Periodontal Risk Assessment
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is a risk factor?
3 things
based on?
an attribute, characteristic or exposure that increases the likelihood of a person to develop a disease of health disorder based on epidemiological evidence
in this context: developing periodontitis or reoccurrence of periodontitis
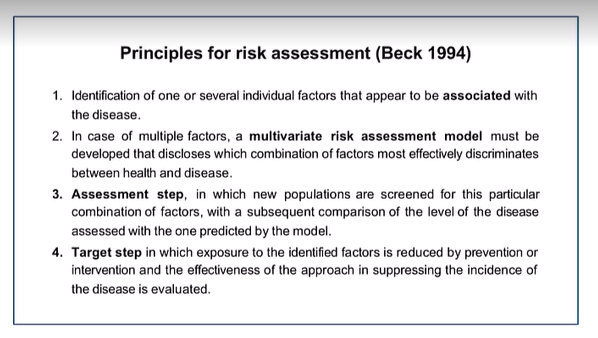
What are the principles of risk assessment Beck 1994?
factors associated with the disease
If multifactorial: a multiverse risk assessment model
assessment step - screen populations
target step - exposure to factor is reduced by prevention or intervention and the effectiveness in this approach in supressing disease
Why is it important to identify risk factors for periodontal disease? (4 main ideas)
Create pt risk profile - understand High, moderate and low risk
Characterisation of the patient - anticipate this pt will have more issues/more likely develop the disease/develop severe disease
Establish priorities - Limited resources so target those of higher risks/needs
Targeted and effective interventions
When do we assess for risk factors?
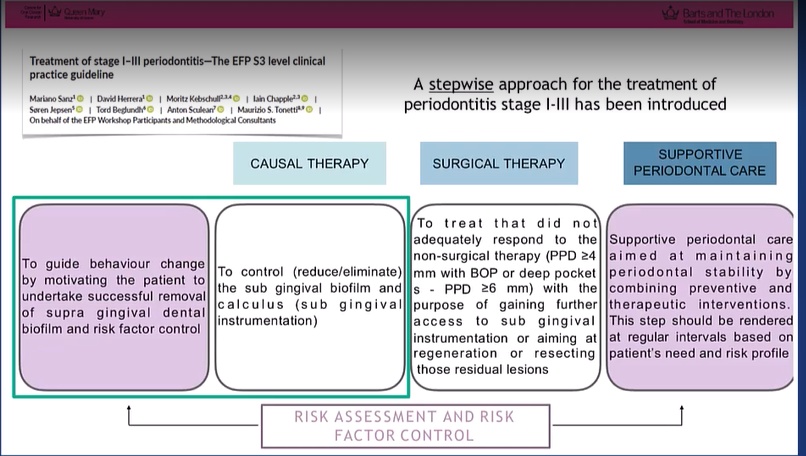
According to S3 guidelines - we follow a step-wise approach
risk factor control is at the very beginning
and must be checked throughout the therapy
highlighted in step 4 - life long periodontal care and we have to regularly assess the risk profile as this can change so must be updated
How strong is the evidence for risk factor control?
Very strong Grad A in the S3 guidlines

