rates of reaction
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on several factors, including temperature, reactant concentrations (or pressures), surface area of solid reactants, and the presence or absence of a catalyst. One method to measure the rate of a reaction is by determining the rate at which a product, such as a gas, is formed. In this practical, you will investigate how the concentration of hydrochloric acid affects the rate of reaction when added to magnesium. You will measure the rate of reaction by observing the rate at which hydrogen gas is produced.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
aim
investigate the relationship between concentration, temperature, surface area and rate of reaction
equipment
hydrochloric acid
measuring cylinder
conical flask
pipette
delivery tube
delivery tube and bung
trough of water
clamp and stand
magnesium
stop clock
thermometer
ice/water bath/bunsen burner
steps (concentration)
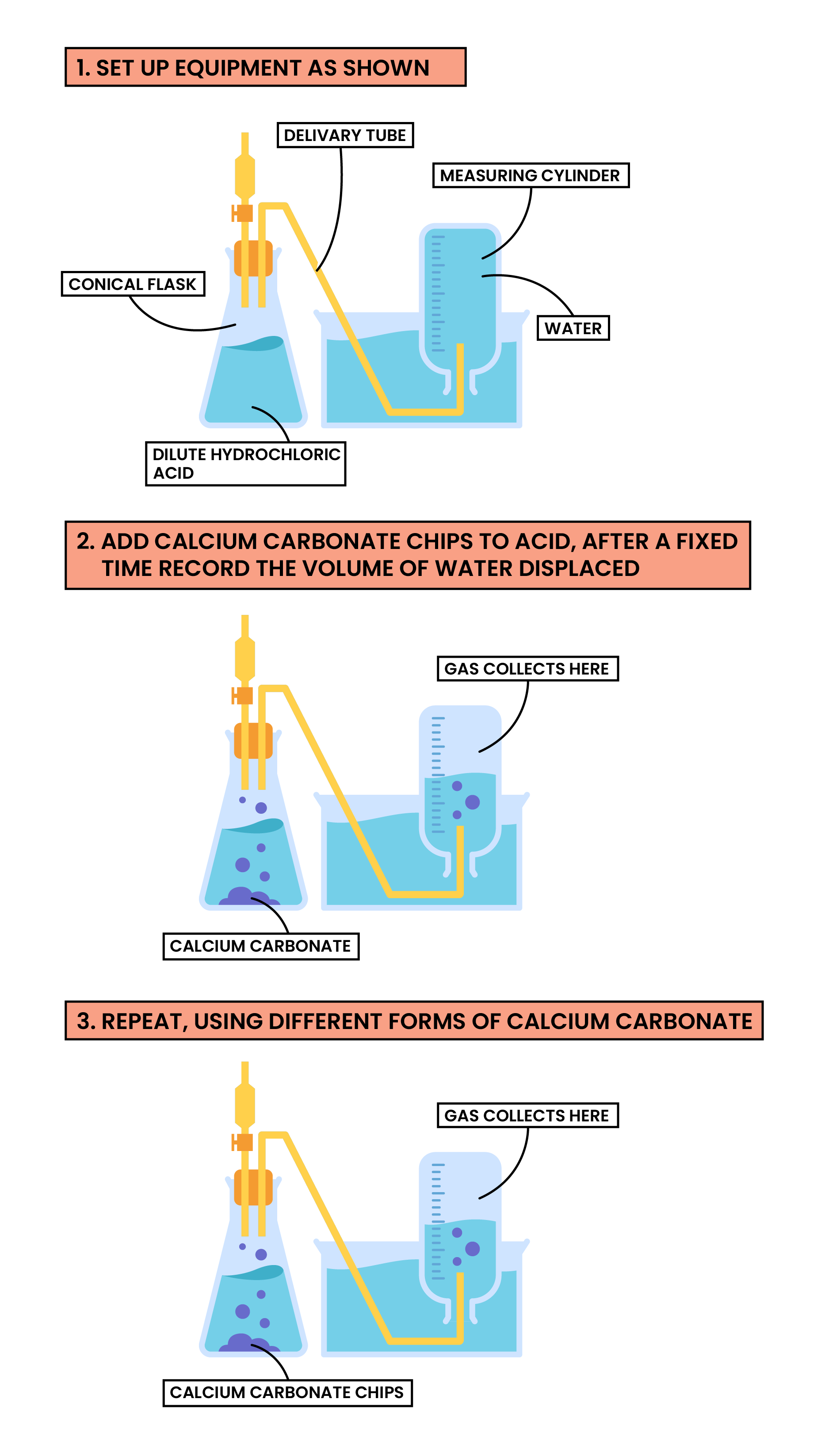
comparing 2 and 1mol/dm³ of hydrochloric acid
measure 50cm³ of one in a measuring cylinder using a pipette
pour hydrochloric acid into a conical flask with a bung and delivery tube
push the measuring cylinder into the trough and slowly lower the top of it into the water to eliminate the risk of air bubbles
clamp the measuring cylinder in place
place the delivery tube underneath the cylinder
add the magnesium to the conical flask, start the stop clock, put the bung immediately on the top of the conical flask
