Breast US Quiz
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UT 303 - small parts 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Galactocele
retroareolar mass developed shortly after childbirth from the occlusion of a lactiferous duct
sonographically - oval, circumscribed, fat/fluid levels that shift position, posterior enhancement, no blood flow
Hamartoma
varying amount of normal or dyplastic fibrous, epithelial, and fatty breast tissue
sonographically - oval, mixed echo pattern, compressed surrounding tissue
Fibroadenoma
most common type of benign solid mass in breast
sonographically - oval, circumscribed, homogenous, solid mass, often shows vascularity
Gynecomastia
enlargement of breast tissue in men
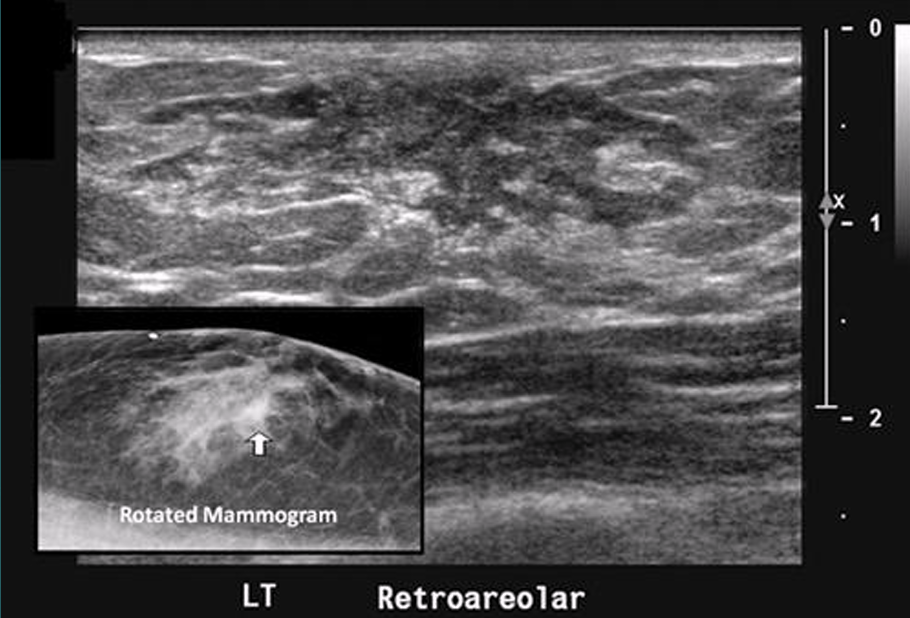
Complex cyst
contains both solid and cystic components
thick walls or thick septations
Ipsilateral
belonging to or occurring on the same side
Heterogenous cyst
texture is irregular, not smooth
Sebaceous cyst
cyst located within the dermal layer and has a tract connecting it to the skin
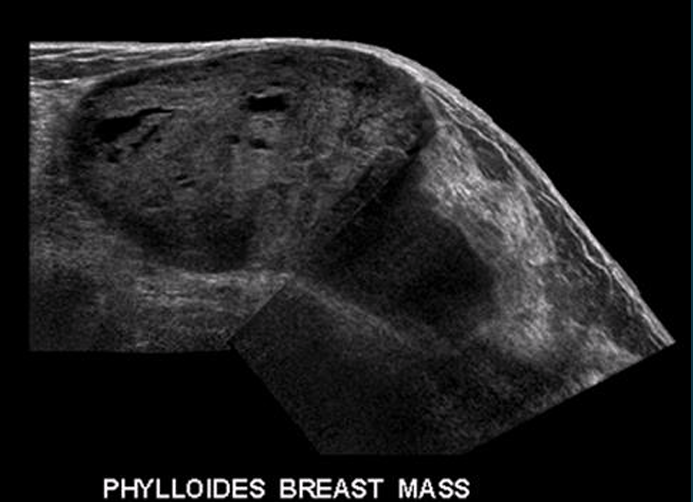
Phyllodes tumor
rare breast tumor that originates from the connective tissue of the breast and grows in a leaflike pattern, can be benign
Acini
milk producing glands
Inflammatory carcinoma
rare and aggressive form of breast cancer
symptoms: reddening and swelling, may or may not have distinct lump, skin looks like an orange peel
sonographic appearance: thick, echogenic skin, dilated lymph vessels and veins, and hypervascular
BI-RADS
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Benign mass characteristics
oval, round shape
parallel orientation
well-circumscribed borders
abrupt interface
enhancement or some shadowing
surrounding tissue is compressed
gross calcifications
no vascularity
Malignant mass characteristics
irregularly-shaped
taller than wide orientation
indistinct, angular, microlobulated, or spiculated borders
echogenic halo (desmoplasia)
posterior shadowing, sometimes enhancement, or combination of enhancement and shadowing
duct changes, cooper’s ligaments changes, edema, architectural distortion, skin thickening, skin retraction
microcalcifications
vascularity present within or around lesion
Noninvasive carcinoma
has not spread, confined within duct/lobule
DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ)
Most common noninvasive cancer that has not spread beyond the milk duct, but its presentation means an increased risk in future invasive cancer
Typical cure rate - 99-100%
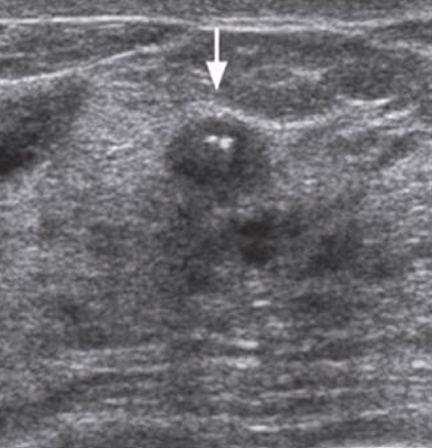
LCIS (lobular carcinoma in situ)
