Anatomy and Physiology II- Exam 4
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
261 Terms
Gastroenterology
study of the stomach and intestines
Gastrointestinal tract (GI tract)
a long tube, about 25 feet in length; open at both ends for the transit of food during processing; includes the:
1. mouth
2. pharynx
3. esophagus
4. stomach
5. small intestine
6. large intestine
7. rectum
8. anal canal
Accessory structures
structures that contribute to the food processing; include:
1. teeth and tongue
2. salivary glands
3. liver
4. gallbladder
5. pancreas
Mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces; mixing waves
Chemical digestion
breaking down food with enzymes; catabolic process; primarily accomplished with pepsin
Steps of digestion
1. ingestion
2. secretion
3. mixing and propulsion
4. digestion
5. absorption
6. defecation
Ingestion
taking food into the mouth (eating)
Secretion
the release of water, acid, buffers, and enzymes into the lumen of the GI tract; accomplished by both the GI tract cells and accessory organs
Mixing and propulsion
alternating contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles within the walls of the GI tract
Digestion
consists of mechanical and chemical digestion
Absorption
the passage of these digested molecules from the lumen of the GI tract, across the wall of the tract, and into the underlying blood or lymph for distribution to cells throughout the body
Defecation
the emptying of the rectum to eliminate indigestible substances from the GI tract; elimination of feces from the digestive tract through the anus
