Marieb Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 Test Bones and Skeletal Tissue
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Paget's Disease
excessive and haphazard bone deposit and reabsorption;
Treatment includes calcitonin bihosphonats; high ratio of spony bone compared to compact bone, usually a localized disease process
Osteoporosis
Bones are porous and thin but bone composition is normal;
the bone disorder in which bone resorption outpaces bone deposit, leaving the person with thin and often very fragile bones;
from a lack of calcium
Osteomalacia
Bone is formed poorly mineralized and soft. Deforms and is painful on weight bearing;
Rickets in adults; abnormal softening of bones caused by deficiencies of phosphorus or calcium or vitamin D;
Greenstick
An incomplete fracture or cracking of the bone without actual separation of the parts; common in children whose bones have relatively more collagen in their matrix and are more flexible than those of adultsf

Comminuted
Bone fragments into many pieces
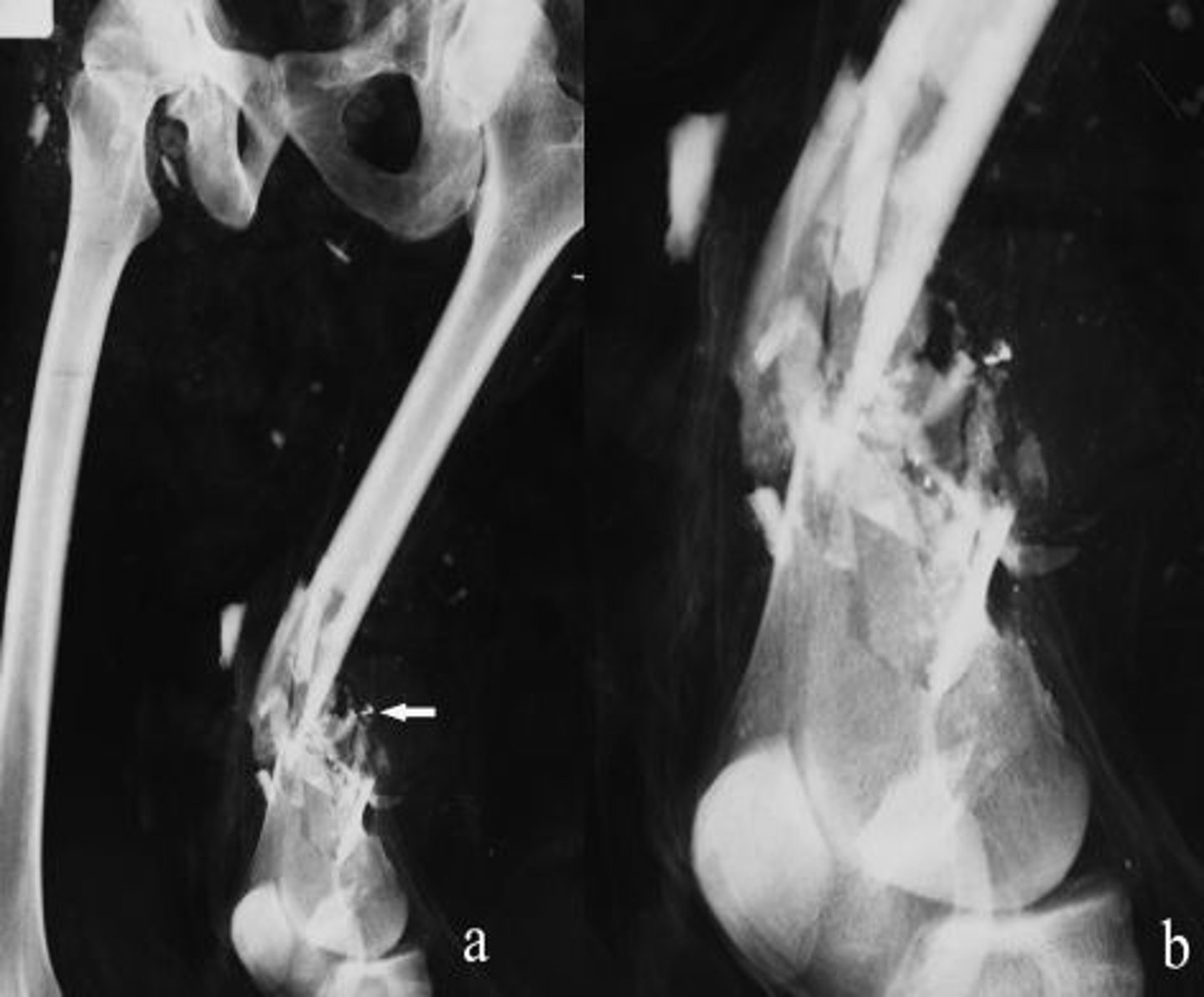
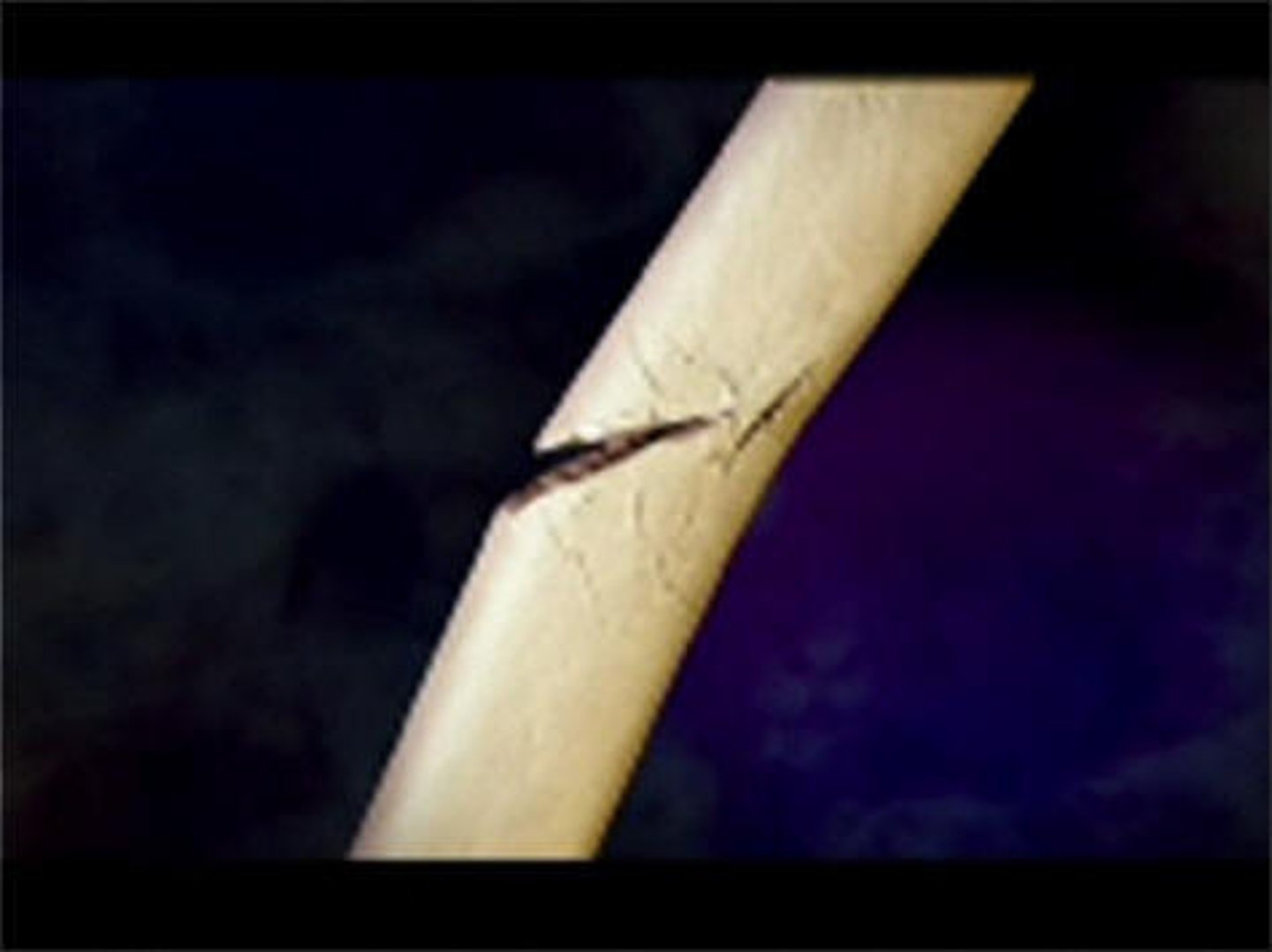
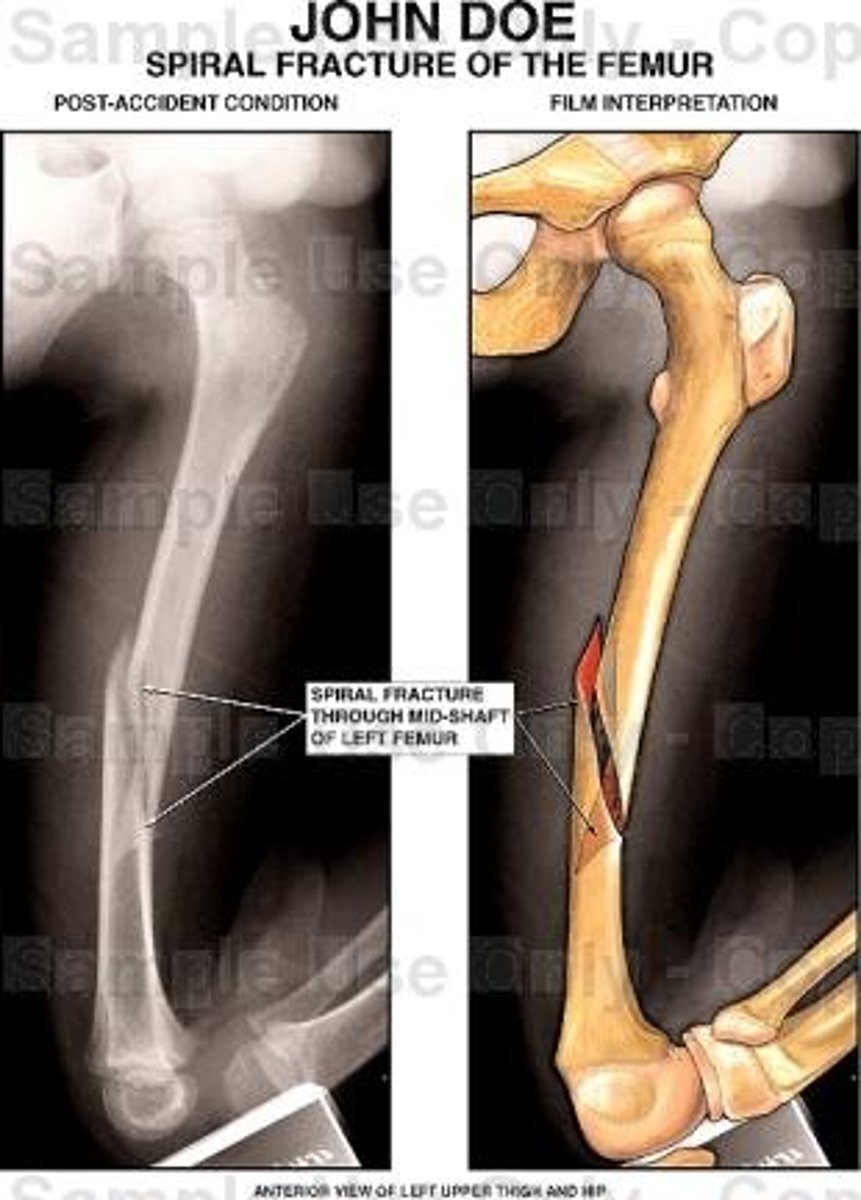
Spiral
Common sports fracture resulting from a twisting force
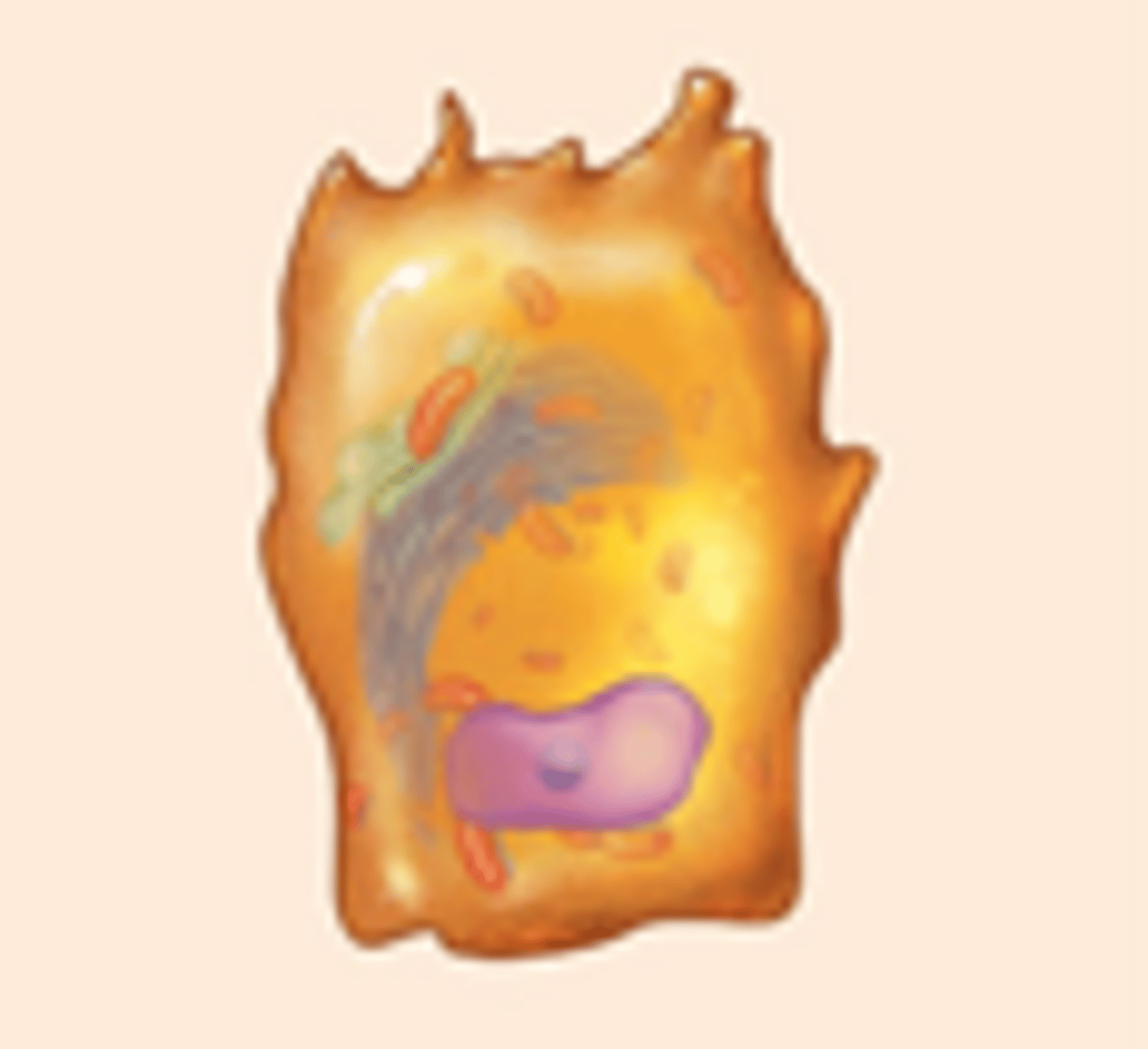
osteoblasts
cells that can build bony matrix
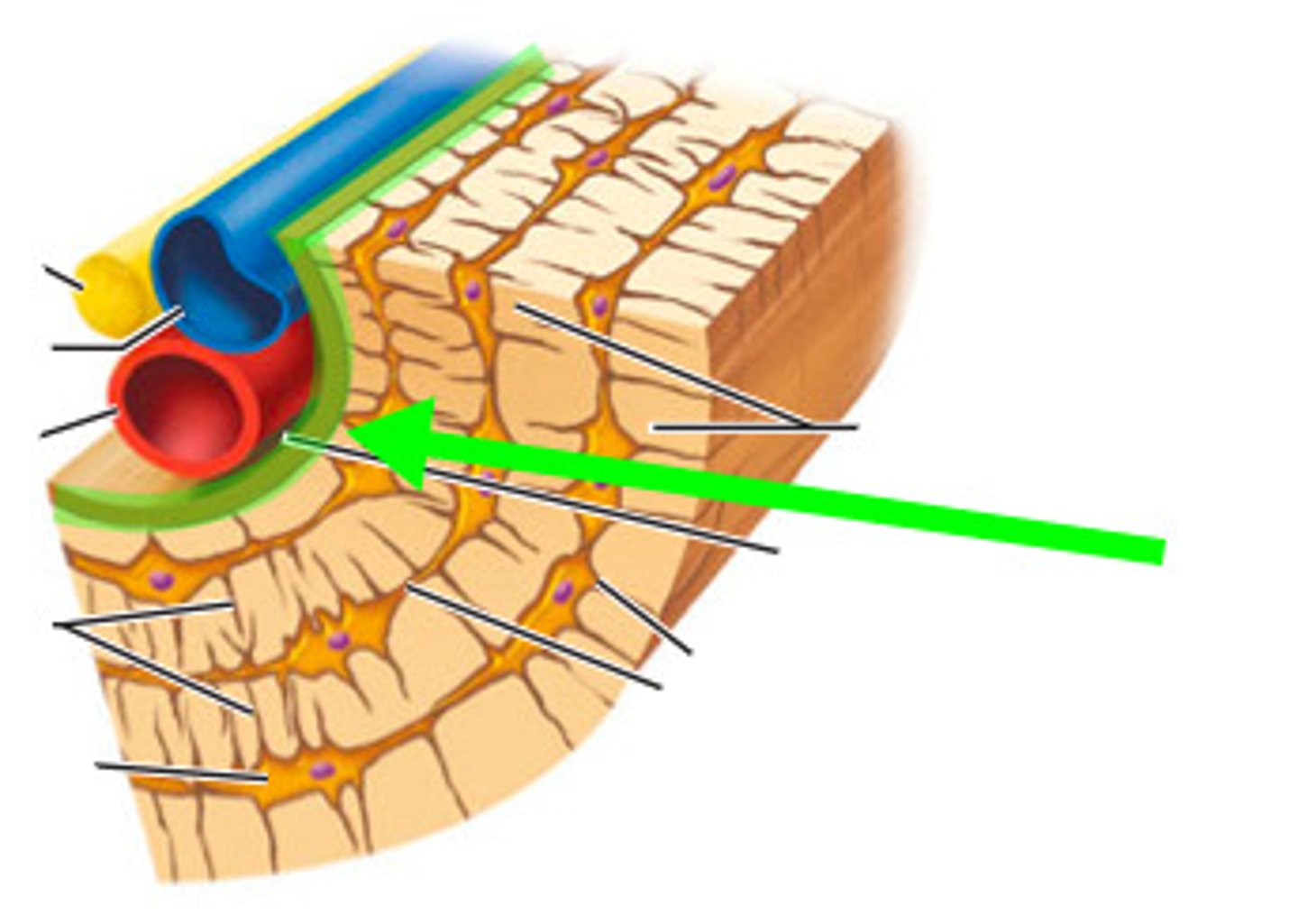
endosteum
the lining of the marrow cavity;
delicate connective tissue membrane on internal bone surfaces; covers spongy bone; contains octiogenic cells that can differentiate into other bones
intramembranous ossification
Ossification centers form in the fibrous connective tissue membrane for _____ ____ to take place;
forms flat bones
epiphyseal line
the appearance of this structure signal the end of bone growth;
hyaline cartilage that separates epiphysis from metaphysis
chondrocytes
the cells responsible for the early stages of endochondral ossification when cartilage is formed (later the cartilage will be converted to bone)
spine
Sharp, slender, often pointed projection.
facet
Smooth, nearly flat articular surface.
