Ophthalmic Medical Assisting Exam
1/239
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Questions from practice COA exam from American Academy of Ophthalmology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
What does the abbreviation IJCAHPO stand for?
A) Internal Joined Command of Alternate Healthcare Personnel in Ophthalmology
B) International Joined Committee of All Healthcare Personnel in Ophthalmology
C) International Joint Commission on Allied Health Personnel in Ophthalmology
D) Internal Joint Committee of All Health Personnel in Ophthalmology
C) International Joint Commission on Allied Health Personnel in Ophthalmology
What responsibility routinely falls to the ophthalmic medical assistant?
A) Diagnosing certain conditions
B) Making prognostic estimates
C) Performing certain diagnostic tests
D) Prescribing treatment for certain problems C) Performing certain diagnostic tests
C) Performing certain diagnostic tests
What disease is associated with increased pressure inside the eye?
A) Retinal detachment
B) Cataract
C) Glaucoma
D) Macular Degeneration
C) Glaucoma
What eye care professional routinely fills prescriptions for eyeglasses?
A) Ocularist
B) Optician
C) Ophthalmic Medical Technician
D) Orthoptist
B) Optician
What does an orthoptist do?
A) Fits prostheses
B) Evaluates strabismus
C) Dispenses contact lenses
D) Grinds eyeglass lenses
B) Evaluates strabismus
What instrument does an ophthalmologist use to examine the retina and optic nerve?
A) Ophthalmoscope
B) Phoropter
C) Retinoscope
D) Lensometer
A) Ophthalmoscope
What eye care professional would fit a patient with a prosthetic eye?
A) Ocularist
B) Optician
C) Orthoptist
D) Optometrist
A) Ocularist
What is the first IJCAHPO level of certification?
A) Certified Ophthalmic Medical Technologist
B) Certified Ophthalmic Registered Nurse
C) Certified Ophthalmic Technician
D) Certified Ophthalmic Assistant
D) Certified Ophthalmic Assistant
What is the primary function of the medial rectus muscle?
A) Rotates the eye inward toward the nose
B) Rotates the eye outward toward the temple
C) Rotates the eye downward and inward toward the nose
D) Rotates the eye downward and outward toward the temple
A) Rotates the eye inward toward the nose
In what order is visual information from the retina transmitted to the visual cortex?
A) Bipolar cells to ganglion cells to lateral geniculate body
B) Ganglion cells to bipolar cells to lateral geniculate body
C) Lateral geniculate body to bipolar cells to ganglion cells
D) Bipolar cells to lateral geniculate body to ganglion cells
A) Bipolar cells to ganglion cells to lateral geniculate body
Which part of the eye provides two-thirds of the eye's focusing power?
A) Retina
B) Conjunctiva
C) Sclera
D) Cornea
D) Cornea
The contraction of what muscle(s) affects globe rotation (incyclotorsion and excyclotorsion)?
A) Superior oblique
B) Superior oblique, inferior oblique
C) Superior oblique, inferior oblique, superior rectus
D) Superior oblique, inferior oblique, superior rectus, inferior rectus
D) Superior oblique, inferior oblique, superior rectus, inferior rectus
What membrane lines the inner eyelid?
A) Bulbar conjunctiva
B) Epithelium
C) Palpebral conjunctiva
D) Tarsus
C) Palpebral conjunctiva
What structure separates an internal hordeolum (chalazion) from an external hordeolum (stye)?
A) Descemet membrane
B) Orbicularis muscle
C) Levator muscle
D) Tarsal plate
D) Tarsal plate
The contraction of what muscle(s) results in enlargement of the pupil?
A) Sphincter
B) Dilator
C) Sphincter, medial rectus
D) Sphincter, medial rectus, lateral rectus
B) Dilator
What structure is responsible for secreting the aqueous humor?
A) Ciliary body
B) Iris processes
C) Zonules
D) Choroid
A) Ciliary body
What is the process where the lens changes shape to allow an individual to focus on a near target?
A) Accommodation
B) Presbyopia
C) Glaucoma
D) Cataract
A) Accommodation
What kind of vision loss is associated with injury or degeneration of the macula?
A) Night- or dim-light vision
B) Peripheral vision
C) Distance vision
D) Detailed central vision
D) Detailed central vision
The crystalline lens regularly comes into contact with what fluids and tissues?
A) Iris, zonules, aqueous humor, vitreous
B) Iris ciliary body, aqueous humor, zonules
C) Zonules, aqueous humor, iris, cornea
D) Zonules, cornea, aqueous humor, vitreous
A) Iris, zonules, aqueous humor, vitreous
What cells and glands of the eye and adnexa contribute to tear production?
