ECON 248 14.4 The Aggregate-Supply Curve
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
The () is the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level.
Aggregate Supply Curve
Supply of goods increase when the ().
Price Rises
Increased price levels are a result of a increase in ().
General Price
When the general price of goods and services increases, workers will ask for a (), although it takes time for them to recognize that the general price has increased and their () is lower. This is called ().
Wage Increase, Real Wage Rate, Sticky Wage Theory
When price level and wage rates grow at the same rate, then we follow a (), while if price rises while wage rate stays consistent, a () is used.
Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve, Short Run Aggregate Supply Curve
Firms will only increase wages when workers realize the real wage rate has fallen or they get higher profits. Otherwise, they just increase ().
Production
the long-run aggregate supply curve is a (), instead of being () like in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
Vertical Line, Upward-Sloping
The reason why the long run supply curve is vertical is because () does not depend on the ().
Natural Level Of Output, Price Level
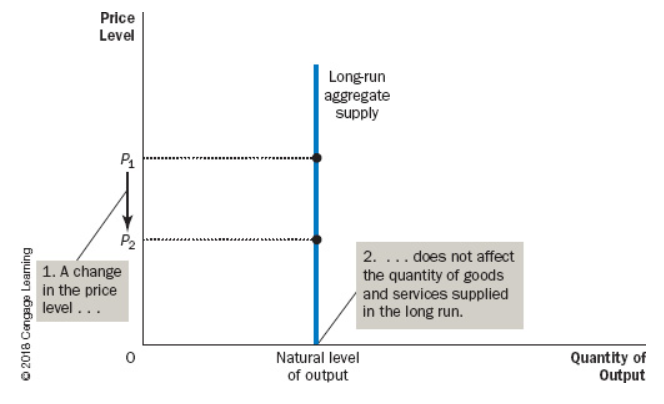
If () increases, both types of supply curves will increase, while if wage rate increases and natural level of output stays the same, short run supply would (), while long run aggregate supply would only see a () along the curve.
Natural Level of Output(Potential GDP), Shift Left, Movement
The following variables and factors of production which shift the aggregate supply curve are…
Labour, Capital, Technology, Natural resources, Expected Price Level
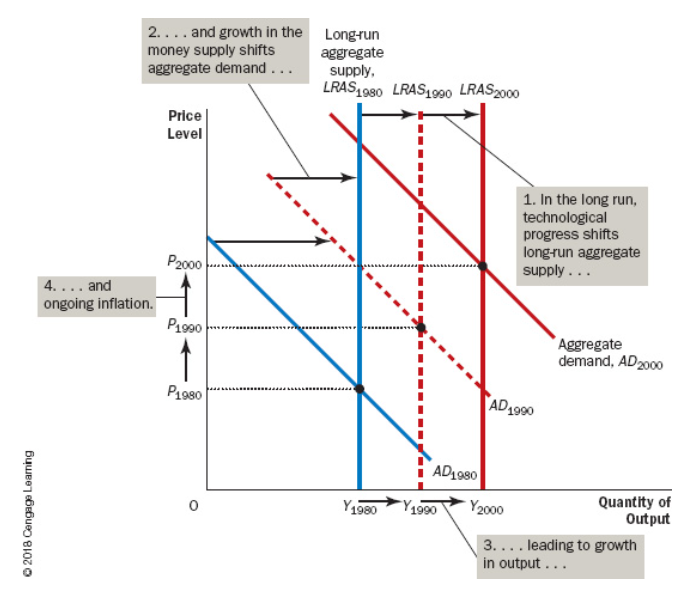
Only changes in () will directly change the real GDP.
Real Variables
Economic growth comes from an increase in (), while inflation comes from an increase in ().
Aggregate Supply, Aggregate Demand
The theory which explains why the short run aggregate supply curve slopes upwards is (), stating that the prices of goods change very slowly due to the costs of adjusting prices.
Sticky Price Theory
The theory which explains why the short run aggregate supply curve slopes upwards is (), stating that changes in overall price level temporarily mislead suppliers about what’s occurring in individual markets.
Misperceptions Theory