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa
four tissue layers that make up the GI tract
Mucosa
inner layer of GI tract tissue; consists of the epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa
Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa
three layers of the mucosa
Epithelium
inner layer of the mucosa; that lines from the mouth to the esophagus; non-keratinized stratified squamous cells; simple columnar epithelium lines the stomach and intestines are needed for secretion and absorption; also includes goblet cells and enteroendocrine cells
Mouth, esophagus
from the _______ through the _______ is lined with non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelial cells
Stomach, intestines
the ______ and _______ are lined with simple columnar epithelium that aid in secretion and absorption
Goblet cells
mucus secreting cells
Enteroendocrine cells
hormone secreting cells that help regulate digestion; located in the mucosa;
1. CCK cells
2. S cells
3. K cells
Lamina propria
second layer of the mucosa; contain blood and lymph vessels, nerves, connective tissue, and MALT cells; aid in immunity
Mucosa-associated lymph tissue
MALT cells; aids in immunity
Muscularis mucosa
outer layer of the mucosa; allows for local, independent movement; contraction aids in secretion; includes rugae and plicae
Rugae
temporary folds in the stomach lining
Plicae
permanent folds that remain regardless of distension; in the small intestines
Submucosa
second layer of the GI tract; loose connective tissue with lots of blood and lymph vessels; contains the submucosal plexus which controls GI secretions
Submucosal plexus
"brains of the gut" part of the enteric nervous system; controls secretion of the GI tract
Muscularis
the third layer of the GI tract; involved in voluntary swallowing and involuntary peristalsis and segmentation
Skeletal muscles
muscles that lines the mouth, pharynx, and superior part of the esophagus which control voluntary swallowing and also forms the external anal sphincter
Smooth muscles
muscles that lines the GI tract from the middle of the esophagus to the anus; includes circular and longitudinal fibers; creates peristalsis and segmentation
Peristalsis
coordinated muscular contractions that move food boluses through the GI tract; occur behind the bolus to push it forward; governed by hormones and neurons
Segmentation
alternating contractions and relaxations of the circular layer of the muscularis; mixes food with digestive enzymes that have been secreted and increases contact between bolus and mucosa
Myenteric plexus
located between the inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle layers; controls that strength frequency of the muscular contractions
Serosa
outermost layer of the GI tract; also the visceral peritoneum; secretes slippery, watery (serous) fluid
Peritoneum
the serous membrane in the abdominal cavity; largest serous membrane in the body
Parietal peritoneum
portion of the peritoneum that lines the wall of the abdominal cavity
