Chapter 8 Color Vision - 9/16/24 lecture
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
From 540 nm on there is no wavelength discrimination
Where and what is the neutral point?
It’s where they perceived as white (496 nm)
Where is the point of best wavelength discrimination located for dichromats?
At the neutral point
What is the wavelength with the perception of least saturation?
570 nm
Draw the saturation discrimination chart
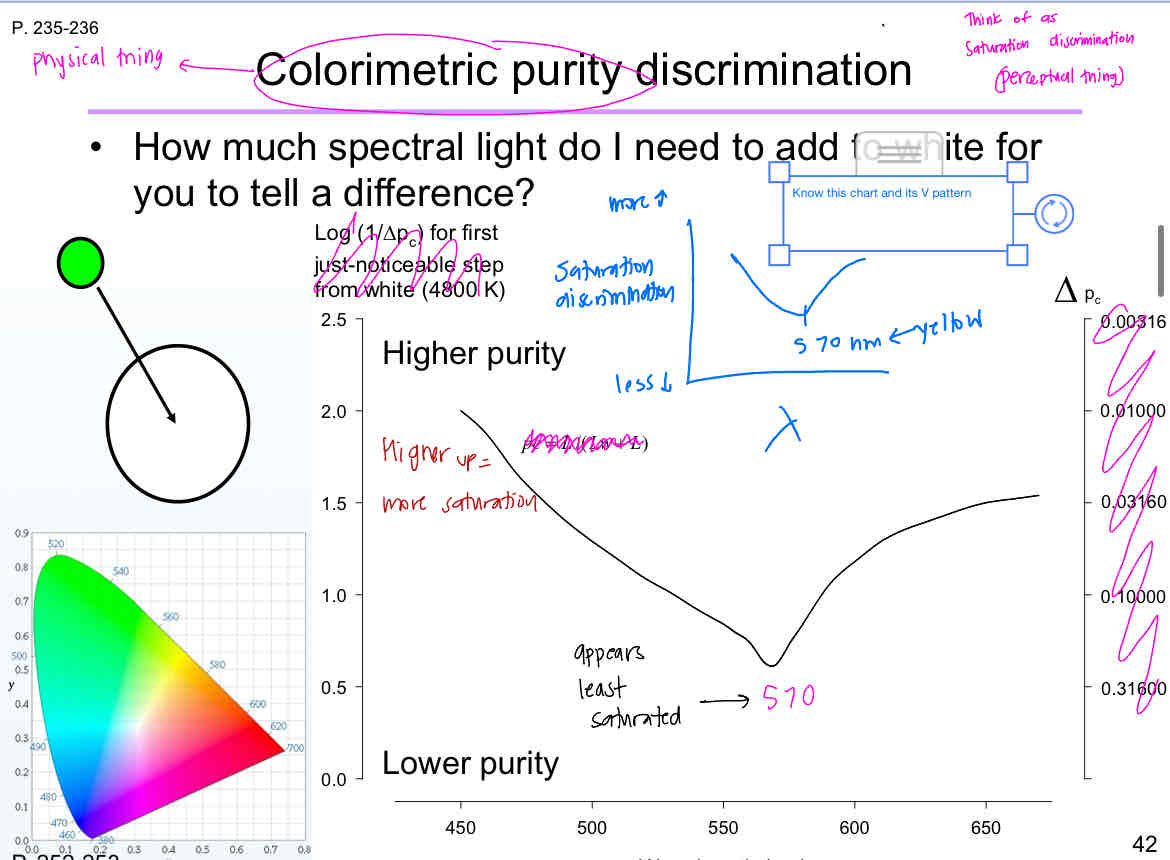
The point of worst saturation discrimination is at which point?
