1.03 Ocular surface - cornea, sclera and conjunctiva
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
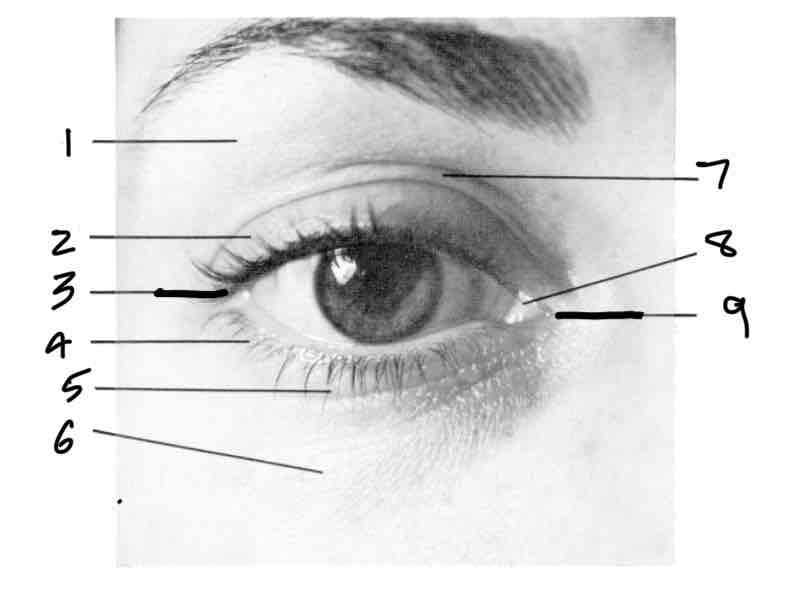
Label
Orbital portion of lid
Tarsal portion of lid
Lateral/temporal canthus
Tarsal portion of lid
Inferior palpebral furrow
Orbital portion of lid
Superior palpebral furrow caruncle
Medial/nasal canthus
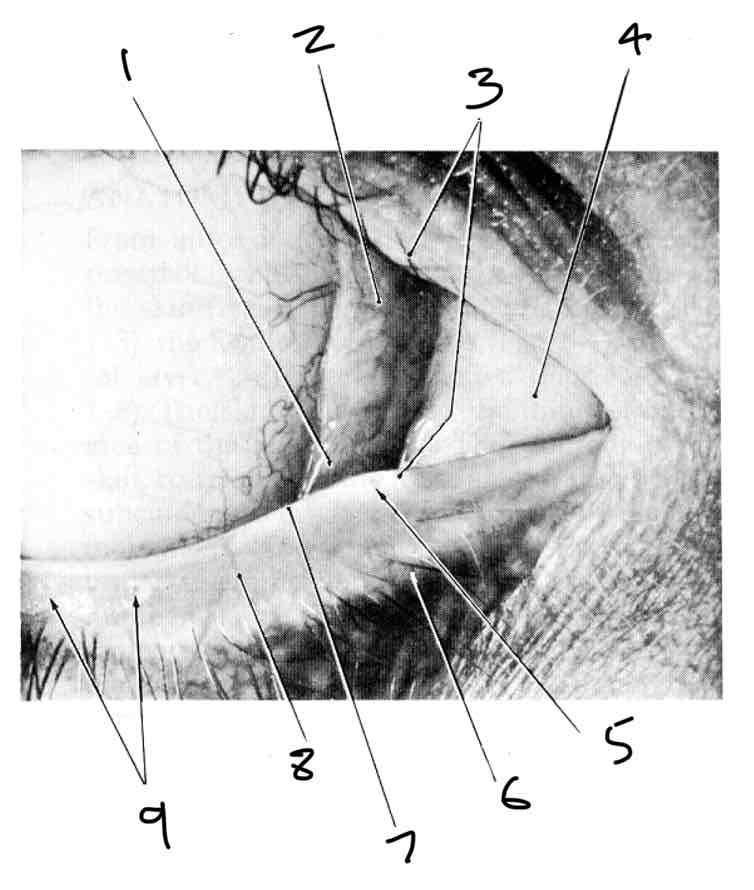
Label the medial canthus
Lacrimal lake
Semilunar fold
Lacrimal papillae
Lacrimal caruncle
Lacrimal punctum
Front edge of lid Superior
Rear edge of lid
Gray line
Orifices of tarsal glands
What dees lid margin contain
Cilia (lashes)
What is the ocular surface
The ares between the open eyelids thats exposed to the environment
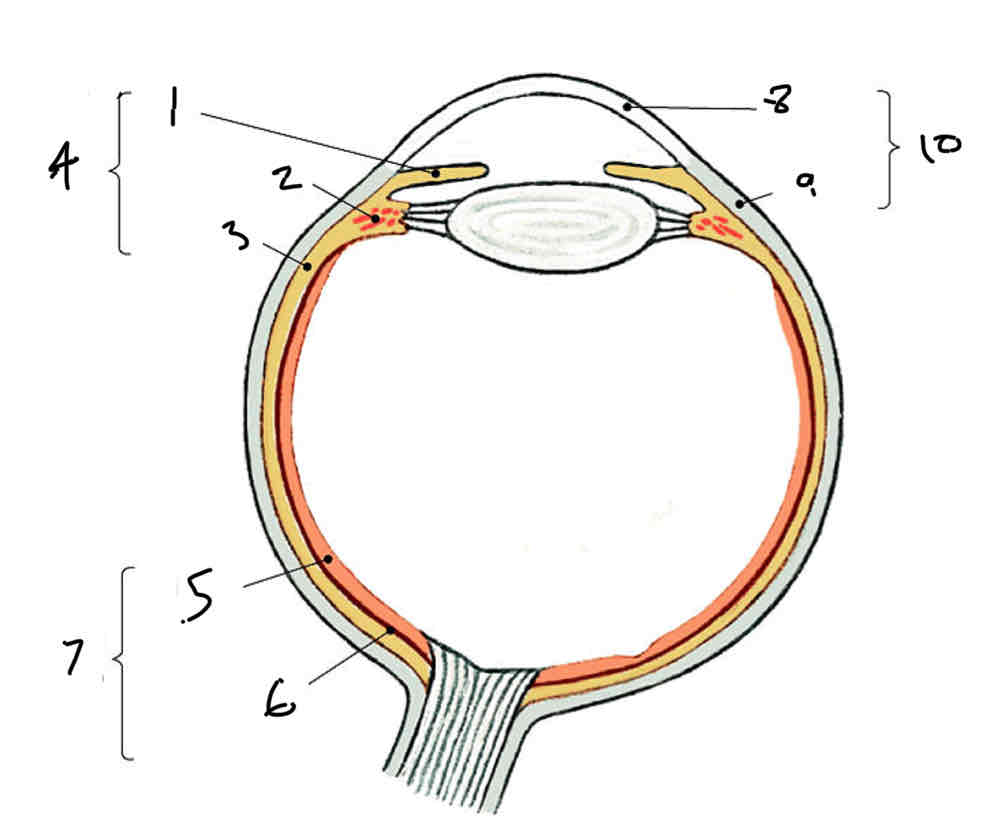
Label
Iris
Ciliary body
Choroid
Vascular tunic
Neural part
Pigmented part
Neural tunic (retina)
Cornea
Sclera (fibrous tunic)
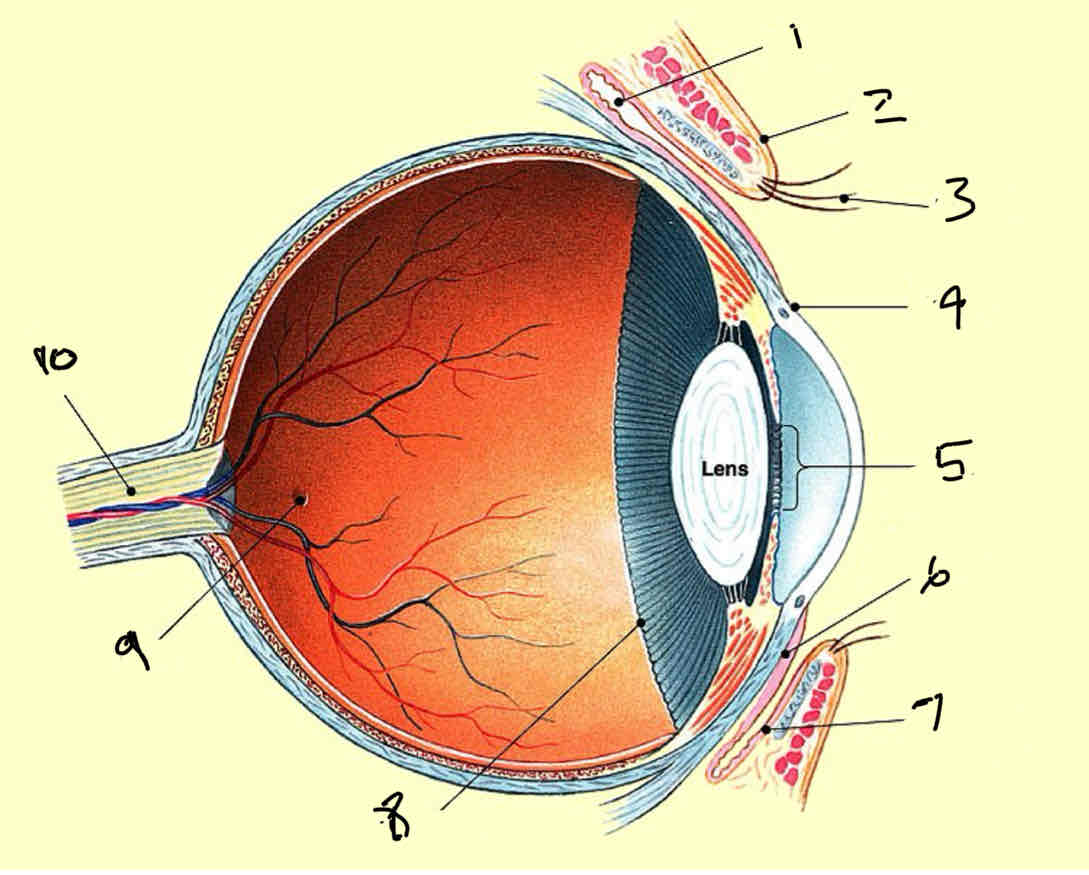
Label
Fornix
Eyelid
Eyelash
Limbus
Pupil
Ocular conjunctiva
Palpebral conjunctiva
Ora serrata
Focea
Optic nerve
Functions of the sclera

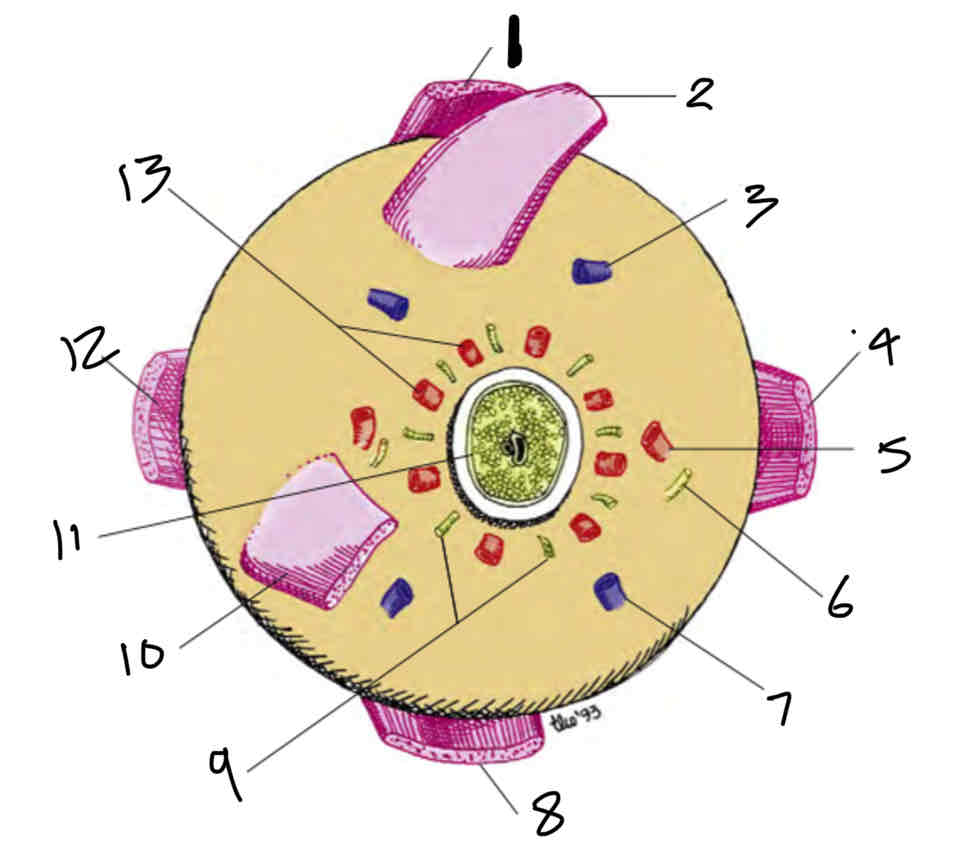
Label the posterior view of the sclera
Superior rectus muscle
Superior oblique muscle
Vortex vein
Medial rectus muscle
Long posterier ciliary artery
Long ciliary nerve
Vortex vein Medial rectus
Inferior rectus muscle
Short ciliary nerves