arises in lobules
Invasive carcinoma
has spread to surrounding tissue
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)
most common
found most common in UOQ
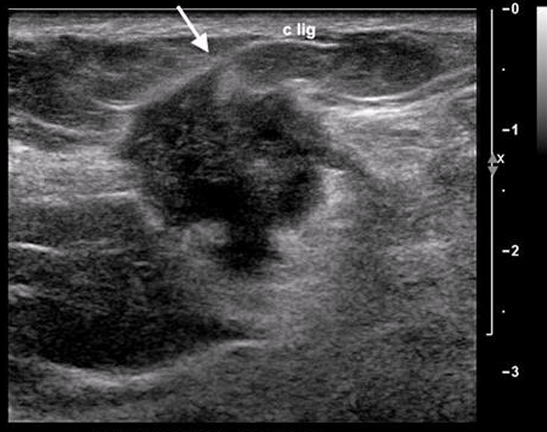
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)
higher rate of being multifocal, multicentric, and bilateral
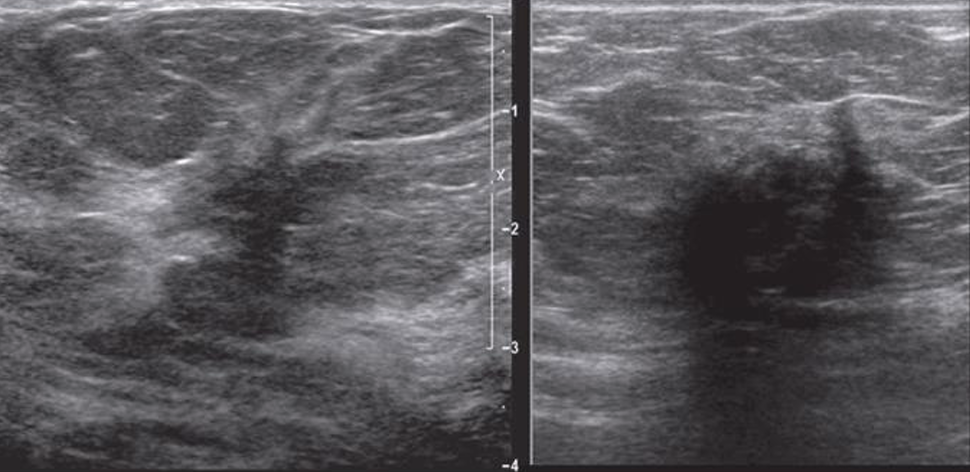
Paget disease (of the nipple)
Involves reddening, ulceration, eczema-like crusting of the epidermis of the nipple and areola
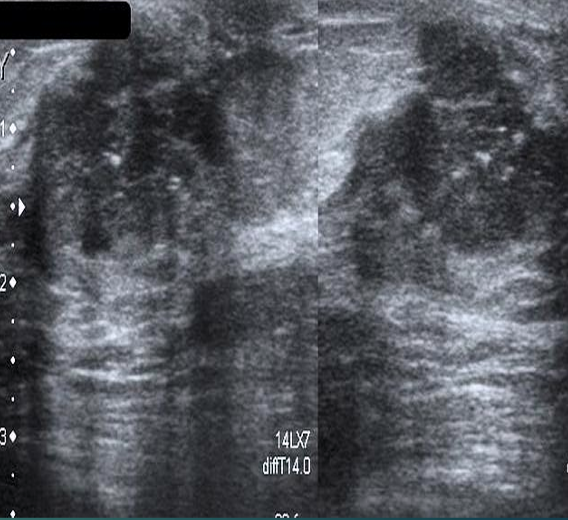
Subgroups of IDC
medullary
colloid
papillary
tubular
inflammatory carcinoma
Medullary carcinoma
Well-marginated cellular tumor containing prominent lymphocytes and plasma cells
Discrete, round, soft, and mobile
Rapid growing, most in UOQ
Sonographically - oval, solid, hypoechoic, distal enhancement, echogenic halo, prominent vascularity
Colloid (mucinous) carcinoma
Uncommon, circumscribed gelatinous lesion
Slow growing with high and low density
Sonographically - oval, circumscribed, with possible lobulation and microlobulation, isoechoic/hypoechoic, homogenous or mildly heterogenous
Papillary carcinoma
Malignant transformation of large duct papilloma
Focal/multifocal; slow growth
Intracystic (complex lesion with solid and cystic components or mural node)
Grows extensions/branches into adjacent ducts
tubular carcinoma
incites prominent reactive fibrosis
Slow growth
Starts often in TDLUs or from radial scars
Has thick echogenic halo and frank spiculation
Sonographically - small, irregular, hypoechoic with frank speculation or surrounded by a thick echogenic halo; acoustic shadowing; skin retraction
Breast anatomy
Fat
Ducts
Lobules/TDLUs
Nipple
Areola
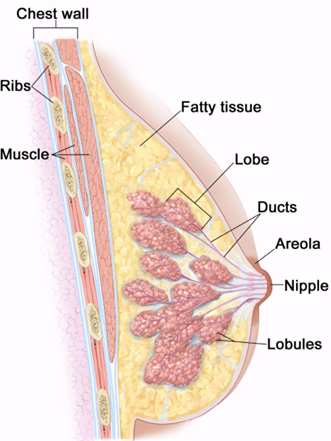
3 layers of the breast
Subcutaneous fatty layer (premammary zone)
Fibroglandular layer (mammary zone)
Retromammary zone
Subcutaneous fatty layer
Pre-mammary zone
Cooper ligaments here
Fibrous connective tissue that shapes and supports breasts
Fibroglandular layer
Mammary zone
15-20 lobes per breast, 20-40 TDLUs per lobe
Terminal ductal lobular units (TDLUs)
Functional units of the breast
Produces milk during lactation
Retromammary zone
Made of fatty tissue and separates pecs from mammary zone
Muscles behind breast
Pectoralis major - beneath the upper ⅔ of breast
Pectoralis minor - sits behind the pectoralis major
A
Skin
B
Fat lobule
C
Cooper ligament
D
Fibroglandular zone
E
Muscle
BI-RADS 0
Incomplete, needs more information
BI-RADS 1
negative, routine age-appropriate screening
BI-RADS 2
benign, routine age-appropriate screening
image: cyst
