisions
reduce overall costs if business gets supplies at best possible price and doesn't waste time being inefficient ensures products amp high-quality, a reasonable price and delivered onetime, which improves customer satisfaction and brand reputation
importance of quality
controls costs by wasting less competitive advantage add value
quality control
The checking for quality at the end of the production process
quality assurance
Checking that quality is being maintained through each process involved in making the product
The sales process
product knowledge speed and efficiency of service customer engagement responses to customer feedback post-sales service
importance of good customer service
customer satisfaction customer loyalty, repeat purchased customers persuaded to spend more with the business good brand image market share and sales
gross profit equation
sales revenue - cost of sales
net profit equation
Gross Profit - other operating expenses & interest
gross profit margin equation
Gross profit/sales revenue x 100
net profit margin equation
net profit/sales revenue x 100
average rate of return equation
average annual profit (total profit/no of years)/ cost of investment x 100
types of data that can be used by businesses to make decisions
financial data marketing data market data
limitations of financial information to make decisions
may not be possible to compare two different sources of data can be hard to tell causes of changes in data as variables such as economic climate have an impact no qualitative data
hierarchal structure
long chain of command with more layers of management communication between top and bottom is difficult and slow as more people need to pass on message each manager has a narrow span of control, which is more effective as employees can be closely monitored
flat structure
short chain of command wide span of control
Centralised organisation
an organisation where all the important decision-making power is held at Head Office, or the centre
decentralized organization
authority to make most decisions is shared out
insufficient communication
inefficiency slow demotivation
excessive communication
confusion feeling overwhelmed slow
barriers to effective communication
noise, distance, personalities jargon
ways of working
part-time full-time flexible hours
types of employment contracts
permanent temporary freelance
impact of technology on ways of working
efficient communication remote working
key job roles
directors: strategy senior managers: organize carrying out of strategy supervisore/team leaders: look after specific projects operational and support staff: specific tasks within projects
Job description
formal title, propose, main duties, who job holder will report to and whether they will be responsible for any other staff
Person Specification
lists qualifications, experience, skills and attitudes needed for job
Application form
A form to use when applying for a job gives firm info they need so are quick to process and more relevant than open-ended letters
Curriculum Vitae (CV)
A brief list of the main details about a person, including name, address, qualifications and experience.
internal recruitment
seeks job applicants from inside the organization
cheaper, quicker, they already know about the firm
no new ideas, leaves a vacancy to fill
external recruitment
the process of seeking new employees from outside the firm
advert seen by more people so it is likely they will find someone really suited
expensive
types of training
formal: expensive but higher quality informal: cost-effective but bad habits can be passed on self-learning: using internet
importance of ongoing training
learning new processes, how to use new technology and help emlployees develop
use of target setting and performance reviews
people who meet target can be rewarded with a bonus people who don't can be given training or support
why businesses train and develop employees
more productive more motivated up to date with new technology increases staff retention
importance of motivation in the workplace
attracting employees retaining employees productivity
financial methods of motivation
remuneration: payment for work done bonus: lump sum added to pay once a year commission: extra pay to sales staff for every item they sell promotion: put in a job role that pays more fringe benefits: a reward that is not part of main income e.g company car or gym membership
non-financial methods of motivation
job rotation: occasionally moving workers from one job to another, less boredom job enrichment: when a worker is given greater responsibility, new challenges autonomy: giving workers freedom to make their own decisions, makes them feel trusted and valued
adv and disadv of part time employees
Advantages of part-time employees: flexibility, reduced labor costs, increased productivity, and access to a wider pool of talent.
Disadvantages of part-time employees: less commitment, reduced benefits, less training, and scheduling challenges.
adv and disadv of full time employees
Advantages: Full-time employees receive benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans. They also have job security and a steady income.
Disadvantages: Full-time employees can be expensive for companies due to salaries, benefits, and taxes. They may also be less flexible than part-time or contract workers, making it harder for companies to adapt to changing needs.
adv and disadv of flexible working
Advantages of flexible working: Improved work-life balance, increased job satisfaction, reduced stress, and better health. Disadvantages of flexible working: Difficulty in managing and monitoring remote workers, potential communication issues, and the need for a reliable internet connection.
adv and disadv of permanent employees
Advantages: Permanent employees receive job security, benefits and opportunities for career growth within the company. They also have a better understanding of the company culture and can contribute to its success.
Disadvantages: Permanent employees are more expensive than temporary or contract employees. They may also become complacent and resistant to change, which can hinder the company's ability to adapt to new challenges. Additionally, layoffs or downsizing can be more difficult and costly with permanent employees.
adv and disadv of temporary employees
Advantages: Cost-effective, flexible workforce, easy to hire and fire, specialized skills, can fill sudden vacancies.
Disadvantages: Lack of loyalty, inconsistent quality, limited benefits, training costs, potential legal issues.
advntages and disadvantages of freelance contracts
Advantages: Flexibility, autonomy, higher income potential, diverse work opportunities, and ability to work remotely.
Disadvantages: Inconsistent income, lack of job security, no employee benefits, self-employment taxes, and difficulty in finding clients.