Fluid Mechanics L2 - Fluid Mechanics and Cardiovascular Terminology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Statics
F = 0
Dynamics
F = ma
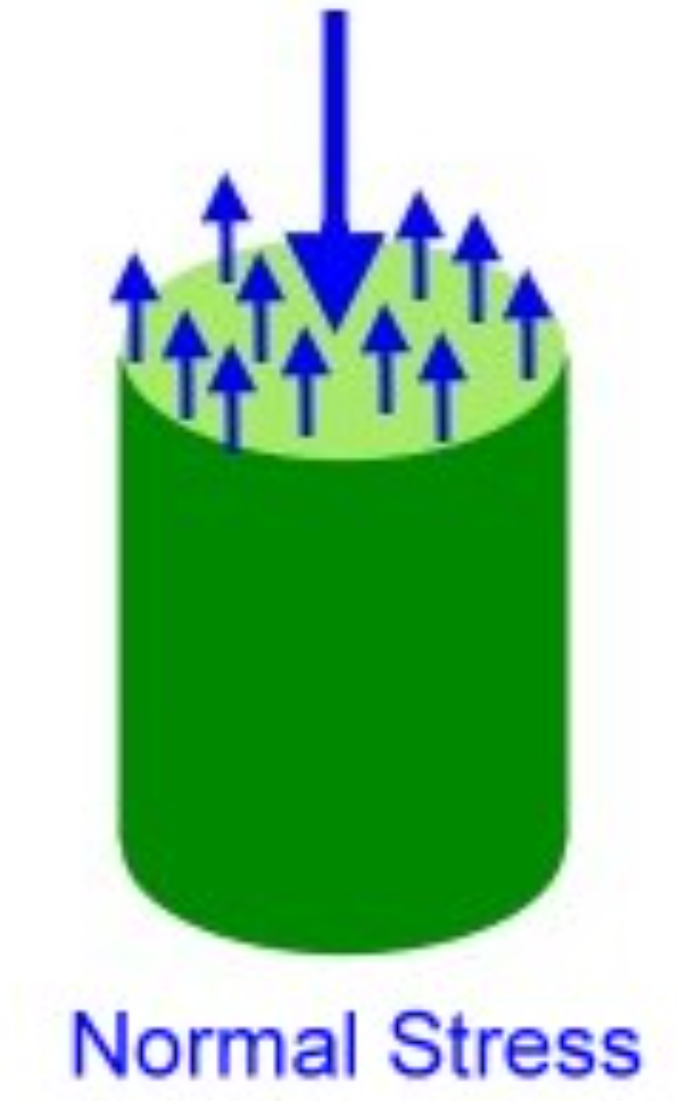
Normal Stress
σ (or pressure) = F/A
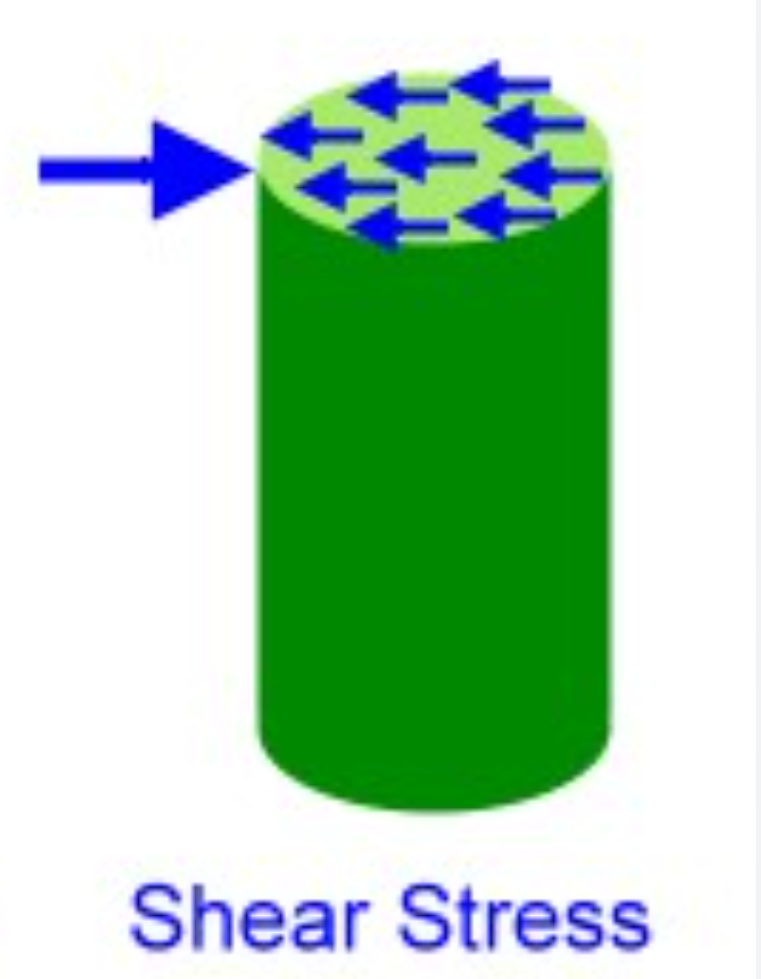
Shear Stress
τ
Fluid
Any material that deforms continually under the application of shear stress
How does a solid resist applied shear stress?