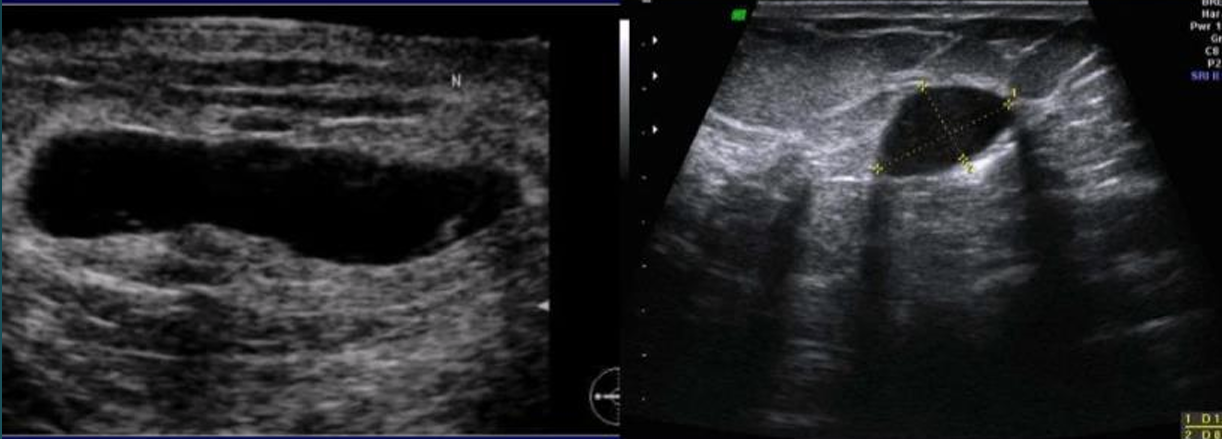
BI-RADS 3
probably benign, 6-month follow up with continued periodic surveillance
image: fibroadenoma
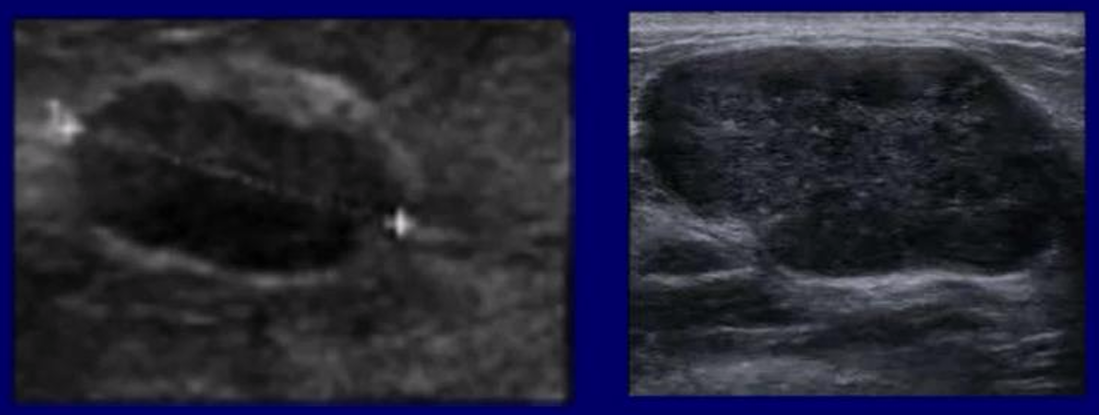
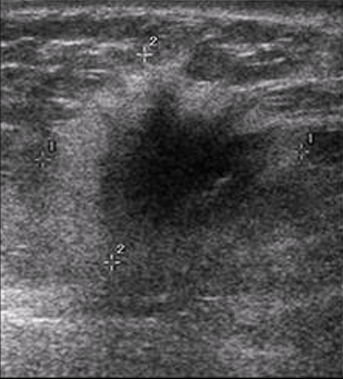
BI-RADS 4
suspicious, tissue diagnosis (biopsy)
image: US does not show all the features of a fibroadenoma, no posterior enhancement
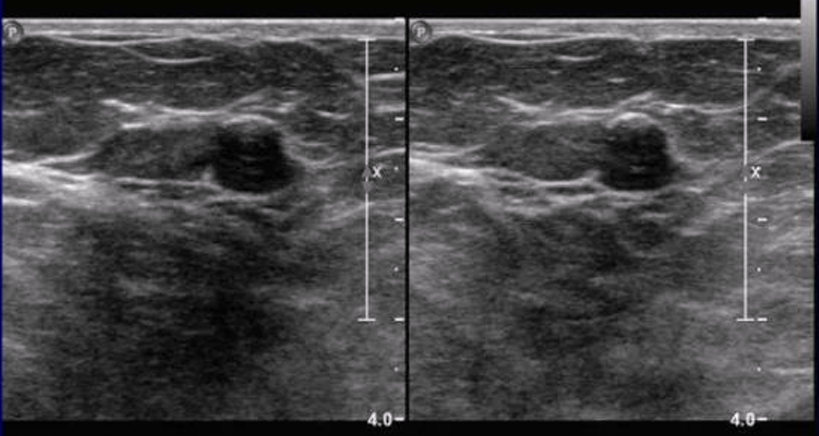
BI-RADS 4A
low suspicion, tissue diagnosis (biopsy)
BI-RADS 4B
intermediate suspicion, tissue diagnosis (biopsy)
BI-RADS 4C
moderate suspicion, tissue diagnosis (biopsy)
BI-RADS 5
highly suggestive of malignancy, tissue diagnosis (biopsy)
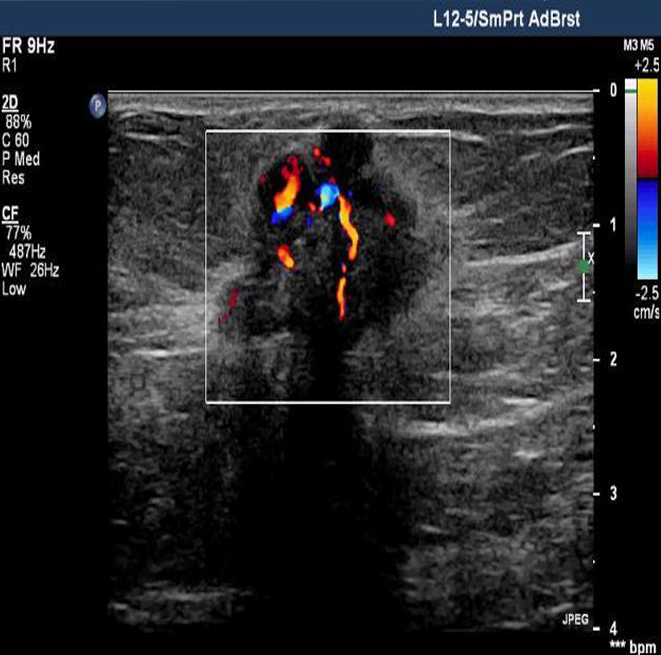
BI-RADS 6
known biopsy-proven malignancy, surgical excision when clinically appropriate
Young breast parenchyma
dense echogenic pattern and fibrous tissue elements
Pregnant/lactating breast parenchyma
larger and denser glandular portions, less echogenic
Mature breast parenchyma
fatty tissue starts replacing glandular tissue
Postmenopausal breast parenchyma
ducts atrophy and fibrous tissue replaced by fat
Where do most cancers and precancers in the breast occur?
mammary/fibroglandular layer in the TDLUs
What is one of the main advantages of US when looking at the breast?
Original role of US in breast imaging is to differentiate between cystic and solid lesions
Does not use ionizing radiation
Only real time imaging modality
Normal lymph node appearance
Oval, reniform (kidney-shaped)
Circumscribed, smooth margins
Symmetric hypoechoic cortex with hyperechoic fatty hilum
Doppler flow at hilum
Intramammary nodes < 1 mm
Abnormal lymph node appearance
Rounded, lobulated, irregular shape
Enlarged diameter
Eccentric cortical thickening
Displayed, indented, or absent fatty hilum
Markedly hypoechoic cortex
Heterogenous cortex
Indistinct cortical wall
Transcapsular blood flow
Side asymmetry
What is the relationship between menopause/HRT and how are fibrocystic breasts affected?
HRT (hormone replacement therapy) replaces the hormones women stop producing during menopause
Normally, as women age, symptoms of fibrocystic breasts diminish after menopause
If women take HRT, symptoms of fibrocystic breasts are unchanged
Prolactin
Stimulates milk production
Baby suckling → pituitary gland releases prolactin → stimulates additional milk production from the acinis
Radial vs. anti-radial scanning planes
Radial - follows course of the ducts
Anti-radial - perpendicular to radial plane
___ are the gold standard and widely used for screening of breast cancer
mammograms
What breast lesion is most affected by estrogen?