Visceral peritoneum
portion of the peritoneum that covers the organs and constitutes their serosa
Peritoneal cavity
the space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum; contains a small amount of serous fluid
Greater omentum
tissue that extends from the greater curvature of the stomach and drapes down over the anterior small intestines and then doubles back to attach to the transverse colon
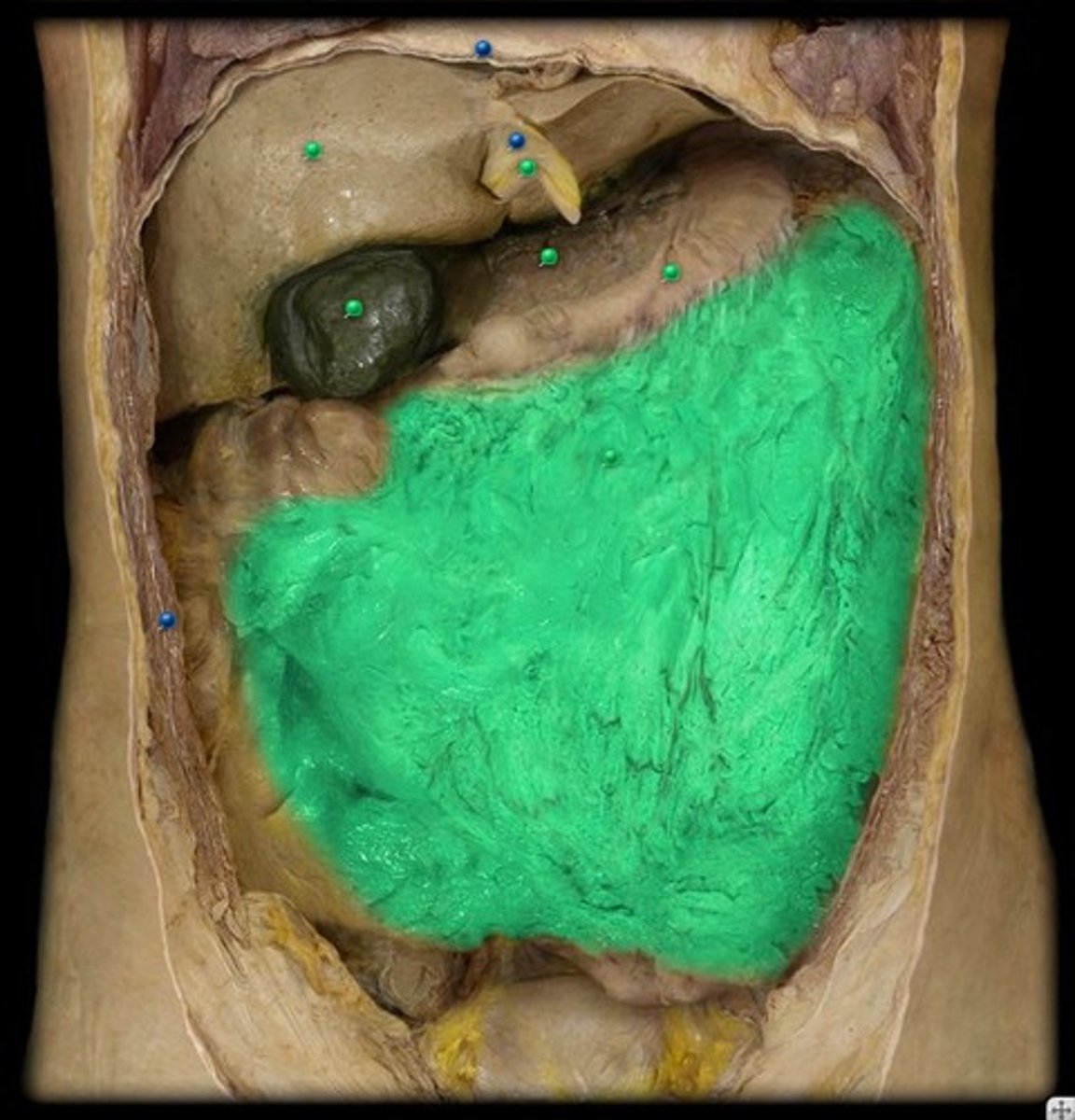
Lesser omentum
tissue that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach
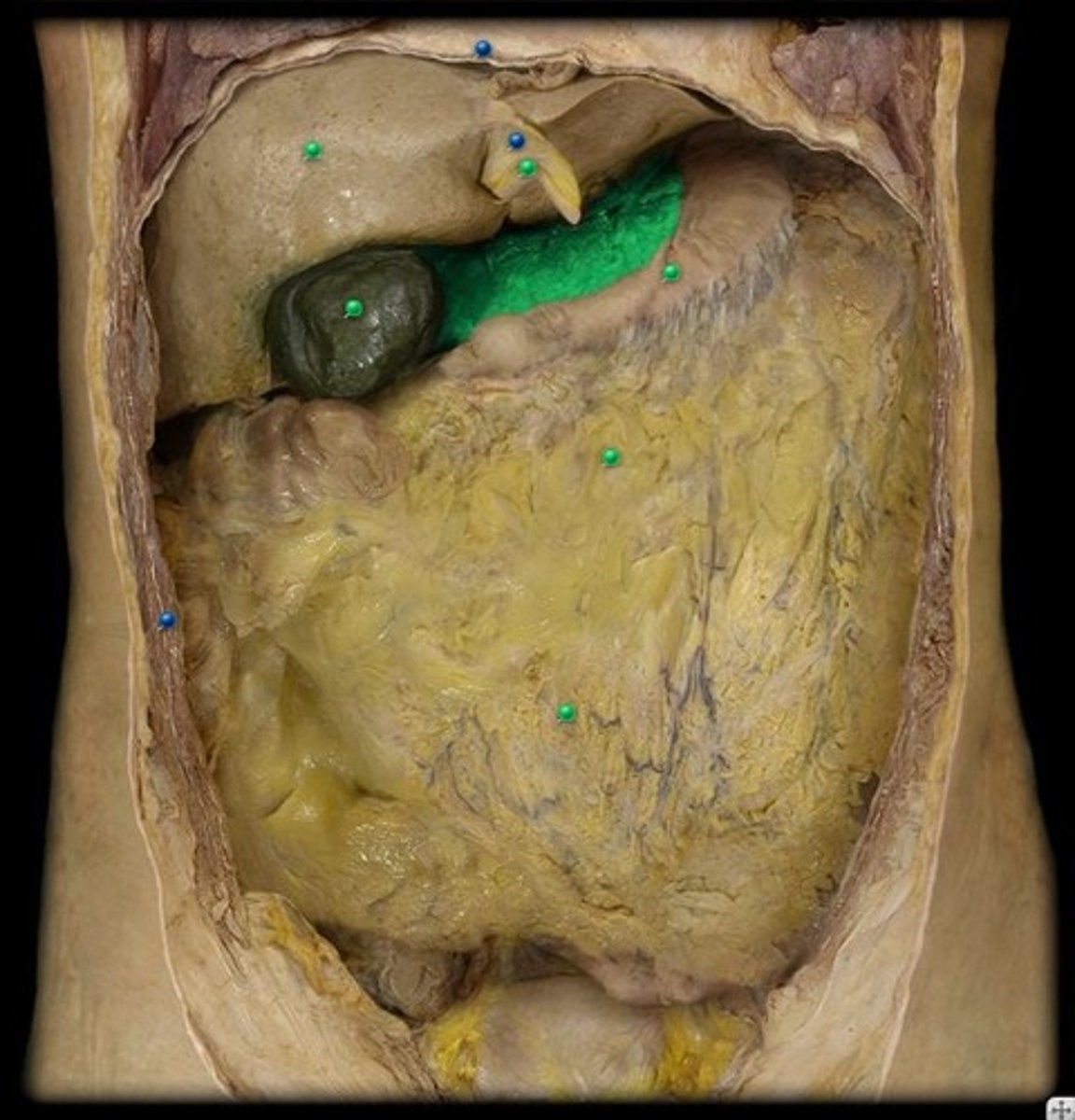
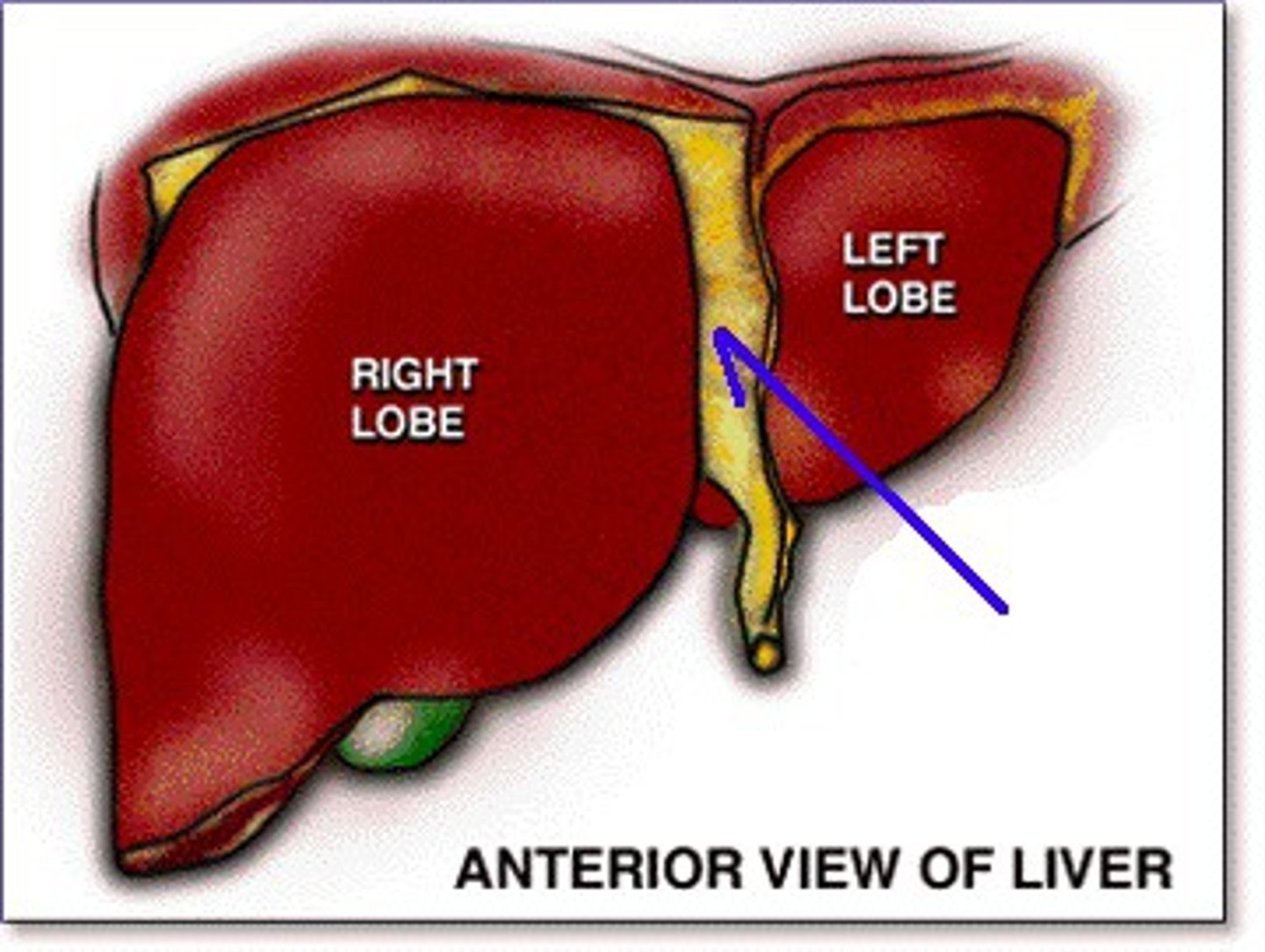
Falciform ligament
tissue that attaches the liver to the anterior body wall and separates the left and right lobes of the liver
Mesentery
attaches the small intestine to the posterior wall of the abdomen
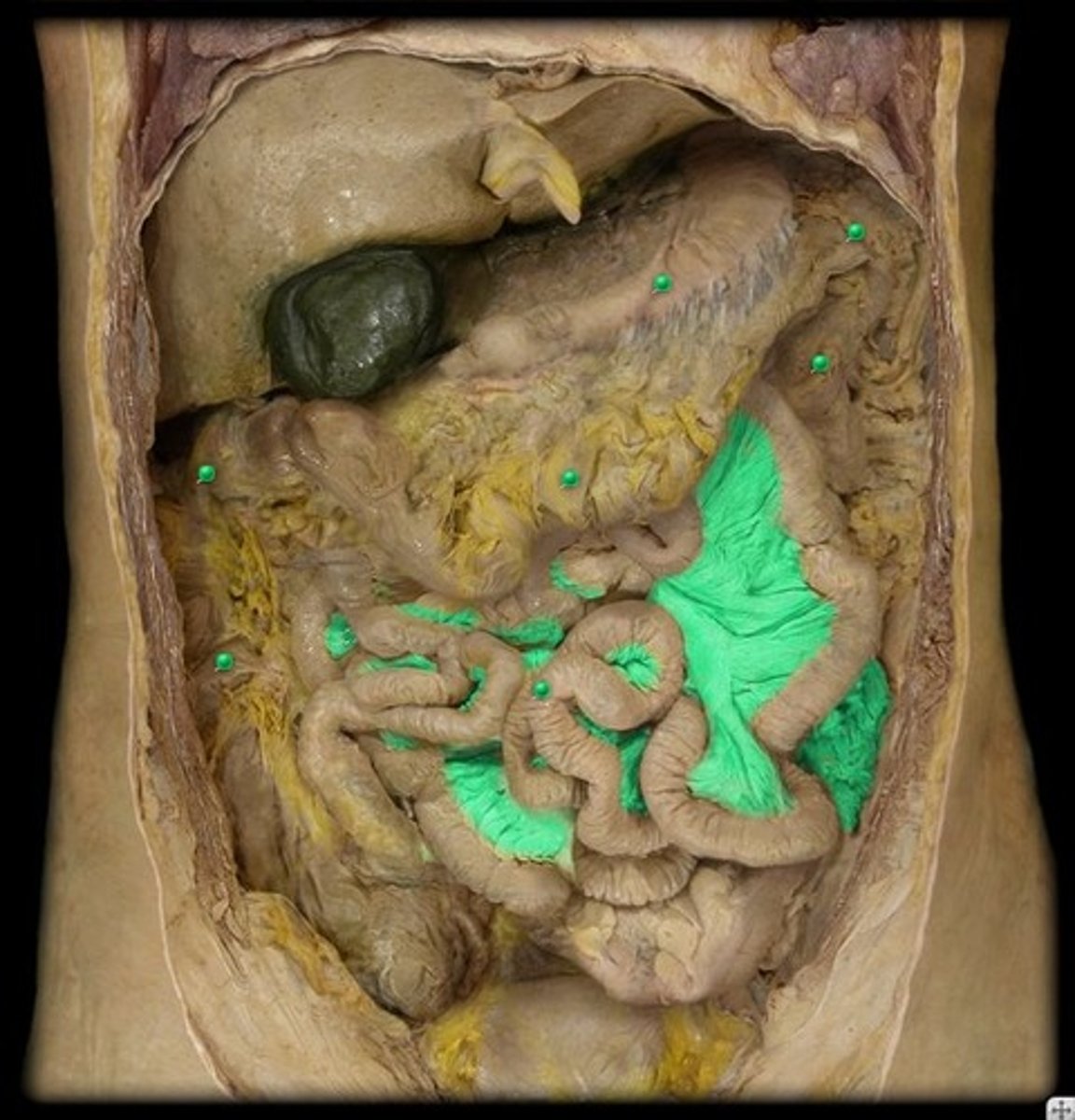
Mesocolon
attaches the colon to the posterior wall
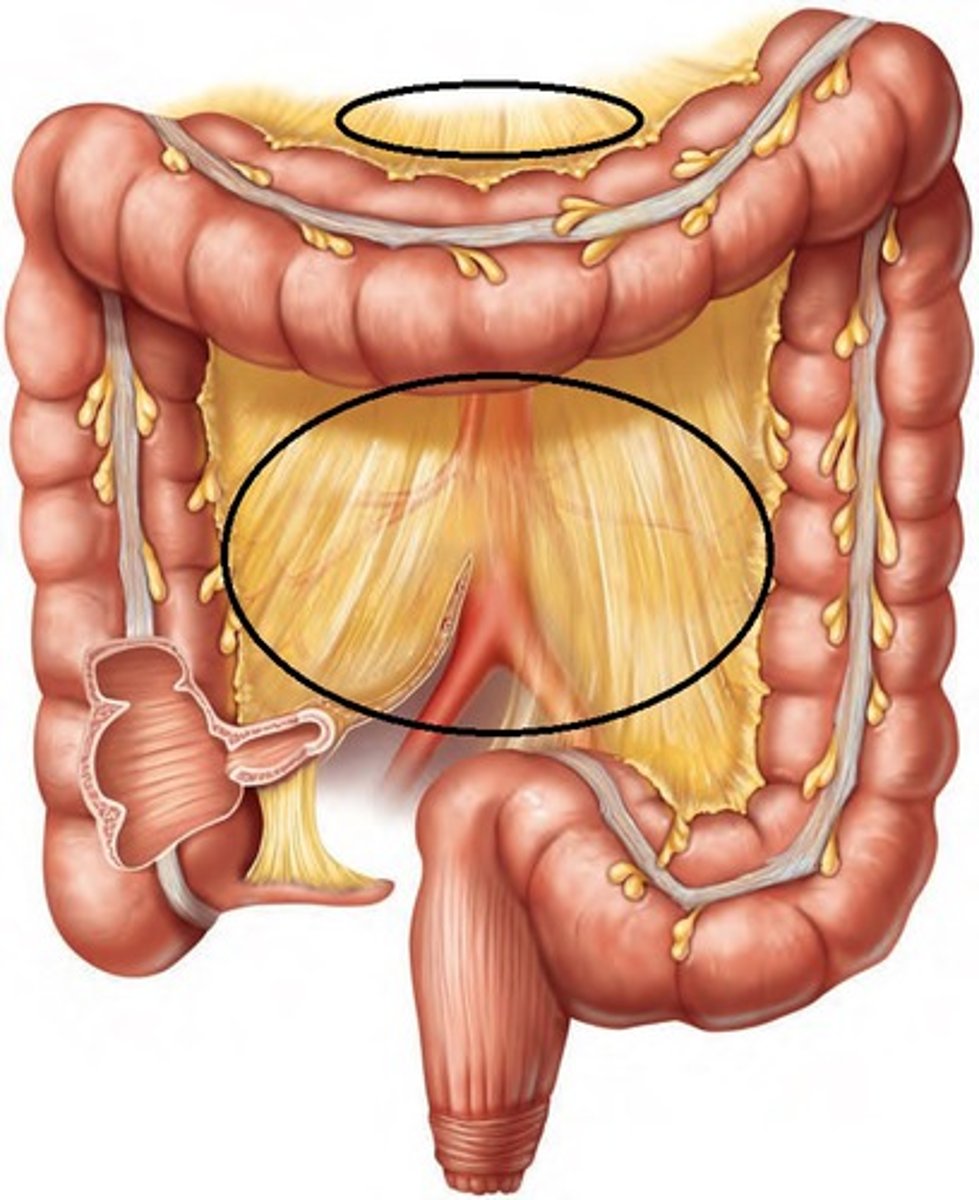
Retroperitoneal
the region posterior to the abdominal peritoneum; include the SAD PUCKER organs
Peritonitis
acute inflammation of the peritoneum
SAD PUCKER
suprarenal glands, aorta, duodenum, pancreas, ureters, colon, kidneys, esophagus, rectum; located at the retroperitoneal
Stratified squamous epithelium
the mouth is lined with ____________ which provides protection against abrasion and high temperatures
Tongue
a skeletal muscle covered in mucous membrane; forms the floor of the oral cavity
Lingual frenulum
