1. intro to the nervous system + spinal cord
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
The nervous system
the most complex system in the human body.
coordinates the activity of the muscles, monitors the organs, constructs and stops input from the senses, and initiates actions.
what is the building subunit of the nervous system?
Neuron
Neurons → Circuits
afferent neuron
1st neuron that receives info from the environment
Structural subdivisions of the Nervous System
CNS + PNS
CNS central nervous system
brain and the spinal cord
PNS peripheral nervous system
consists of the nerves going to and from the central nervous system.
Functional subdivisions of the Nervous System
Somatic part
Visceral part
Somatic part
innervates structures (skin and most skeletal muscle) derived from somites in the embryo
mainly involved with receiving and responding to information from the
external environment.
Visceral
innervates organ systems in the body and other visceral elements, such as smooth muscle and glands.
involuntary
concerned mainly with detecting and responding to information from the
internal environment.
Autonomic Nervous System-ANS)
The visceral motor component is commonly referred to as the autonomic division of the PNS
regulates individual organ function and homeostasis
for the most part is involuntary, reflexive control
ANS innervates:
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
secretory cells (glandular epithelium)
motor and sensory components of ANS
1. sensory nerves monitor changes in the viscera
2. motor nerves mainly innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
Visceral part of the nervous system (Autonomic Nervous System)
The ANS is most important in two situations:
1. The Sympathetic Nervous System
In emergencies that cause stress and require us to "fight" or take "flight" (run away)
2. The Parasympathetic Nervous System
In non-emergencies that allow us to "rest" and "digest."
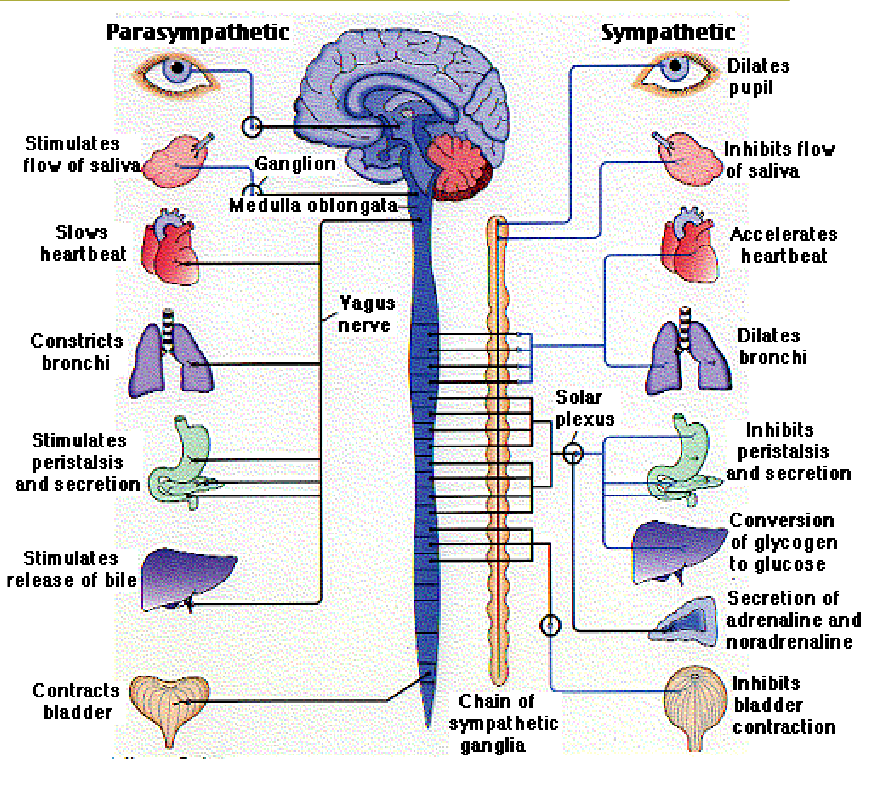
ANS regulates structures associated with
digestion
circulation
respiration
excretion
reproduction
body temperature
Peripheral components of the ANS: Sympathetic
Spinal levels: T1 -L2/L3
Paravertebral ganglia
Prevertebral ganglia
Peripheral components of the ANS: Parasympathetic
Brain stem - Cranial Nerves
Spinal levels: S2-4
Ganglia close to target muscles
Neurons categories: general
General somatic afferents (GSA)
General somatic efferent (GSE)
General visceral afferent (GVA)
General visceral efferent (GVE)
Neurons categories: General somatic afferents (GSA)
Somatic sensory neurons carry information from the periphery into the CNS
also called somatic sensory afferents.
Neurons categories: General somatic efferent (GSE)
Somatic motor fibers carry information away from the CNS to skeletal muscles
also called somatic motor efferent
Neurons categories: General visceral afferent (GVA)
Visceral sensory neurons and their processes, related to ANS referred to as are associated primarily with chemoreception, mechanoreception, and stretch reception.