Fibrocystic breast disease, breast cancer (any type), fibroadenomas, gynecomastia
The breast parenchyma is made of ___ lobes
15 - 20
Where does primary breast cancer metastasize?
ipsilateral lymph node
lungs
brain
liver
Where do most breast cancers occur?
UOQ (in the mammary zone)
American women’s lifetime risk of breast cancer is
1 in 8
Male breast cancer makes up ___ of breast cancers
1%
symptoms of fibrocystic breasts
tenderness
pain
fullness
nodularity
nipple discharge
bilateral masses associated with menses
rope-like texture
cyst on ultrasound
anechoic
oval or round
well-circumscribed, smooth borders
horizontal
posterior enhancement, through transmission
cyst on mammogram
Circumscribed radio opaque oval/round mass
Fibroadenoma on ultrasound
Hypoechoic
Often oval or round, sometimes macrolobulated
Well-circumscribed, smooth borders
Horizontal
Sometimes minimal posterior enhancement
Sometimes gross calcifications
Fibroadenoma on mammogram
Circumscribed radio opaque oval/round mass
infected cyst
cyst features worrisome for acute inflammation or infection include uniform isoechoic wall thickening, hyperemia of the cyst wall, and possible internal fluid debris level
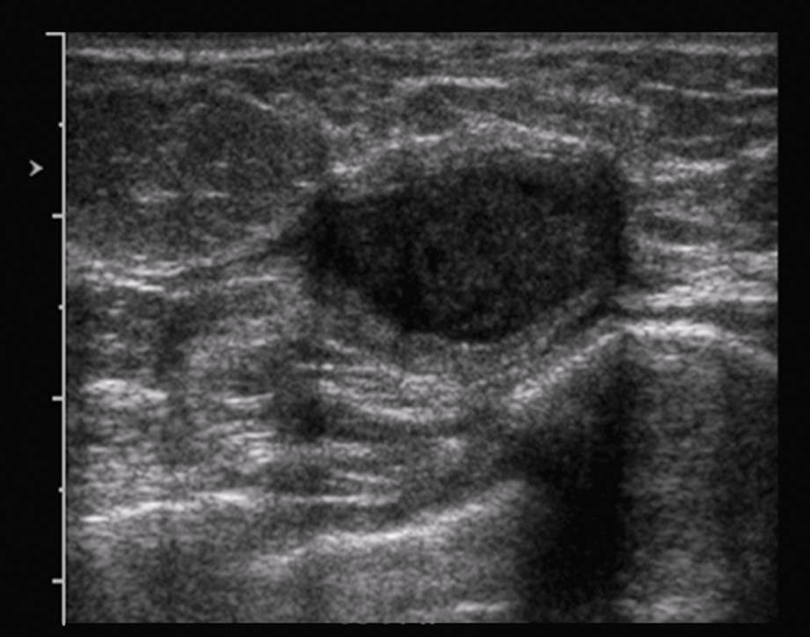
cancer metastasis to breast
melanoma
leukemia
lymphoma
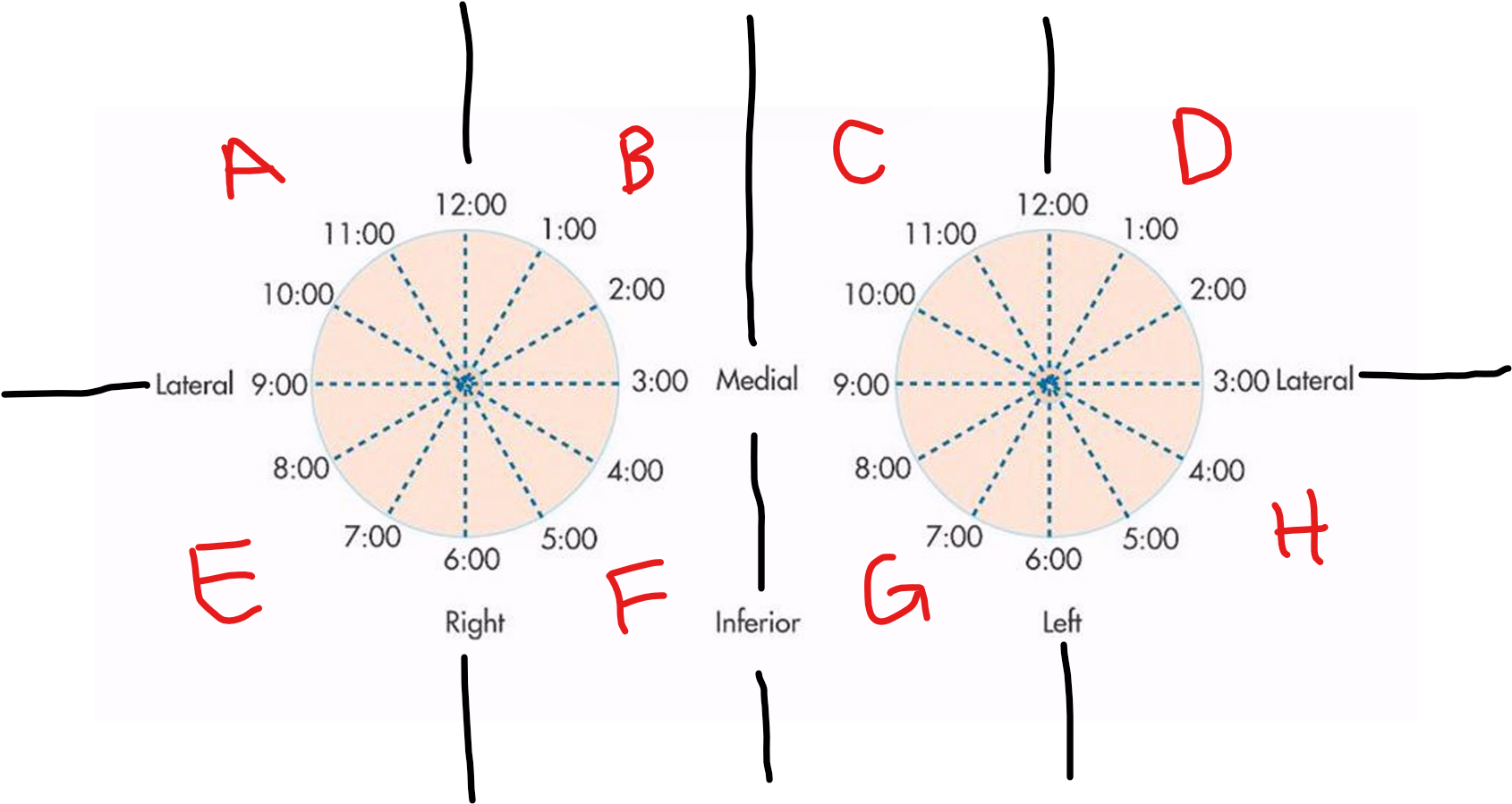
A
RUOQ
B