Inferior oblique muscle
Optic nerve
Lateral rectus muscle
Short posterior ciliary arteries
Where in the eye is the sclera the thickest
At the back
Where is the conjunctiva located
Overlies the sclera and the underside of the eyelid
Not part of the same tunic of sclera
Functions of the conjunctiva

What is the conjunctiva composed of
Loose areolar connective tissue (lamina propria containing a rich blood supply with a covering of epithelial cells
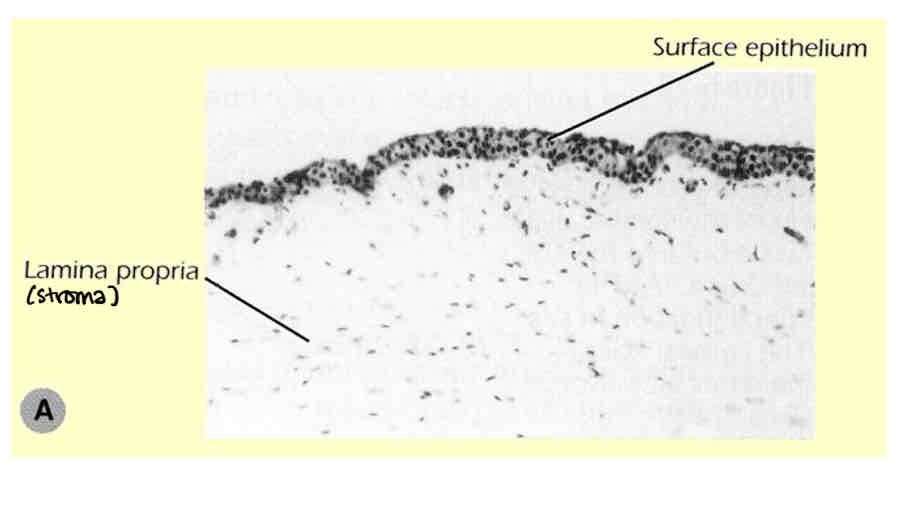
Special features of the conjunctiva
Can renew itself if damaged (sclera cant)
Many blood vessels - provides metabolic needs for other structures of the eye
Why is the fornix region of the conjunctiva uneven
So fornix can stretch
Where are most goblet cells located
In the fornix region of the conjunctiva (bular and palpebral)
What happens to the number of functional goblet cells as you age
Decrease
What does the bulbar conjunctiva cover
Starts at the limbus and covers all the visible area of sclera
Ends at fornicies (superior and inferior)
What does the palpebral conjucntiva cover
Starts are fornicies and covers the entire internal surfaces of the eyelids
Ends at the eyelid margins
What is the fornix conjunctiva
The transition region between bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva
There are 2 fornix regions superior and inferior
