IGCSE 🤍
1/171
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
How many chromosomes are in egg cell?
23 chromosomes
Where does the embryo grow?
The uterus (womb) is where the embryo grows
What does ovary produces?
ovary produces ova and sex hormones
what passes through urthra?
Semen and urine pass through uretha
sprem
a muscular tube that stores sperm
What are the steps of pregnancy?
Once the embryo had implanted, the placenta develops
During pregnancy the amnion (amniotic sac) encloses the developing embryo
provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing embryo
removes waste such as urea and carbon dioxide
secretes female hormones that maintain the pregnancy
What is the role of amniotic fluid?
to protect the developing embryo
What are the secondary sexual characteristics?
Male:
underarm hair grows
facial hair starts to grow
voice breaks
Female:
underarm hair grows
period starts
hips widen
What are the properties of glucose?
stored as starch
used in respiration to release energy
stored in fruit as sucrose
turned into proteins with the addition of nitrogen so the plant can grow
turned into cellulose to make cell walls
What does the rate of photosynthesis rely on?
1) Light intensity: the higher this is, the faster the rate of photosynthesis provided there is lots of carbon dioxide and the temperature
2) Amount of CO2: the higher the carbon dioxide level, the faster the rate of photosynthesis again, provided there is plenty of light and a suitable
3) Temperature: as the temperature rises, the rate of photosynthesis increases - provided there is plenty of carbon dioxide and light. This is due to the temperature affects the enzymes controlled photosynthesis
What experiment is used to test for starch?
Iodine Test
What color changes would we observe if starch is present?
Blue-blackish color
Why is ethanol used in the test for starch using iodine?
Ethanol removed the green pigment chlorophyll from the leaf so the results can be seen more clearly
How do you test for CO2?
The soda lime absorbs CO2, so if you leave the plant in the sealed bell jar for a while it will stop photosynthesizing and use up its starch reverses for energy, therefore if you tested a leaf for starch it won’t a positive result
What would be your independent variable for an investigation?
changing one variable (light intensity, temperature or CO2) and all the other variables in the investigation must say controlled
dependent variable
the variable measured which will be the number of bubbles of oxygen in a minutes (repeating the experiment to make it more reliable)
What is the property of a unicellular organisms?
a large surface area
What does xylem transport?
water and dissolved minerals
What does phloem transport?
sugar and amino acids
In what direction does xylem flow?
flows in one direction
flows upwards
In what direction does phloem flow?
flows up or down
movement knows as translocation
Why do unicellular organisms have no need for lungs?
they do this as they can just obtain the oxygen they need by diffusion through that cell membrane meaning they don’t need a transport system
Why do multicellular organisms tend to require?
they require transport systems to supply all their cells with what they need fast enough
What does the transport system involves?
a network of veins (or vascular bundles) that run between the roots all the way through the plant to the leaves
diffusion
movement of any substance from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration (down the concentration gradient)
osmosis
the diffusion of water molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
active transport
the movement of substance from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution against the concentration gradient (requires energy from respiration)
the movement of substances from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
What are two ways of osmosis?
dilute solution contains a higher concentration of water molecules
concentrated solution contains a lower concentration of water
partially permeable (semi-permeable)
allows water and small molecules to pass through, but no longer molecules such as starch water potential; how ‘free’ water molecules are able to move (the concentrated a solution is, the lowest its water potential)
What happens to plant cells in pure water?
the cell swells up and the cytoplasm pushes against the cell wall and the cell become turgid
hypertonic
more dilute solution outside the cell
Why is turgor important for plants?
Structural Support: keeps cells rigid, helping plants maintain their shape and stand upright for optimal light absorption
Growth: enables cell expansion
Nutrient Transport: aids in the movement of water and nutrients through the plant
Stress Resistance: turgor helps plants cope with environmental stresses by regulating water loss
What happens to a plant cell in concentrated solution?
the cell contents lose water by osmosis and the cells shrink
the cell membrane starts to pull away from the cell wall. the cell wall becomes flaccid
hypertonic
more concentrated solution outside the cell
What happens to a cell in highly concentrated solution?
the cell membrane pulls away from the cell completely; this is plasmolysis
eventually the cell contents shrink so much that the membrane and cytoplasm spilt away from the cell and cytoplasm split away from the cell and cytoplasm split away from the cell and gaps appear between the cell and cell membrane
hormone
chemicals released by plants that regulate their growth
auxins
control the growth of plants by regulating cell division and elongation in plant cells
tropism
a plant growth response to a stimulus, it can be positive (towards) or negative (away from)
phototropism
a plant growth response towards or away from light
gravitropism
a plant growth response towards or opposite the direction of gravity
positive tropism
growth towards a stimulus
negative tropism
growth away from a gravity
What are the properties of auxins?
made in the meristem in the growing tips of steams and roots
diffuse from this tissue to other cells, regulating cell division and elongation (also they stimulate or inhibit elongation in non-meristem tissue
shoots (stimulated by auxins and so WILL elongate) and roots (inhibited by auxins and so will NOT elongate) response differently to auxins
What are the two types of reproduction?
sexual and asexual
What is another another name for sex cells?
