Dental Anatomy Exam 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Anatomic position
standing erect, arms at the sides, face and palms are forward
saggital plane
a vertical plane that divides the body into right and left portions.
Median Plane (or midsagittal)
An invisible vertical line that divides the body into equal left and right portions
Frontal Plane
A vertical line that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections.
Transverse Plane
A horizontal line that divides the upper portion and the lower portions of the body.
Anterior/ventral
Front of the body
Posterior/dorsal
Back of the body
upper right quadrant
teeth #1-8
upper left quadrant
teeth #9-16
lower left quadrant
teeth #17-24
lower right quadrant
teeth #25-32
sextants
6 areas
oral cavity anterior
lips (labia)
oral cavity posterior
pharynx
oral cavity lateral
buccal (cheeks)
oral cavity inferior
floor of the mouth
oral cavity superior
palate
space between the lips or cheeks and teeth
vestibule
areas surrounded by teeth or alveolar ridges, back to the palatine tonsils
oral cavity proper
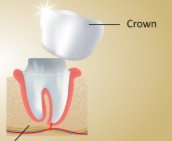
crown
portion of the tooth above the gum line covered by enamel
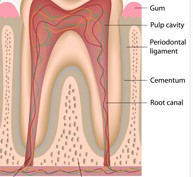
root
portion of tooth below the gum line covered by cementum
sublingual ducts
bartholin’s duct
submandibular gland
Whartons duct
parotid gland
stensons duct — parotid papilla
four types of papillae of the tongue
circumvallate, foliate, filiform, and fungiform
circumvallate papillae
large papillae with taste buds—divides anterior portion of the tongue from the posterior
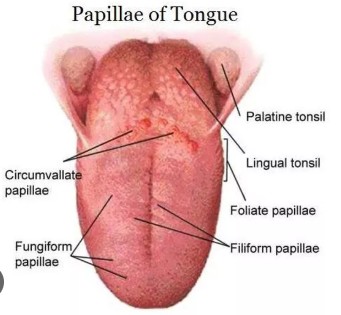
filiform papillae
no taste buds, covers 2/3 of dorsal side of the tongue
foliate papillae
on the side walls of the tongue; contains taste buds; fold near the posterior border
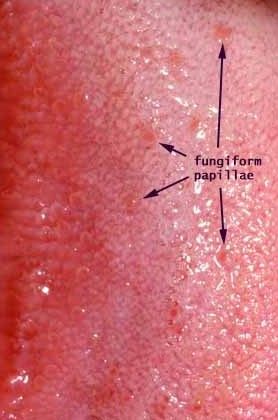
fungiform papillae
mushroom-like dots that contain taste buds and are located on the tip and sides of the tongue
alveolar process
bones that hold the root in the jaw
alveolus
tooth socket
The primary dentition consists of __ teeth
20
permanent dentition
32 adult teeth
enamel % of inorganic and organic material
96% inorganic and 4% organic
Dentin % of inorganic and organic material
70% inorganic, 30% organic
Cementum % of inorganic and organic material
50% inorganic, 50% organic
types of cementum
acellular and cellular
acellular cementum
covers most of the anatomic root
cellular cementum
confined to the apical third of the root
clinical crown
the portion of the tooth that is visible
anatomical crown
occlusal or incisal to the CEJ; covered with enamel
anatomical crown
remains the same
clinical crown
can change
odontoblasts
Cells that form dentin and live in the pulp
odontoblastic process
extended through the dentin
pharynx
where the oral cavity ends and the respiratory and digestive pathway begins
sublingual caruncle
duct opening for the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
major salivary glands
parotid, submandibular, and sublingual
ranula (mucocele)
clogged sublingual duct
enamel
hardest tissue in the body
dentin
second hardest tissue
cementum
hard as bone
pulp
soft tissue within a tooth, containing nerves and blood vessels
cementum function
provides a medium for attachment of the tooth to the alveolar bone
Cementum is formed by ___
cementoblasts
apical vs coronal
apical refers to the direction or area towards the root tip, and coronal refers to the direction or area towards the crown of the tooth