foramen
Round or oval opening through a bone
ramus
Armlike bar of bone
Hematopoiesis
refers to the formation of blood cells within the red marrow of cavities of certain bones
spongy bone
What is replaced more often: compact bone or spongy bone?
shape
what are bones classified by
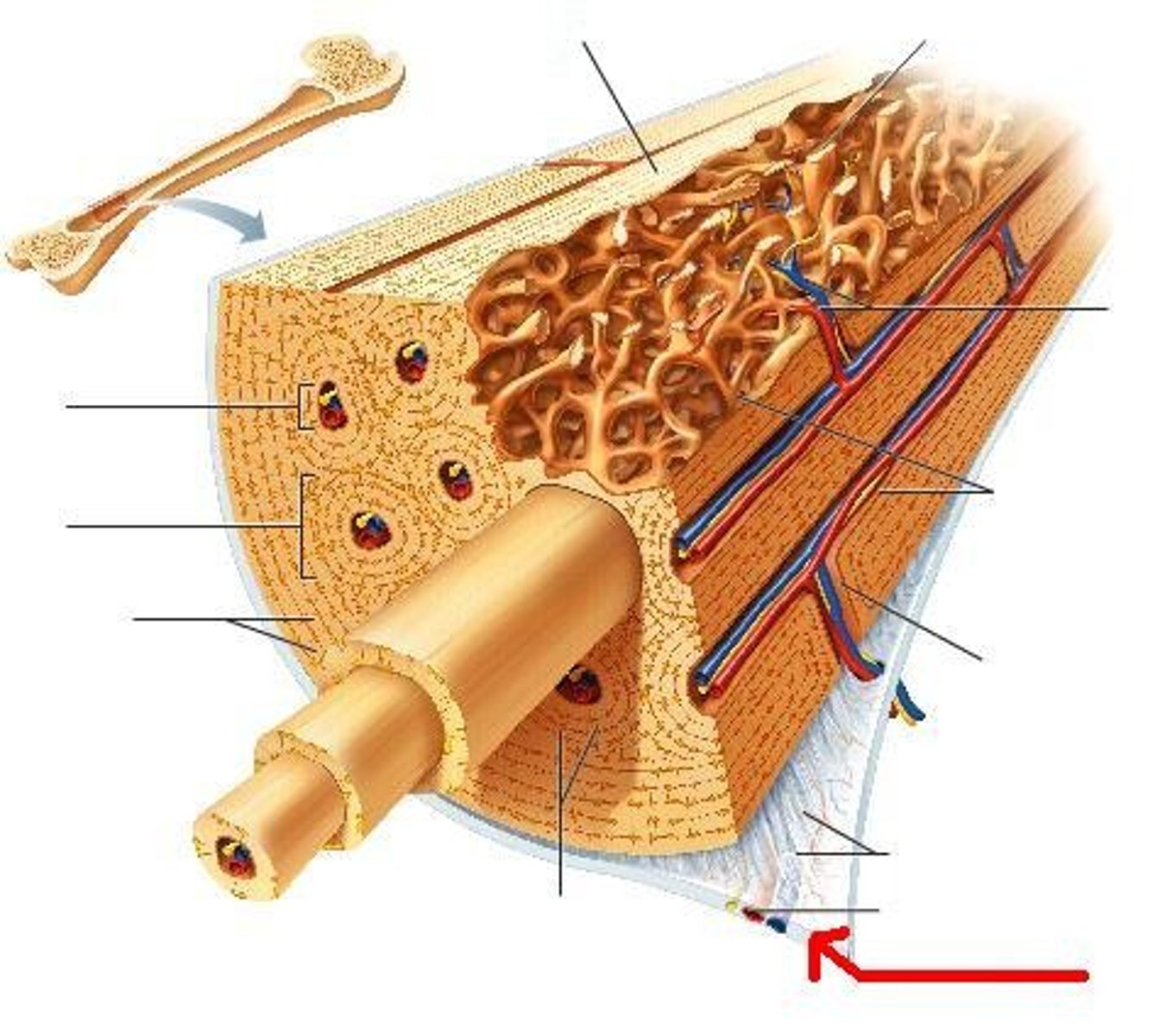
periosteum
tissue that serves to protect the bone and supply the bone with nerves and blood
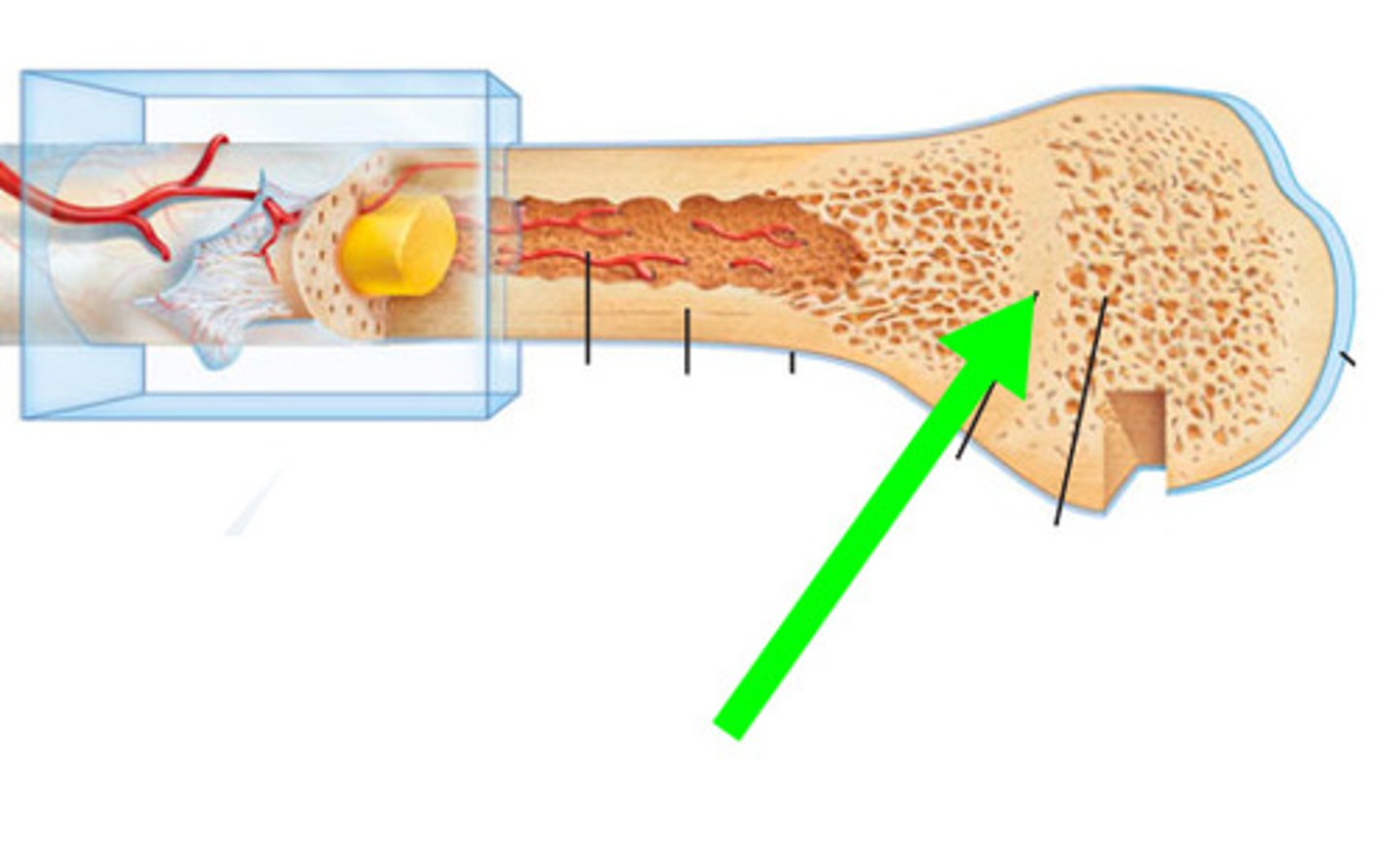
medullary cavity
central cavity of long bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow (adipose tissue) is stored; hence, also known as the marrow cavity.