Gametes
How many chromosomes does egg and sperm have?
23 chromosomes
What is an allele?
Alternative of a gene
What are the properties of asexual reproduction?
only involves one parent
gives rise to genetically identical offspring known as clones
the cells in your body divide into two identical cells for growth to replace worn-out tissues
What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
many identical offspring can be produced when conditions are favorable which is faster
more efficient because only on parent is involved in the process of reproduction
What are the properties of sexual reproduction?
involves a sex cell from two parents
these two special sex cells (gametes) join together to form a zygote which goes on to develop into a new individual
Which cells are in the gametes of plants in sexual reproduction?
ovules and the pollen
Which cells are in the gametes of plants in sexual reproduction?
oval eggs and the sperm
Why is sexual reproduction so important?
The variation it produces is a great advantage in making sure that a species survives. Variation makes it more likely that at least a few of the offspring will have the ability to survive difficult conditions.
Explain ehen it’s useful to have variation on the offspring.
Variation in offspring is important for survival and adaption, it creates genetic diversity, helping species adjust to changing environments , resist diseases, and avoid extinction with variation, some individuals may develop traits that improve survival and reproduction, driving evolution and making populations more resilient.
continuous variation
gradual transition between two extremes, this features are determined by a number of different genes and are affected by the environment
discontinuous variation
little or no environmental impact on the features this features are determined by a single gene or chromosomes
What do genes control?
The development of characteristics however they may be changed by the environment
What is the blood and what does it act as?
Blood is a tissue. It acts as a transport system.
What are the four main components of the blood?
Red blood cell - carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells in the body
White blood cell - engulf pathogens, produce antibodies + antitoxins
Platelets - help blood to clot at wound
Plasma - liquid that carries everything in the blood
What name is given to the shape of red blood cells?
a biconcave shape
How does the red blood cell adapt to its function?
Due to its biconcave shape, it creates a large surface area and allows for absorbing oxygen
It DOESN’T have a nucleus - this allows more room to carry oxygen
They contain red pigment called haemoglobin
In the lungs, haemoglobin binds to oxygen to become oxygenhaemoglobin → reverse happens in body cells = splits up = to release oxygen to cells

What are the properties of white blood cells?
Some change shape and engulf pathogen. This is called phagocytosis
They produce antibodies to fight microorganisms
They also produce antitoxins and these neutralize/counteract any toxins produced by pathogens
Unlike red blood cells they DO have a nucleus
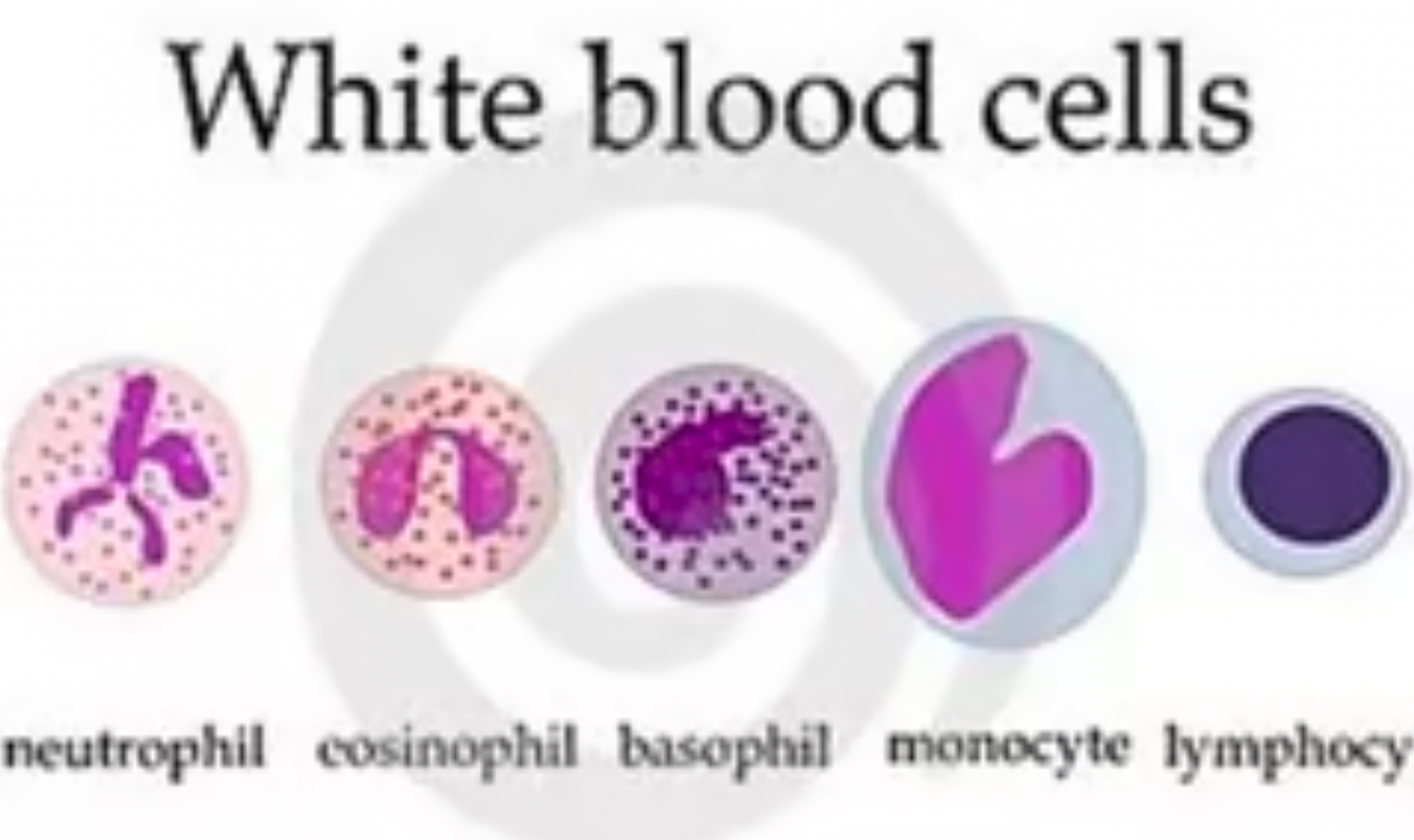
What platelets role?