The neutral point
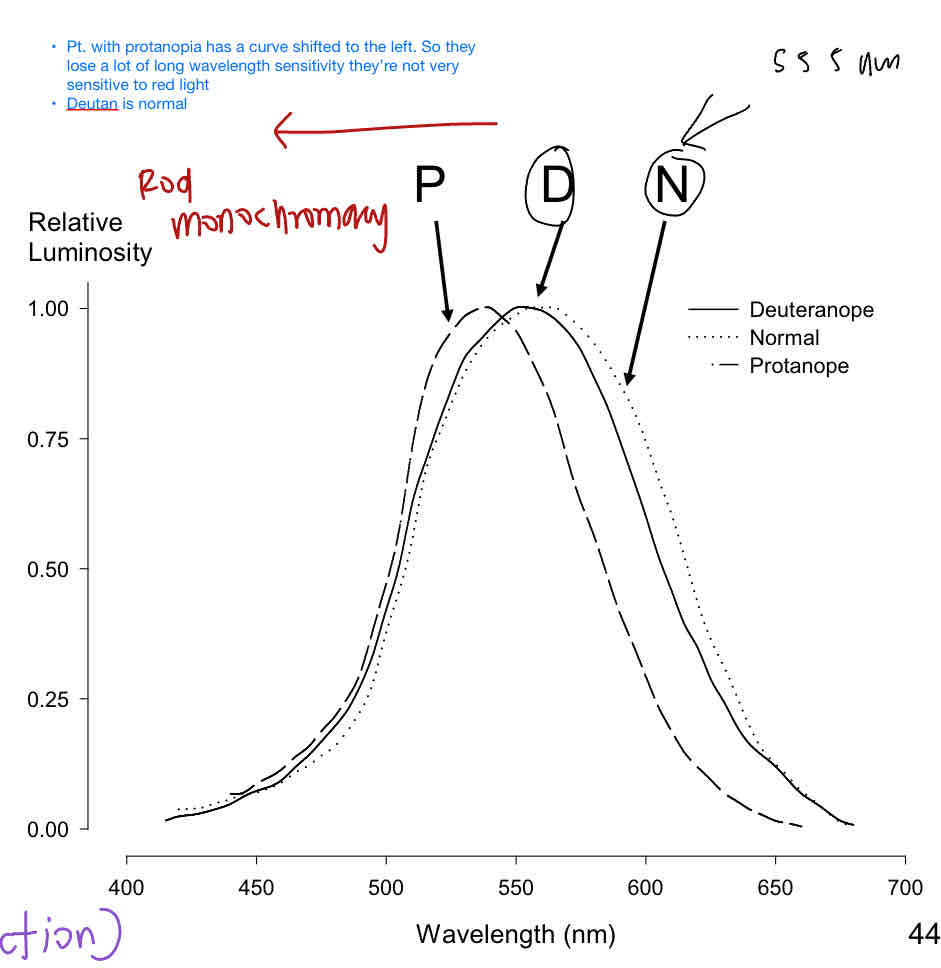
Luminosity: Patients with protanopia have a curve shifted to the left. They lose a lot of long wavelength sensitivity so they’re not very sensitive to which color?
Red
Which play a role in the luminosity function?
A. S
B. M
C. L
Only M and L. S is not involved in your brightness perception
Who has worse red light sensitivity?