fold of mucous membrane that attaches to the midline of the undersurface of the tongue; offers support to aid in movement
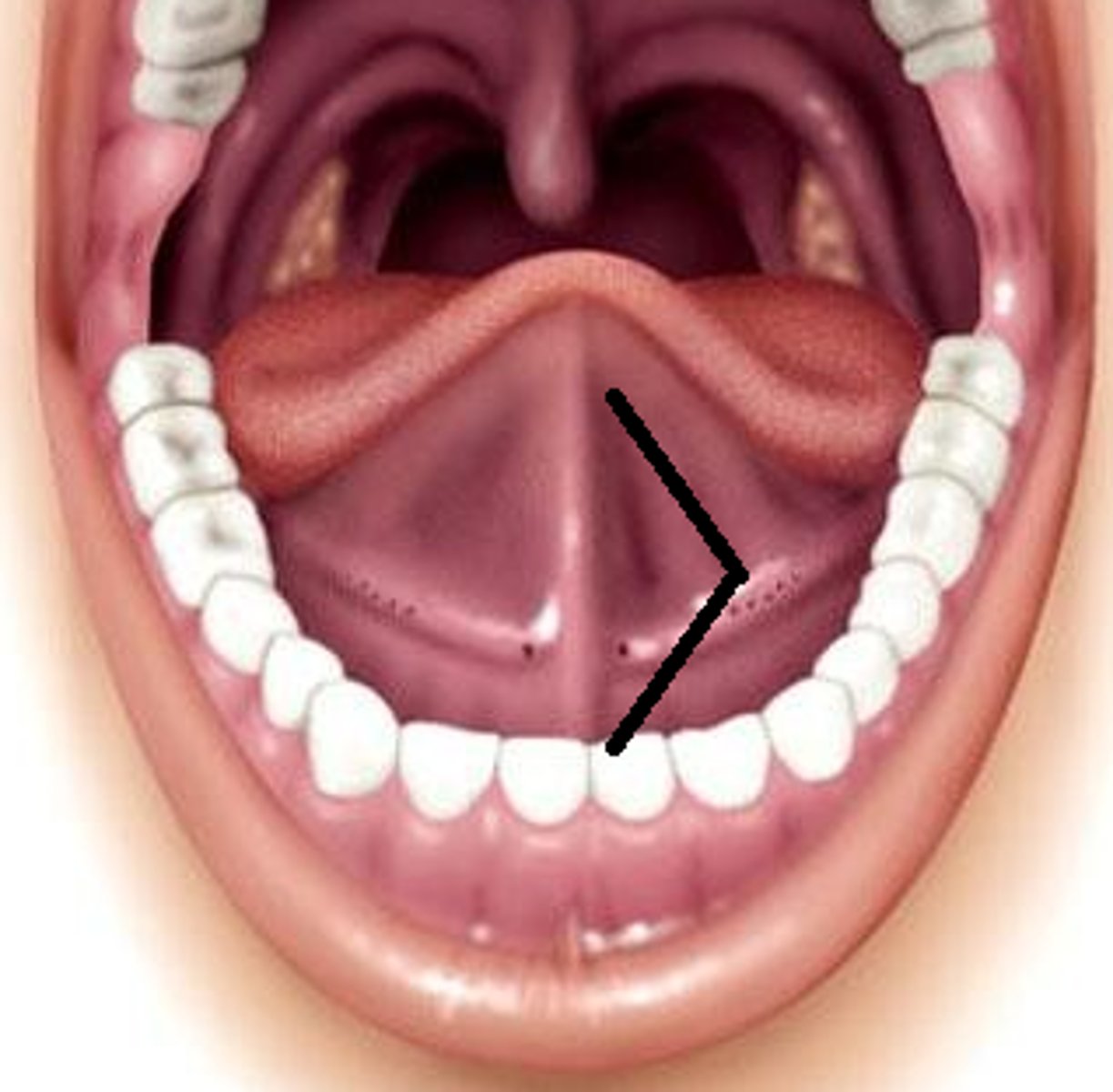
Superior labial frenulum
mucosal fold connected to upper lip
Inferior labial frenulum
mucosal fold connected to lower lip
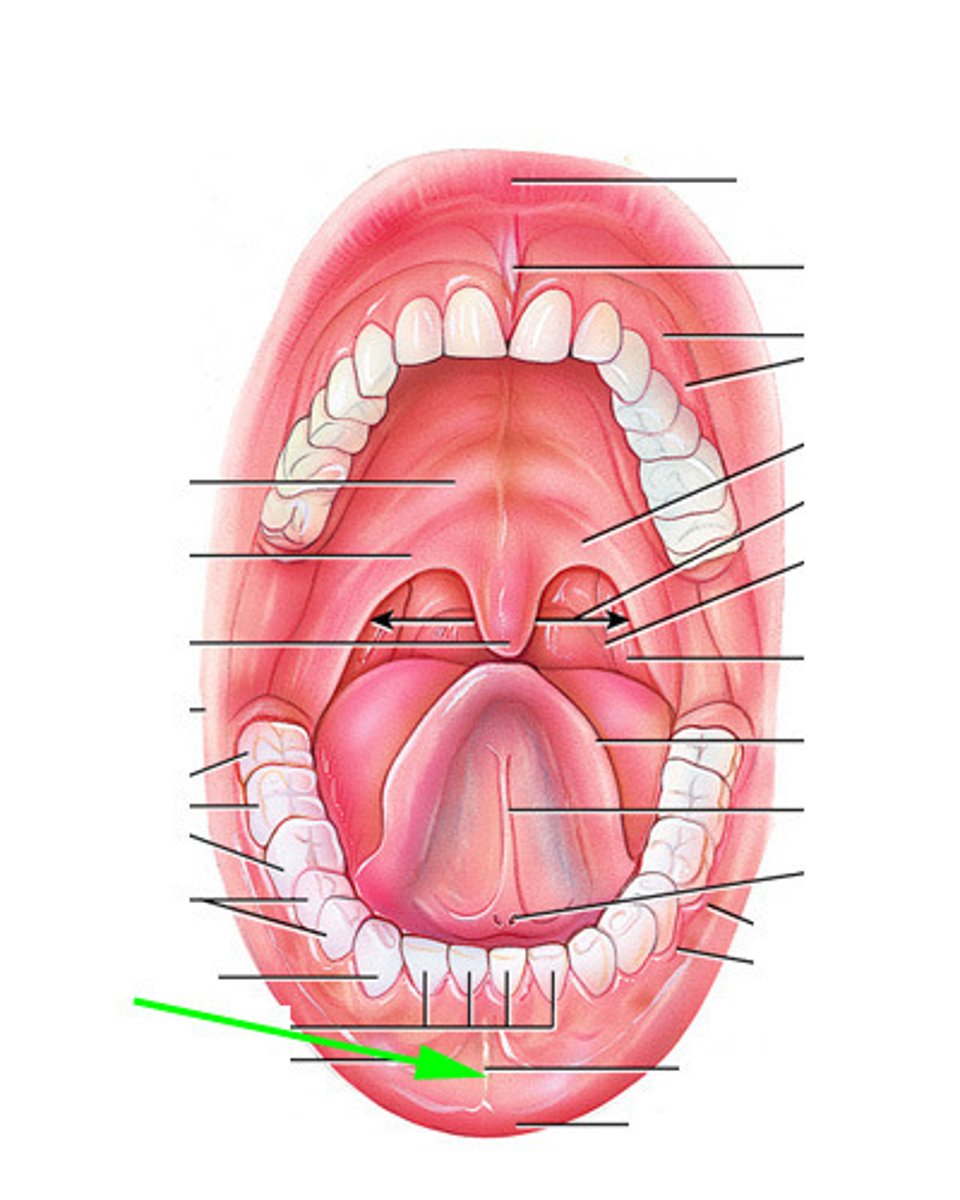
Uvula
the part of the soft palate that hangs down in the back of the throat; prevents food from entering the nasal cavity
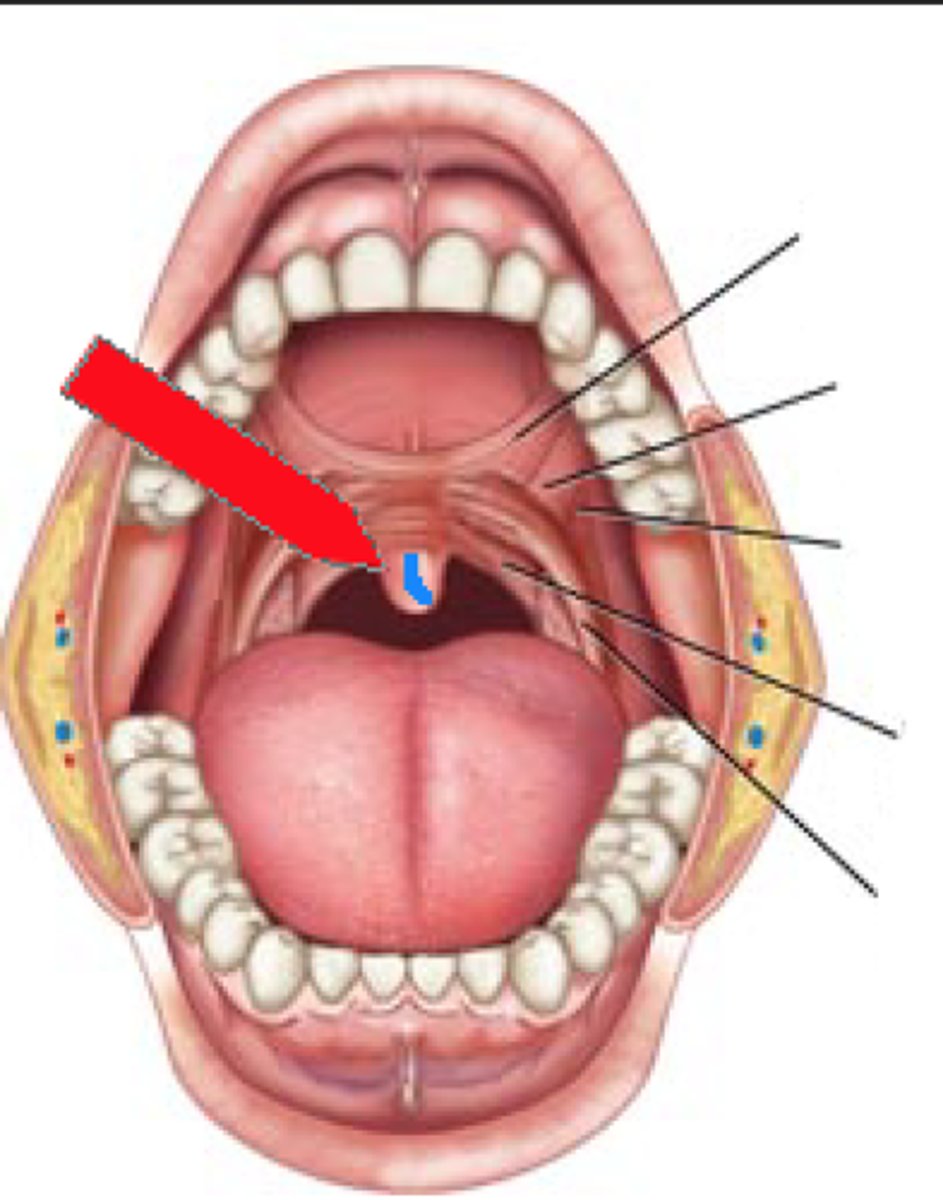
Gingivae
gums
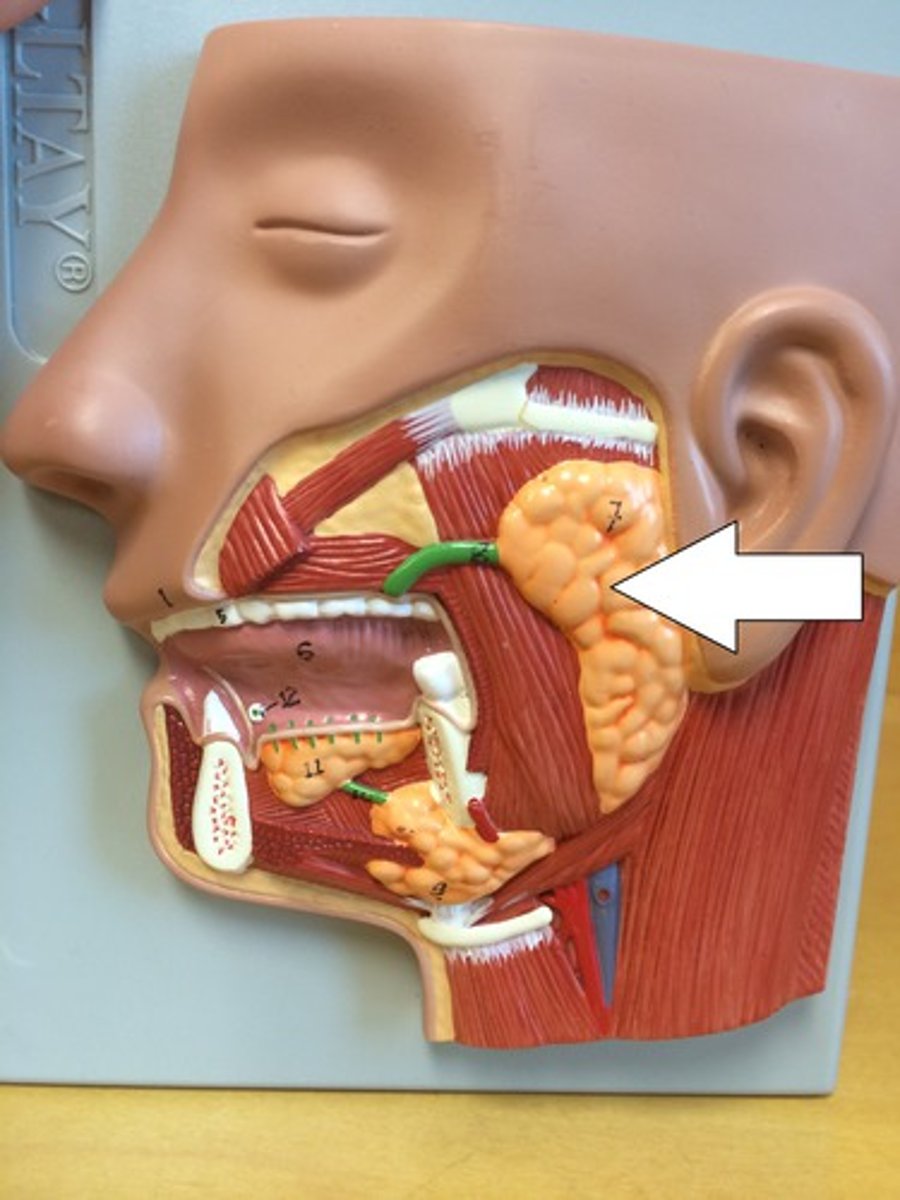
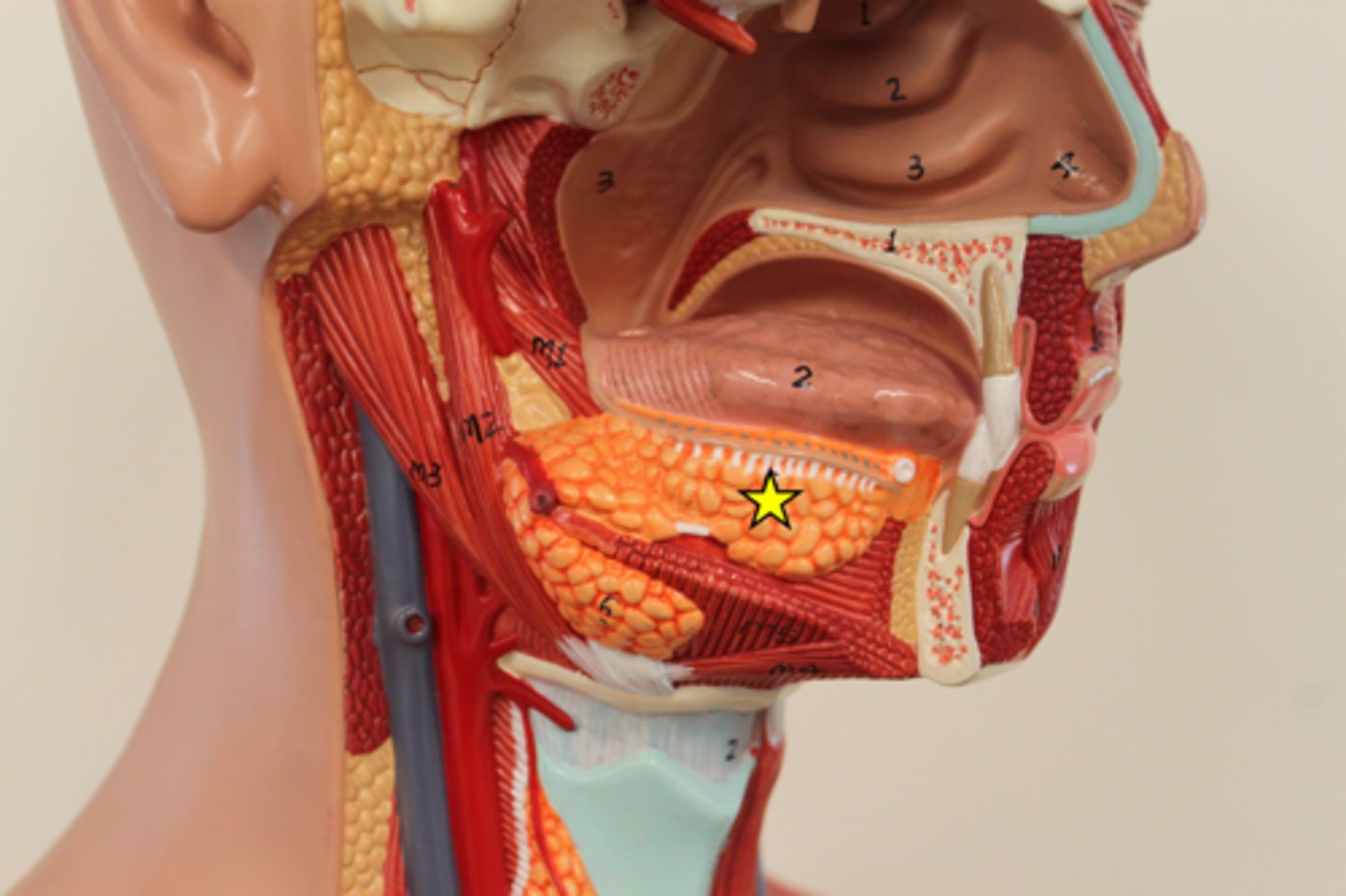
Salivary glands
three extrinsic: parotid, submandibular, sublingual; produce saliva which aids in lubrication, dissolving food, protection, and taste
Parotid gland
largest salivary gland; located in the cheek
Submandibular gland
salivary gland located under the jaw
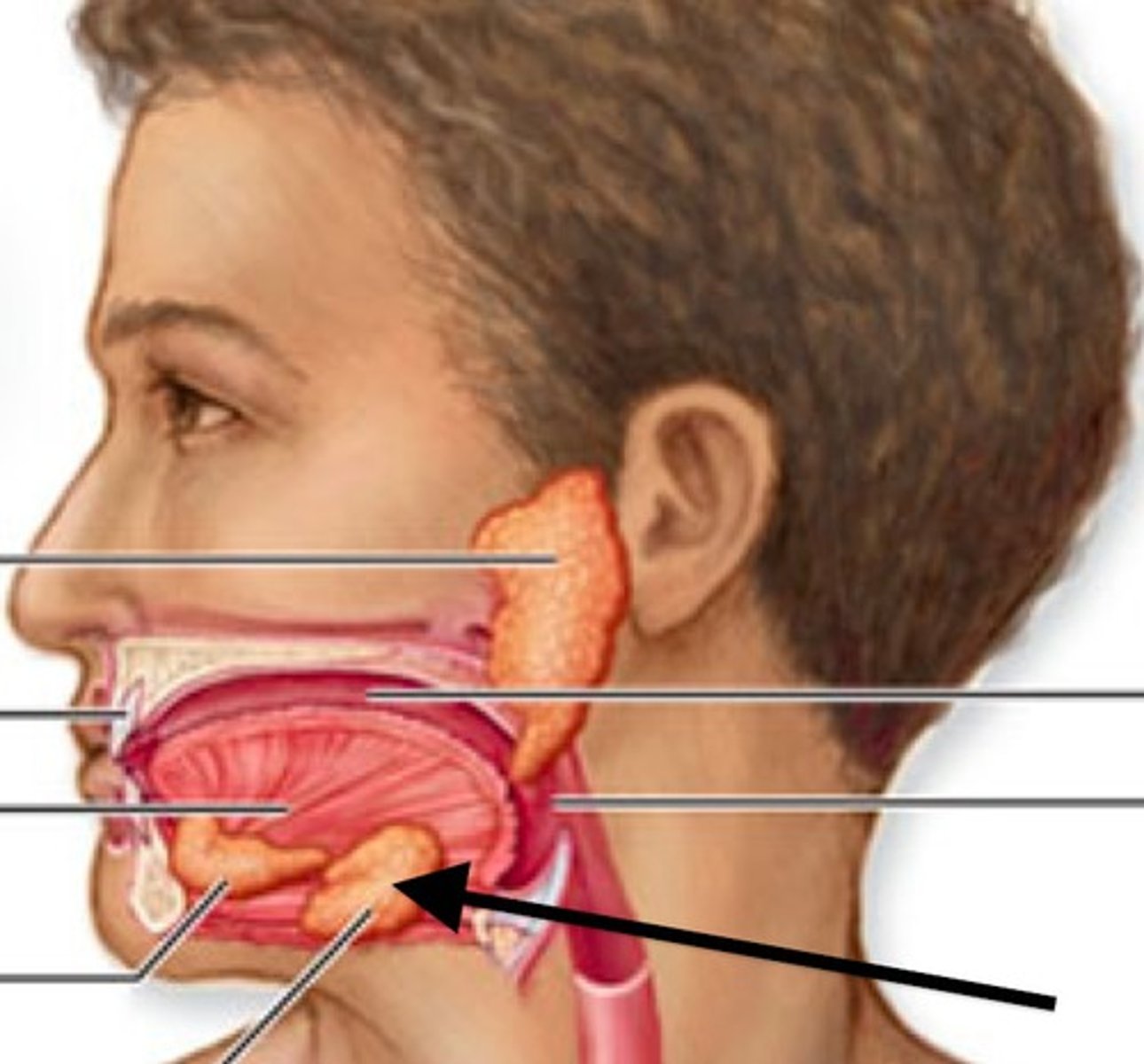
Sublingual gland
salivary gland under the tongue
99, 1
saliva is ______% water, ______% solutes and enzymes
Lysozyme
enzyme in saliva that kills bacteria
Salivary amylase
enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch
P-ANS
division of the nervous system that has primary control over salivation; produces thinner saliva with more enzymes
S-ANS
division of the nervous system that stimulates thicker saliva that contains more mucus and less digestive enzymes
Mumps
an inflammation and enlargement of the parotid salivary glands, caused by the mumps virus; symptoms include fever, malaise, pain, swelling of the glands, and possible sterility in adult males
Mastication