Bulbar conjunctiva dimentions in order
Temporal > medial, superior = inferior
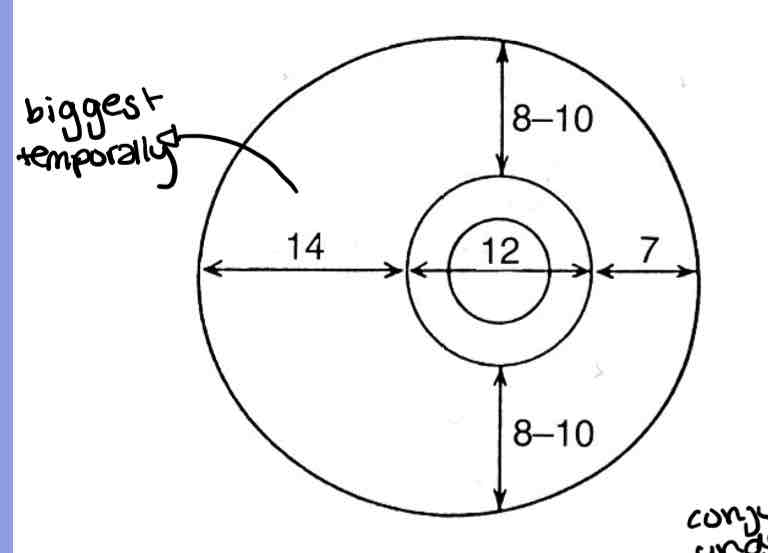
Palpebral conjunctiva dimentions in order
Lateral > medial, superior > inferior
Does the bulbar conjunctiva have blood vessels
No
You can see the underlying scleral/episcleral blood vessels
Why is there no conjunctiva over the cornea
Too loose and would reduce vision
What are the palisades of vogt
Finger like processesRadial ridges/folds at the limbus
Contain stem cells to regenerate corneal epithelium
Loops of capillaries run through the palisades and terminate at the margin of the cornea
What does anterior ciliary artery supply
The anterior region of the eye (conjunctiva, sclera, iris and ciliary body)
and forms the episcleral arteries
What does the episcleral venous plexus do
Drains blood from the limbal region
What is present at the scleral limbus
Loops of capillary blood vessels which terminate at the limbus and dont enter the transparent cornea
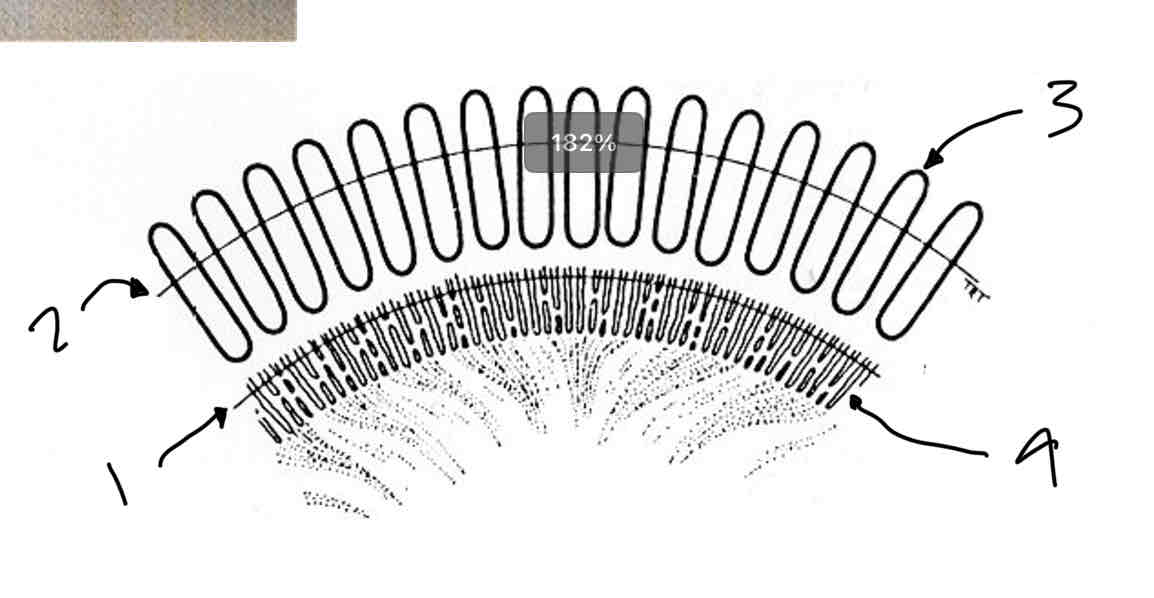
Label the limbus
Corneal limbus
Scleral limbus
Palisades of vogt
Finger like processes
What is the ‘normal’ appearance of the palpebral conjunctiva
When the eyelid is inverted if its light it is healthy

Functions of the cornea
Image formation
allows light to enter the eye
Acts as a positive (convex) refracting surface