What does assessment of risk profile mean?
the risk assessment is a process in which we perform qualitative and quantitative evaluations of the probability that a negative even occurs (periodontitis progression/recurrence) as a consequence of being exposed to specific factors
What are the 3 levels to assessment of risk profile?
site level
tooth level
patient level
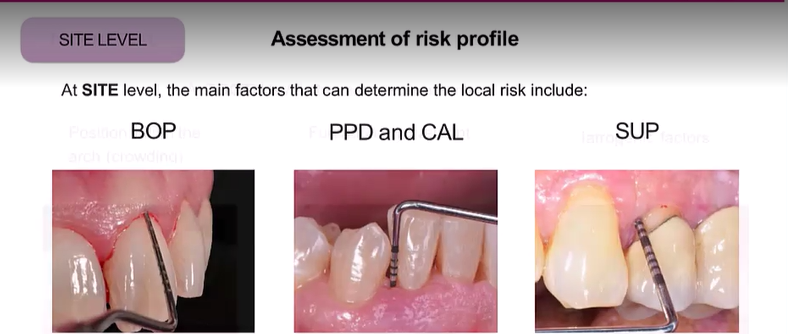
Assessment of risk profile: site level what are 3 main factors that can determine the local risk?
BOP No bleeding is a good indicator of stability rather than saying because there is bleeding there is instability
PPD and CAL
Suppuration
Why is assessing site specific parameters important?
establish 2 things?
decide what?
important to assess disease activity and to establish if there is current inflammation
Critical when we need to decide if the sites need to be re-instrumented during the supportive care or not
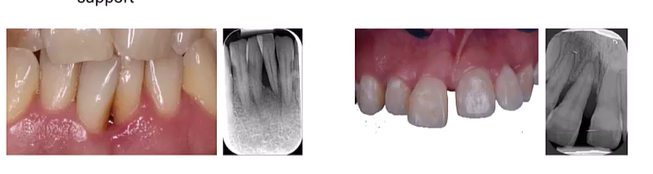
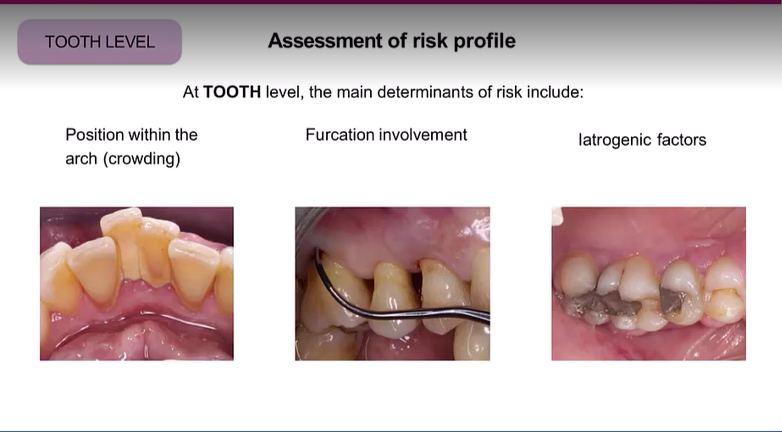
At tooth level, the main determinants of risk include? (5)
Crowding - plaque retentive factor
Furcation - applies only to multirooted teeth
Iatrogenic factors - overhanging fillings/prothesis
residual periodontal support
mobility (hypermobility and flaring)
The risk assessment at the tooth level can be used to evaluate 2?
and decide what?
prognosis and function of the teeth
as well as need for specific therapeutic measures during supportive care
Patient related factors: Non-modifiable (4) and acquired/modifiable/environmental (7)
Non-modifiable:
Age/sex(men tend to have worse condition, perhaps women care more about oral hygiene/sexual dimorphism in immune response greater in men)/ethnicity/genetics
Acquired/modifiable/environmental:
Smoking
Systemic disease (diabetes (uncontrolled)
medications
stress and psychological factors
malnutrition
socio-economic status
compliance with recall system
should try to address the modifiable factors first
Blue = most amount of information
What can pt factors tell you about periodontitis? (3)
the onset, severity and progression
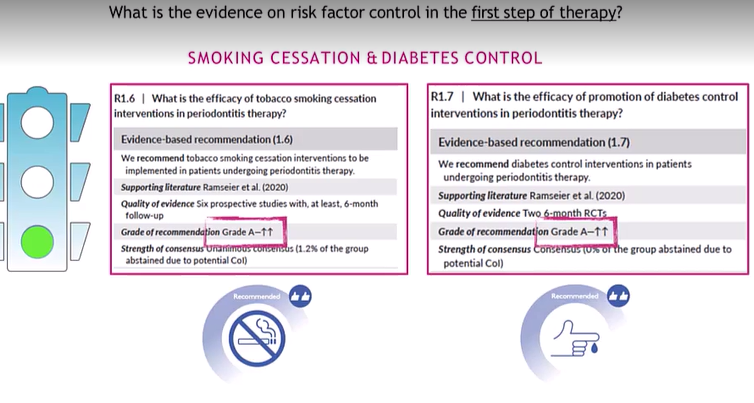
What is the grade of evidence for smoking and diabetes control?
High evidence that they are modifiers of the grade when it comes to diagnosis of periodontitis
Grade A
Assessment of risk profile is important to obtained a what for the patient?
this can be used at what stage of therapy to set what?
how is it also important in the 4th stage of therapy? (2)
Individualised risk profile
initial step of therapy to set priorities in the treatment plan
set the frequency and complexity of recalls during SPC (supportive periodontal care) (maybe see them every 3/6/12 months