A. Patients with protanopia
B. Patients with Rod mochoromacy
Rod monochromacy
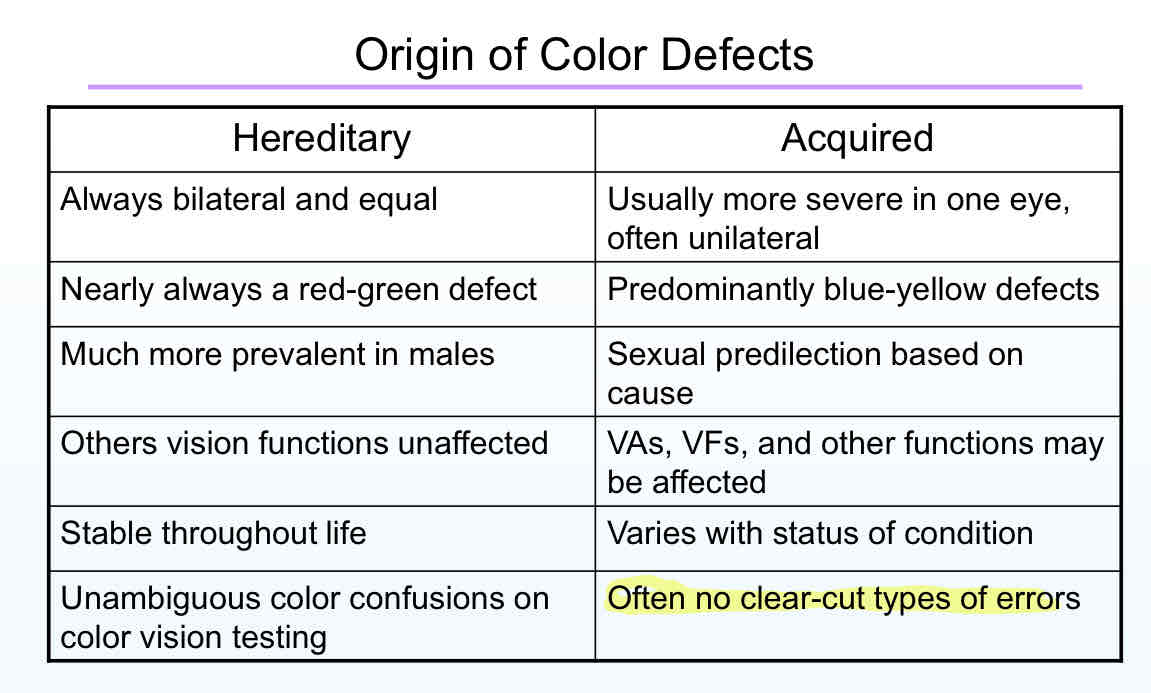
Acquired color defects are more often
A. Blue-yellow
B.red-green
A. Blue-yellow
Red green is almost always congenital x linked
What is the Sloan Achromatopsia test used for?
Rod monochromacy
T/F: people with normal color vision will have a harder time with the Sloan achromatopsia test
True
What’s the difference between isomers and metamers
Isomers: two lights that look the same and are physically the same (referring to SPD) spectral power distibutions
Metamers: two lights that look the same but are physically different
What is illuminant C?
The gold standard type of light for color vision test
The anomaloscope is the gold standard testing for which color deficiency?
Red-green
What is your task in the anomaloscope?
Patients need to make a metameric match
the light wil look the same but will be physically different
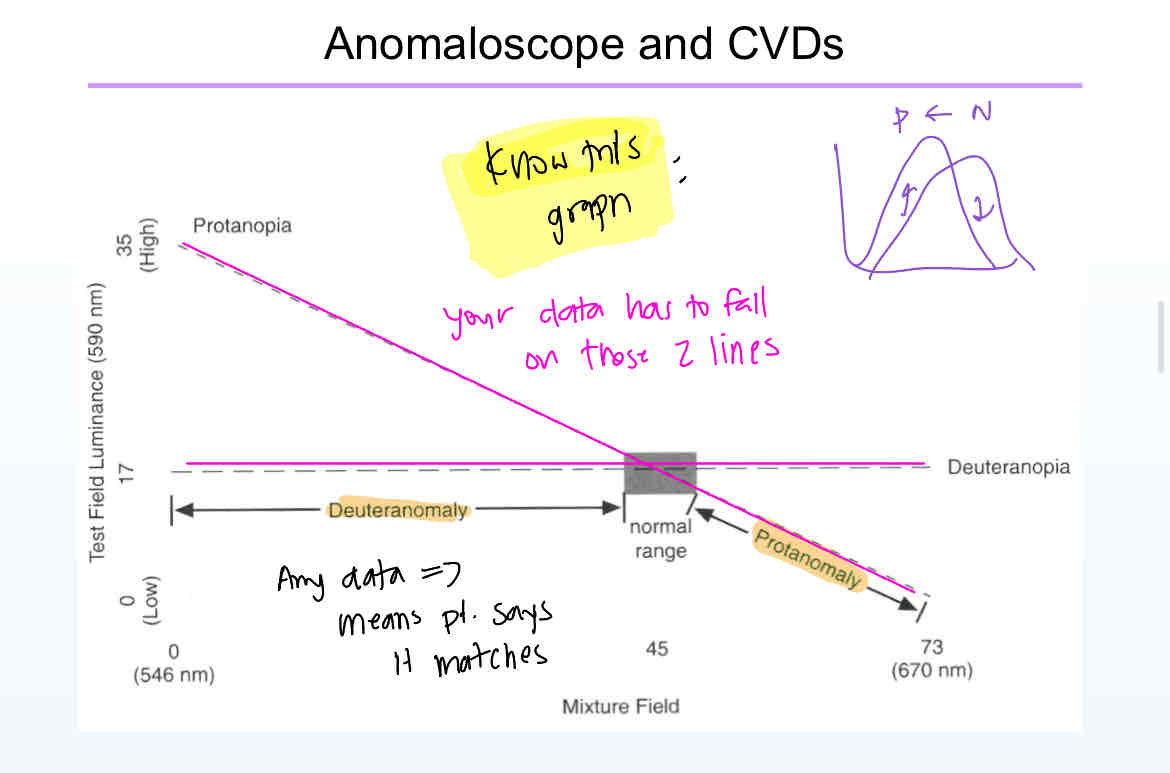
It uses 546 nm and 670 nm in an additive mixture to match a 589 nm light
D’s and P’s have a shared confusion line on the spectral locus between which wavelength ranges?
540 nm and 700 nm
On an amaloscope, reds are perceived as ____ and greens are perceived as ______ for protanopes. That’s why their curve is a diagonal line
Red: dark
Green: bright
Patients with deuteranopia, has the exact same luminosity function as a color normal, so their line appears _____
Flat
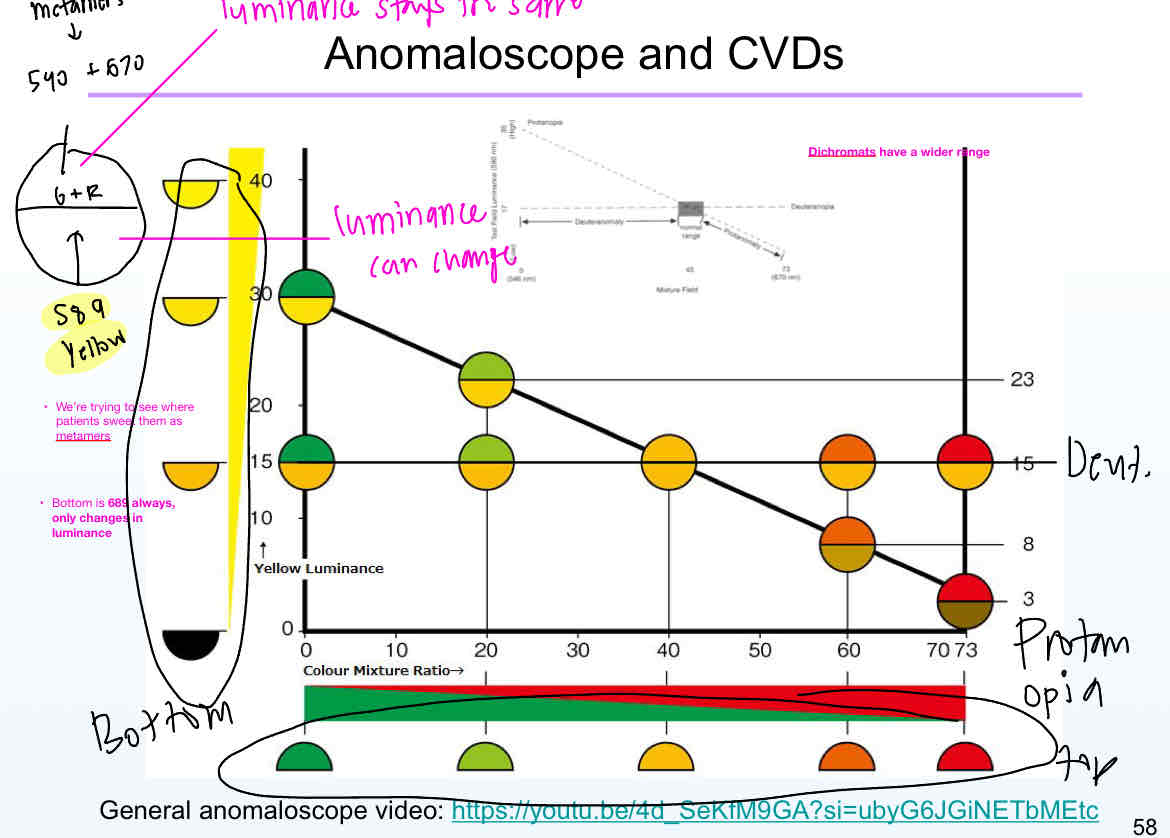
T/F: a person with DA can have a very tiny matching range and still be color deficient