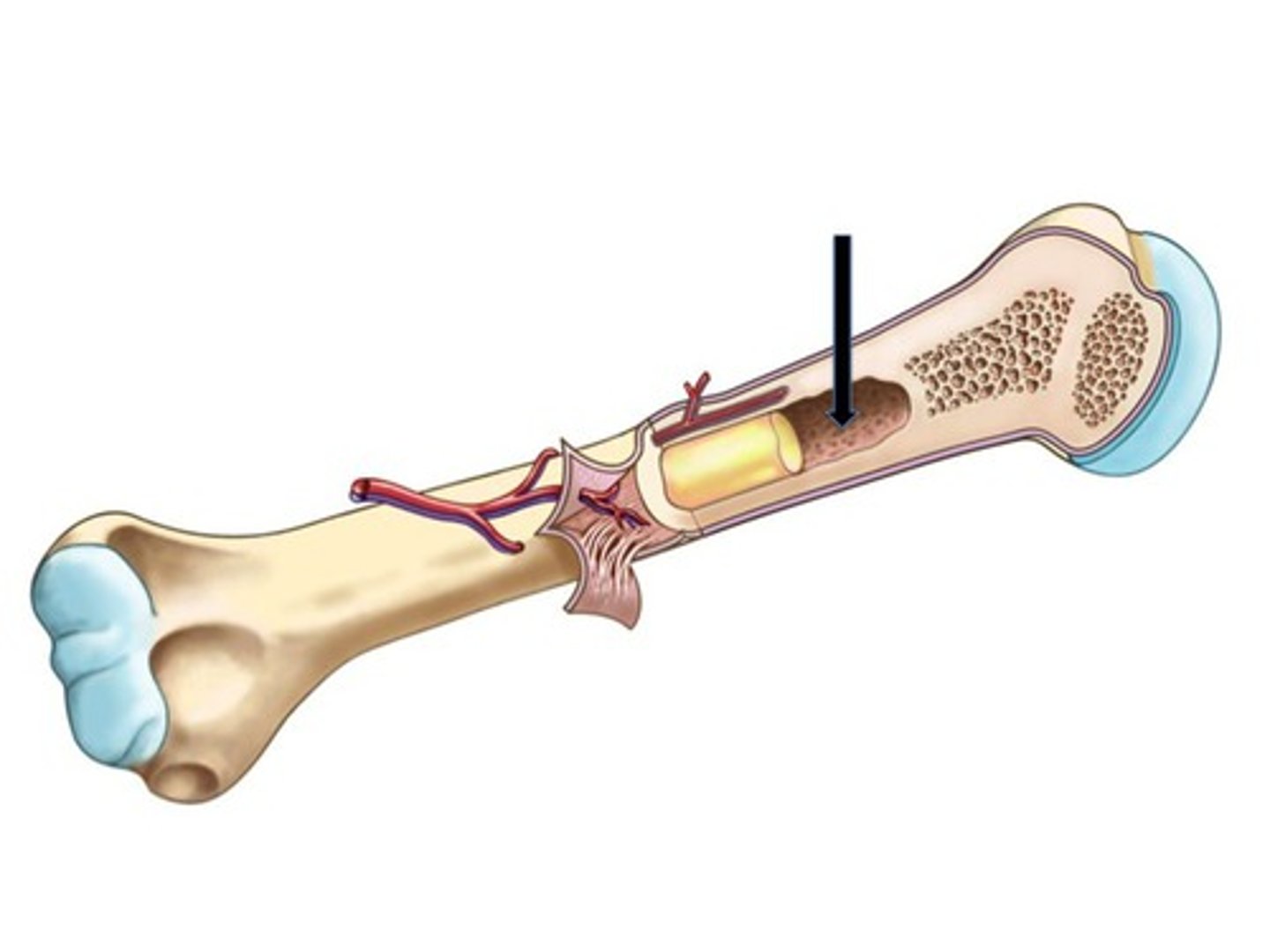
5
In children all bone marrow is red until about what age
tree trunk
the structural unit of compact bone (osteon) resembles the growth rings of what plant part?
osteoid
the unmineralized organic portion of the compact bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue;
secreted by osteoblastes; made of protoglycans and glycoprotiens and collagen fibers
hydroxyapatite
65% of bone mass is this compound
no
do all bones stop growing by the end of adolescence?
trabeculae
what part of spongy bone is oriented toward lines of stress
parathyroid
the hormone primarily involved in the control of bone remodeling;
stimulates osteoclasts to release calcium into blood;
encourages the digestive system to absorb more calcium and the kidneys to retain more calcium in blood
alternating
each consecutive bone lamella has collagen fibers that wrap in what directions
cartilage
has a flexible matrix that can accommodate mitosis of chondrocytes
does not
closure of the epiphyseal plate does/does not stop all bone growth
compact bone
only location of an osteon, contains osteocytes, lamellae, and a central canal;
bone tissues adapted to support weight and withstand torsion stresses;
dense outer layer; smooth and solid
fat
Yellow bone marrow contains a large percentage of ________.
osteoblast
The cell responsible for secreting the matrix of bone is the ________.
decreased epiphyseal plate activity
What can a deficiency of growth hormone during bone formation cause?
diaphysis
A fracture in the shaft of a bone would be a break in the ________.
main section of a long bone.