help blood clots
What are the properties of platelets?
Small fragments of cells. They DON’T have a nucleus
They help blood clot at a wound to stop blood pouring out + stop pathogens getting in
Lack of platelets can cause excessive bleeding and bruising
Describe plasma
Pale, straw-coloured liquid
What do plasma’s cells carry?
RBCs, WBCs, platelets, nutrients in amino acids + glucose, CO2, wea, hormones, proteins, antibodies & antitoxins
How does the immune system response to disease using white blood cells?
by releasing chemicals that break the organisms down and destroy it
What is the function of lymphocytes (white blood cell)?
produce antibodies to destroy microorganisms
What is the function of phagocytes (white blood cell)?
digest and destroy bacteria and other microorganisms that have infected our bodies
How does muscle tissue allow the heart to do its job?
by keeping the heart pumping and blood circulating around the body
What happens when blood stops flowing in one or more of these arteries?
When blood stops flowing, it can cause a heart attack
Explain the thickness of muscle tissue of the muscle is not the same in all parts of the heart.
it depends on the amount of myocardium present
myocardium
the muscular tissue of the heart
What do heart valves do?
prevent backflow of blood
How do heart valves work?
The heart muscles contracts and relaxes, causing values to open and close, allowing blood to flow into the ventricles and atria at different times
What structures hold the flaps of the heart valves in position?
chordae tendineae
chordae tendineae
strong, fibrous connections between the valve leaflets and papillary muscles
What forms the circulatory system?
The heart, blood vessels and the blood
What are the different types of blood vessels?
Artery: carries blood away from the heart
Vein: carry blood towards the heart
Capillaries: carry blood to all cells in the body
What are the properties of each blood vessels?
Arteries: thick muscular wall, small lumen and elastic fibres
Vein: elastic fibres, very large lumen and this muscular wall (veins have an extra structure called valves)
Capillaries: wall is one cell thick, very small lumen, has a nucleus, they are small and narrow
What is the direction of the blood flow?
Arteries → Capillaries → Veins
What do capillaries form?
a large network of small blood vessels linking the arteries and veins
What do arteries blood contain?
contains useful substances (oxygen and glucose)
What do veins blood contain?
contains waste (carbon dixode) that is carried away and removed
rate
How an amount changes over time
What is the formula for the rate of blood flow?
Rate of blood flow = Volume of blood / Time taken
What are the units for the rate of blood flow’s formula?
Rate: ml/sec
Volume of blood: cm3, ml, l, etc.
Time taken: sec, mins, hours, etc.
Per second: s-1
haemoglobin
an iron-contaning protein
What is the function of haemoglobin?
associates (combines) with oxygen to form oxyhaeoglobin when there is a high concentration of oxygen in the surroundings
What are the steps of phagocytosis?
1) detects bacterium
2) changes shape forming pseudopodia surroundings bacterium
3) encloses bacterium inside the vacuole
4) secretes digestive enzymes to break down bacterium
what’s the word equation of photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
what’s the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
what are the steps for a leaf for starch?
1) Gather materials: leaf, iodine solution, a test tube, a Bunsen burner
2) Prepare leaf: Boil leaf in water for a few minutes to denature the chlorophyll which gives a blue-black color of starch is present
turgid
when cell swells up and the cytoplasm pushes agaisnt the cell wall in pure water
flaccid
when the cell contents lose water by osmosis and the cells shrink in a concentrated solution
plasmolysis
when the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall completely in a highly concentrated solution
cuticle
a wavy layer that helps to prevent water loss
epidermis
the outermost layer of cells (both on upper + lower surfaces of the leaf)
mesophyll
the middle where photosynthesis takes place
divided into 2 types:
palisade: cells packed tightly together (contains lots of chloroplasts)
spongy: loosely arranged cells with air spaces between them, allowing for gas exchange
vascular bundles
transports water, minerals and sugar throughout the leaf
2 types of bundles
xylem: transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves
phloem: transports sugars produced by photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plants