What is one method for multilevel assessment of risk for periodontitis?
Periodontal risk assessment (PRA)

What are the 6 parameters in the PRA ?
BOP %
Number of residual pockets PPD>4 mm
Number of teeth lost
BL/age
systemic/genetic diseases
environmental factors (Smoking)
each parameter has its own scale for minor/moderate and high risk profiles
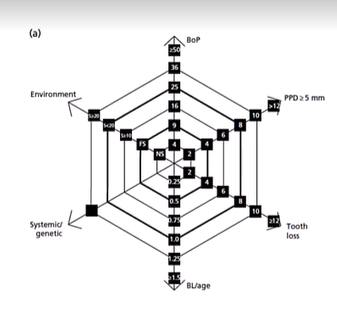
What does a completed diagram look like?
You obtain an area, the bigger the area the bigger the risk - can explain to patient at first risk assessment and can redo throughout journey of assessment so better visualisation for the patient
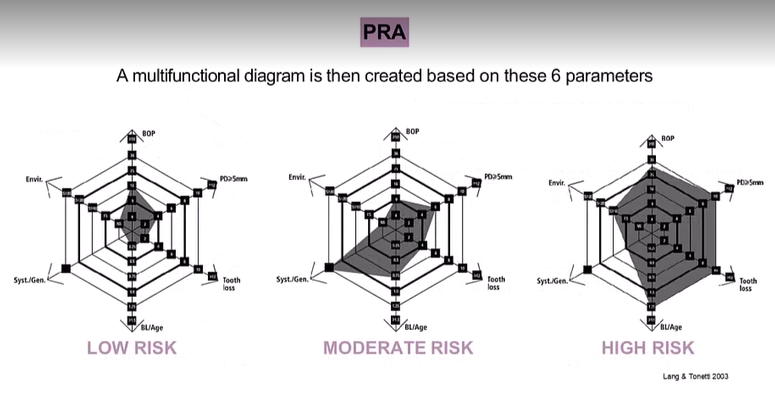
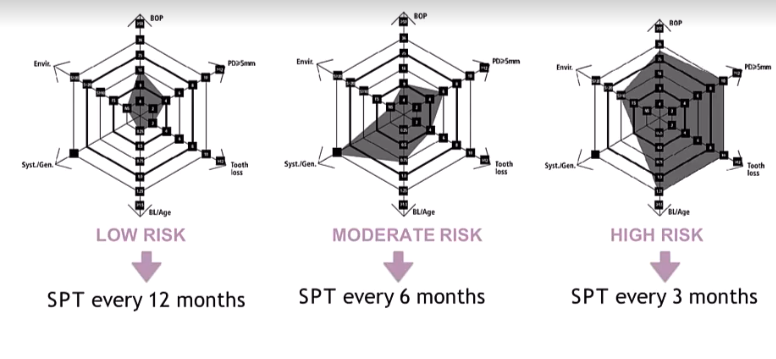
A comprehensive evaluation of these factors after active periodontal therapy will provide an individualised total risk profile and determine the frequency and complexity of the SPT visits, what is the recall period for SPT for each risk?
Low - when all parameters are at low risk and max one in mod risk
Mod - at least 2 in mod and max of 1 in high risk
high - at least 2 in high risk
can do and save in patient notes - easy for patient to understand
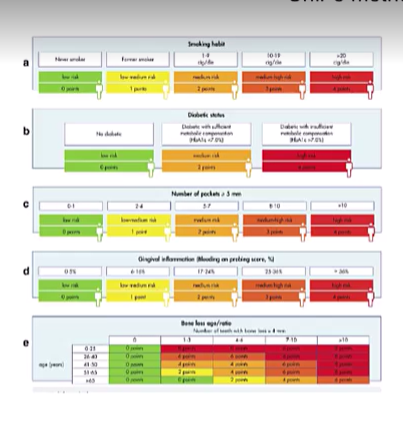
What is another method and what are the parameters?
Same as the PRA but no missing teeth included,
UniFe method
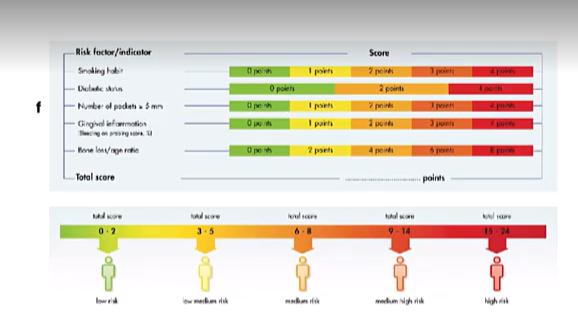
a score is assigned to each parameter and the final sum will provide the level of risk
What are the suggested recall times?
4-6 months in low risk
1- months in high risk
tailor the recall based on risk factors of the patient
The frequency of SPC visits and risk assessment:
the majority of data in lit support what recall periods?
and what is the evidence for this?
What is the evidence for reducing the this recall period?
therefore?
Cyclic 3 months based recalls are the most effective in reducing risk of periodontitis progression and reoccurence
Recolonisation by putative periodontal pathogens occurs within 3 months after instrumentation of deep pockets
ability of pt to maintain aqequate supragingival plaque control is able to influence the subgingival microbiota and therefore increase/reduce the recall frequency based on pt needs
pt risk is dynamic and changes overtime , so adapt the frequency of SPC recall


