Chemical Bonding
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about chemical bonding, covering ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds, electronegativity, Lewis structures, VSEPR theory, and valence bond theory.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Ionic Bond Formation
Formation of ionic bonds occurs between a metal atom and a non-metal atom. Compounds formed between elements of very different electronegativities
Covalent Bond Formation
Formation of covalent bonds occurs between two nonmetal atoms.
Metallic Bonding
Metal cations are imbedded in a sea of mobile valence electrons.
Three Types of Interactions Within a Molecule of covalent bonds
Electrons and nuclei attract one another, electrons repel each other, and nuclei repel each other.
Covalent Bond
Shared electron density
Bond Length
The separation distance at which the molecule has the maximum energetic advantage over the separated atoms. each chemical has a characteristic bond length and energy
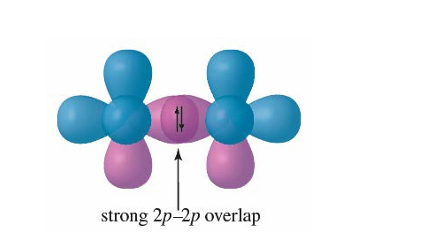
Sigma Bond
The strongest type of covalent chemical bond, formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal attractive forces lead to an unsymmetrical distribution of bonding electrons.
Electronegativity
A numerical value of how strongly an atom attracts the electrons in a chemical bond. Decreases down a Group and increases from left to right across a Period
Properties of Ionic Compounds
High melting and boiling points, brittle, and able to dissolve in water, and good conductivity when molten or dissolved(better).
Properties of Covalent Compounds
Strong forces within molecules and weak forces between them, low melting and boiling points, soft, and no conductivity of solutions. network solids
Properties of Metals
White and lustrous, conduct heat and electricity, malleable and ductile
Conventions
Each atom is represented by its elemental symbol, only valence electrons appear, lines represent shared electron pairs, and dots represent nonbonding electrons.
building lewis structures
by themselves do not imply any particular geometry for a molecule or ion,
Octet
A set of four electron pairs associated with an atom.
Lone Pairs
Nonbonding pairs of electrons.
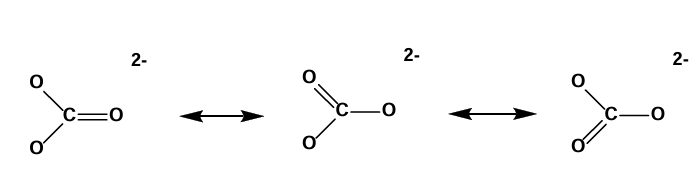
Resonance Structures
Representations of molecules as composites of equivalent Lewis structures.
VSEPR Theory
VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion), VB (valence bond)
Electronic Geometry
Geometric arrangement of electron density around central atom.
Molecular Geometry
Arrangement of atoms around central atom (i.e. does NOT include lone pairs).
Different electronic geometry
linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, octahedral
different molecular geometry
linear, bent, trigonal pyramidal, tetrahedral, t-shaped and seesaw, square planar, square pyramidal and octahedral.
2 regions of electron density, no lone pairs
the electronic and molecular shape is linear, the angle is 180,
3 regions of electron density, no lone pairs
the electronic and molecular shape is trigonal planar, the angle is 120
4 regions of electron density, 2 lone pairs
the electronic shape is tetrahedral and molecular shape is bent, the angle is 109.5
4 regions of electron density, 1 lone pairs
the electronic shape is tetrahedral and molecular shape is trigonal pyramidal, the angle is 109.5
4 regions of electron density, 0 lone pairs
the electronic and molecular shape is tetrahedral, the angle is 109.5
5 regions of electron density, 2 lone pair
the electronic shape is trigonal bipyramidal, and molecular shape is T-shaped, the angle is 120 and 90
5 regions of electron density, 1 lone pair
the electronic shape is trigonal bipyramidal, and molecular shape is seesaw, the angle is 120 and 90
5 regions of electron density, 0 lone pair
the electronic and molecular shape is trigonal bipyramidal, the angle is 120 and 90
6 regions of electron density, 2 lone pair
the electronic shape is octahedral, and molecular shape is square planar, the angle is 90
6 regions of electron density, 1 lone pair
the electronic shape is octahedral, and molecular shape is square pyramidal, the angle is 90
6 regions of electron density, 0 lone pair
the electronic and molecular shape is octahedral, the angle is 90
Dipole Moment and equation
A covalent bond with asymmetrical distribution of electron density.

Valence Bond Theory
Electrons are either localised in bonds between two atoms or localised on a single atom.
Hybrid Orbitals
Combinations of atomic orbitals. sp is linear (and 2 groups), sp2 is trigonal planar (3 groups), sp3 is tetrahedral (4 groups)