1.3 - pillars of sustainability, unsustainable development, justice and inequality
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
sustainability
ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
three pillars of sustainability
economic
environmental
social
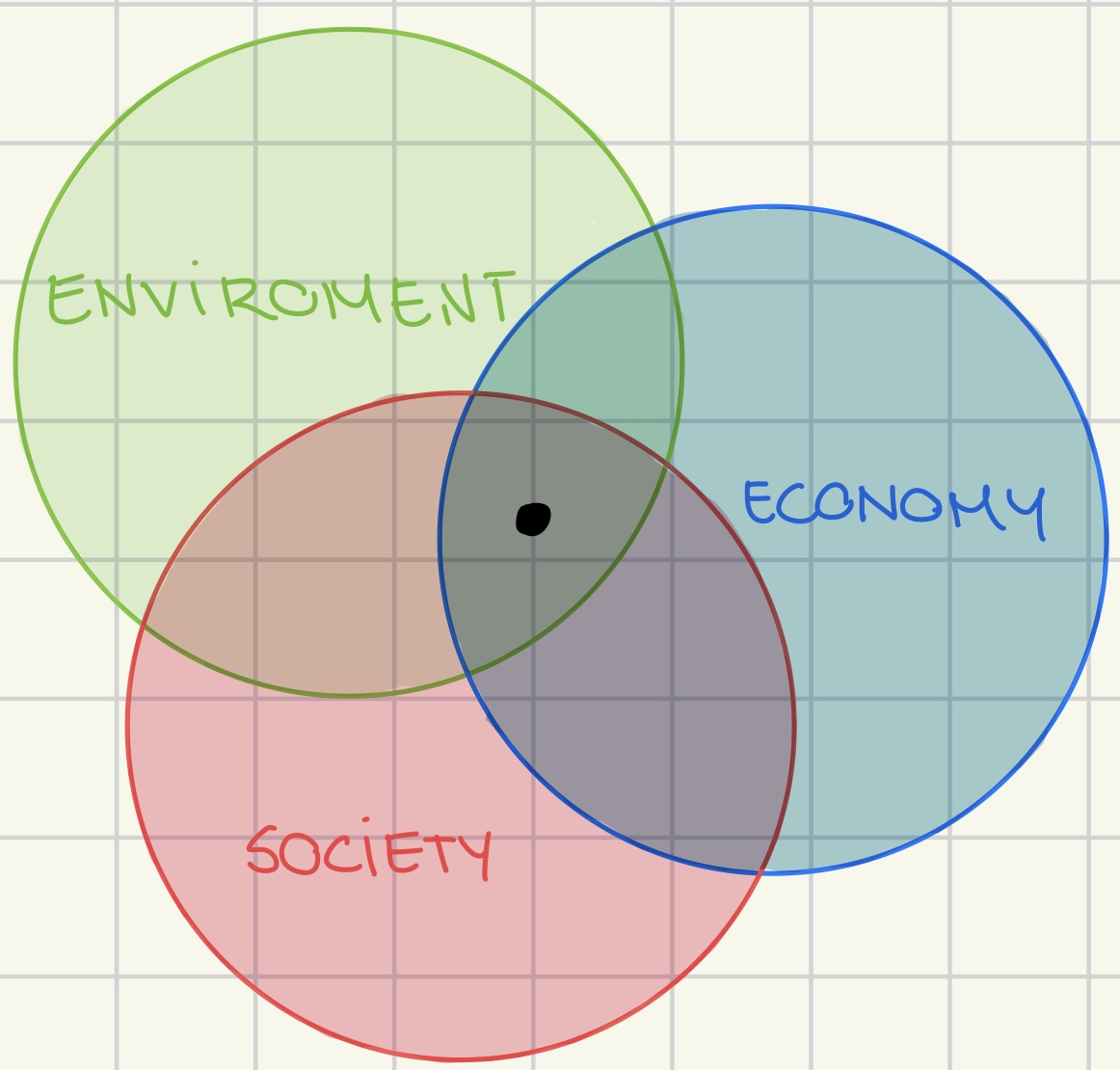
environmental sustainability
responsible use and management of natural resources that allows:
replacement of resources
recovery of ecosystems
regeneration of ecosystems
environmental performance index EPI
data driven summary, that ranks 180 countries on:
climate change performance
environmental health
ecosystem vitality
economic sustainability
ability of an economy to support a defined level of economic production indefinitely
efficient management of resources
sustainable development
ensuring that needs are met without compromising future generations.
social sustainability
ability of a society to maintain well-being and quality of life for all its members while ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Earth overshoot day
the date each year when humanity's demand for ecological resources exceeds what Earth can regenerate in that year.
sustainability indicators
green GDP
value of goods/services that were produced without costs to environment
human development index (HDI)
social, economic, and environmental health of a system.
carbon footprint calculator
biocapacity
tragedy of commons
individuals/groups acting in their own self-interest deplete shared resources, leading to long-term negative consequences for the entire community.
example of tragedy of commons
Newfoundland cod fisheries collapse 1990’s
over fishing
technological advancements
failed control of fishing activities
depletion of cod population
unemployment
example unsustainable use of natural resources
Ghana, Africa
world’s largest digital dumping site
e-waste recycled to extract valuable materials
human hazards: air pollution → respiratory problems, toxins
environmental justice
right of all people to live in pollution-free environment and have equitable access to natural resources regardless of their:
race
gender
socio-economic status
nationality
examples of environmental injustice
Deepwater Horizon, Gulf of Mexico
drilling rig exploded → massive oil spill
contamination of marine and coastal ecosystems
affecting community of fishing and tourism
health problems
loss of cultural heritage
inadequate support and compensation
Union Carbide, Bhopal India 1984
tons of toxic gas from pesticide plant
death and illness
contaminated soil and groundwater
uncleaned chemical waste
Union Carbide refused to take responsibility
inequality
uneven distribution of resources, opportunities, and privileges among society
examples of environmental inequality
food inequality Haiti, Caribbean
often natural disasters and political instability
poor infrastructure for water and sanitation
deaths, malnutrition, hunger
water toxicity in Flint Michigan, USA
switch from lake to Flint river caused water pipes to corrode
lead and contaminants in drinking water
energy inequality Beirut, Lebanon
widespread blackouts to poor management
scales of sustainability and environmental indicators
individual
choices in lifestyle/consumption
business
sustainable practices
community
collaboration to address issues
city
sustainable initiatives
country
policies, laws,systems
global
international efforts