Important points
importance of frequent recalls
important of pt compliance

Another study
high risk - multiple factors - more difficult to influence behaviour change - so higher frequency recalls needed
S3 guidelines evidence strength for frequency of visits and adherence to SPC?
Adherence to SPC should be promoted
Risk assessment in patients who have implant rehabilitation? what are the 3 levels?
Implant level (site level)
Prosthesis level (tooth level)
Patient level
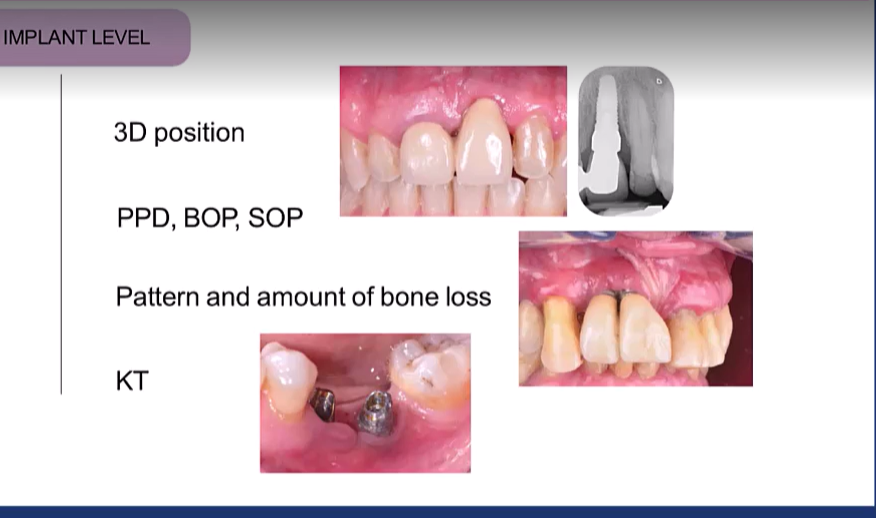
Implant level: (6)
3D position of the implant
PDD, BOP, Suppuration on probing SOP
P attern and amount of bone loss (vertical bone loss around implant)
Presence of KT (presence of keratinized tissue)
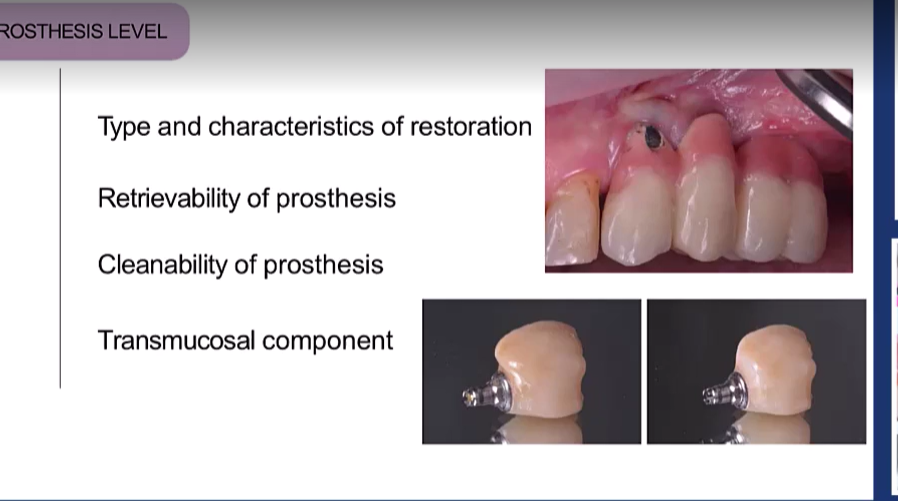
Prothesis level? (4)
Type and Characteristics of restoration
Retrievability of prosthesis
Cleanability of prosthesis
Transmucosal components
these are factors you can control