diploe
internal layer of spongy bone in flat bones

estrogen
what deficiency due to menopause is implicated in osteoporosis
secondary ossification centers
Ossification of the ends of long bones is produced by what
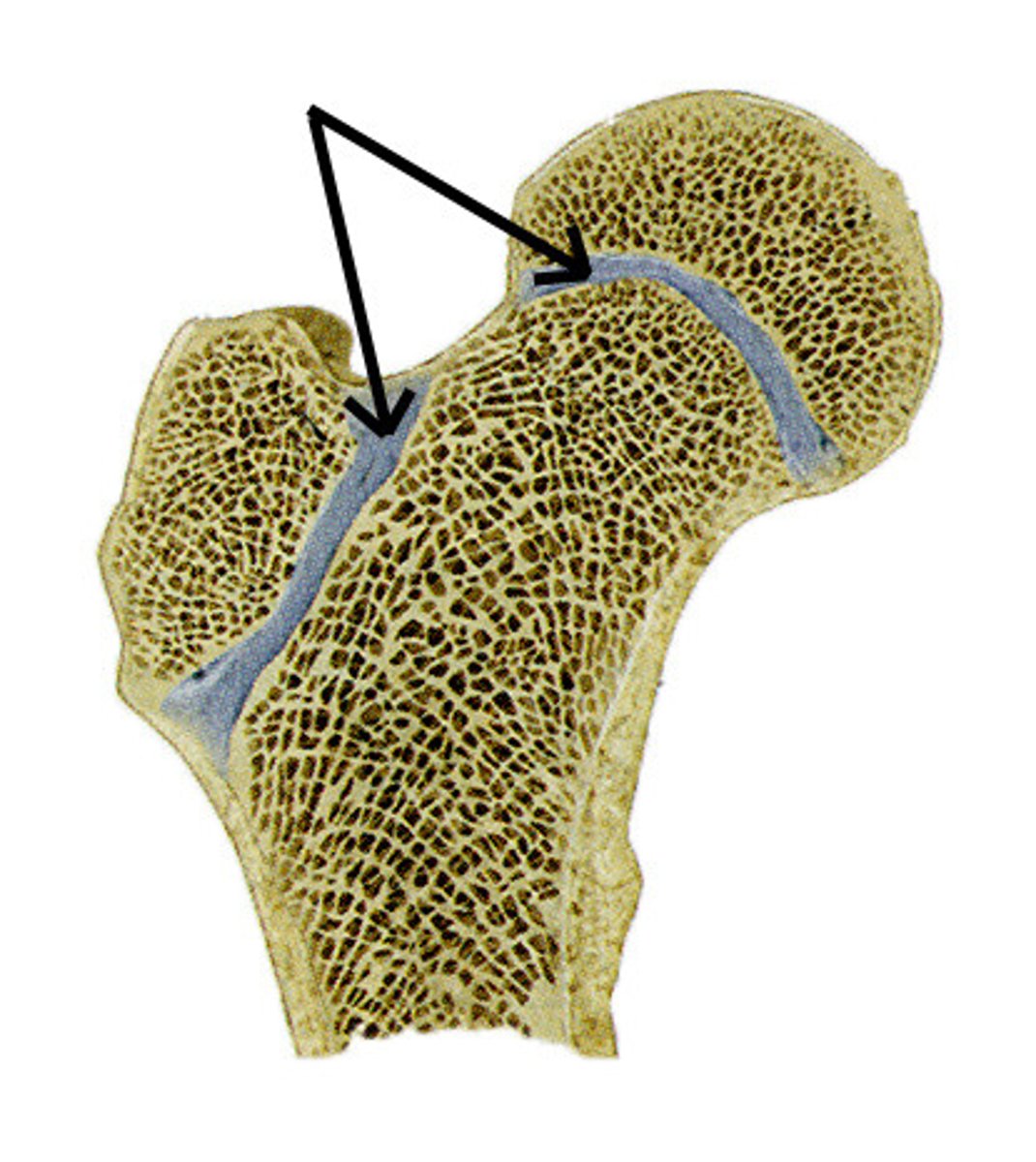
epiphyseal plate
area where bone longitudinal growth takes place;
allows the diaphysis of the bone to increase in length until early childhood;
presence of this bone indicates that bone length is increasing
growth hormone
Which of the following is the single most important stimulus for epiphyseal plate activity during infancy and childhood?