Maintains image quality by providing a smooth, renewable ocular surface
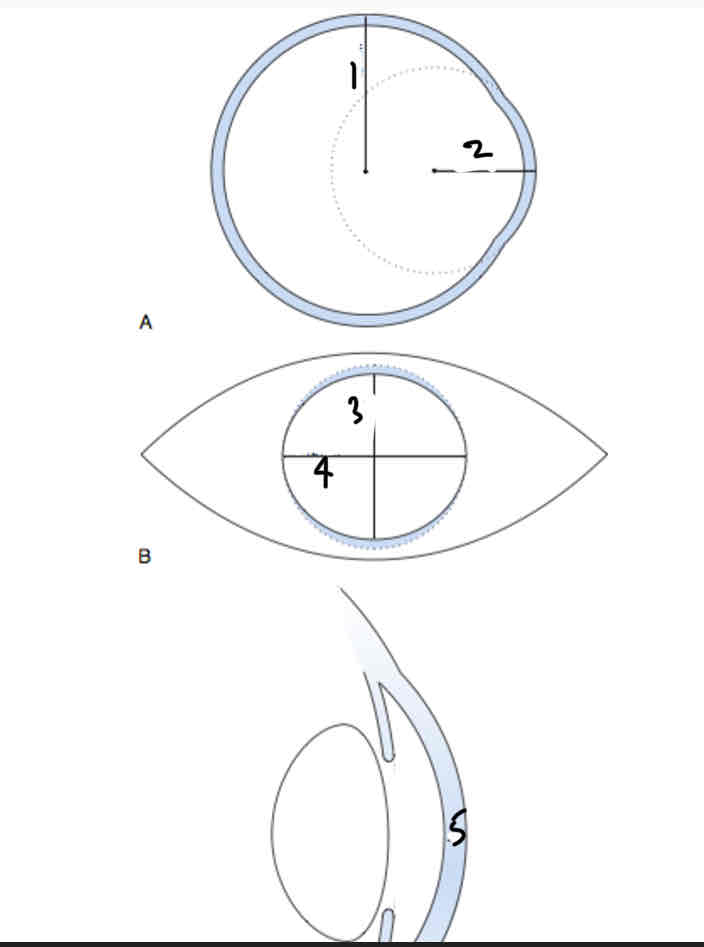
Dimensions of the cornea
12mm
8mm
11mm
12mm
.53mm
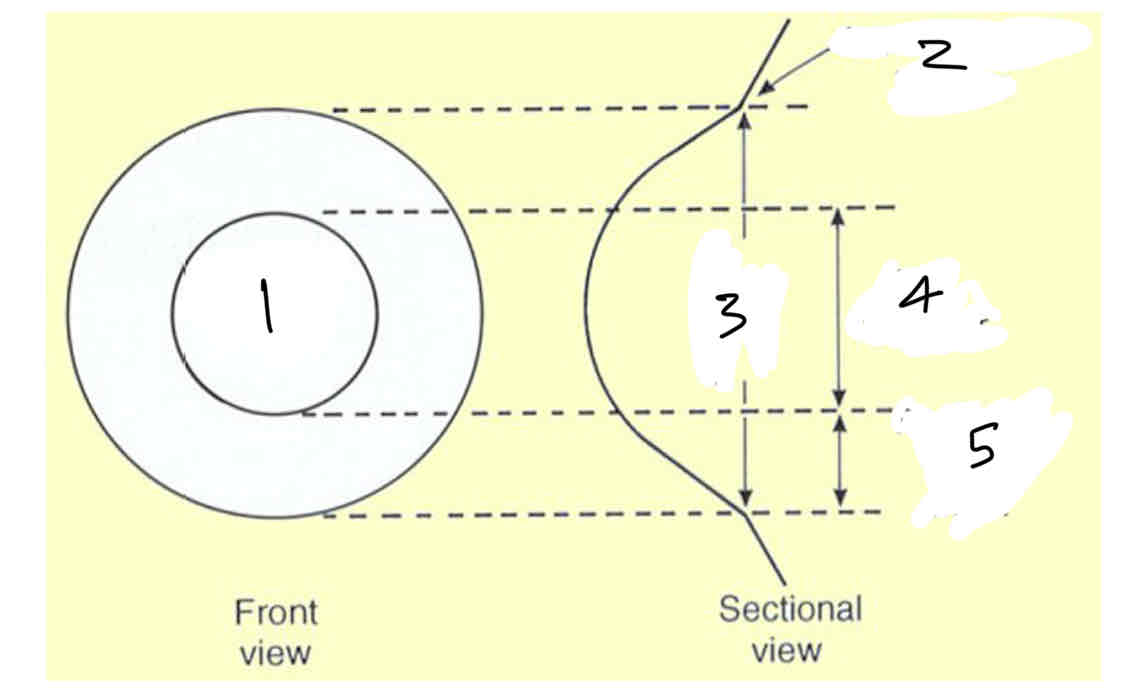
Label the zones of the cornea
Optical zone
Corneal scleral junction
Diameter chord
Capdiameter
Pripheral zone width
Approximate diameter of the corneal zones
central optical
Paracentral (mid)
Peripheral
Limbal
Central optical 3-4mm
Paracentral (mid) 4-7mm
Peripheral 7-11mm
Limbal 11-12mm
Characteristics of the corneal zones
central optical
Paracentral (mid)
Peripheral
Limbal
central optical - most spherical, symmetic - overlies pupil
Paracentral (mid) - gnerally spherical but flatter than central zone
Peripheral - cornea flattens the most here
Limbal - next to the scleral sulcus and the sclera
The optical powerr if the cornea is determined by… Therefore…
Its curvature
Therfore power varies acoss the corneal surface
Lowest radius of curvature is _ and gives the _ power
At the centre
Greatest power (43D)
Highest radius of curvature is _ and gives the _ power
At the periphery
Lowest powerr (37D)
Where is the sclera the thinnest
Anterior to the equator of the eye
List the Layers of the sclera
Tenons capsule/Fascia Bulbi
Episclera
Scleral stroma
Lamina fusca
Decribe the tenons capsule
