Nitroxigenic Transmission
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and information about Nitric Oxide as a neurotransmitter, including its properties, signalling mechanisms, and implications in disease.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the main properties of Nitric Oxide as a neurotransmitter?
Free radical ~ highly reactive
Membrane permeant so doesnt need receptors to diffuse into target
Perfectly suited for short range transmission
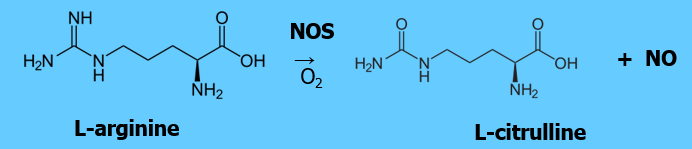
How is NOS synthesised?
L-arginine is oxidised to citrulline + NO
What criteria define a substance as a neurotransmitter?
Synthesis on demand
Storage in synaptic vesicles
Release by exocytosis
Actions at post-synaptic receptors
Inactivation/uptake
Which enzyme synthesizes Nitric Oxide?
Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS).
What is the role of soluble guanylyl cyclase in NO signalling?
sGC acts as a receptor for NO → cGMP levels increase → protein kinase cascade → depolarisation (lowering of intracellular Ca2+) → neuronal signal
How is NO involved in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle?
As a vasodilator, NO promotes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle through cGMP signaling.
What role does Calcium (Ca2+) play in the synthesis of NO?
Ca2+ is required for the activity of neuronal NOS (actions due to an influx of ions) but not for inducible NOS (iNOS).
How does NO signalling in the PNS lead to smooth muscle relaxation?
Synthesis of NO is triggered by an influx of Ca2+ ions
cGMP levels increase
There is co-transmission of ACh, NO and VIP (released simultaneously)
All pathways act together to promote smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation in salivary glands
What are the implications of NO in the central nervous system (CNS)?
NO regulates excitability, firing, long-term potentiation and depression, and plays a role in learning and memory.
Excess NO may be neurotoxic
High densities in the cerebellum and accessory olfactory bulb
What are NANC neurones?
Non-adrenergic, Non-cholinergic
What neurotransmitters/peptides do co-transmission with NO?
VIP - eye, salivary glands, cerebral arteries
ACh - salivary glands
ATP - rabbit portal vein
Glutamate, GABA - cerebellum
How does Nitric Oxide exert its effects on overactivity?
It increases neurotransmitter outflow and plays a role in their basal release
How does NO contribute to neurotoxicity in stroke?
In a stroke, oxygen uptake increases, as overall oxygen level is lower.
NO + O2- → ONOO- (peroxynitrite - causes oxidative injury)
ROS production triggers the release of glutamate → neuronal Ca2+ overload → prolonged NO synthesis → neurotoxicity
What is the role of NO in Parkinson’s Disease?
Excess NO contributes to degeneration of dopaminergic neurones in the substantia nigra
Activated microglia → ↑ iNOS → ↑ NO