the process of chewing; mixing the food and creating a bolus of food
Bolus
food that has been chewed, mixed with saliva and made into a clump which can travel down the GI tract to the stomach
Chemical
the only ________ digestion in the mouth is caused by the enzymes in the saliva
Deglutition
the process of swallowing
Emesis
vomiting
Voluntary
from the mouth to the pharynx, it is ________ swallowing
Skeletal, mucous
the pharynx is composed of _______ muscle and _______ membrane
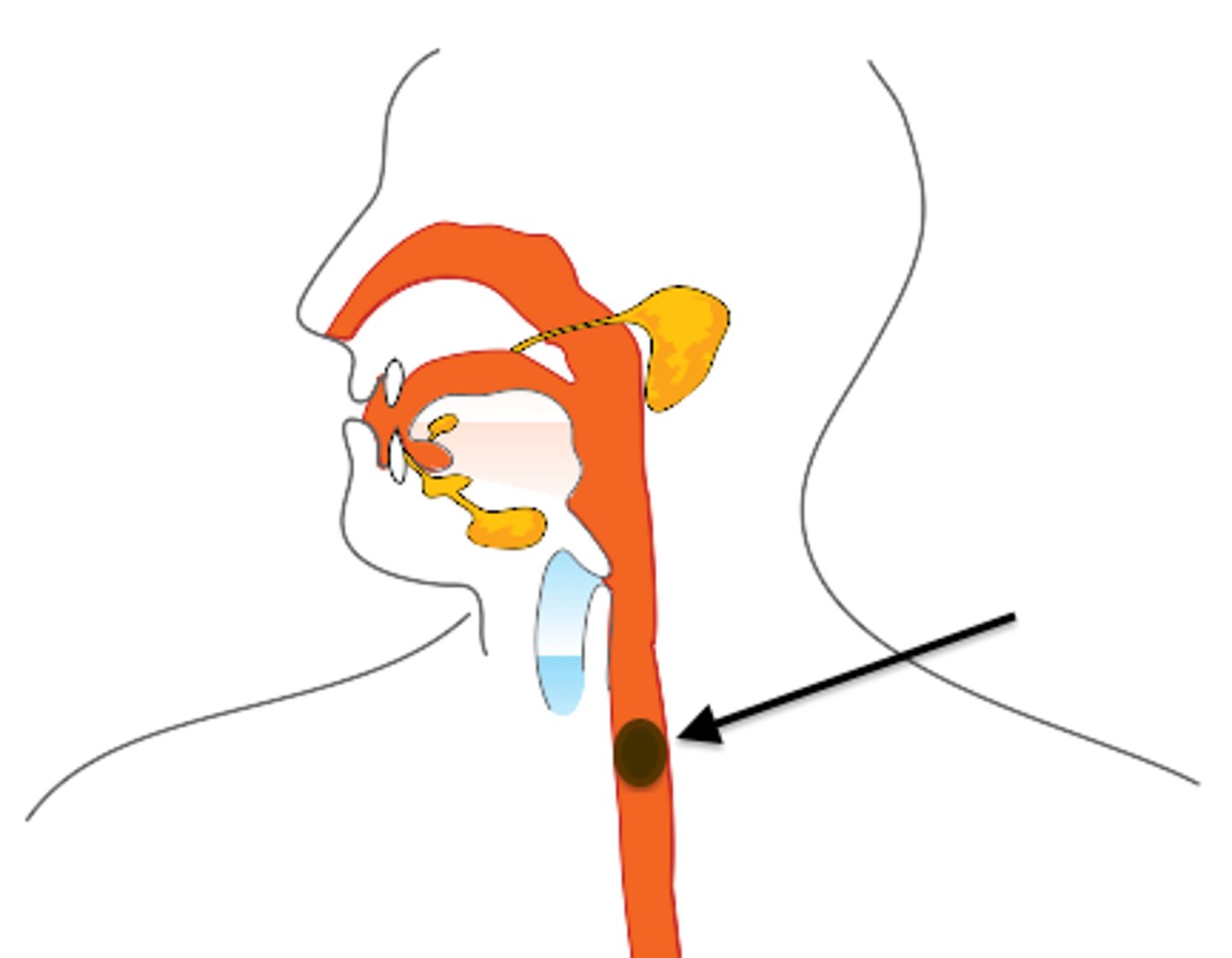
Nasopharynx
upper part of the pharynx; aids in respiration only
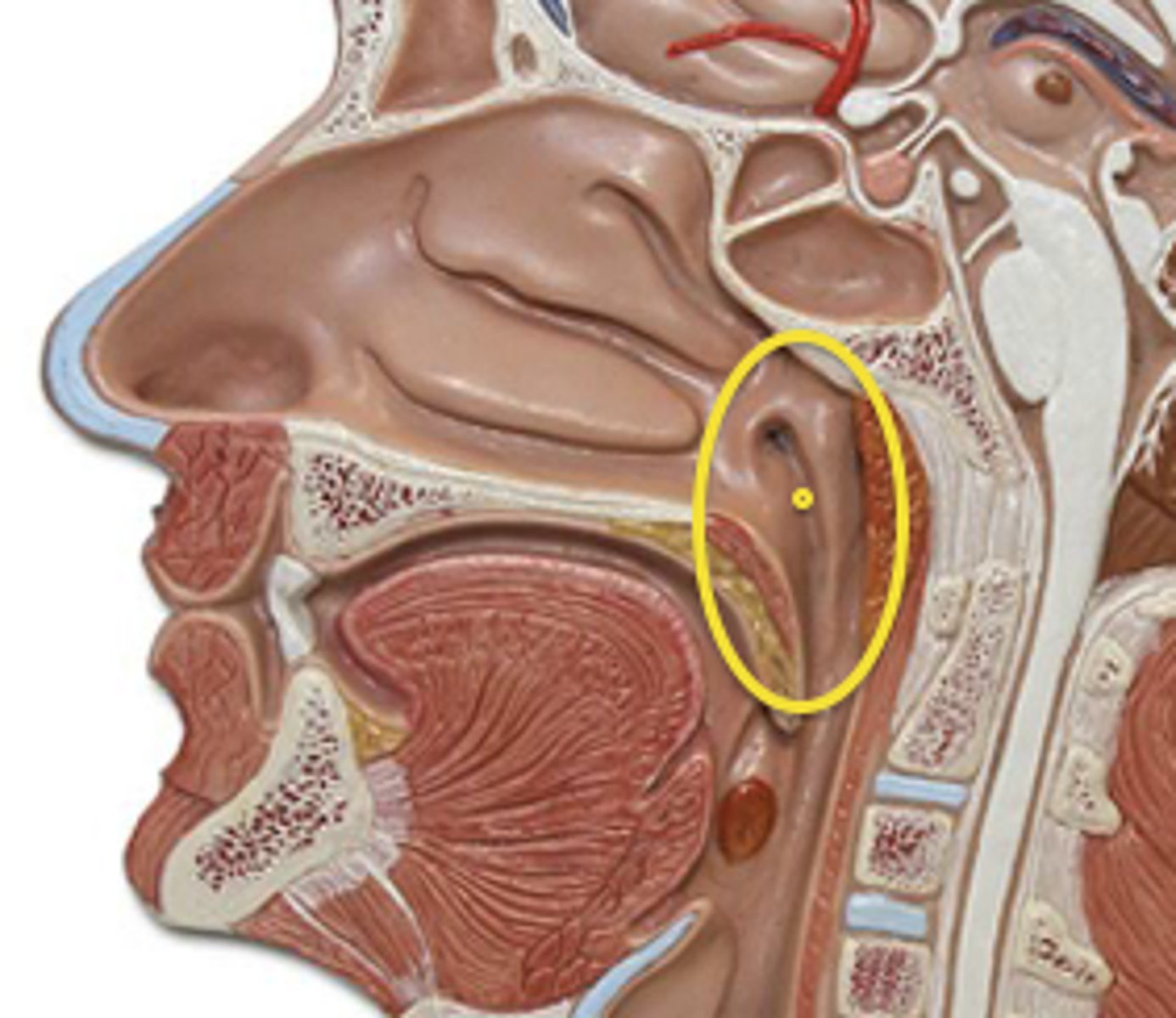
Oropharynx
central part of the pharynx; aids in digestion and respiration
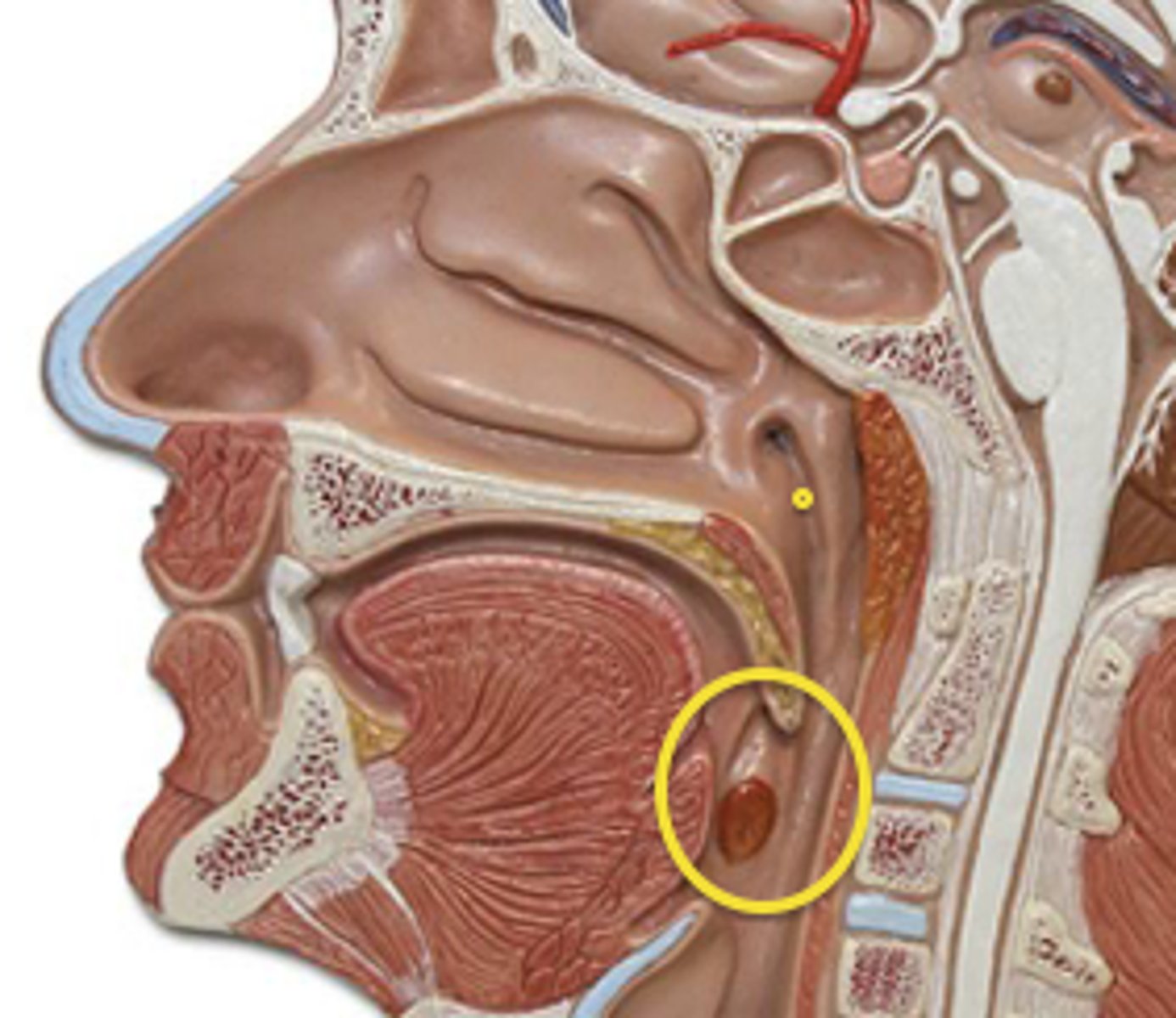
Laryngopharynx
lower part of the pharynx; aids in digestion and respiration
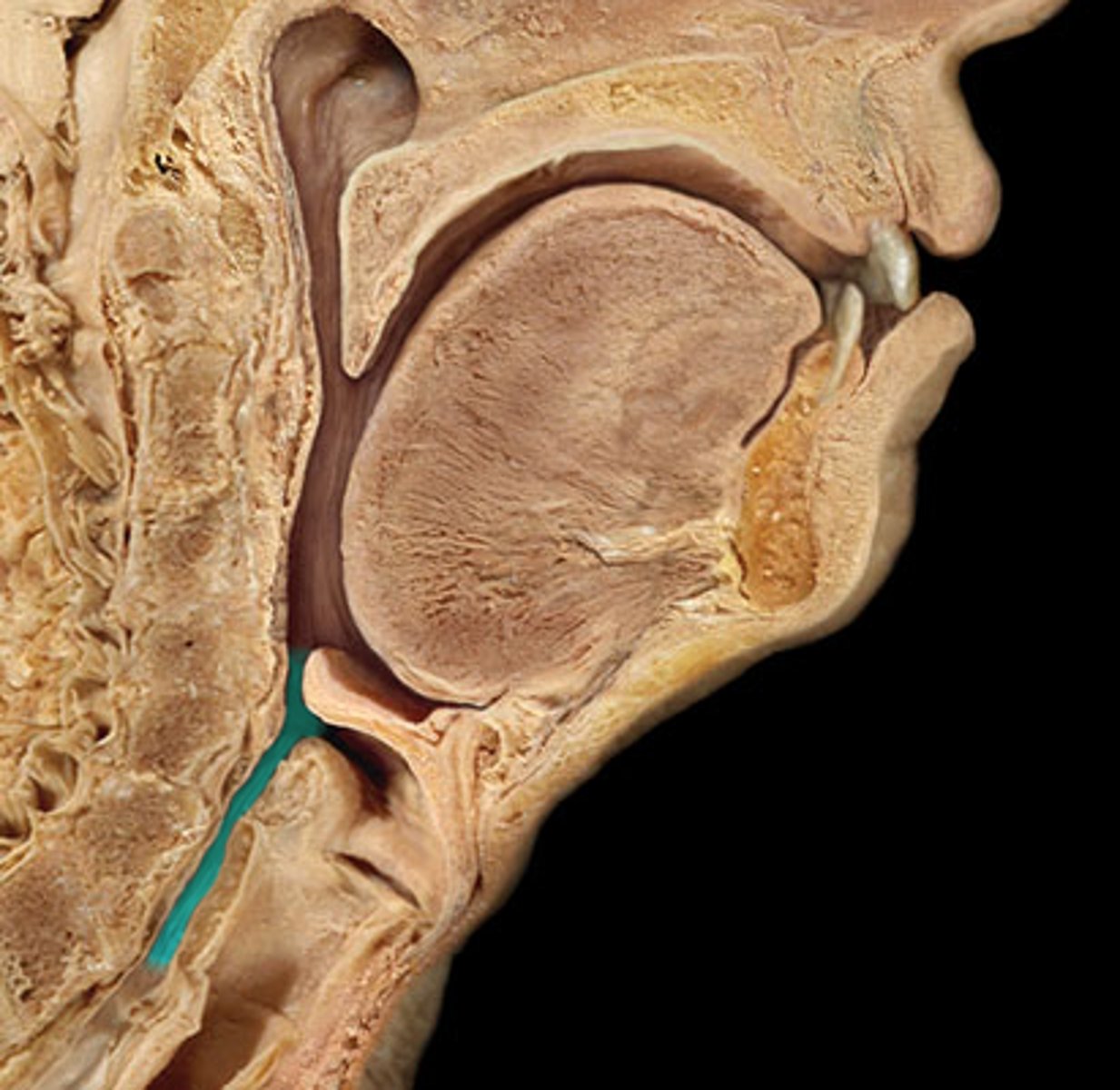
Esophagus
a collapsible, muscular tube that is posterior to the trachea and connects the pharynx to the stomach; lined with stratified squamous epithelium for protection; secretes mucus with no enzymes
Skeletal, skeletal and smooth, smooth
the upper 1/3 of the esophagus is ________ muscle
the middle 1/3 of the esophagus is ________ and _______ muscle
the lower 1/3 of the esophagus is _______ muscle
Upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
the muscular ring located at the top of the esophagus that prevents food from entering the mouth
Lesser esophageal sphincter (LES)