Its a connective tissue layer covering the eye from limbus to optic nerve - collagen bundles radial from limbus
Lies between conjunctiva and episclera at the limbus (connecting external and interal)
Contains no blood vessels
Describe the episclera
Most external layer of the sclera
Loose vascularied surface layers of sclral connective tissue
Collagen bundles circumferential
Describe the scleral stroma
Thickest part of the sclera
Layers of collagen fibres as in the cornea but much less regular and unevenly spaced so opaque
What is the limbus
Region of transition from cornea to sclera/conjunctiva
Opaque to transparent
Its external part involves bulbar conjunctiva and its interal part involves the anterior angle
What is limbal conjunctiva formed by
An epithelium and a loose connective tissue stroma
What is limbal stroma composed of
Scleral and corneal tissues that merge
Conjunctival stromal vessels form what
Peripheral corneal arcades which extend anteriorly to termination of bowmans layer
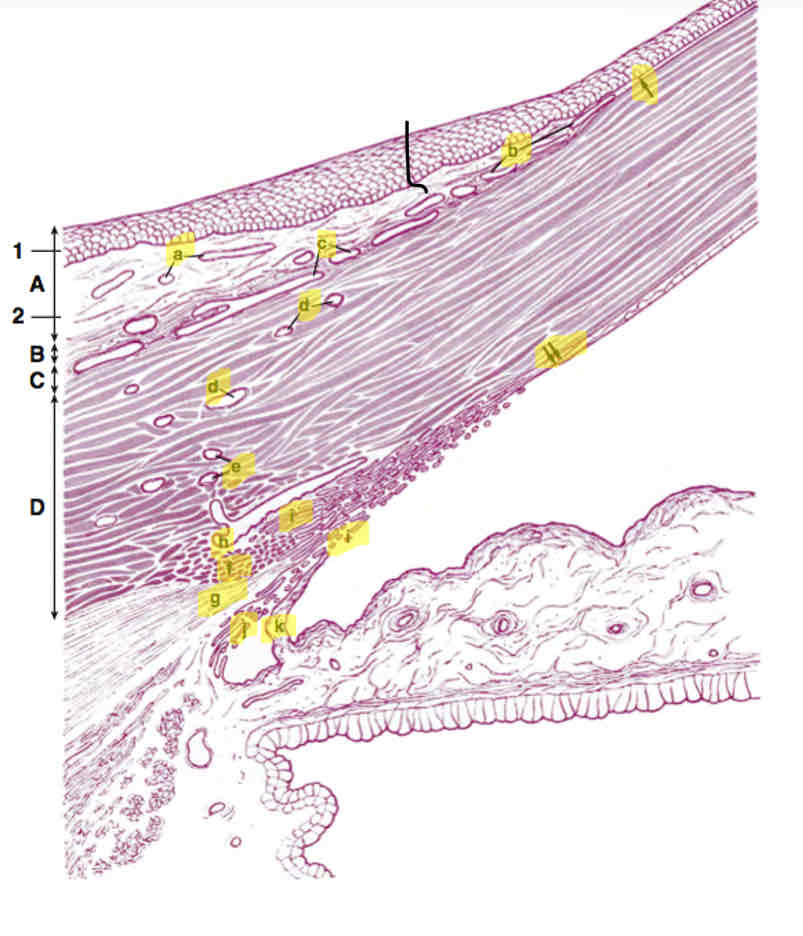
label Anterior angle
A. Limbal conjunctiva
a. Conjunctivaal stromal vessels
B. Tenon capsule
b. Peripheral cornealarcades
C. Episclera
c. Episcleral vessels
D. Limbal stroma
d. Vessels forming intrascleral plexus
e. Vessels forming deepscleral plexus
f. Collagen fibres (scleral spur)
g. Ciliary muscle
h. Schlemms canal
i. Trabecular meshwork