recent research on impact of implants found what?
emergence profile of the Implant more than 45 degrees
history of periodontitis

Another study
treatment of implant disease is much les predictable than for periodontitis so prevention is emphasised


risk factors control evidence in peri - implant diseases
EFP guidelines
diabetes and smoking
Grade 0 recommendation - open, not robust evidence if you don’t find KT, but in pt with deficiency of KT mucosa and experience pain on brushing might decide to increase KT width
Thickness of peri-implant tissue - low grade, augment thickness of tissue to tx peri-implant disease not much evidence - negative recommendation
OHI - Grade A
grade 0 - impact of bruxism and parafunctional habits

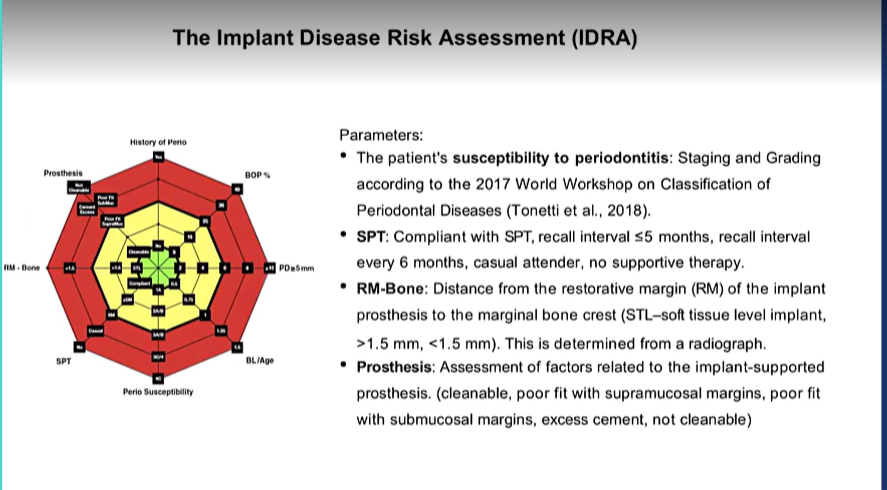
What tool is used for Peri-implant disease risk assessment
The implant disease risk assessment IDRA

What are the parameters? (7)
History of periodontitis:
BOP of implant and tooth sites
PD >5 mm at implants and teeth
BL/age - BL estimated from a periapical or bitewing at the most severely affected tooth
Perio susceptibility
SPT compliance
RM bone - more cleansable
Prosthsis
the 3 risk and recalls
less evidence for this
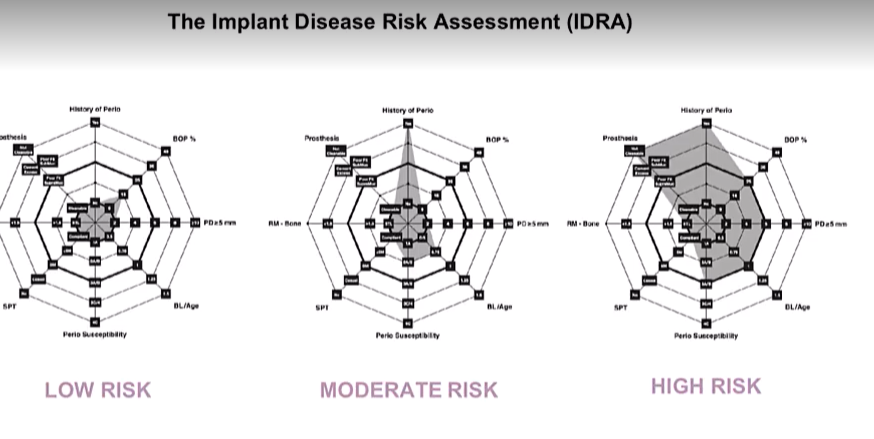
evidence for SPIC supportive peri-implant care

suggested minimum recall SPIC intervals?