A) Goblet cells, meibomian glands, lacrimal gland
B) Meibomian glands, ciliary body, goblet cells
C) Lacrimal gland, meibomian glands, ciliary body
D) Ganglion cells, lacrimal gland, ciliary body
A) Goblet cells, meibomian glands, lacrimal gland
What is the primary function of the iris sphincter and dilator muscles?
A) To change the pupil size to control the amount of light entering the eye
B) To raise and lower the eyelid
C) To determine the direction and movement of the eyeball
D) To change the curvature of the lens
A) To change the pupil size to control the amount of light entering the eye
What is amblyopia?
A) Continual movement of the eyes from side to side and up and down
B) Poor vision in an eye secondary to visual deprivation in the first decade of life
C) Abnormal drooping of an upper eyelid
D) 3-dimensional visual perception
B) Poor vision in an eye secondary to visual deprivation in the first decade of life
What is diplopia?
A) Swelling from large amounts of fluids
B) Paralysis
C) Double vision
D) Deviation of 1 or both eyes
C) Double vision
What is the defining feature of wet-age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in comparison to dry AMD?
A) The presence of yellow retinal deposits known as drusen
B) The presence of aberrant blood vessels leaking fluid in the central retina
C) Progressive atrophy of the affected retinal layers
D) Progressive loss of central and peripheral vision
B) The presence of aberrant blood vessels leaking fluid in the central retina
In what condition do the orbital contents swell, pushing the eyeball forward?
A) Blepharitis
B) Exophthalmos (proptosis)
C) Ectropion
D) Exotropia
B) Exophthalmos (proptosis)
What differentiates pterygia from pingueculae?
A) Pterygia are caused by chronic sun exposure
B) Pterygia extend onto the surface of the cornea
C) Pterygia can become inflamed and red when irritated
D) Ptyergia can be located nasally or temporally
B) Pterygia extend onto the surface of the cornea
Primary open-angle glaucoma results in damage to what part of the eye?
A) Lens
B) Optic nerve
C) Iris
D) Nasolacrimal sac
B) Optic nerve
What is the term for the inward deviation of the eye that occurs only when 1 eye is covered?
A) Esophoria
B) Esotropia
C) Exophoria
D) Exotropia
B) Esotropia
An embolic retinal artery occlusion due to atherosclerosis is best classified as what type of process?
A) Degenerative
B) Metabolic
C) Ischemic
D) Neoplastic
C) Ischemic
What is the term for an abnormal physical change that a physician observes while examining a patient?
A) Etiology
B) Symptom
C) Sign
D) Syndrome
C) Sign
What is the cause of presbyopia?
A) Flattening of the central cornea due to age
B) Overuse of reading glasses or "cheaters"
C) Progressive weakening of the ciliary muscles
D) Progressive hardening of the crystalline lens
D) Progressive hardening of the crystalline lens
What is a chalazion?
A) An inward turning of the eyelashes
B) A drooping upper eyelid
C) An inflammation of the lacrimal sac
D) A lump that develops after inflammation and infection
D) A lump that develops after inflammation and infection
What term best describes pooling of what blood cells at the bottom of the anterior chamber in the setting of an infectious or inflammatory process?
A) Hyphema
B) Hypopyon
C) Keratitis
D) Scleritis
B) Hypopyon
What sign of symptom most strongly suggests the presence of a retinal detachment rather than a posterior vitreous detachment?
A) Multiple large, new floaters
B) Flashing lights
C) A new, unilateral peripheral defect on confrontational visual fields
D) Elevated intraocular pressure
C) A new, unilateral peripheral defect on confrontational visual fields
What term describes bilateral, elevated optic nerves due to increased intracranial pressure?
A) Acute angle-closure glaucoma
B) Primary open-angle glaucoma
C) Optic neuritis
D) Papilledema
D) Papilledema
What retinal infection typically occurs in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) who have CD4 counts less than 50?
A) Cytomegalovirus retinitis
B) Histoplasma capsulatum retinitis
C) Acute retinal necrosis
D) Autoimmune retinitis
A) Cytomegalovirus retinitis
What are the common ocular manifestations of myasthenia gravis?
A) Ptosis, diplopia
B) Proptosis, diplopia
C) Pain, vasculitis
D) Pain, proptosis
A) Ptosis, diplopia
What type of herpes simplex virus usually produces genital infections?
A) Type 1
B) Type 2
C) Type 3
D) Type 4
B) Type 2
What is the common ocular manifestation of Sjogren syndrome?
