APH CH 6 integumentary system and burns
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
4 major types of membranes
serious
mucous
synovial
cutaneous
Function
• Lines body cavities that lack openings to outside
• Secrete watery serous fluid (lubrication)
Serous Membrane
Tissue Type
• Layer of simple squamous and loose connective
Serous Membrane
Body Example
• Inner lining of cavities and covers organs in… thorax, abdomen
Serous Membrane
Function
• Lines cavities and tubes that open to outside of body
• Goblet cells secrete mucus
Mucous Membrane
Tissue Type
• Epithelium over loose connective tissue
Mucous Membrane
Body Examples
• Cavities… Oral, nasal, tubes of digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive system
Mucous Membrane
Function
Inner lining of joint cavities
Secretes synovial fluids for lubrication
Synovial Membrane
Tissue Type
Dense connective tissue over loose connective and adipose tissue
Synovial Membrane
Body Examples
Synovial joints: knee, elbow, hip
Synovial Membrane
• Body Example – Skin
Cutaneous Membrane
Composed of stratified squamous epithelium
Epidermis
Prevents: excessive water loss, mechanical injury, effects of harmful chemicals, and keeps out disease-causing microorganisms
Epidermis
Lacks blood vessels (because it is composed of stratified squamous epithelium)
Epidermis
Stratum Basale- deepest layer of epidermis;
close to the dermis
Epidermis
Nourished by dermal blood vessels
Epidermis
As this layer divides and grows, older epidermal cells are pushed away from the dermis towards the skin surface
Epidermis
Farther cell moves = poorer nutrient =
death
Process where older cells harden
Keratinization
Cytoplasm fills with tough, fibrous, waterproof keratin protein
Keratinization
Many layers of tough, highly packed dead cells accumulate in the outer epidermis (4-5 layers depending on thickness of epidermis in different regions)
Keratinization
1) stratum corneum:
outer most layer
2) stratum lucidum:
found only in thick areas (palms and soles)
3) stratum granulosum:
may be missing where epidermis is thin
4) stratum spinosum
5) stratum basale:
next to basement membrane
Cell division increases where skin is rubbed causing growth of thickened areas called ________ (hands and feet); or ______ on toes
calluses; corns
Melanin: Produced by specialized cells in the epidermis called ________
melanocytes
Dark pigment that provides skin color
Melanin
Function
- Absorbs ultraviolet radiation in sunlight
Melanin
Function
- Prevents mutations in the DNA of skin cells
and other damaging effects
Melanin
Skin Color - due largely to ________
melanin
All people have about the ______ number of melanocytes
same
inner layer
dermis
Thicker than epidermis
dermis
Contains connective tissue consisting of collagenous and elastic fibers, epithelial tissue, smooth muscle tissue, nervous tissue, and blood
dermis
__________ is anchored to the dermis to the epidermis and separates the two skin layers
Basement membrane
Beneath the dermis
Subcutaneous Layer
Made of masses of loose connective and adipose tissue
Subcutaneous Layer
Binds skin to underlying organs
Subcutaneous Layer
stretchy skin
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
a disorder of the connective tissues affecting the skin, ligaments and internal organs
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
The collagen that strengthens the skin and determines its elasticity becomes defective, resulting in, among other things, a loosening of the skin and hypermobility of the joints
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
In more serious cases, it can cause the fatal collapse or rupturing of blood vessels.