How to know if tooth was lost due to periodontitis?
was it wobbly when you lost the tooth
what where the circumstances in which yu lost your tooth
was it decay/broken
if they have generalised perio - most likely due to that
The other lecture:
Another way for talking about risk assessment?
attempt to predict the probability for a pathological event to occur
it originates from estimates calculated using information obtained from groups of people and then extrapolated to individuals
Definition of periodontal disease?
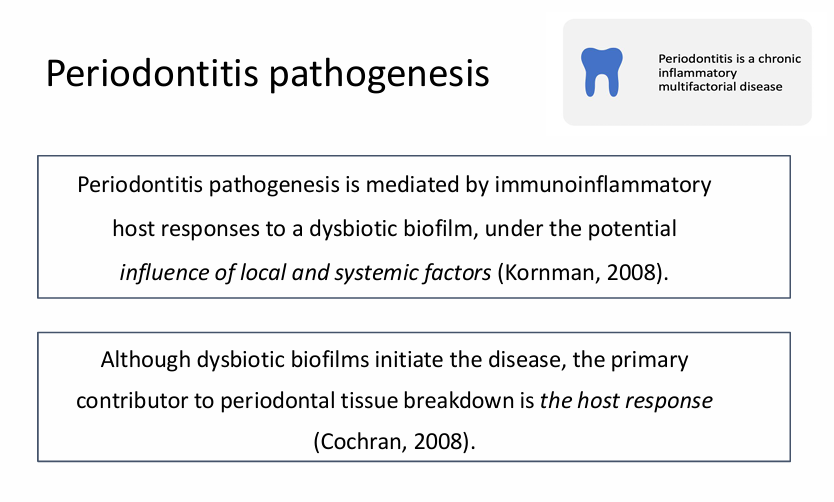
mediated by what? in response to? 2 possible influences?
what is the main contributor to periodontal tissue breakdown and what initiates the disease?
immunoinflammatory host response
response to a dysbiotic biofilm
local and systemic factors
biofilm initiates the disease, the host response is responsible for the break down
Periodontal disease is single factor or no?
no its multifactorial

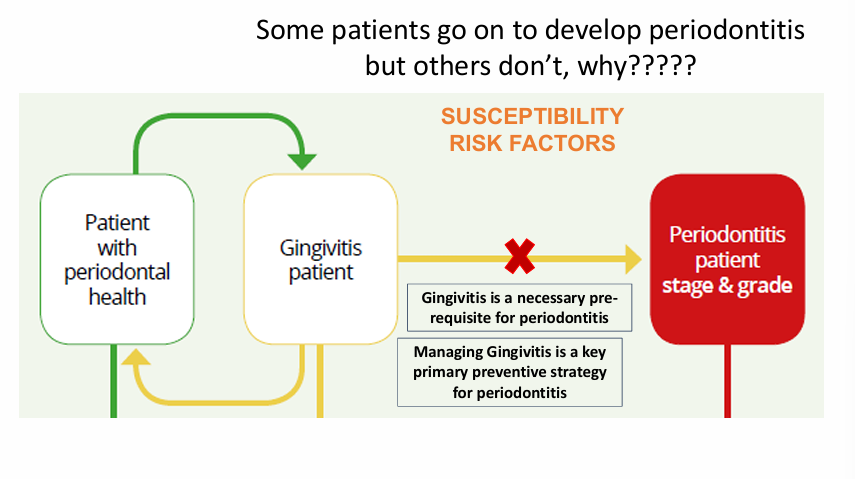
periodontal health, gingivitis and periodontitis interplay?
it is generally accepted that a patient with gingivitis can revert to a state of Health
Gingivitis is a necessary prerequisite for periodontitis but some patients go on to develop periodontitis and others don’t