skeletal system
what has the functions of support, protection, movement, storage of minerals, hematopoiesis (blood cell production), and triglyceride (fat) storage?
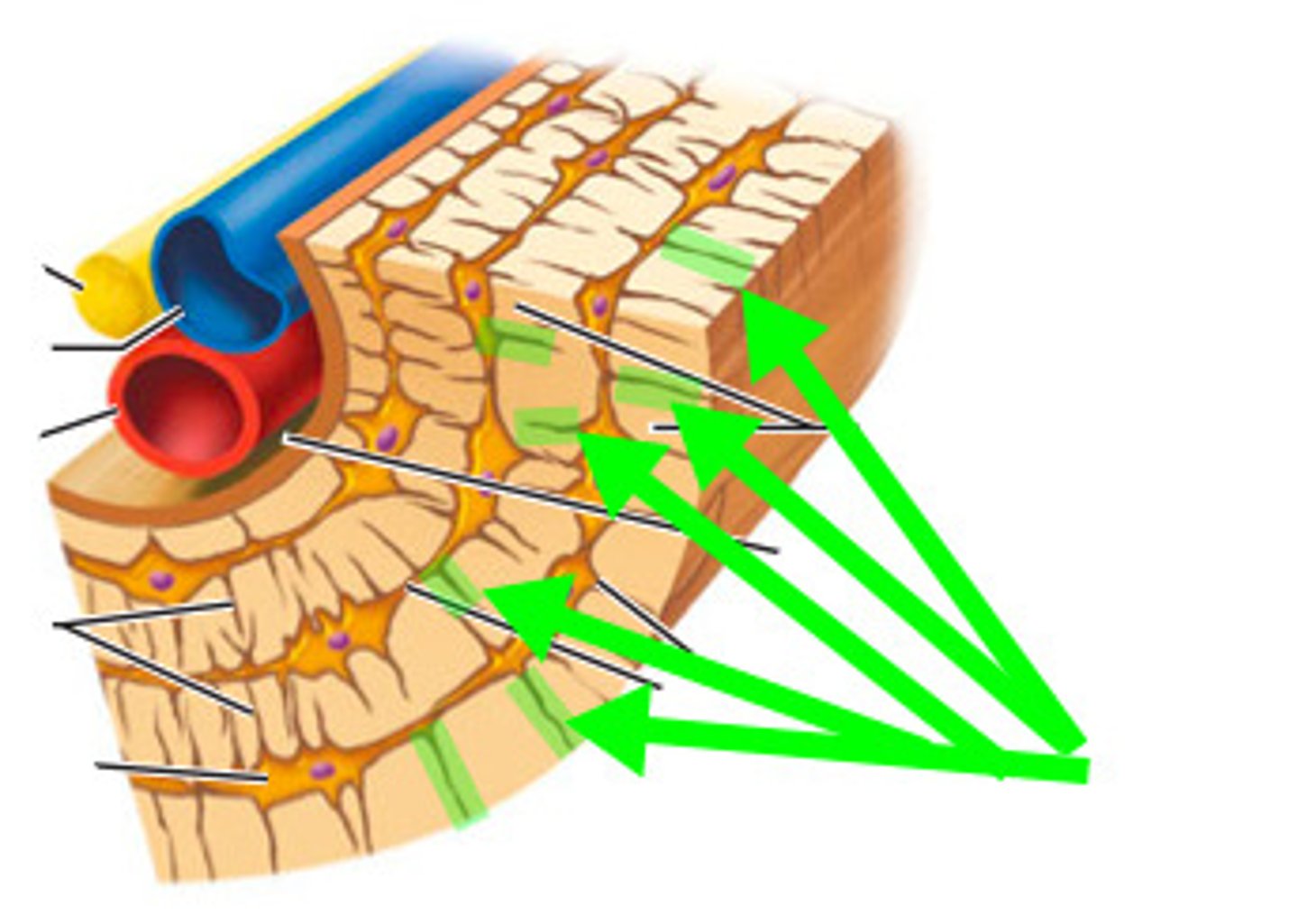
osteon
the structural unit of compact bone that is riddled with passageways that serve as conduits for nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels;
its system is an elongated cylinder oriented parallel to long axis of bone
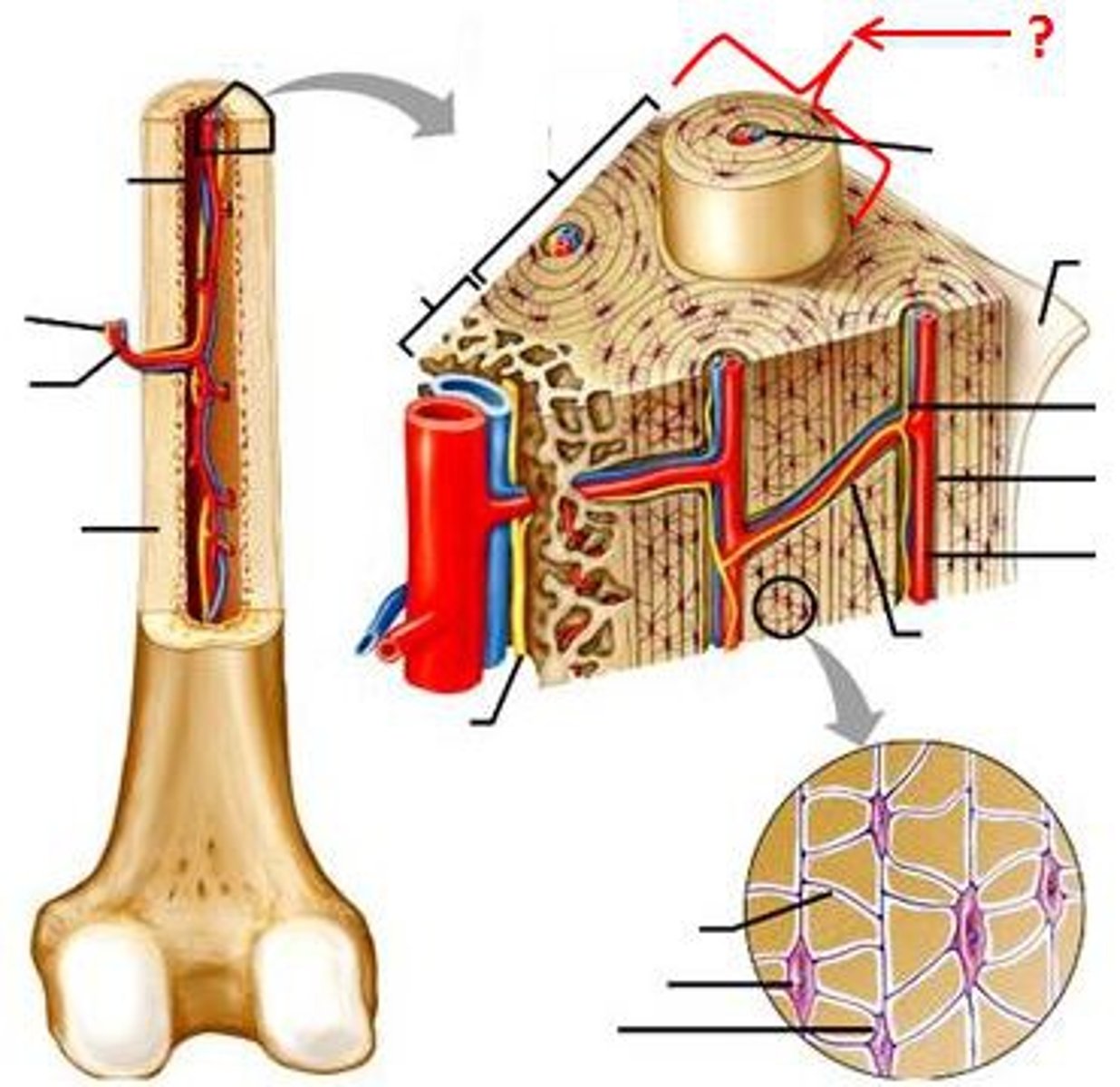
osteogenic