water is forced out of the measuring cylinder as gas is produced
record change in water every time
repeat for other concentration of hydrochloric acid
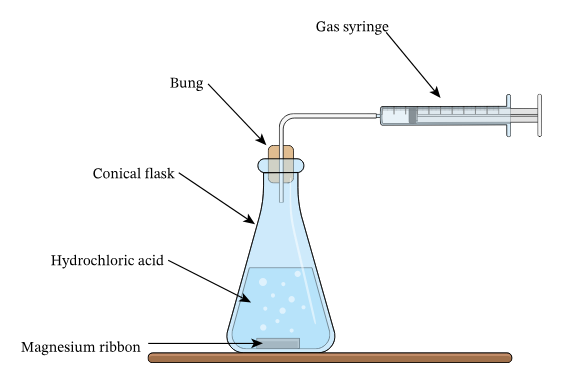
alternative (concentration/surface area)
use a gas syringe connected to delivery tube and measure volume of gas collected every 10 seconds
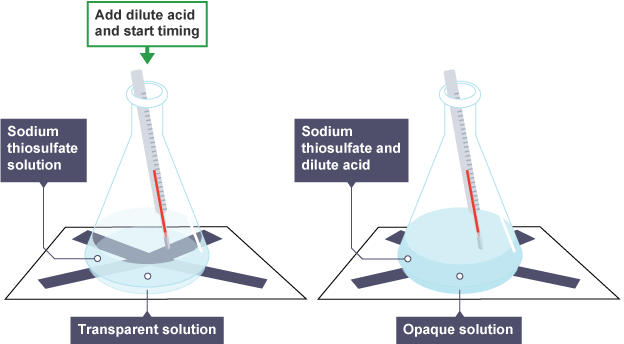
steps (temperature)
using a measuring cylinder, add 50 cm3 of dilute sodium thiosulfate solution to a conical flask
place the conical flask on a piece of paper with a black cross drawn on it
using a different measuring cylinder, add 10 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid to the conical flask. swirl the flask to mix its contents, and start a stop clock
look down through the reaction mixture. when the cross can no longer be seen, record the time on the stop clock
measure and record the temperature of the reaction mixture, and clean the apparatus as directed by a teacher
repeat steps 1 to 5 with different starting temperatures of sodium thiosulfate solution.
steps (surface area)
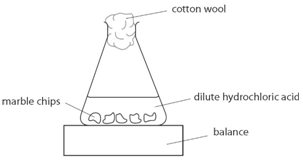
prepare 3 sets of marble chips, one for each size. adjust the numbers so each set has the same mass
add a measures volume of dilute acid to the conical flask. plug flask with cotton wool
place flask and marble chips on balance and record mass
remove cotton wool and add the chips to the acid, start the stop clock
record the mass each 30s