Neurons categories: General visceral efferent (GVE)
visceral motor neurons related to ANS.
spinal nerves what should we know abt this?
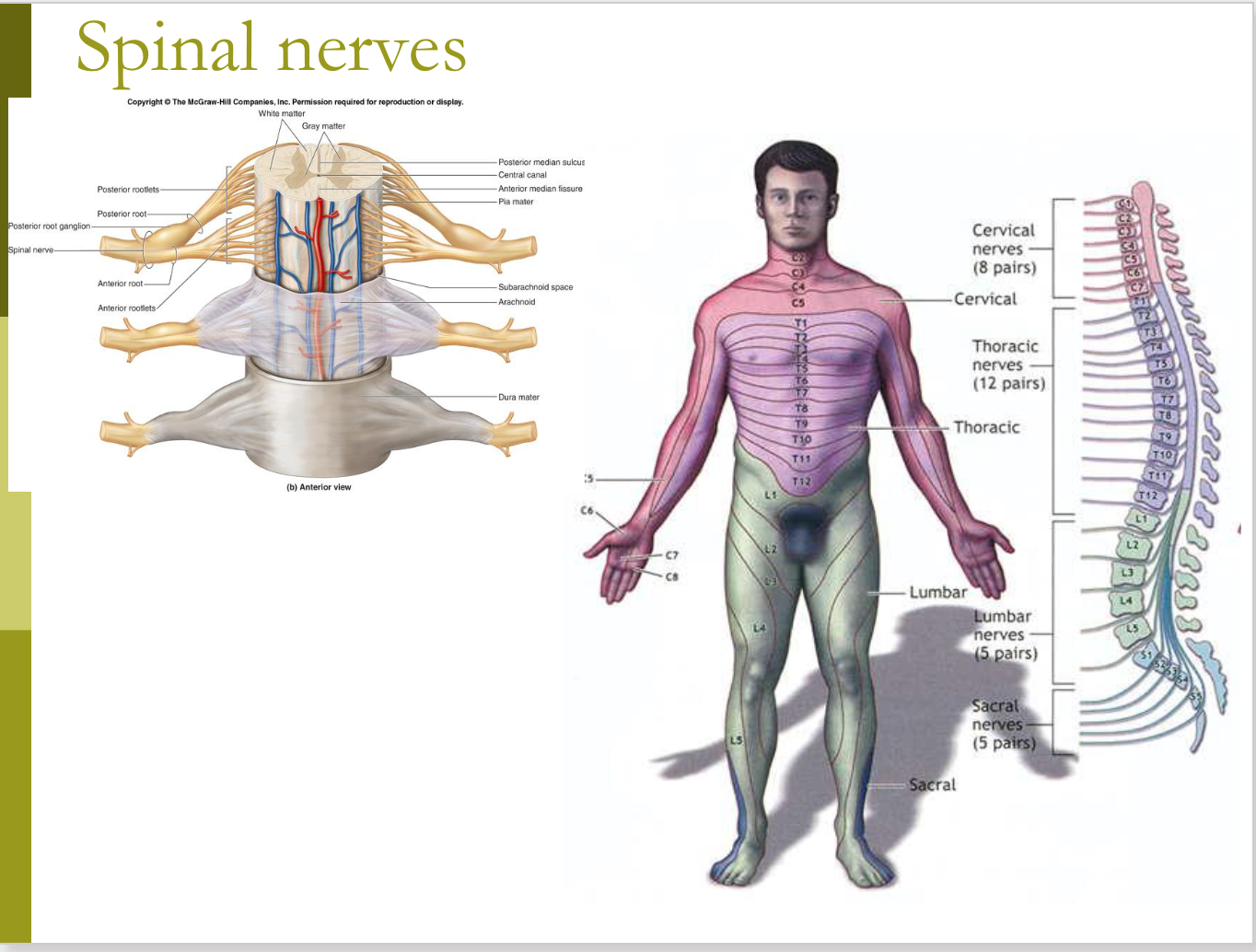
Dermatomes
the area of skin supplied by a single spinal cord level, or on one side, by a single spinal nerve.
Each dorsal root fibers from all spinal cord segments will supply the sensory innervation to a skin segment in the human body.
Somatic sensory fibers originally associated with that somite enter the posterior region of the spinal cord at a specific level and become part of one specific spinal nerve
Myotome
the portion of a skeletal muscle innervated by a single spinal cord level or, on one side, by a single spinal nerve
each spinal nerve carries somatic motor fibers to muscles that originally
developed from the related somite.
The spinal cord is responsible for
Motor reflexes
Conduct sensory information from the environment to the brain.