RUIQ
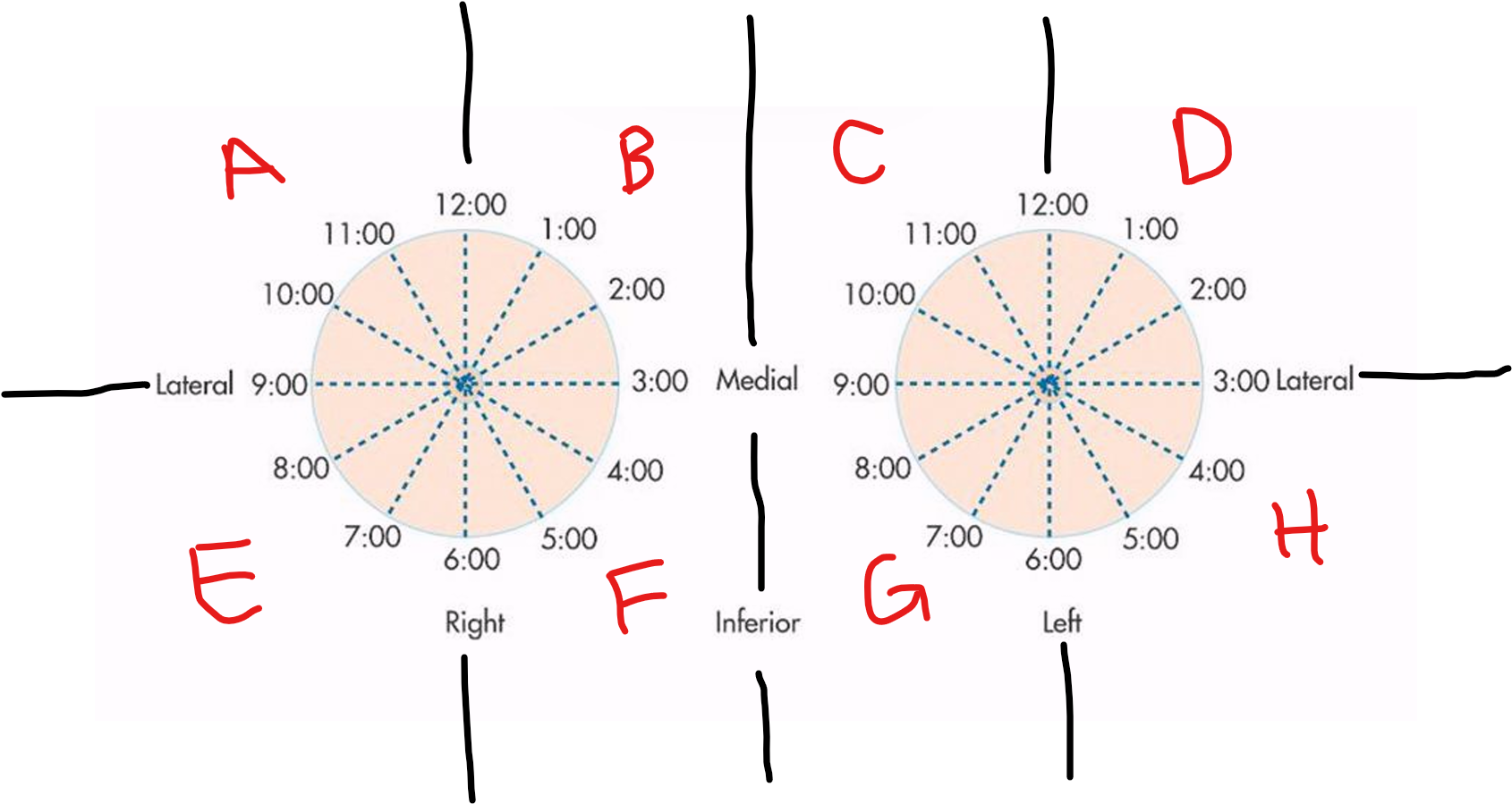
C
LUIQ
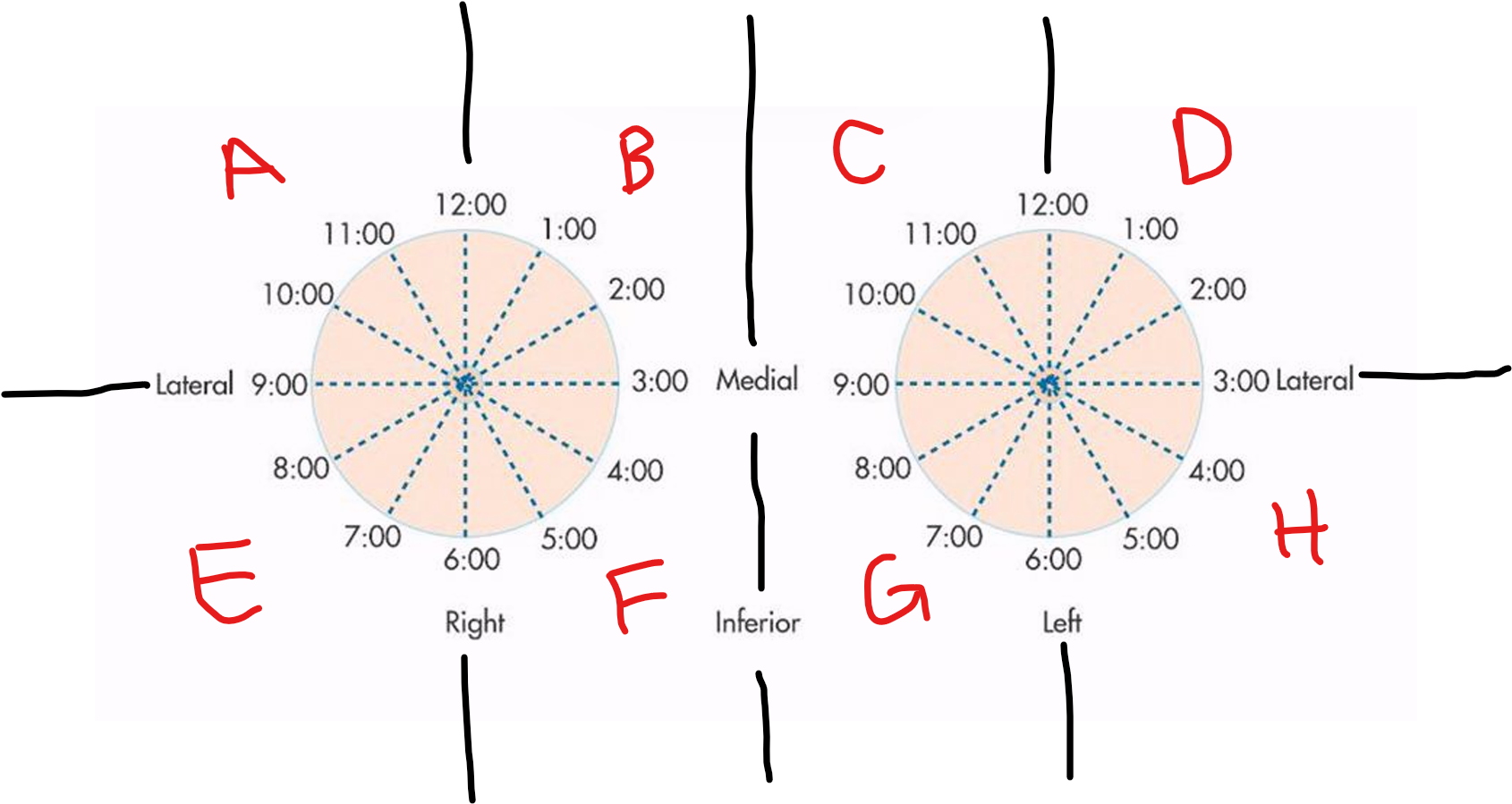
D
LUOQ
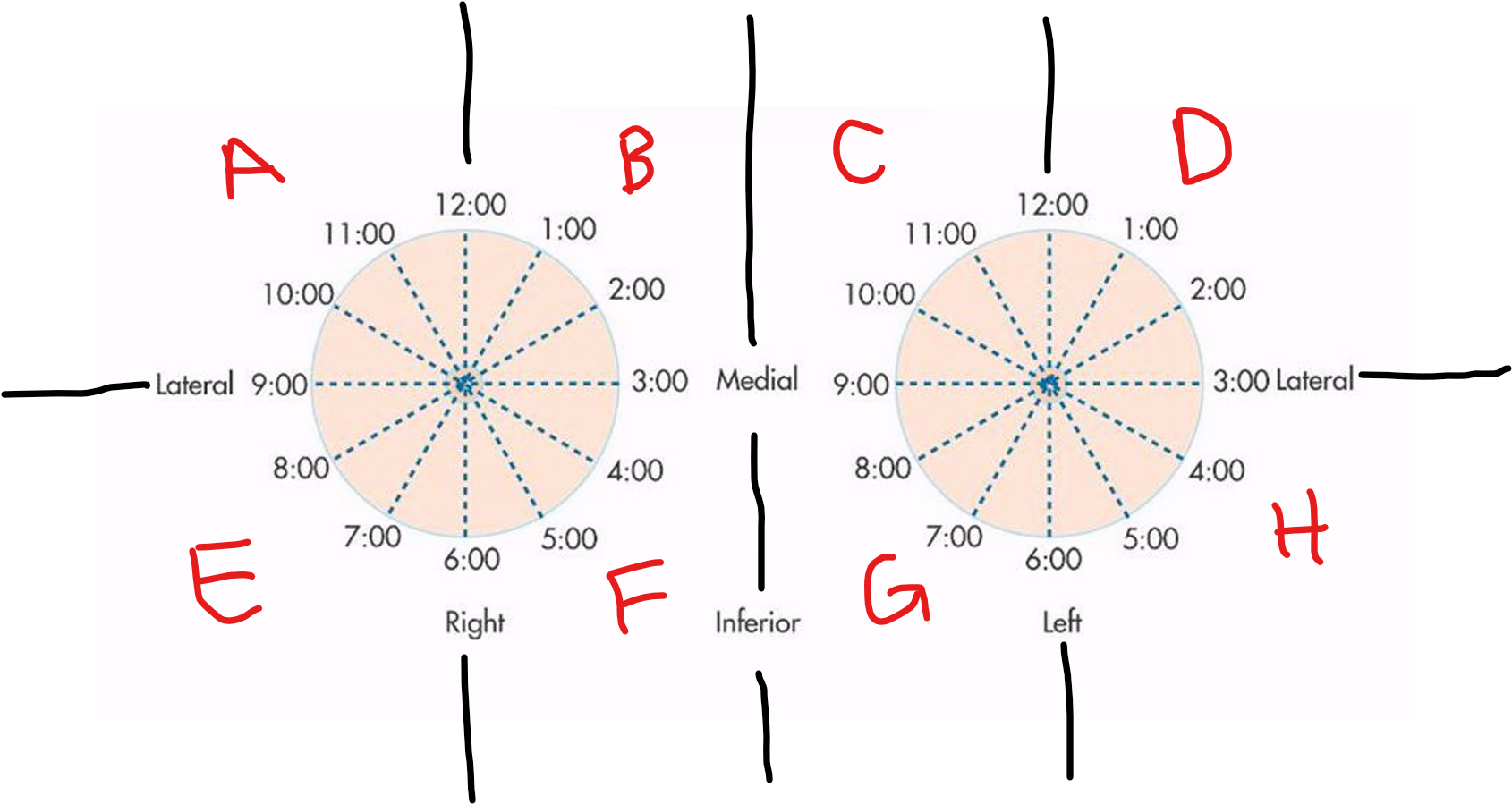
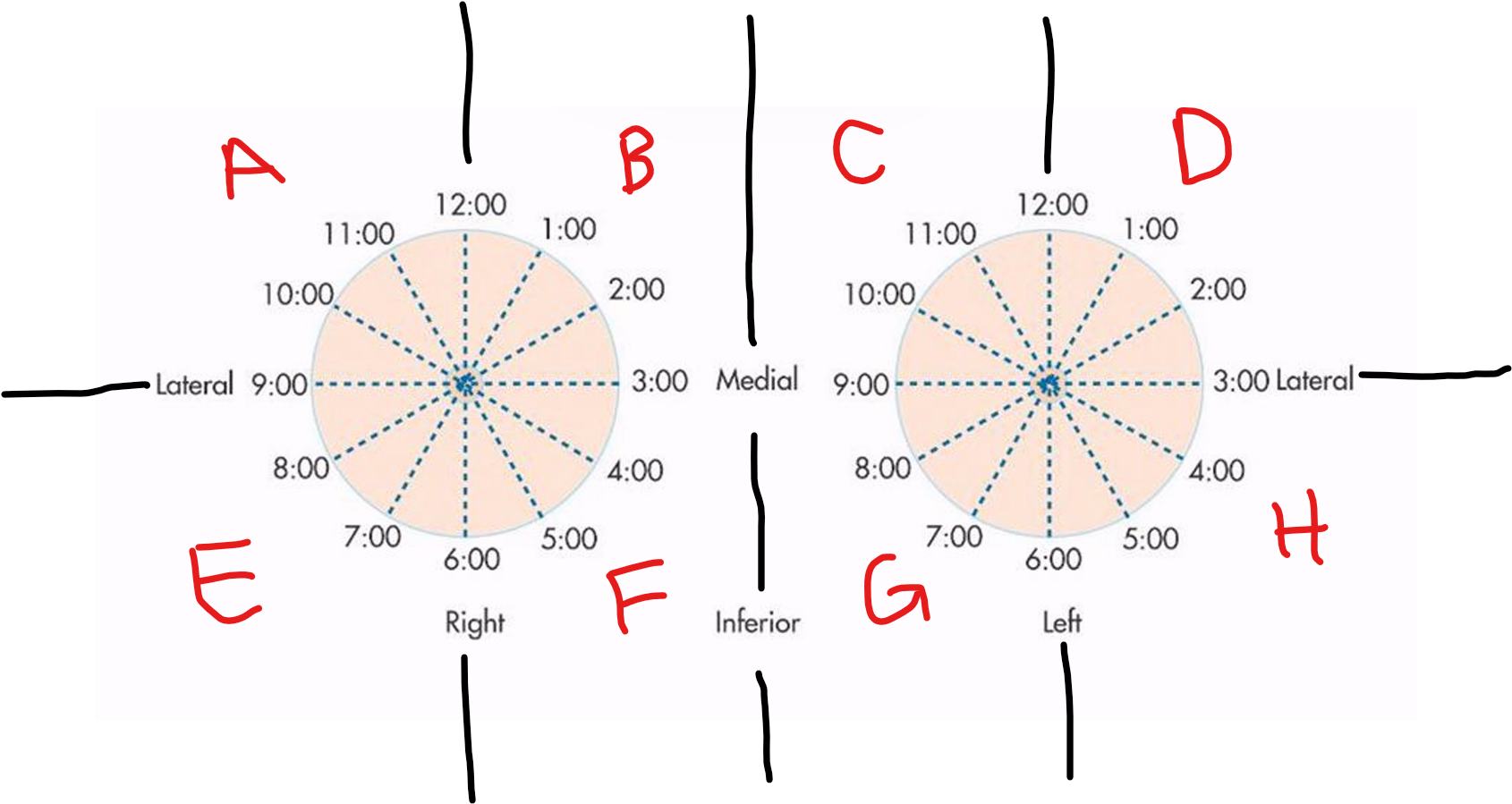
E
RLOQ
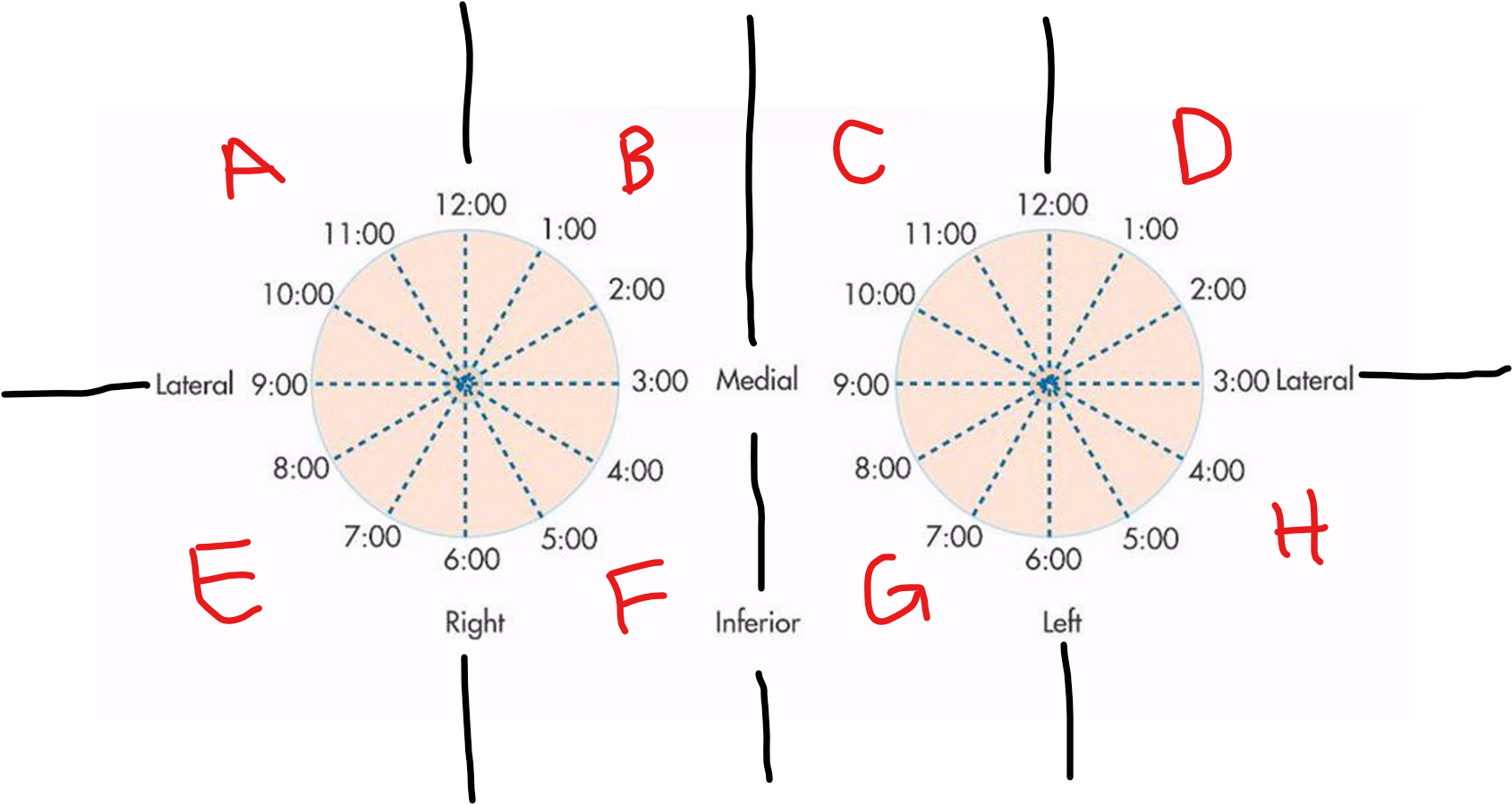
F
RLIQ
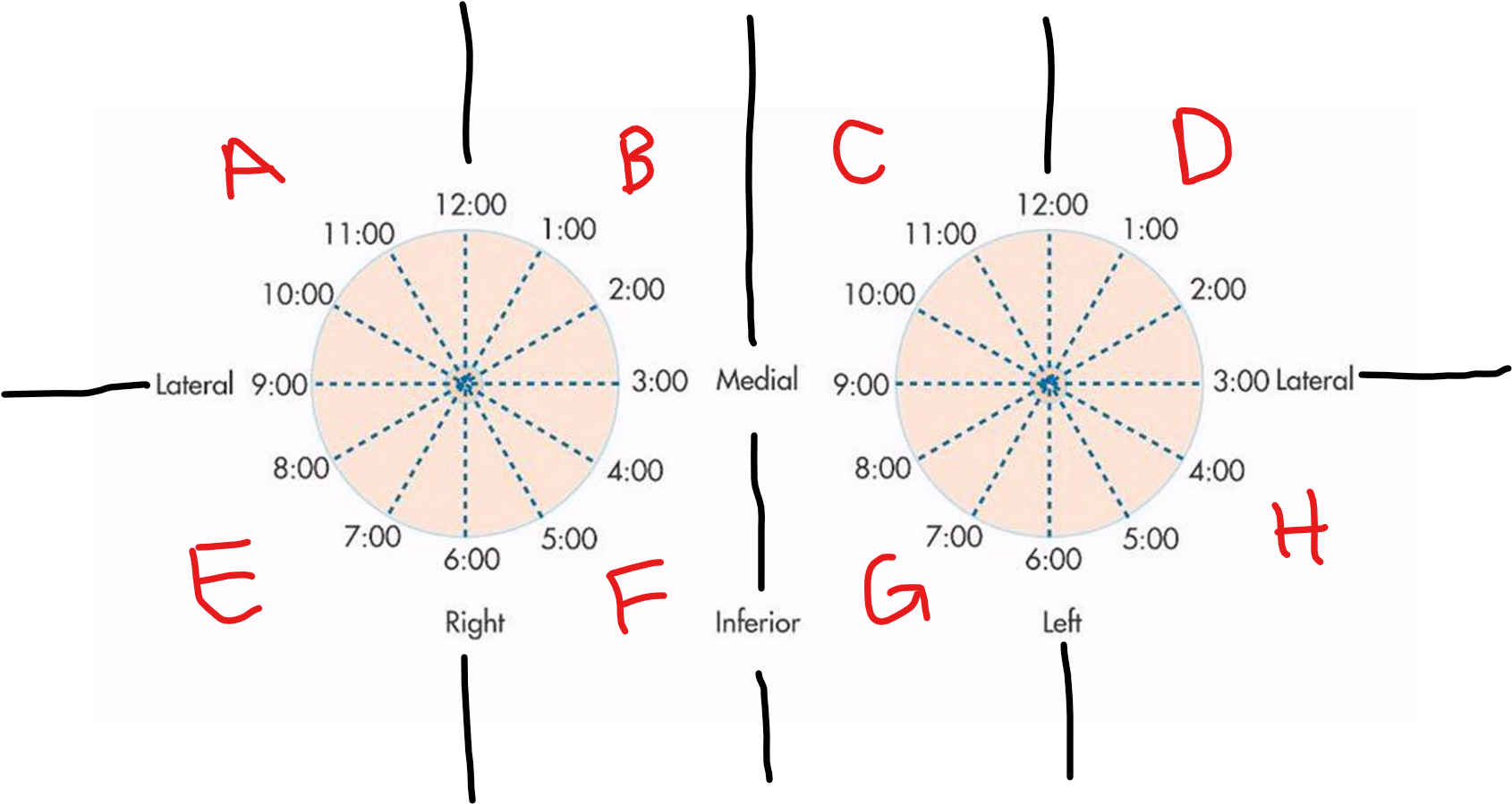
G
LLIQ
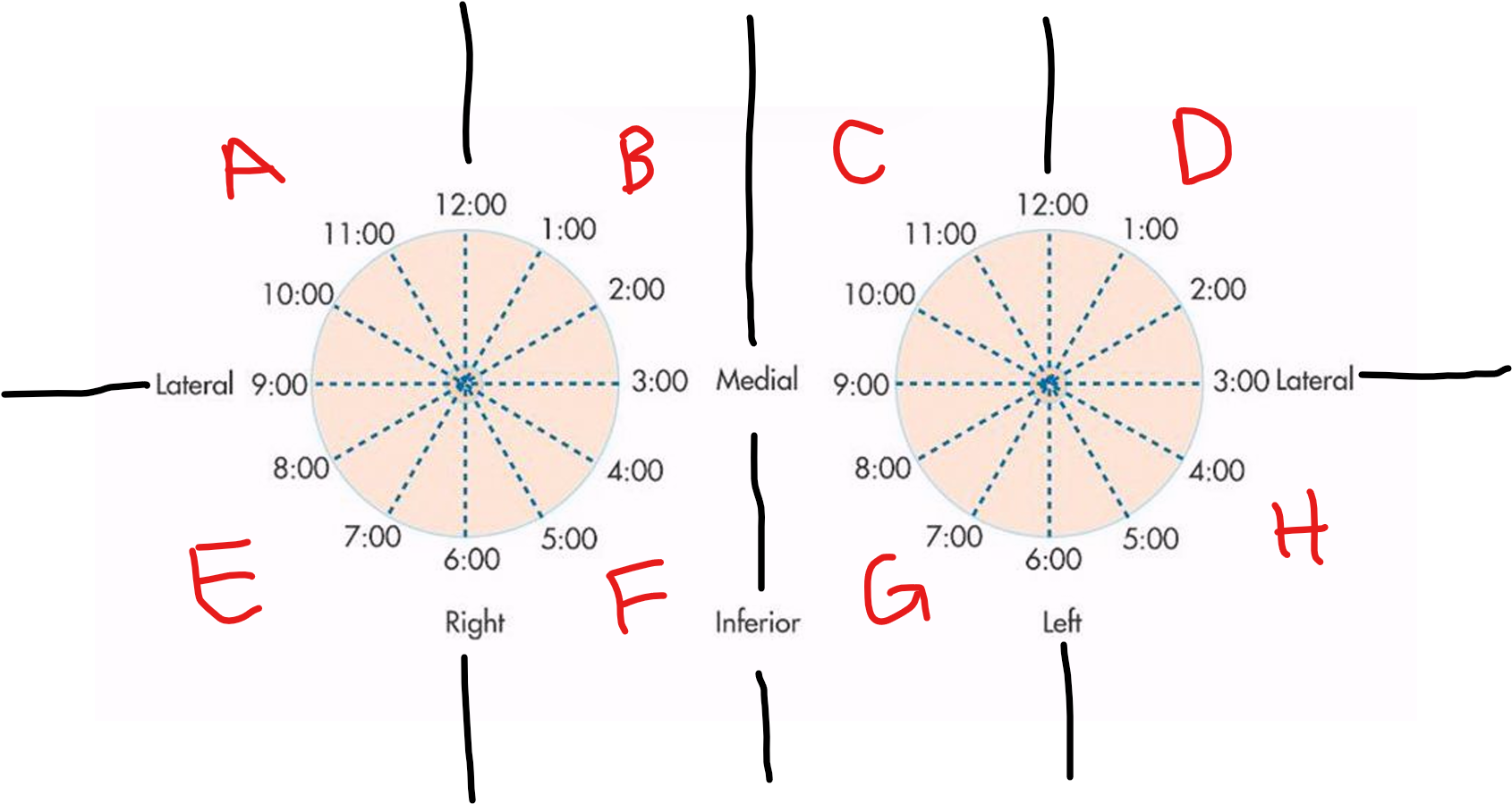
H
LLOQ