3.3 Carbohydrates
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a monomer?
A small, basic molecular unit that can join with others to form a polymer (e.g. glucose, amino acids, nucleotides).
What is a polymer?
A large molecule made up of many monomers joined together (e.g. polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids).
What reaction forms polymers?
Condensation reaction – joins monomers with covalent bonds, releasing a water molecule.
What reaction breaks down polymers?
Hydrolysis reaction – breaks covalent bonds using water, splitting polymers into monomers.
Which elements make up carbohydrates?
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O).
What is glucose?
A hexose monosaccharide (C6H12O6), main energy source in respiration.
What is a hexose sugar?
A monosaccharide with 6 carbon atoms (e.g. glucose, galactose, fructose).
What is a pentose sugar?
A monosaccharide with 5 carbon atoms (e.g. ribose, deoxyribose).
What is ribose?
A pentose monosaccharide found in RNA, ATP, and NAD.
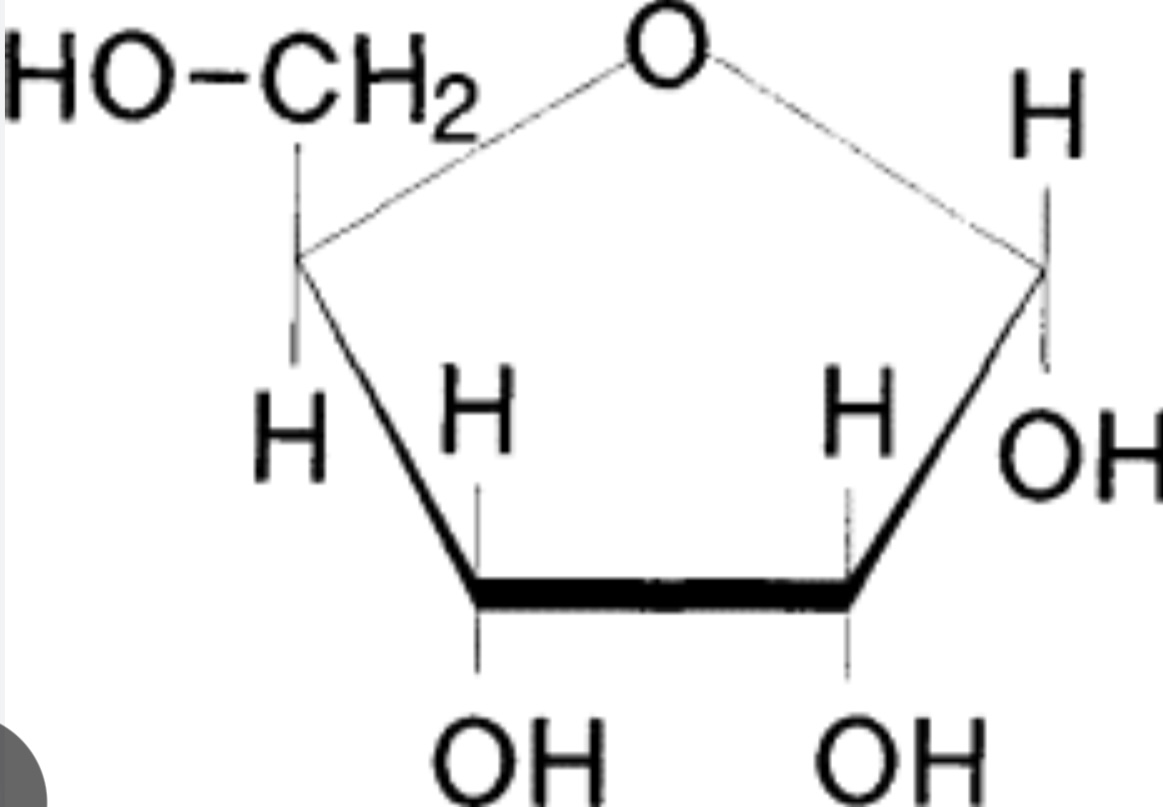
What is deoxyribose?
A pentose sugar in DNA with one fewer oxygen atom than ribose.
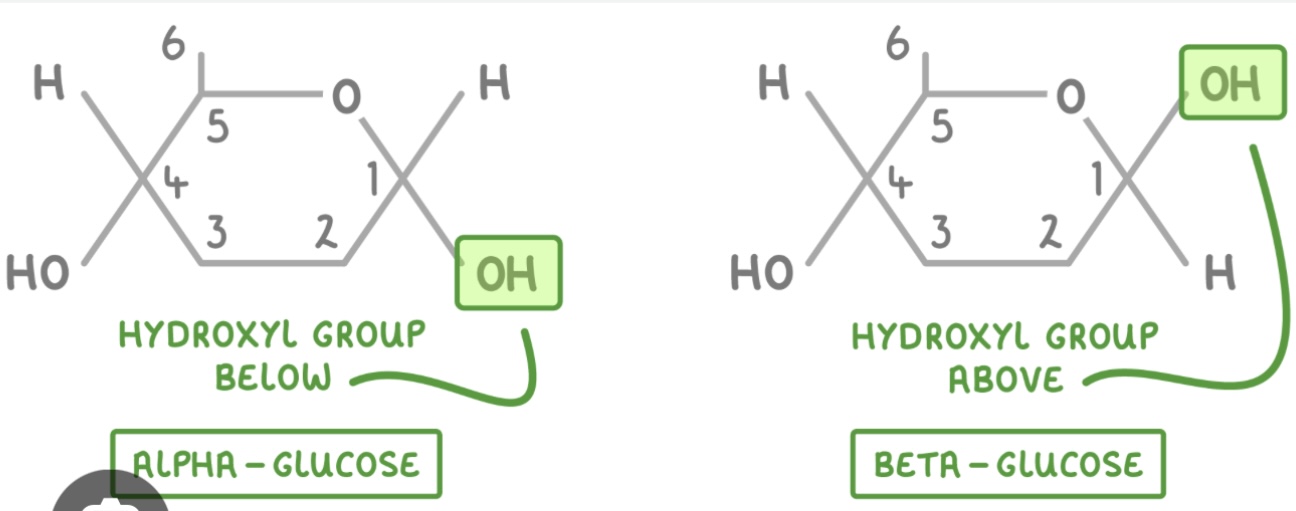
What is the structural difference between α-glucose and β-glucose?