true because that match range is shifted to the left
T/F: Your range gotta stand the entire line to be normal
True
What’s the difference between deuteranopia and protanopia?
They are both types of red-green color blindness that makes it difficult to distinguish between red and green. The main difference is that deuteranopia is caused by missing green cones, and protanopia is caused by missing red cones
How would a high color temperature light appear?
Blue ish white
What 3 factors are important in valid color light source?
Color temperature, color rendering index, and illuminance level
What is the ideal color temperature for a light source?
6000 - 7000K (blueish-white)
What is the ideal color rendering index?
90 out of 100
What is the ideal illuminance level for a valid light source? (Tested on)
Greater than or equal to 500 lux
Do we trust the Ishihara test to do the diagnosis?
No. It’s good at screening but not good at diagnosis
T/F: The HRR psesudochromatic plate book that we have has both red/green and blue/yellow screening. On top of the screening, it’s considered reliable for diagnosis.
True. It can diagnose not perfectly but better than Ishihara.
In terms of screening ability, its as good as Ishihara
Would a CVD see something in a hidden digit test?
Yes. They would see a 2 while a normal CVN wouldn’t see anything

T/F: the fewer the matches in the anomaloscope, the worse your color vision false
False, fewer = better
On the anomaloscope, DA/PA range can only go up to _____
72
T/F: HRR is better at determining severity than Ishihara
True
