Imprinting and Uniparental Disomy
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mechanisms and associated disorders
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Imprinting mechanism
DNA methylation, post-translational histone modification, chromatin structure, noncoding RNAs (RNAi)
Uniparental disomy occurrence
can occur as a random event during the formation of egg or sperm cells or may happen early in fetal development, UPD for some chromosomes have no adverse effect on an individuals but can result in abnormality through aberrant genomic imprinting
UPD definition
two copies or parts of a chromosomes inherited from one parent
heterodisomy: same parental source, 2 chromosome
isodisomy: same parental source, same chromosome
When UPD is associated with phenotypic abnormalities
chromosome or chromosome segment involved carrier genes are imprinted
genes express autosomal recessive condition from a single carrier parent
CFTR gene location
chromosome 7
Cytogenetic warnings for UPD: Mosaic
aneuploid cell line with gain/loss of chromosome
not all mosaicisms have potential to become UPD
other UPD cytogenetic warnings
robertsonian translocation, inversion, unusual heteromorphic chromosomal pattern, knowledge of parental translocation/inversion
Trisomic rescue
lose trisomy —> become disomic
maternal upd more likely since nondisjunction happens more frequently in oogenesis
2/3 —> loss becomes normal phenotype
1/3 —> loss leads to UPD
Monosomic rescue
one chromosome from a normal gamete is duplicated when paired with nullisomic gamete to restore euploidy
dup can be mitotic or meiotic
often seen with isochromosome formation, needs to happen soon after fertilization
nondisjunction at meiosis II —> isodisomic
Gametic complementation
fusion of 2 particular gametes, both coincidentally abnormal, one nullisomic other disomic for same chromosome
rare, can expect heterodisomic and isodisomic lines
segmental UPD
somatic recombination where exchanged region is imprinted
UPD in Prader-Willi
Maternal 15q11-13, SNRPN and ZNF127
no mutations detected in specific gene, SNRPN methylated so not expressed since no paternal band
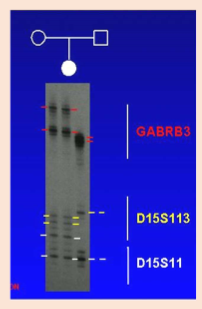
Prader-Willi molecular analysis
Absence of paternal alleles
maternal UPD also confirmed by inheritance of both copies of maternal 15 in child
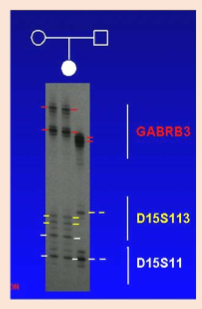
UPD in Angelman
paternal 15q11-13, unknown gene
actual mutations detected in UBE3A, SNRPN not methylated and expressed
UPD in Silver-Russell Syndrome
chromosome 7, unknown genesS
Silver Russell Syndrome features
low birth rate d/t intrauterine growth retardation, short stature, triangular shaped face, scaphocephaly (long narrow head at birth), normal head size appearing large b/c reduced body length/weight, 5th finger clinodactyly (incurving), poor appetite, developmental delays
UPD in Beckwith-Wiedemann
paternal, 11p15.5 often segmental, candidate imprinted genes are IGF2(pat) and H19(mat)
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome features
macroglossia (large tongue), giantism and organomegaly, abdominal wall defects, ear creases, renal abnormalities, predisposition for developing Wilms’ Tumor
Maternal UPD chromosome 14
14p32, include reciprocally imprinted DLK1 and GTL2 genes
Maternal UPD chromosome 14 features
low birth weight, developmental delay, precocious puberty, small hands, scoliosis, broad forehead, fleshy nasal tip, otitus media