A) Keratoconus
B) Keratomalacia
C) Interstitial keratitis
D) Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
D) Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
What is a cancer that spreads to other parts of the body called?
A) Radiologic
B) Localized
C) Metastatic
D) Systemic
C) Metastatic
The eyes are considered part of what body system?
A) Endocrine
B) Nervous
C) Respiratory
D) Cardiovascular
B) Nervous
What autoimmune condition causes selective muscle weakness by interfering with proper nerve transmission in skeletal muscles?
A) Rheumatoid arthritis
B) Sarcoidosis
C) Myasthenia gravis
D) Sjogren syndrome
C) Myasthenia gravis
What is a waste product of metabolism in the body?
A) Carbon dioxide
B) Oxygen
C) Hemoglobin
D) Hormones
A) Carbon dioxide
What is a common eye disorder associated with multiple sclerosis?
A) Papilledema
B) Infectious retinitis
C) Optic neuritis
D) Anterior uveitis
C) Optic neuritis
What is the most common cause of proptosis in an adult?
A) A tumor behind the eye
B) Thyroid eye disease
C) Severe nearsightedness (high myopia)
D) An orbital abscess
B) Thyroid eye disease
What is the characteristic feature of proliferative diabetic retinopathy?
A) Leakage of fluid from vessels
B) Proliferation of blood vessels
C) Oozing of exudates
D) Retinal hemorrhage
B) Proliferation of blood vessels
What is the correct transposition of the plus-cylinder prescription +1.00+3.00x90 to its minus-cylinder form?
A) +4.00-3.00x90
B) +2.00-3.00x180
C)+4.00-3.00x180
D) +3.00-1.00x90
C) +4.00-3.00x180
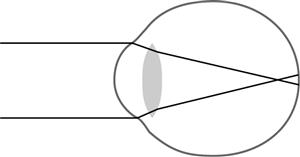
This figure shows the focal point of light rays in an eye that is which of the following?
A) Myopic
B) Presbyopic
C) Emmetropic
D) Hyperopic
A) Myopic
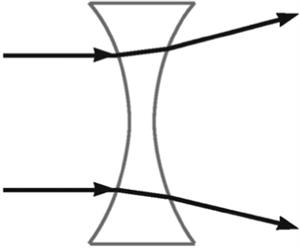
This figure illustrates what property?
A) Light-divergent property of a convex lens
B) Light-divergent property of a concave lens
C) Light-convergent property of a convex lens
D) Light-convergent property of a concave lens
B) Light-divergent property of a concave lens
What is the change in power called between the upper and lower segments of a bifocal lens?
A) Circle of least confusion
B) Refractive index
C) Principal meridian
D) Add
D) Add
What is the best technique for determining the total refractive power requirement of the eye?
A) Perform retinoscopy after administering cycloplegic eye drops, which block accommodation
B) Find the lens power that causes motion of the retinal reflex
C) Measure the prescription of the patient's existing eyeglasses
D) Balance the correction of both the patient's eyes
A) Perform retinoscopy after administering cycloplegic eye drops, which block accommodation
What is a toric cornea characteristic of?
A) Hyperopia
B) Myopia
C) Presbyopia
D) Astigmatism
D) Astigmatism
What does a lens contain if the lensometer mires cannot be centered?
A) Sphere
B) Cylinder
C) Spherocylinder
D) Prism
D) Prism
The distance portion of an eyeglass lens is -2.00 D and the bifocal add is +3.00. What is the power of the lens through the bifocal segment?
A) +1.00 D
B) +5.00 D
C) +3.00 D
D) -1.00 D
A) +1.00 D
What type of substance permits the passage of light without significant disruption?
A) Opaque
B) Transparent
C) Translucent
D) Electromagnetic
B) Transparent
What type of lens best corrects hyperopia combined with astigmatism?
A) Cylindrical
B) Spherical
C) Spherocylindrical
D) Multifocal
C) Spherocylindrical
What is the first step in performing manual lensometry or keratometry?
A) Focus the eyepiece
B) Lubricate the instrument
C) Position the eyeglasses
D) Position the patient
A) Focus the eyepiece
What is the power in diopters of a convex lens with a focal length of 0.50m?
A) 0.20 D
B) 0.50 D
C) 2.00 D
D) 5.00 D
C) 2.00 D
What antimicrobial drug is often compounded to increase potency?
A) Trimethoprom-polymyxin B
B) Acyclovir
C) Moxifloxacin
D) Vancomycin
D) Vancomycin
What disease should be brought to the ophthalmologist's attention in a patient using oral corticosteroids?