muscular ring located at the bottom of the esophagus that prevents food from leaving the stomach and entering the esophagus; when it dysfunctions, it causes GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
GERD; upward flow of acidic substances from the stomach into the esophagus; causes a burning feeling in the chest
Swallowing stages
1. voluntary stage
2. pharyngeal stage
3. esophageal stage
Voluntary stage
first stage of swallowing; the tongue helps force food bolus into the esophagus
Pharyngeal stage
second stage of swallowing; breathing is temporarily interrupted as food passes through the oropharynx into the esophagus; the soft palate and uvula close of the nasopharynx and epiglottis and vocal cords prevent pulmonary aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration
"food going down the wrong pipe" into the trachea/lungs; prevented by the epiglottis closing off the larynx and the vocal cords closing to block off the trachea
Esophageal stage
third stage of swallowing; the food bolus passes through the esophagus into the stomach via peristalsis
Circular, longitudinal
during peristalsis, _______ muscle fibers above the bolus squeeze the bolus forwards and _______ muscle fibers around the bottom of the bolus contract, shortening and widening the lumen of the esophagus at the region the bolus is entering
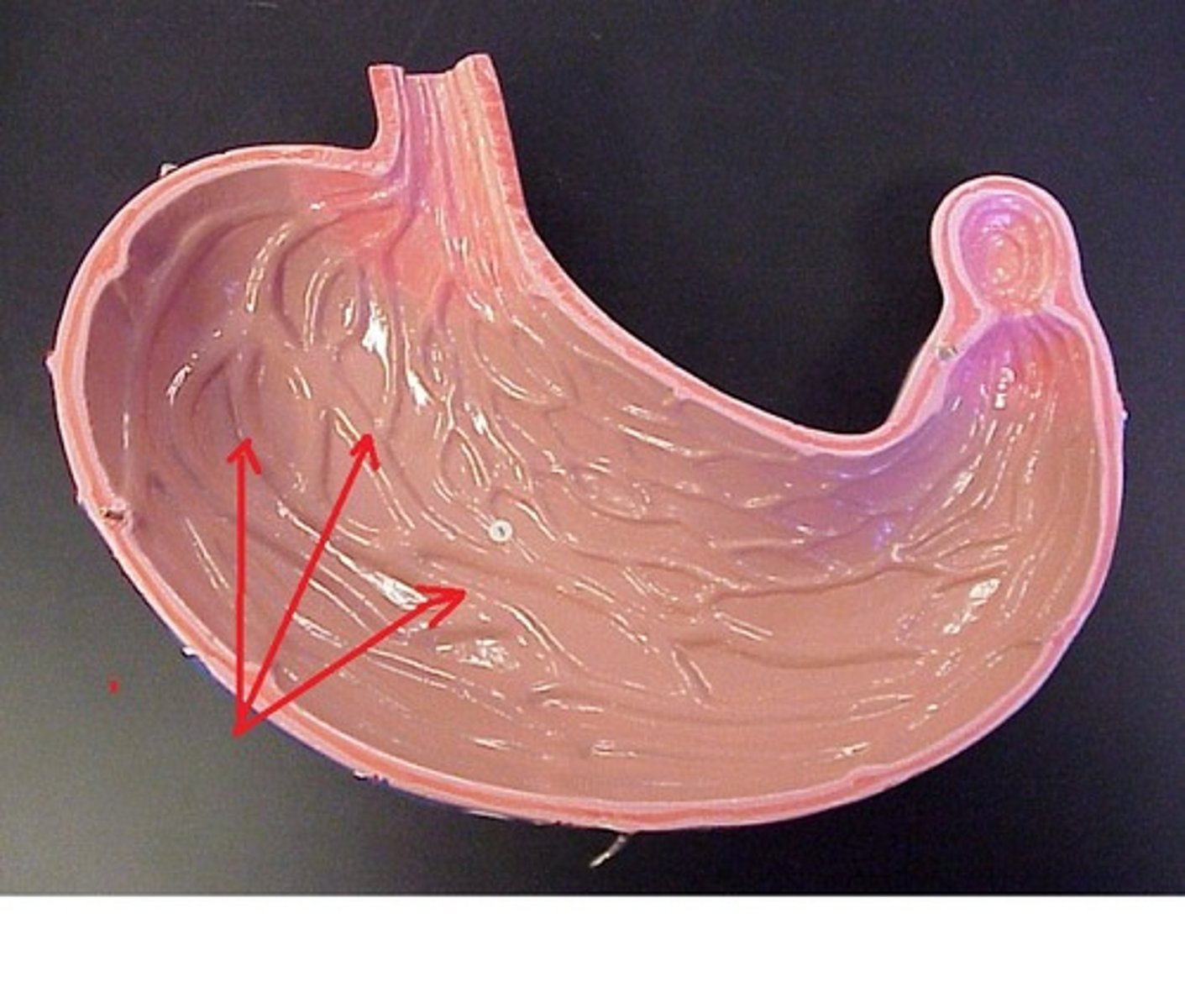
Stomach
J-shaped, muscular pouch that expands to hold chyme
pyloric sphincter
a ring of muscle at the end of the stomach that controls food leaving the stomach
Chyme
food that is in the stomach and has already been mixed with digestive enzymes