j. Uveal meshwork
k. Iris process
1.epithlium
2.loose connective tissue stroma
Arrow. Bowmans layer
Double arrow. Decements membrane
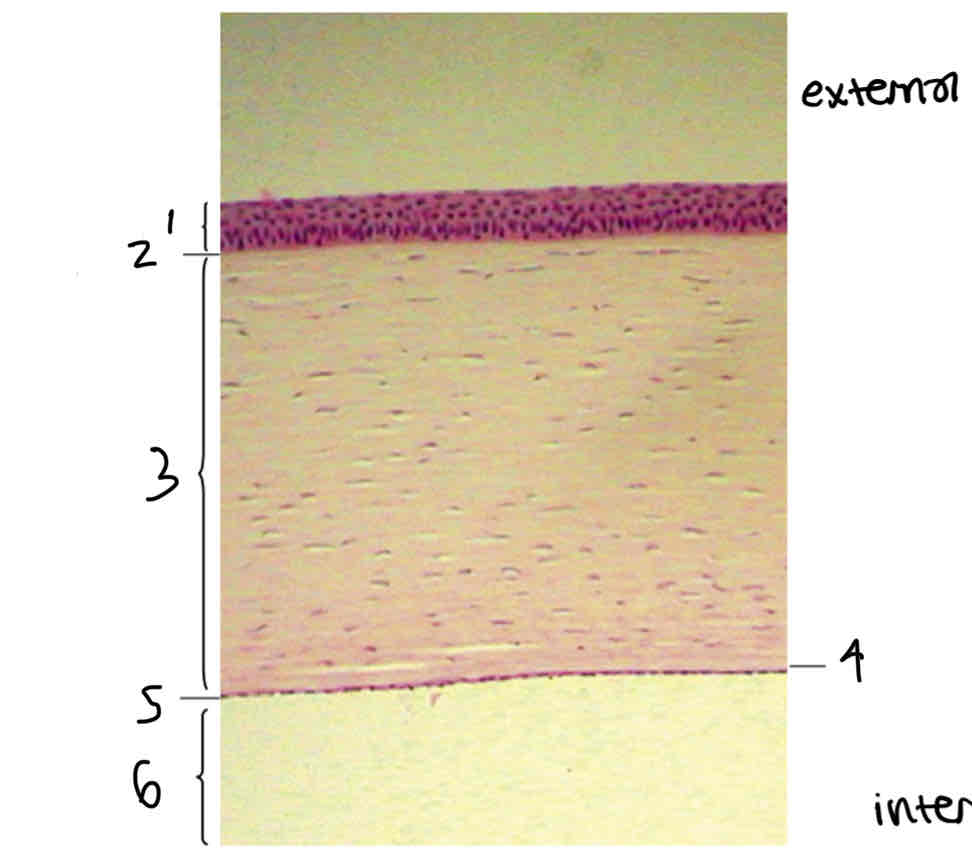
Label layers of cornea
Corneal epithelium
Bowmans layer
Corneal stroma/substantia propia
Decemets membrane
Corneal endothelium
Anterior chamber
Which layers of the corneal are made of collagen
Bowmans kayer
Corneal stroma
Decemets membrane
What is the most external layer of the cornea
Epithelium
What types of cells make up the corneal epithelium
Structure of corneal epithelium
Stratifed squamous
6 cells thick columnar basal cells Rest on a thin basement membrane
Squamous surface cells are removed by blinking and replaced by cells underneath
Cells migrate from basal to to surface layer, changing shape as they do
Renewal of cells in the corneal epithlium
Cells at the edge of the cornea (limbus) divide and migrate into the cornea to form basal cells.
Basal cells migrate from basal layer to surface layer and transform/change shape into wing cells and then squamous cells
Squamous surface cells are removed by blinking and replaced by cells underneath
Basal cells → wing cells → squamous cells
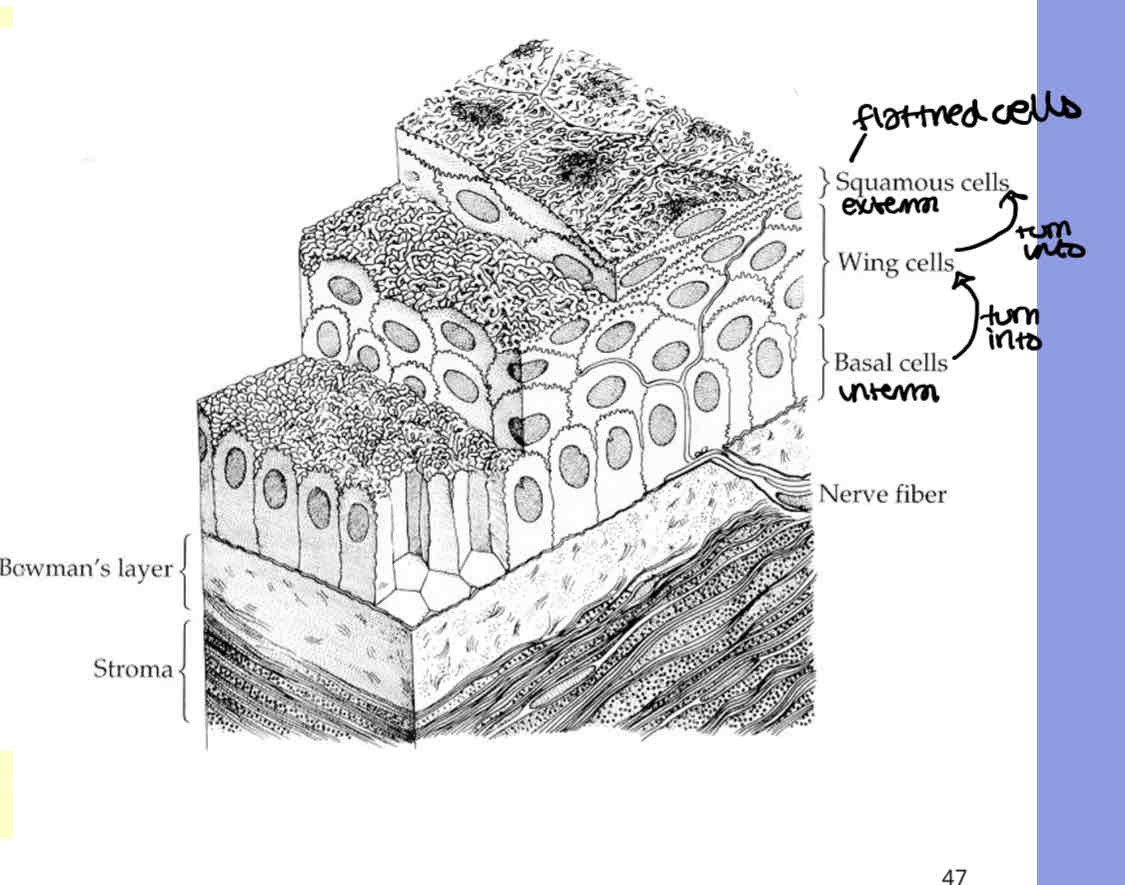
Label the cells in the corneal epithlium
Squamous cells
Wing cells
Basal cells
Basement membrane
bowmans layer