Contain pathways for motor impulses going out to the peripheral muscles
contains autonomic efferents
Central Nervous system grey + white matter
Grey matter: aggregation of cell bodies ~ Cortex, Nuclei
White matter: Bundles of neuronal axons~ Tracts, Fibers, Columns
Peripheral Nervous system: Grey + white matter
Grey Matter: Ganglia
White Matter: Fibers
The spinal nerves are distributed as:
31 pairs of spinal nerves.
8 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral
1 Coccygeal
Spinal Cord Structure
Spinal Cord Structure
Subarachnoid space
Conus medullaris
The Cauda Equina
The Filum Terminale
Cervical enlargement
Lumbar enlargement
Meninges
An outer dura mater, middle arachnoid and pia mate.
Subarachnoid space has:
Cerebrospinal fluid
The amount of white matter _______ in a ________ direction.
The amount of white matter increases in a caudal-to-rostral direction.
A(n) ______ of grey matter volume in the __________ enlargements for _________________
An increase of grey matter volume in the cervical and lumbosacral enlargements for innervation of the limbs.
The lateral horn of grey matter is characteristic of the ____________.
The lateral horn of grey matter is characteristic of the thoracic and upper lumbar segments only.
Cervical spinal segments contain the largest number of fibers in the _______
Cervical spinal segments contain the largest number of fibers in the white matter
Cervical enlargement to innervate
the arms
Lumbar enlargement to innervate
the legs
where do Afferent fibers (sensory) enter the spinal cord?
Dorsal roots
dorsal root ganglia
has cell bodies of afferent fibers
where do Efferent fibers (motor) leave the spinal cord?
Ventral roots
axons of alpha motor neurons.
axons of gamma motor neurons.
Transverse section of the spinal cord- White and Grey Matter
has a roughly H-shaped or butterfly outline.
The central canal is lined by ependymal epithelium.
The dorsal horns: Sensory
The ventral horns: Motor
The lateral horn/intermediate zone : containing sympathetic efferent neurons is added in the thoracic and upper lumbar segments.
structural classes of neurons
multipolar neuron
bipolar neuron
unipolar neuron
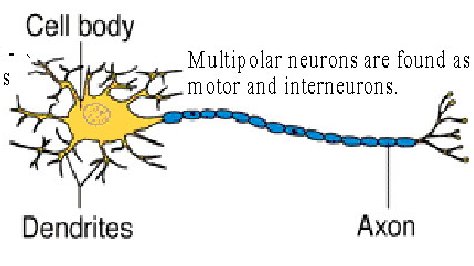
structural classes of neurons: multipolar neuron
has many dendrites + one axon
motor + interneurons
ex: motor neuron at ventral horn
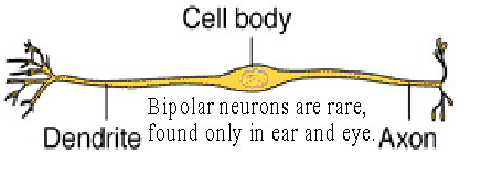
structural classes of neurons: bipolar neuron
one dendrite and one axon attached to the cell body
only found in the eyes and ears
structural classes of neurons: unipolar neuron
have one process from the cell body to an axon
dendrites branches at the receptors + axon leads to the spinal cord or brain
most of the bodys sensory neurons
ex: cell of the dorsal root ganglion
white matter consists of 3 funiculi
1. The dorsal funiculus
Medial Fasciculus Gracilis
Lateral Fasciculus Cuneatus
2. The lateral funiculus.
3. The ventral funiculus
The dorsolateral tract (of Lissauer) located between
the apex of the dorsal horn and the surface of the cord
Rexed's Laminae
Laminae I-VI: Posterior/dorsal horn
Laminae VII-IX: Anterior/ventral horn
SPINAL GRAY MATTER: Lateral gray horn or intermediate area know fs
1. Intermediolateral cell column (IML)
2. Intermediomedial cell column (IMM)
1. Intermediolateral cell column (IML)
T1-L3
preganglionic sympathetic neurons for the ANS (GVE)
2. Intermediomedial cell column (IMM)
S2-S4
preganglionic parasympathetic neurons for the ANS (GVA)
Long ascending fibers
sensory
found in all funiculi
(white matter)
Long descending fibers
(white matter)
motor
found primarily in the lateral and anterior funiculi.
Shorter propriospinal fibers
(white matter)
in a thin shell surrounding the grey matter called the propriospinal tract.
Proprioception
Proprioception
sensing stimuli arising within the body regarding position, motion, and equilibrium.
Spinal Cord Injury
damage to the spinal cord that results in a loss of function such as mobility or feeling.
Frequent causes of damage are trauma
(car accident, gunshot, falls, etc.) or disease (polio, spina bifida.. etc.).