By deforming
What happens when a constant shear force is applied to solid
Solid eventually stops deforming at some fixed strain angle
What happens when a constant shear force is applied to fluid
Fluid never stops deforming and approaches a constant rate of strain
In a fluid at rest, the normal stress is called what?
Pressure
A fluid at rest is at a state of how much shear stress?
τ = 0
liquid have weaker/stronger cohesive forces than gases
Stronger
liquids form a ___________ indicated by _____________
Free surface; three lines
characteristic of liquid
Incompressible (unable to squeeze or compress)
characteristics of gases
Deformable and compressible
What is on free surface?
Atmospheric pressure
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
Two plate model
The fluid that is in contact with the top plate will move with the same velocity and move to the same displacement as the top plate
Viscosity
Resistance to flow; interaction between molecules
Viscous flow
Frictional effects are significant; consider friction
Inviscid flow
Neglecting viscous terms for simplification (no viscosity); no friction
Example of high viscosity
Honey
Example of low viscosity
Water, air
External flow
Unbounded; flows over a surface or object without being confined by solid boundaries all around it
Internal flow
Bounded by solid; fluid moving through a pipe or duct
Open channel flow
Flow where the fluid is bounded by a solid surface from below and has a free surface exposed to the atmosphere.
Laminar
Layered; lower velocity; highly viscous; modeled and predictable; ex: blood
Turbulent
Chaotic; higher velocity; lower viscosity; hard to model
Transitional
Flow that falls between laminar and turbulent flow
Reynolds number
Re = (density*velocity*diameter)/viscosity
dimensionless number
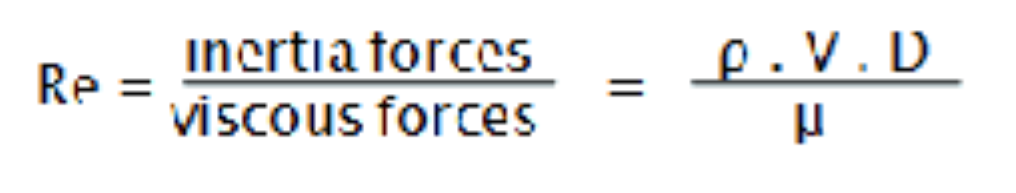
Forced flow
Pump; ex: heart or fan
Natural flow
Ex: heat dissipating
Is blood steady or unsteady?
Unsteady because heart pumping causes it to flow at changing velocities
Steady flow
Flow where fluid properties at any point in space do not change with time.
Unsteady flow
Flow where fluid properties at any point in space change with time.
Transient flow
Flow where fluid properties are changing over a temporary period of time.
Fully developed flow
When the fluid's speed and direction (velocity) pattern becomes constant and no longer changes as it flows
Period flow
A type of unsteady flow where fluid properties change in a repeating pattern over time.
What is 1, 2, 3-D flow characterized by?
Its velocity distribution and if it varies by one, two, or three dimensions
What are the different coordinates for 1, 2, 3-D flow?
Rectangular V(x,y,z) or cylindrical V(r,θ,z)
Steady flow entering a circular pipe:
Fluid flow at pipe surface is what and why?
0 due to no-slip condition
Steady flow entering a circular pipe:
At entrance, flow is what and why?
2-D because velocity changes in both r and z directions, not angular θ
Steady flow entering a circular pipe:
Fully developed flow is what and why
1-D since the velocity varies in radial (r) direction but not angular (θ) or axial (z) direction - symmetric about the axis of the pipe
Why do we need to study fluid mechanics as BMEs?
1/3 deaths in US due to cardiovascular disease (1.5 times cancer)
Our body is 65% water
Purpose of blood circulation
Transport
O₂ and CO₂
Communication
Growth factor signals
Heat Exchanger
Protection
Immune system
What does the left side of the heart do?
Takes blood all around the body
List order of blood flow
Left side of heart → oxygenated blood → systemic arteries → capillaries → systemic veins → deoxygenated blood → right side of heart → lungs