ap psych unit 3 - lessons 5-7, myers' textbook terms
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
developmental psychology
branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the lifespan.
explores 3 major themes:
nature and nurture
continuity and stages
stability and change
fetal alcohol syndrome
physical and cognitive function deficits in children caused by their mother’s heavy drinking during pregnancy.
social learning theory
theory that we acquire our gender identity in childhood, by observing and imitating others’ gender-linked behaviors and by being rewarded or punished for acting in specific ways
schema
a mental framework or concept that organizes and interprets information, helping people make sense of the world.
assimilation
Incorporating new information into an existing schema.
ex. child thinks all birds can fly and then sees a penguin, they might add it into their bird schema.
accommodation
modifying an existing schema or creating a new one to add new information that doesn't fit.
ex. child is told a tomato is a tomato and not a "special apple," they change by creating a new "tomato" schema.
telegraphic speech
the early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram — “go car” — using mostly nouns and verbs.
part of two word stage
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (understanding).
linguistic relativism
the idea that language influences the way we think. can lead to linguistic determinism
linguistic determinism
hypothesis that language determines the way we think.
behaviorism
theory that human behavior is learned through interaction with environment.
neutral stimulus
an environmental event or object that does not initially elicit any particular response but can become a conditioned stimulus after being repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
ex. scientist is trying to train a dog to salivate at the sound of a bell, the bell is a neutral stimulus at the beginning of the learning process because it does not produce salivation.
unconditioned stimulus
naturally occurring stimulus that triggers a reflexive response without any prior learning.
ex. the can opener that makes a dog drool.
unconditioned response
unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus.
ex. dog drooling at the can opener.
conditioned stimulus
previously neutral stimulus that, after being repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to elicit a learned response called the conditioned response.
ex. the sound of any can opener.
conditioned response
learned autonomic reaction that occurs in anticipation of a specific stimulus.
ex. dog drooling at the sound of any can opener.
generalization
tendency to respond to stimuli that are similar to the original conditioned stimulus.
ex. after being bitten by a dog, person may fear other dogs.
discrimination
the ability to distinguish between similar stimuli.
acquisition
the initial stage of learning where a new behavior or association is developed through classical conditioning.
ex. the dog begins to associate the sound of the bell with food. this learning process is where the dog starts expecting food at the sound of the bell.
extinction
the process where a learned behavior or conditioned response weakens and disappears over time.
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance of a previously extinguished conditioned response after a period of rest.
higher order conditioning
form of classical conditioning where a new, neutral stimulus is paired with a previously conditioned stimulus to create a new conditioned stimulus.
ex.
(CC) bell is rung before presenting food to a dog, resulting in drooling.
(HOC) bell gets paired with a clicker.
eventually, clicker alone can cause drooling.
counterconditioning
an unwanted response to a stimulus is replaced with a new, more desirable response by pairing the stimulus with a positive one.
ex. a person with a fear of public speaking can be conditioned to feel relaxed by pairing the public speaking with a pleasant, relaxed state like listening to calming music.
one trial conditioning
a strong association between a stimulus and a response is formed after just a single exposure.
ex. not liking a certain food.
biological preparedness
idea that an organism is innately predisposed to learn certain associations more easily than others, because those associations have been adaptive for survival throughout its evolutionary history.
ex. humans fear snakes or spiders more than flowers, because the former posed a greater evolutionary threat to our ancestors.
associative learning
process of learning to link two events or stimuli together, allowing an organism to connect an action or stimulus with its consequence.
ex. dog learning to associate the sound of a bell with food.
operant behavior
voluntary action that an individual takes, which operates on the environment to produce a consequence, either a punishment or reinforcement.
positive punishment
applying something bad as a consequence to prevent the behavior from happening again in the future.
ex. giving a student who is late to class a detention.
negative punishment
removing something good as a consequence to prevent the behavior from happening again in the future.
ex. parent takes away a child's video game privileges after they hit their sibling.
positive reinforcement
applying something good as a reinforcement to increase the likelihood that a specific behavior will be repeated.
ex. giving a dog a treat for sitting on command to strengthen that behavior.