In α-glucose, the OH on carbon 1 is below; in β-glucose, the OH on carbon 1 is above.
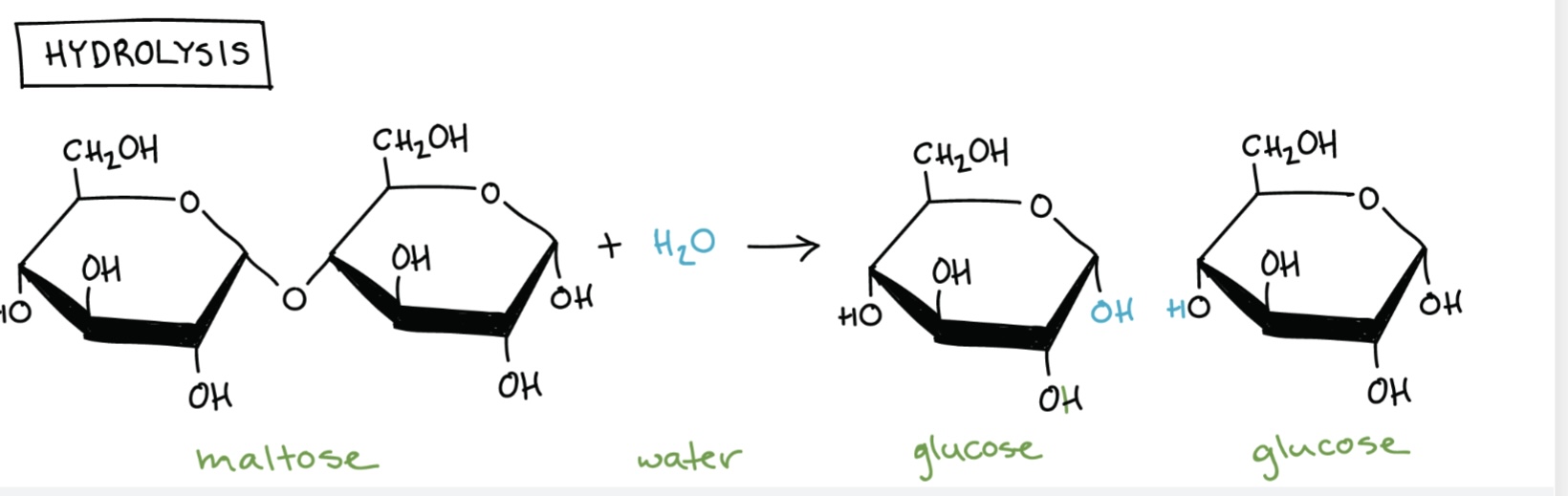
What is a disaccharide?
A sugar formed from two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction.
Name the disaccharides and their monomers.
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Lactose = glucose + galactose.
How are glycosidic bonds formed?
By condensation reactions between hydroxyl groups, releasing water.
How are glycosidic bonds broken?
By hydrolysis reactions, adding water to break the bond.
What is a 1,4 glycosidic bond?
A covalent bond formed between carbon 1 of one monosaccharide and carbon 4 of another.
What is starch?
A storage polysaccharide in plants made of α-glucose; a mixture of amylose and amylopectin.
Structure and function of amylose?
Unbranched α-glucose chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds; coils into helix, compact for storage.
Structure and function of amylopectin?
Branched α-glucose chain with 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds; branches allow rapid glucose release.
What is glycogen?
Animal storage polysaccharide of α-glucose, highly branched and compact, allows rapid glucose release.
What is cellulose?
Structural polysaccharide of β-glucose, straight unbranched chains linked by hydrogen bonds, forming strong microfibrils in plant cell walls.
Why is glucose soluble?
Because of hydrogen bonding with water; allows transport in blood and cytoplasm.
Why is starch good for storage?
Compact, insoluble (does not affect osmosis)
large (does not diffuse out of cells)
branched amylopectin allows rapid glucose release.
Why is glycogen good for storage in animals?
Compact, highly branched (faster glucose release to meet high metabolic demand), insoluble so does not affect osmosis.
Why is cellulose strong?
β-glucose chains form straight structures, hydrogen bonds between chains form microfibrils, giving high tensile strength to plant cell walls.
Why are condensation and hydrolysis reactions important?
They allow the synthesis and breakdown of biological molecules for energy release, storage, and structural functions.