sri lanka
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
sinhala
ancient name of sri lanka
sri lanka
large island in the indian ocean and located at the southern tip of india
center of the international trade due to its position on the west to east sea routes
hills and high rocks
cities, palaces, and temples were constructed on blank and blank rocks
hinduism, islam, buddhism, christianism
religion in sri lanka
Dharma-Dipa
Known as the blank, the island of the buddhist doctrine
son of Ashoka, Mahinda Thera
who introduced buddhism in sri lanka
Sacred Bodhi Tree
Planted in Anuradhapura by Sanghamitta Thera (daughter) considered as one of the oldest trees in the world
Adam’s peal
vertical and unmoving, established as the stable pivot around which the universe revolves - Axis Mundi
is alos the horizontal axis, grounding the gathered creativbe cosmic energy radiating it out in all directions
Sree Padafoot (sacred foot print)
mark of Lord Shiva; for buddhists, it is the footprint of Lord Buddha; muslims and some christians believe adam first stepped down onto earth
Sinhalese
earliest colonizers of Sri Lanka
Hydraulic engineering
construction of water tanks (reservoirs) and irrigation canals
Annuradhapura Period
first capital
situatd with major ports in the northwest and northeast and surrounded by irrigable and fertile land
one of the most prorgressive centers of political power in south asia
popular as ritual and administrative center
Sigiraya
during the annuradhapura period, sinhalese king kassapa created a city in a rock hill called
Polonnoruwa Period
invaded and occupied by Cholan
settled in lower areas
King Vijayabahu
who defeated chola invaders to reunite the country of sri lanka
Jananathamangalam
Polonnoruwa period is also called blank duringg the chola reign
King Parakrama Bahu “The Great”
During the polonnoruwa period, the city was rebuilt by king ?
King Wijayabahu I, King Maha Parakramabahu I, and King Nissankamalla
Important kings during the polonnoruwa period
Kandyan Period
divided into several kingdoms with its capital at Kandy
was once occupied by portugese, dutch, british
Kandenuwara
hill city
naural, rock cut, based on buddhist principles
arch’l character of sri lanka
Anuradhapura
plan:
relationship between building and landscape
Polonnaruwa
plan:
expansion of temple to enshrine colossal buddha statue
Kandyan
plan:
city placed on hill
Anuradhapura
walls:
brick worl
white plastered walls
Polonnaruwa
Walls:
red rick
lime plastered
Kandyan
walls:
mostly timber
painted walls
Dwarapalas
in polonnoruwa, these are door keepeers
Anuradhapura
roof:
earliest remains are natural rock chambers built for hermits-with drip ledges to carry away rain water; these later developed with walls to form enclosure (rock temples)
Polonnaruwa
developed of a stupa covered by a roof
Kandyan
roofs high pitched with wide eaves, slightly curved; finished with terra cotta tiles and eaves tiles with bas-reliefs
Anuradhapura
columns:
square or octagonal sections
hexagon vase or abacus for capitals
Poonnaruwa
Columns:
Pillared building
lotus motifs
Kandyan
timber columns
Polonnaruwa
have 4 entrances for a stupa at cardinal points
colossal statues of the buddha
Kandyan
have richly carved with traditional motifs: lions, lotus, geese, etc.
Stupa
-Places to store ashes of monks who were cremated
1. Temple
2. Dagoba – Focal point of the monastery
3. Bhodi-gara – shrine enclosing a sacred Bodhi Tree
4. Halls for ceremonies, meditation and preaching
5. Court
6. Priory
7. Ponds and bathing places for drinking and ablution
Parts of a Buddhist Monastery
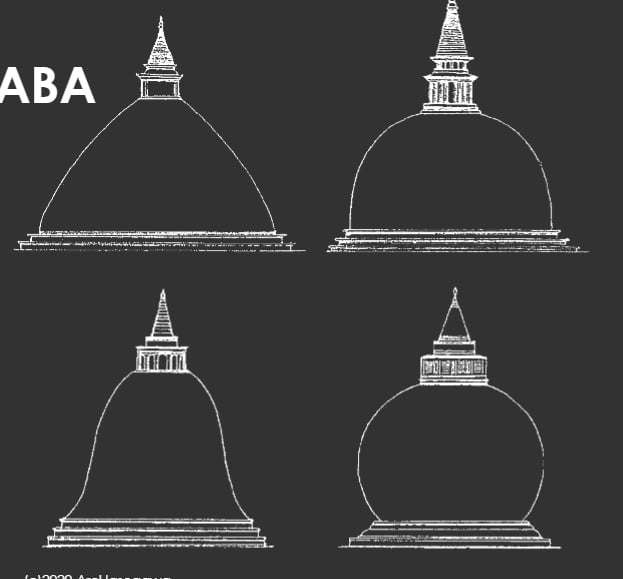
paddy- heap
bell
bubble
pot
Common dagoba shape
Thuparama (anuradhapura)
first buddhist uilding to enshrine collarbone of the buddha which was a gift from india
originally a paddy-heap then converted to a bell shape
Ruwanveliseya
bubble-shape solid brick dome in the center of 2 spacious square terraces, one above the other with the sides facing the cardinal points with pillared portico and step on one side of the lower terrace
Abhyagiri dagaba
founded as a monastery by sinhalese king Vattagamini
Monumental structure 15m higher than St. Paul’s cathedral containing an amount of solid masonry sufficient to build 8k houses large enough to accommodate 40k
samadhi buddha
the statue of the Budhha in deep meditation
Kuttam Pokuna (abhayagiri complex)
pair of ponds
used as a ritual baths by the monks
granite steps go to the bottom of the pond
Thuparama (anuradhapura)
biggest dagoba in the world constructed by King
Sigiriya
most remarkable of all Sri Lanka’s former cities
Monastery Of Mahintale
-Stands on a hill top 300 m.
-Mahinda Thera, Emperor Asoka’s son preached to the court in 3rd c.
-Large number of large steps were constructed to climb it. Stairway has 1840 steps made of granite, leading to the summit.
-Monastery
- regarded as cradle of Sinhalese Buddhism
Kiri Vihara (polonnaruwa)
sri lanka’s best preserved dagoba
Watadage (polonnaruwa)
Developed of a stupa sheltered by a roof and as is a pillared building around a small stupa