negative reinforcement
removing something bad as a reinforcement to increase the likelihood that a specific behavior will be repeated.
ex. when a parent stops nagging a child to do their chores after the chores are finished.
the law of effect
principle that behaviors followed by satisfying consequences are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by unsatisfying consequences.
shaping
learning process that reinforces successive approximations of a desired behavior to teach a new skill.
ex. teaching a child to say "banana" by first reinforcing them for saying "ba," then for "bana," and finally for the complete word "banana".
instinctive drift
tendency for an organism to revert to instinctive behaviors that interfere with a conditioned response, even after being trained to perform a different, learned action.
ex. raccoon is trained to put coins into a box for a reward. eventually, it begins to "rub" the coins together like it would food before putting them in the box.
learned helplessness
concept where an individual develops a sense of powerlessness and lack of motivation after repeated exposure to uncontrollable negative events.
ex. student who stops trying in a subject after repeated failures.
continuous reinforcement
schedule of reinforcement in which a desired behavior is reinforced every time it occurs. these behaviors will likely quickly extinguish when reinforcement stops, as it is an easily predictable pattern.
ex. dog given treat every time it does a task.
partial reinforcement
schedule of reinforcement where a behavior is rewarded only sometimes, rather than every time it occurs.
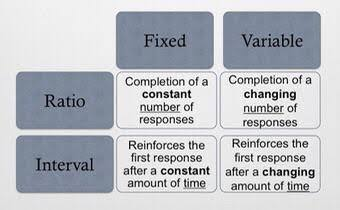
types of partial reinforcement
4 types:
fixed ratio reinforcement
variable ratio reinforcement
fixed interval reinforcement
variable interval reinforcement
classical conditioning
learning process where a neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with a stimulus that naturally triggers a response, causing the neutral stimulus to eventually trigger a learned response on its own.
strange situation experiment
a procedure for studying child-caregiver attachment.
a child is placed in an unfamiliar environment while their caregiver leaves and then returns, and the child’s reactions are observed.
basic trust
a sense that the world is predictable and reliable; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers.
self concept
developed at about age 12, it’s all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves in answer to the question, “Who am I?”
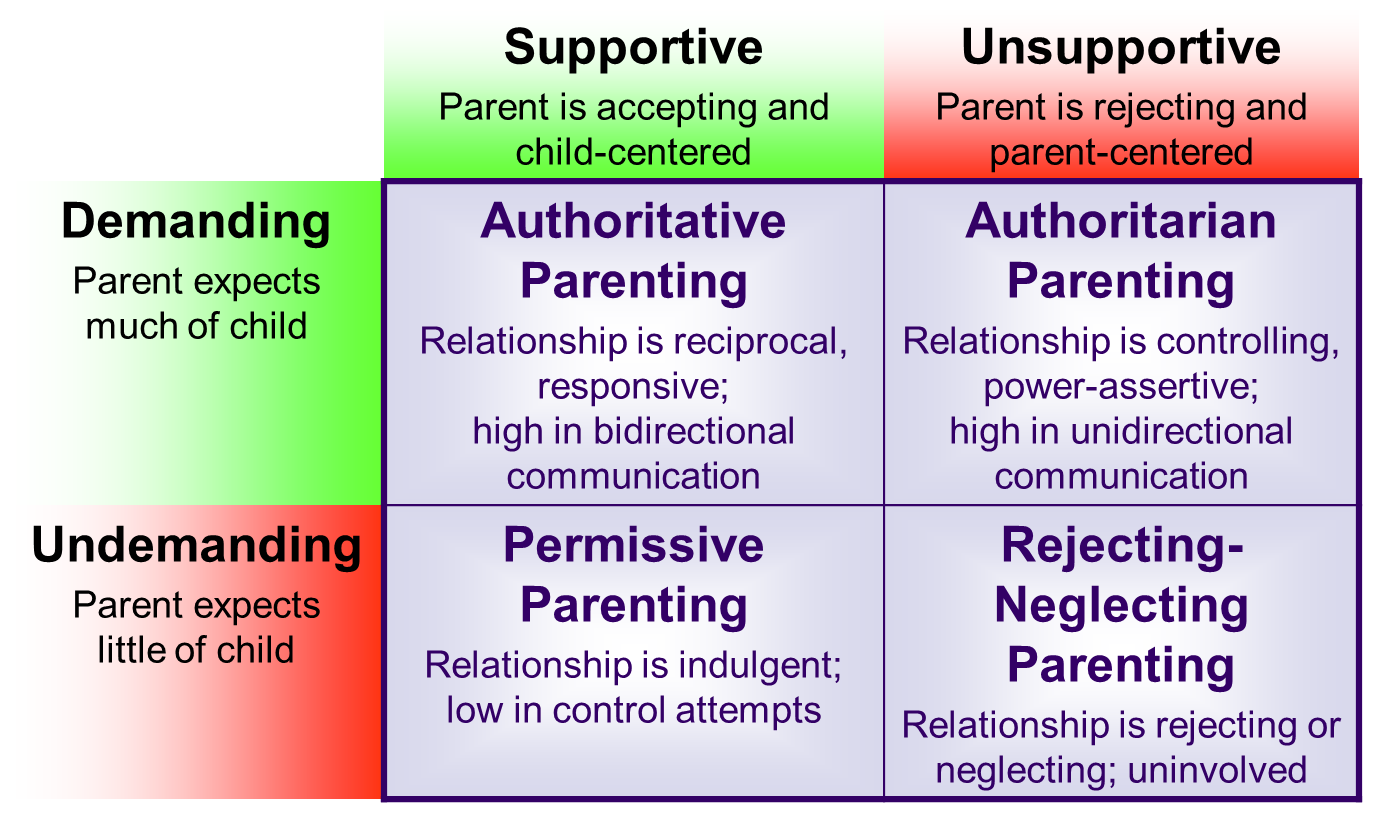
four parenting styles