Why is it easier for the limbus to regenerate cells compared to the cornea
Better blood supply
Function of the corneal epithlium
Renewable barriers to water movement into the cornea
What is bowmans layer made of
A dense meshwork of interwoven collagen fibrils (connective tissue)
What makes corneal stroma transparent
Regular arrangement of collagen fibrils
75-80% water to ensure a fibre arrangement that supports transparency
what type of cells is the corneal endothelium made of
Simple cuboidal epithelium
It is a single layer of metabolically active cells
Regular arrnagement of hexagonal cells
Functin of the corneal endothelium
- Active pumping (active transport) of water out the corneal stroma in order to maintain the required level of water for corneal transparency to keep the regular arrangement
- allows enterence of nutrients from aqueous
- ionic pumps - high metabolic activity
How does the corneal endothelium maintain a high metabolic acitivity
Gets its supply of energy by diffusion as theres no blood vessels running through the endothelium
How can we view the corneal endothelium
Specular reflection using a slit lamp biomiscroscope
Function of decemets membrane
Sitck endothelium to stroma
How does decemets membrance change as you age
Becomes thicker
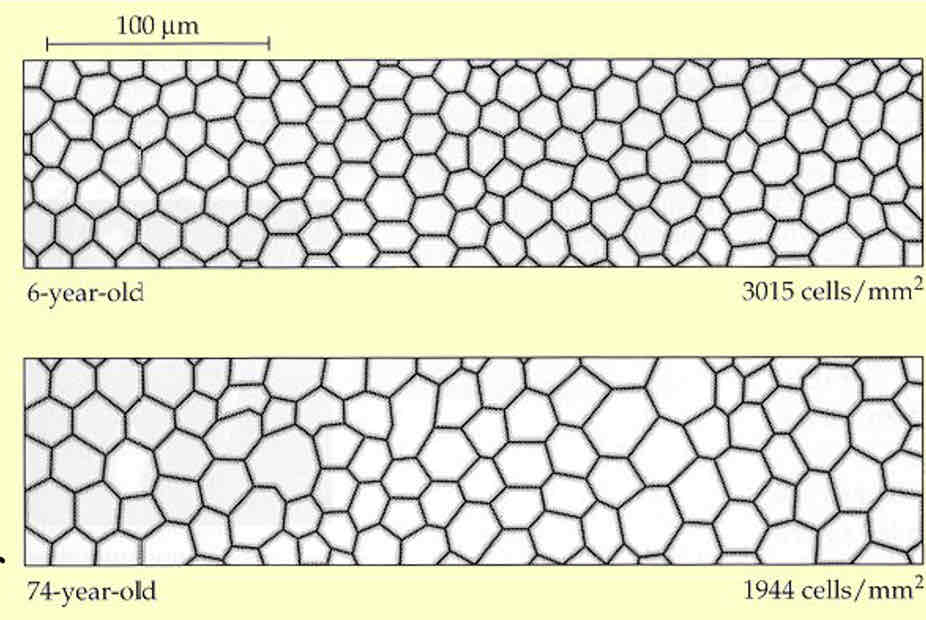
How does endothelial cell layer of the cornea change with age