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Amount of ________ that melanocytes produce affect skin color
melanin
_______ and ________ of the pigment granules affect skin color
Distribution; size
____________ (abundant production = darker skin) affect skin color
Genetics
______________ (ultraviolet light) affects skin color
Sunlight
___________ (radiation) affects skin color
X-ray
_________- carotene in vegetable can turn skin orange
Diet
___________ (in body)- Bilirubin (juandice) affects skin color
Chemicals
Amount of _________ in dermal vessels affects skin color
blood
High oxygen =
hemoglobin is pinkish skin
Low oxygen =
hemoglobin is bluish (cyanosis)
inflammation of liver and causes whites of eyes and skin to turn yellow
Hepatitis
purple skin=
constriction of blood vessels in response to cold
Dermal ridges (papillae) between the epidermis and dermal
Fingerprints
Determined by genes and baby pushing against uterine wall
Fingerprints
Everyone’s __________ are different (including twins)
fingerprints
papillae
Dermal ridges
3 Main Types of fingerprints
Arch
Loop
Whorl
4 Accessory Organs
Hair Follicles
Sebaceous Glands
Nails
Sweat Glands
where most cell division occurrs
hair follicle
condition of excessive hair growth where hair normally doesn’t grow
hypertrichosis
Oil glands associated with hair follicles that secrete sebum
Sebaceous Glands
Keep hair and skin soft, pliable, and waterproof
Sebaceous Glands
Pimples/acne- overactive glands that become plugged and inflamed
Sebaceous Glands
white thing that comes out of pimples
white blood cell
Protective covering at the end of the fingers and toes
Nails
Contains nail plate and nail bed
Nails
½ moon shape at base of nail plate – most active growing area
Lunula
Nail growth occurs by ___________ cells
keratinized
Sweat is carried to the surface by
pores (Sweat Glands)
Sweat glands contain mostly water, but also small amounts of ______, _______ and _______
salt, urea, uric acid
Contains mostly water, but also small amounts of salt, urea and uric acid
Sweat Glands
Responds to increase of body temperature; most common
eccrine (merocrine) glands
Responds to emotions, pain or when frightened; “sex scent”
apocrine glands
squamous cell or basal cell carcinomas
Cutaneous Carcinomas skin cancer
Skin cancer that is non-pigmented epithelial cells
Cutaneous Carcinomas skin cancer
Most common type of skin cancer
Cutaneous Carcinomas skin cancer
Skin cancer found in light-skinned people and +40 years old
Cutaneous Carcinomas skin cancer
Regular exposure to sun light can cause
Cutaneous Carcinomas skin cancer
Slow growing skin cancer
Cutaneous Carcinomas skin cancer
Skin cancer from melanocytes
Cutaneous Melanomas skin cancer
Skin cancer that can affect any age
Cutaneous Melanomas skin cancer
Skin cancer that is short, high intense sunlight
Cutaneous Melanomas skin cancer
Sunscreen
Avoid sun exposure
Regular skin exams
General Prevention of skin cancers
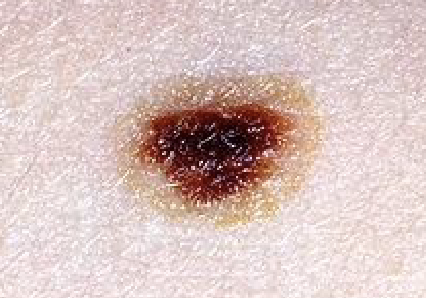
not normal
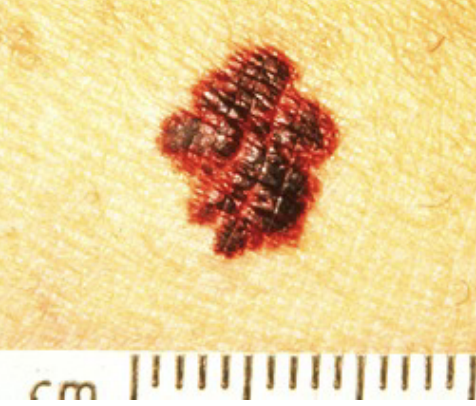
not normal
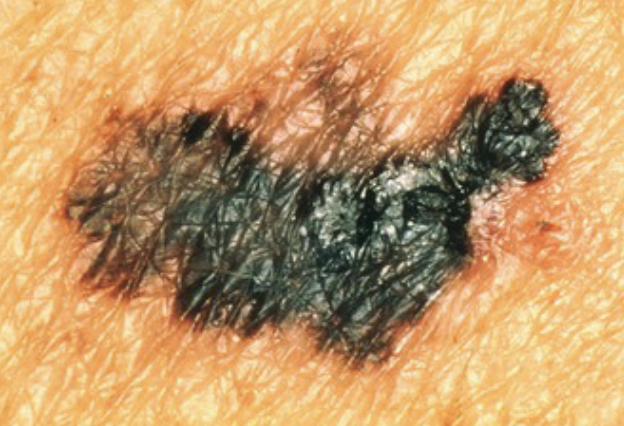
not normal
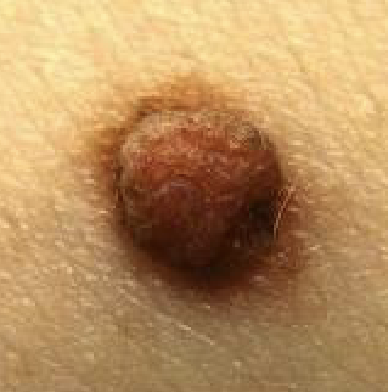
normal
ASYMMETRY:
One half does not match the other
BORDER:
Edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred
COLOR:
Color is not consistent throughout
DIAMETER:
Larger than 6 mm across (about ¼ inch -- pencil eraser), melanomas sometimes are smaller
EVOLVING:
Changes in size, shape, color, appearance, or growing in an area of previously normal skin
this “ABCDE” Rules to Melanoma is not concerning on its own but with other characteristics
DIAMETER:
malignant
cancerous
benign
not cancerous
metastasis
spreading of malignant growth