authoritative (high demand, balanced), authoritarian (high demand, low warmth, strict), permissive (low demand, high warmth), and neglectful (low demand, detached).
social clock
“the right time” to leave home, get a job, marry, have children, or retire — varies from era to era and culture to culture.
operant chamber
a controlled experimental environment used in psychology to study how an animal's behavior is modified by consequences like reinforcement or punishment. typically contains a mechanism (like a lever or key) and a way to deliver a stimulus or reward (like food) or a punishment (like a mild shock).
discriminative stimulus
an environmental cue that signals the availability of a specific consequence, such as a reward or punishment, based on an organism's behavior.
ex. student raising their hand in class is a behavior. teacher asking a question is the discriminative stimulus that signals it is appropriate to raise your hand.
primary reinforcers
a stimulus that is naturally rewarding because it satisfies a biological need.
ex. food, water, shelter
ex. earning food as a reward.
secondary reinforcers
a stimulus that has acquired value through its association with primary reinforcers.
ex. money, praise
ex. earning money and using to buy food.
cognitive map
a mental image of the layout of one's physical environment.
latent learning
learning that occurs without obvious reinforcement and is not demonstrated until there is a reason to use the knowledge.
ex. rats explored a maze, developing a cognitive map of its layout without being rewarded. when a food reward was later placed at the end, they were able to navigate the maze as quickly as rats that had been rewarded from the start, demonstrating the learning that had occurred previously.
insight learning
when we puzzle over a problem and suddenly perceive the solution without trial and error.
mirror neurons
neurons that some scientists believe fire when we perform certain actions or observe another doing so. brain’s mirroring of another’s action may enable imitation and empathy.
token economy
behavior modification system where individuals earn "tokens" for displaying desired behaviors, which they can later trade for backup rewards to reinforce positive actions in settings like classrooms or therapy.
ex. earning stars in class for following rules. once you get a certain amount of stars, you get a prize.
escape learning
is when you perform a behavior to stop an unpleasant stimulus that's already happening.
ex. leaving a loud concert.
avoidance learning
when you perform a behavior to prevent the unpleasant stimulus from ever starting, usually after a warning signal.
ex. putting on headphones before the concert starts.