What are the different types of plates in the Ishihara test
Vanishing plate, Transformation plate, Hidden digit plate,
What is the vanishing plate of the Ishihara test used for?
A. Screening
B. Diagnosing
C. Both
A. Screening
Cannot diagnose because can’t tell the difference between protan and deutan. It’s job is just to catch either one
What plates are on the HRR?
Vanishing plates and diagnostic plates
(Simpler than Ishihara (4 types of plates))
Tritans have less color crossovers
Because there’s less color space for them to cross through
red green dichromats have much more color space they can jump through
What disease follows Kollner’s rule?
Cataracts
Kollner’s rule is an _______ deficiency
A. Acquired
B. Congenital
A. Acquired
It’s a problem at the level of receptors or earlier: vitreous, lens, cornea
Diabetes are affected in the _____ retina
Middle
Does diabetes follow the Kollner’s rukle?
No
According to Kollner’s rule, a problem at levels post-receptoral usually see what kind of color defect?
Red/green (deutan/protan)
Does glaucoma follow Kollner’s rule?
No, its caused by ganglion cell loss, after photoreceptors and were not getting a red green defect
In summary, which two diseases don’t follow Kollner’s rule?
Diabetes and glaucoma
But cataracts do
Glaucoma leads to what color losses?
Blue-yellow
Describe the testing sequence
PIP (HRR) test
Test both red/green and blue/yellow
Farms worth D-15
Test both red/green and blue/yellow
Fail if more than 2 crossovers
Other tests
Is color naming reliable?
No
Acquired vs hereditary color deficiencies