A) Hypothyroidism
B) Spinal stenosis
C) Diabetes mellitus
D) Celiac disease
A) Hypothyroidism
The use of β-adrenergic blockers should be avoided in patients with what medical condition?
A) Epilepsy
B) Asthma
C) Rheumatoid arthritis
D) Diabetes mellitus
B) Asthma
What is the primary function of topical corticosteroids?
A) To keep the external eye moist and maintain the tear film balance (lubricants)
B) To inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, or fungi (antimicrobials)
C) To flush out the eye during surgical procedures (irrigating solutions)
D) To reduce swelling and scarring of the lids and anterior segment (anti-inflammatory and allergic agents)
D) To reduce swelling and scarring of the lids and anterior segment (anti-inflammatory and allergic agents)
What drug is most helpful when performing both a fundus examination and an objective refraction on a pediatric patient?
A) An anesthetic
B) A miotic
C) A mydriatic
D) A cycloplegic
D) A cycloplegic
What type of injection is classified as a form of systemic drug delivery?
A) Intravitreal
B) Subconjunctival
C) Subcutaneous
D) Retrobulbar
C) Subcutaneous
What drug administration route provides the fastest drug delivery into the eye?
A) Subcutaneous injection
B) Intracameral injection
C) Intramuscular injection
D) Intravenous injection
D) Intravenous injection
How do miotics reduce intraocular pressure?
A) By decreasing the production of aqueous humor
B) By contracting the ciliary body muscle and opening the outflow channels for aqueous humor
C) By paralyzing the ciliary body muscle and closing the anterior chamber angle
D) By dilating the pupil and opening the anterior chamber angle
B) By contracting the ciliary body muscle and opening the outflow channels for aqueous humor
What is a common side effect of cycloplegics?
A) Eye redness
B) Blurred vision
C) High blood pressure
D) Corneal edema
B) Blurred vision
What 2 types of eyedrops could stimulate an attack of angle-closure glaucoma in patients with narrow anterior chamber angles?
A) Mydriatics, cycloplegics
B) Mydriatics, antihistamines
C) Anesthetics, dyes
D) Antiallergic agents, anti-inflammatory agents
A) Mydriatics, cycloplegics
What ophthalmic dye is used primarily to diagnose herpes simplex keratitis?
A) Indocyanine
B) Fluorescein
C) Rose bengal
D) Lissamine green
B) Fluorescein
What should the ophthalmic medical assistant do when instilling eyedrops?
A) Administer the medication directly onto the cornea
B) Make certain the dropper makes contact with the conjunctival sac
C) Administer the medication directly into the conjunctival sac
D) Apply indirect pressure to the eyelids
C) Administer the medication directly into the conjunctival sac
What is an adverse effect of topical prostaglandins?
A) Eyelid elevation
B) Blurry vision
C) Eyelash growth
D) Reduced heart rate
C) Eyelash growth
What class of mediations when taken by mouth, can cause tingling in the hands or feet, a metallic taste, and kidney stones?
A) a2-selective agonists
B) ß-adrenergic blockers
C) Corticosteroids
D) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
D) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
What is the primary purpose of standard precautions?
A) To prevent violence in the workplace
B) To reduce the opportunity for harmful microbes to flourish
C) To protect the sterility of a sterilized article
D) To prevent chemical spills from ruining equipment
B) To reduce the opportunity for harmful microbes to flourish
What organism is a common contaminant in cosmetics, swimming pools, and hot tubs?
A) Staphylococcus aureus
B) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D) Mycobacterium
C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What is the best definition of sterilization?
A) The transmission of infectious microbes from reservoir to host
B) The range of procedures used to prevent the spread of infectious microbes in the office
C) The process of inactivating or eliminating most disease-causing microorganisms
D) The destruction of all microorganisms
D) The destruction of all microorganisms.
If the ophthalmic medical assistant accidentally touches the sterile functional surface of a disposable instrument, what should be done with the instrument?
A) Resterilize in the office
B) Wipe with alcohol
C) Wipe with a sterile cloth
D) Discard, no matter its cost
D) Discard, no matter its cost
How should ophthalmic medical assistants deal with open cuts on their hands?
A) Wear gloves to protect patients
B) Wear gloves to protect themselves
C) Wear gloves to protect both patients and themselves
D) Wash their hands before and after working with patients without using gloves
C) Wear gloves to protect both patients and themselves.
Who is most at risk for developing an ocular infection from the protozoan Acanthamoeba?