Cardia
the upper opening of the stomach where the esophagus enters the stomach
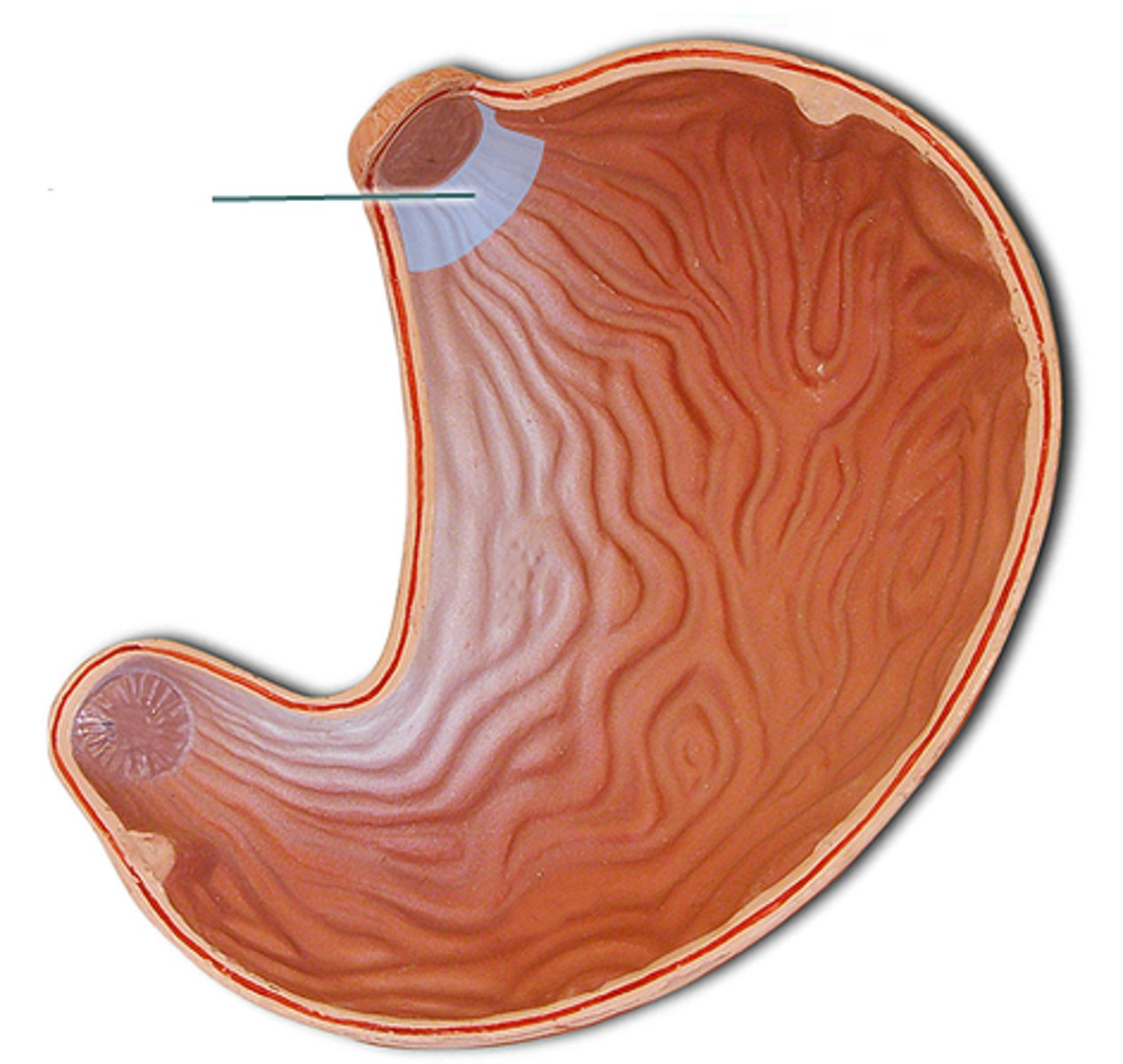
Fundus
the upper portion of the stomach
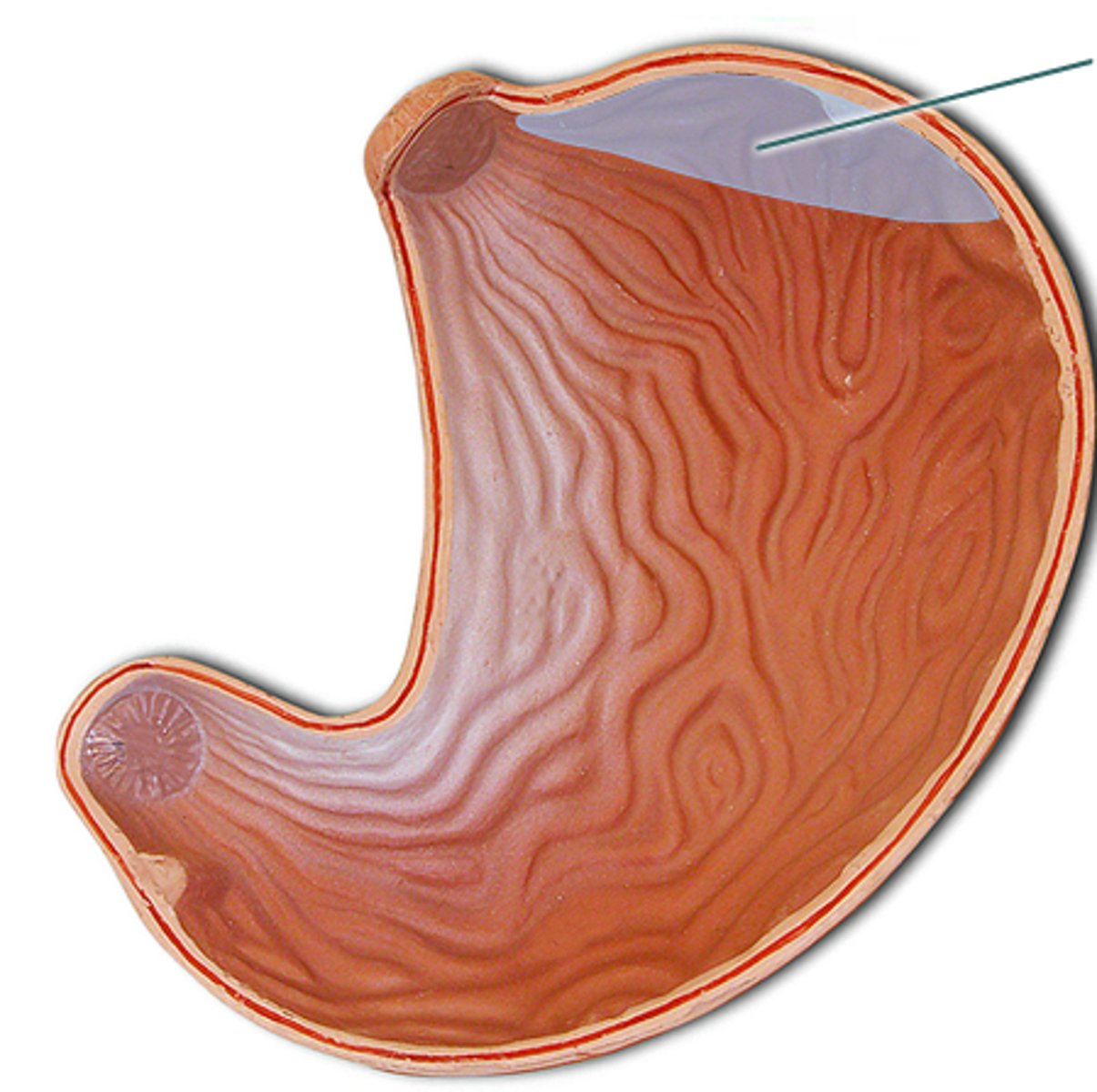
Body
the main part of the stomach
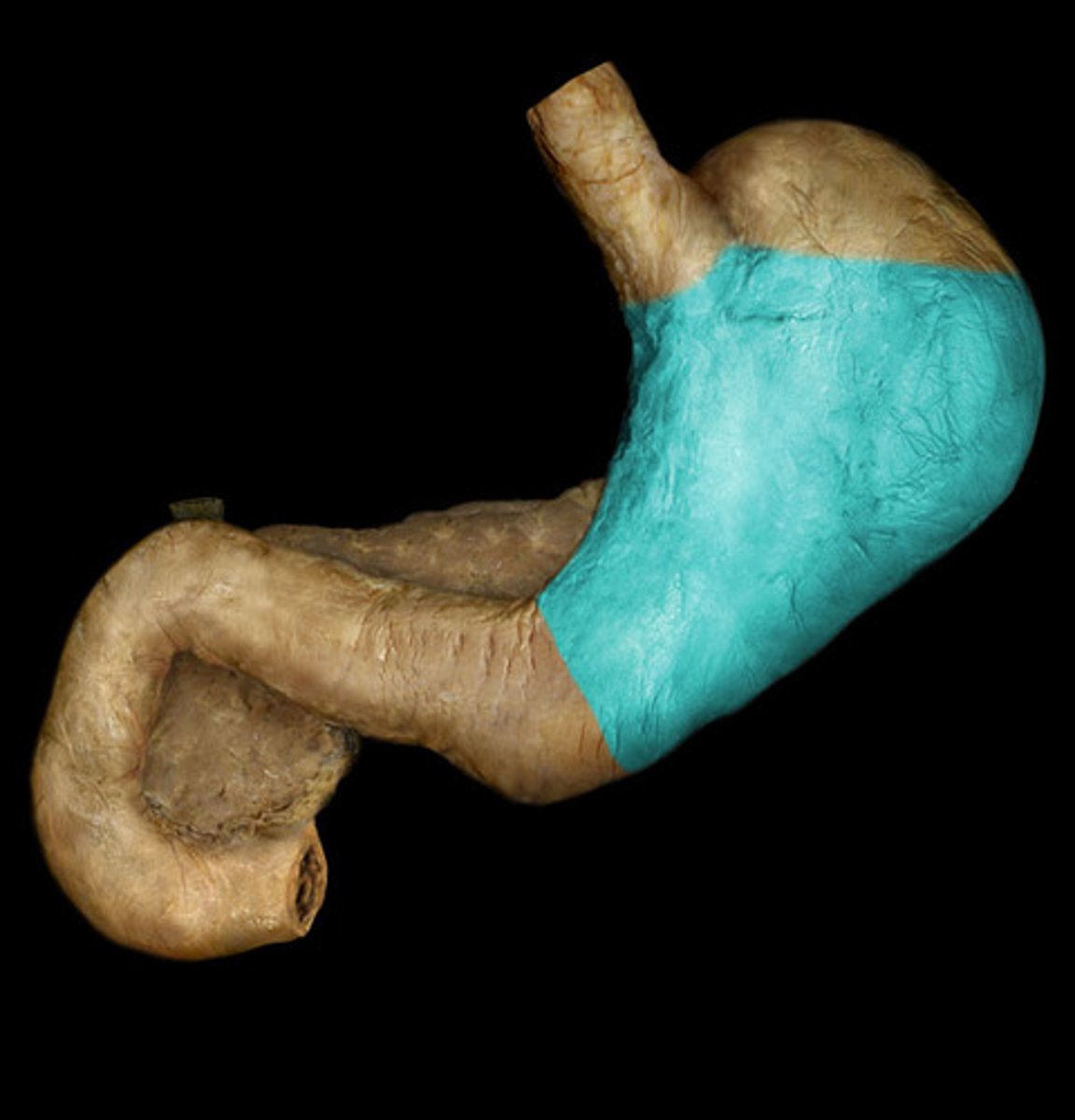
Pylorus
distal region of the stomach, opening to the duodenum
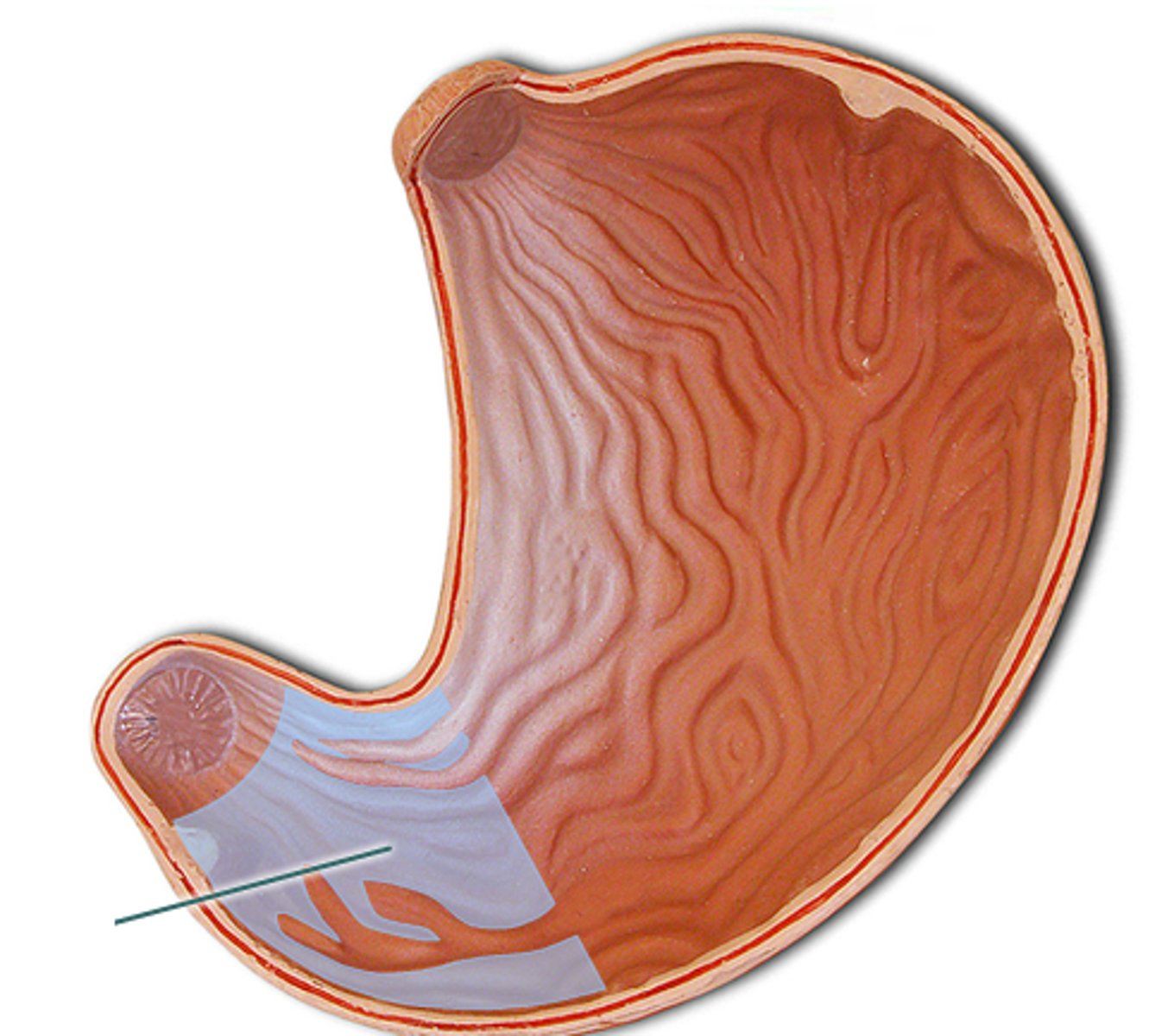
Gastric rugae
temporary, visible folds on the inner stomach which allow the walls to stretch
Pylorospasm
condition of the pyloric sphincter in newborns where the pyloric sphincter involuntarily contractions
Pyloric stenosis
condition of the pyloric sphincter in newborns where the pyloric sphincter is too big and limits amount of food that enters the duodenum; causes projectile vomiting
Gastric pits
invaginations of the surface epithelium into the lamina propria; lined with surface mucous cells; lead to gastric glands
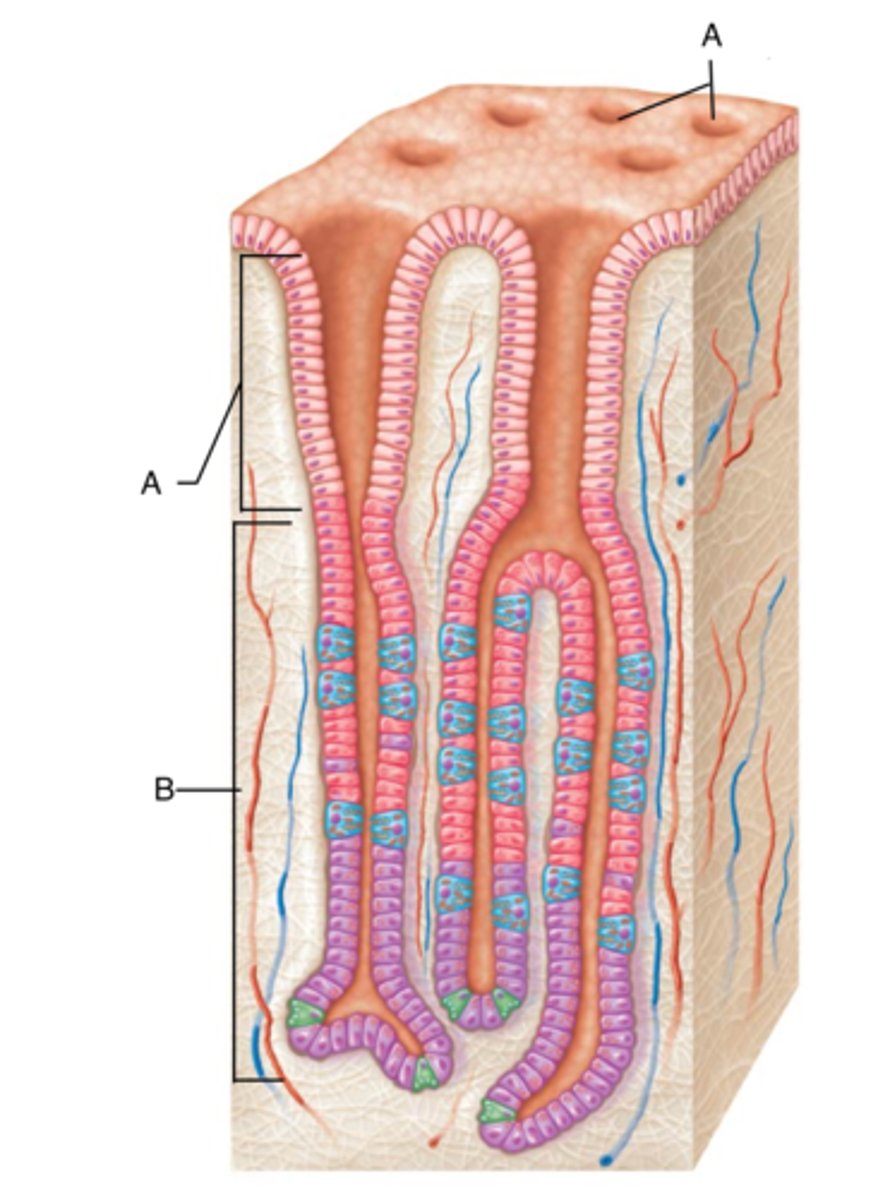
Surface mucous cells and mucus neck cells
mucous secreting cells on the surface of the mucosa which produce a cloudy, viscous, alkaline mucus that forms a thick gel-like coat that adheres to the surface epithelium to protect from abrasions and acidic gastric juices
Exocrine
glands that secrete their products through ducts into an open lumen/epithelium
Endocrine
glands that secrete hormones or other products directly into the blood
Paracrine
cells that secrete substances that act on adjacent cells
Autocrine
cells that secrete substances that act of that same cell