Endothelial cell density decreases as theyre not regenerated so remaining cells increase in size to fill space
Become more irregular
Pump/barrier becomes less effective - more water enters corneal stroma which causes the cornea to swell
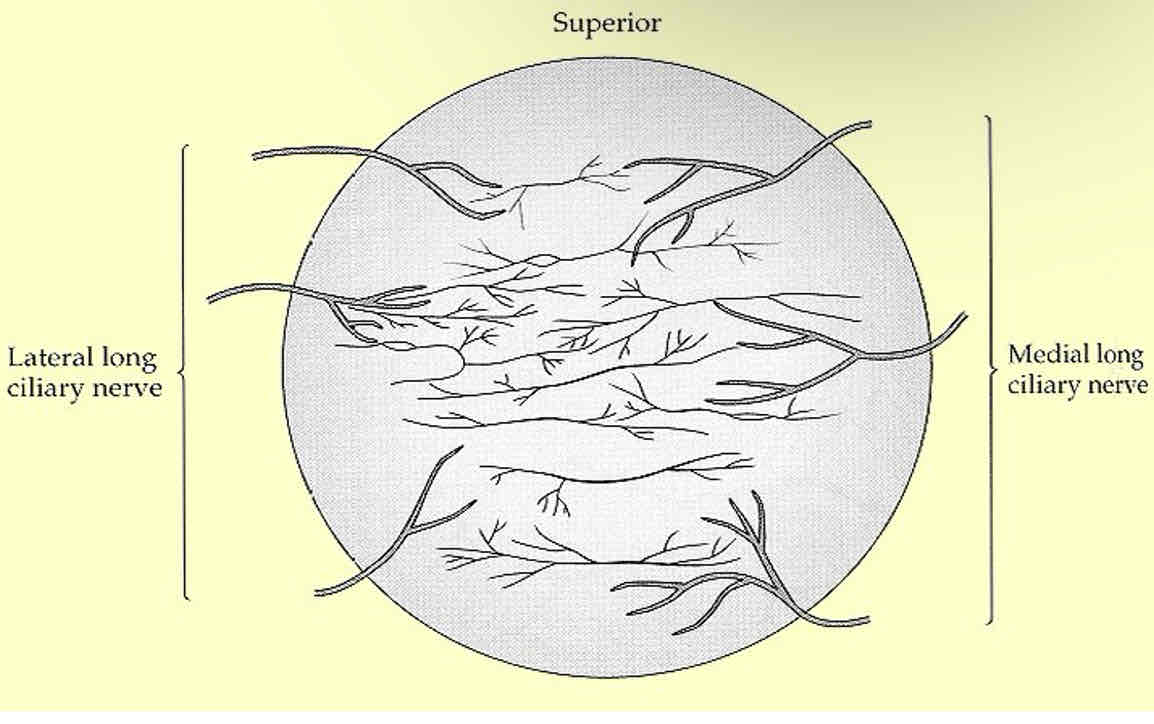
What are the 2 types of nerves and what are they associated with
Sensory - mediates sensation
Motor nerves - controls muscles and glands
Structures can have a sensory supply, motor supply or both
What type of nerves does the cornea have
Sensory nerves
(It has no muscle or glands so no motor nerves)
In which directions do nerves enter the cornea
Medial and lateral directions
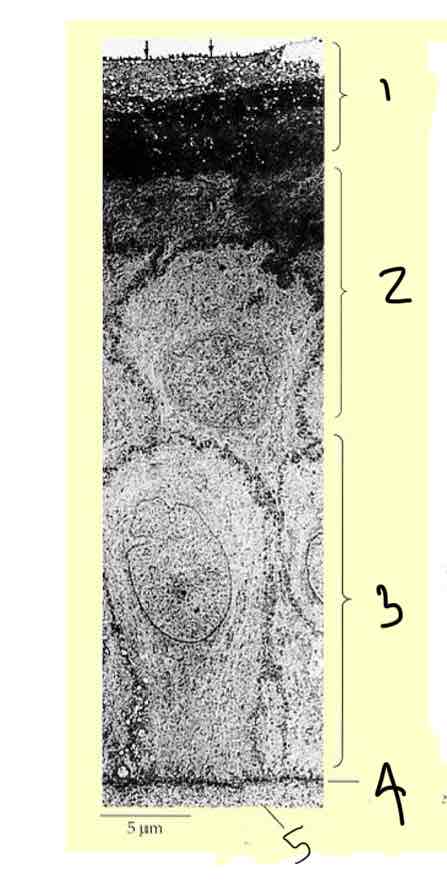
Where are nerves located in the cornea
Mostly in the anterior cornea (external layers)
Nerves in the cornea
Long ciliary nerve to limbal region
Brnaches towards the anterior angle
Nerves absent in posterior stroma and decemets membrane
Nerves terminate in epithelium
Nerves from basal layer run between epithelia to end in squamous cells
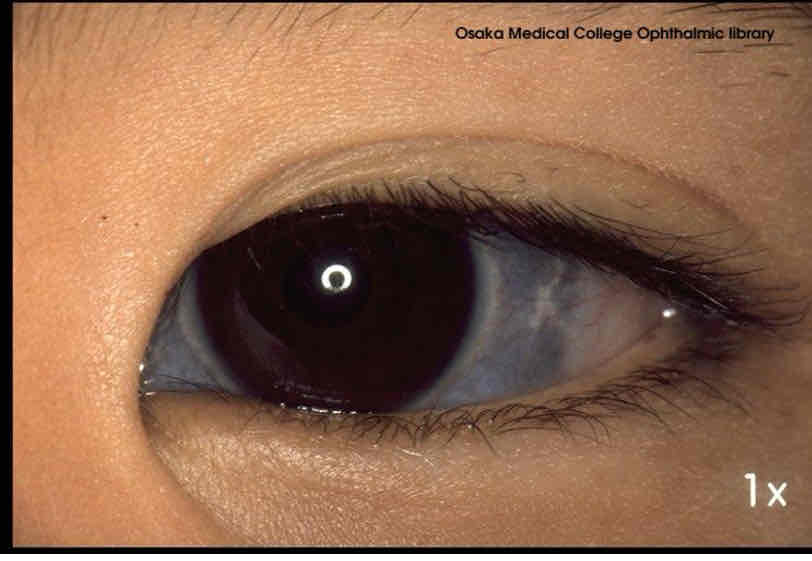
What is a blue sclera
Thin sclera - allows light through
Less opaque - see pigmented choroid
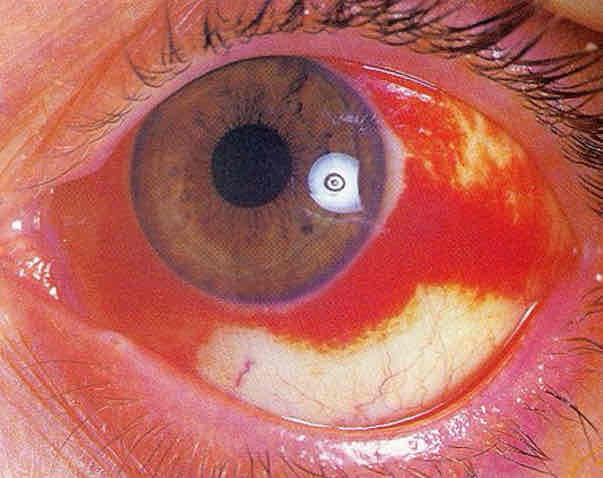
Subconjunctival hemmorage cause
Blood vessels pops and bleeds between episclera and conjunctiva (blood has nowhere to go)