A) Those who eat undercooked or raw meat
B) Those who use homemade salt solutions to clean their contact lenses
C) Those who had chickenpox during childhood
D) Those who use contaminated cosmetics
B) Those who use homemade salt solutions to clean their contact lenses.
What microbe is most likely to cause recurrent fever blisters?
A) Adenovirus
B) Cytomegalovirus
C) Epstein-Barr virus
D) Herpes simplex virus
D) Herpes simplex virus
In an infection caused by MRSA, what is Staphylococcus aureus resistant to?
A) Heavy metals
B) Methicillin
C) Mercury
D) Metabolites
B) Methicillin
What is the best option for disinfecting a tonometer tip?
A) Boiling water
B) Moist heat
C) A germicide
D) Soap and water
C) A germicide
What bacterium is the most likely cause of blepharitis?
A) Staphylococcus aureus
B) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D) Mycobacterium
A) Staphylococcus aureus
Which procedure must be performed before pupillary dilation?
A) Cycloplegic refraction
B) Biomicroscopy
C) Ophthalmoscopy
D) Swinging-light test
D) Swinging-light test
What is the prism and alternate cover test used for?
A) To evaluate depth perception
B) To evaluate peripheral vision
C) To measure deviation in a misaligned eye
D) To measure near visual acuity
C) To measure deviation in a misaligned eye
What step is a necessary part of the Schirmer test?
A) Instill anesthetic drops before testing begins
B) Instruct the patient to close both eyes
C) Illuminate a near target for fixation
D) Remove the testing strip after 5 minutes
D) Remove the testing strip after 5 minutes
Corneal topography is useful for what measurement?
A) Index of refraction
B) Central corneal thickness
C) Refractive error
D) Lens power
C) Refractive error
How does the pinhole occluder determine whether a refractive error is the cause of below-normal visual acuity?
A) Disruption of total internal reflectivity
B) Creation of a virtual image
C) Projection of optotypes
D) Transmission of parallel rays
D) Transmission of parallel rays
In a normal consensual reaction, when a light is directed into the pupil of 1 eye, what will the pupil of the other eye do?
A) Constrict
B) Dilate
C) Remain unchanged
D) Pulsate
A) Constrict
How often should healthy, asymptomatic individuals between the ages of 40 and 64 have a comprehensive medical eye examination?
A) Every 6 months
B) Every year
C) Every 2 to 4 years
D) Every 5 years
C) Every 2 to 4 years
What part of the comprehensive medical eye examination evaluates visual system operation?
A) External examination
B) Pupillary examination
C) Biomicroscopy
D) Ophthalmoscopy
B) Pupillary examination
A reading of 3 on the Goldmann tonometer dial indicates what intraocular pressure?
A) 0.3 mm Hg
B) 3 mm Hg
C) 15 mm Hg
D) 30 mm Hg
D) 30 mm Hg
When conducting the Amsler grid test, it is important to instruct the patient to perform what step?
A) Keep both eyes open
B) Look at all 4 corners
C) Hold the card 12 to 14 inches away
D) Remove readers
C) Hold the card 12 to 14 inches away
An afferent pupillary defect may be detected in patients with what condition?
A) Anterior chamber pathology
B) Media opacities
C) Optic nerve damage
D) Amblyopia
C) Optic nerve damage
Intraocular pressure is measured by flattening a small area of the central cornea using what procedure?
A) Keratometry
B) Applanation tonometry
C) Indentation tonometry
D) Schiøtz tonometry
B) Applanation tonometry
Near visual acuity measurements can be recorded in units from what system?
A) Jaeger
B) Snellen
C) Farnsworth-Munsell
D) Hruby
A) Jaeger
What is gonioscopy used to view?
A) External structures of the eye
B) Structures of the anterior chamber angle
C) Vitreous
D) Optic nerve head
B) Structures of the anterior chamber angle
What does the number 100 represent when reading the Snellen activity recording 20/100?
A) Size of the largest optotype seen by the patient
B) Distance in feet from the patient to the chart
C) Distance in meters from the patient to the chart
D) Distance in feet at which a normal eye can see a particular line on the chart
D) Distance in feet at which a normal eye can see a particular line on the chart
What instrument can be used to evaluate a patient's risk of developing glaucoma?
A) Pachymeter
B) Ophthalmoscope
C) Gonioscope
D) Exophthalmometer
A) Pachymeter
What is the term for horizontal latent strabismus with the eye deviating outward?
A) Exophoria
B) Exotropia
C) Esophoria
D) Esotropia
A) Exophoria
What term refers to observing the movements of both eyes together?
A) Versions
B) Ductions
C) Binocular
D) Comitance
A) Versions