Bones are covered and lined by a protective tissue called periosteum. The inner (osteogenic) layer consists primarily of ________ cells
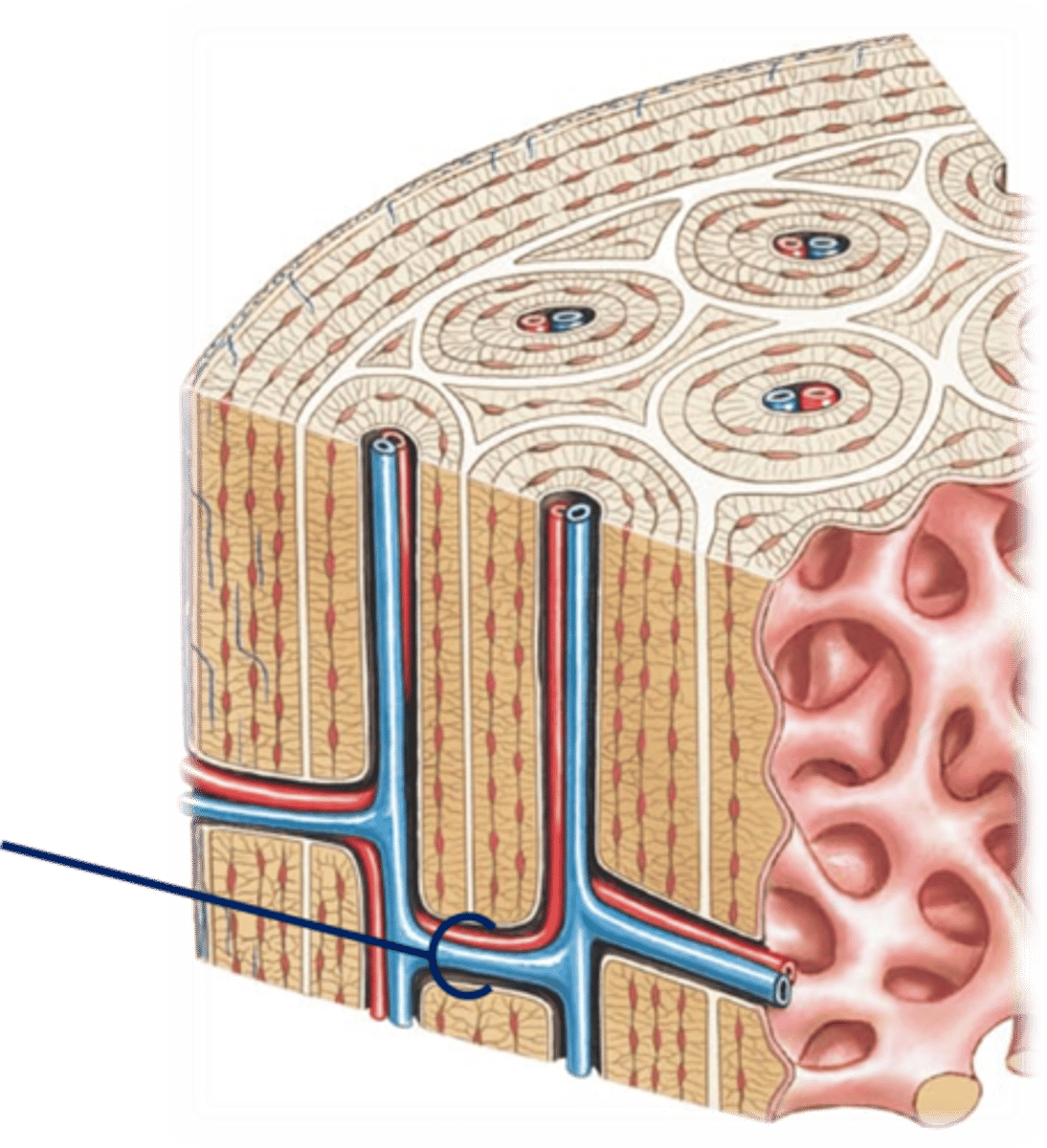
perforating Sharpey's fibers
The periosteum is secured to the underlying bone by ________.
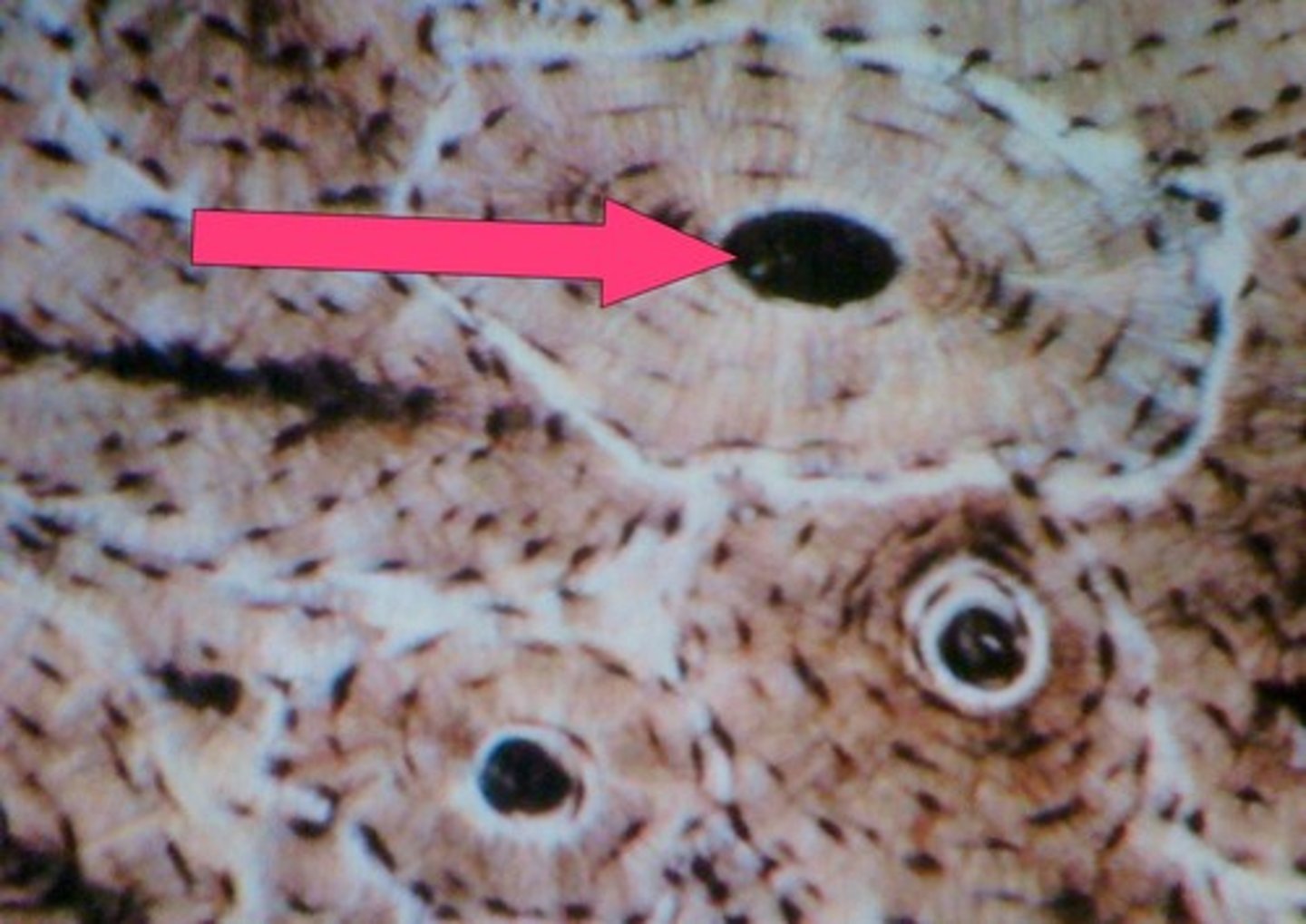
central Haversian canal
what runs through the core of each osteon is the site of blood vessels, nerve fibers, and lymphatic vessels.
sacrificial bonds
The resilience of bone is thought to come from the __________ ______ in or between collagen molecules
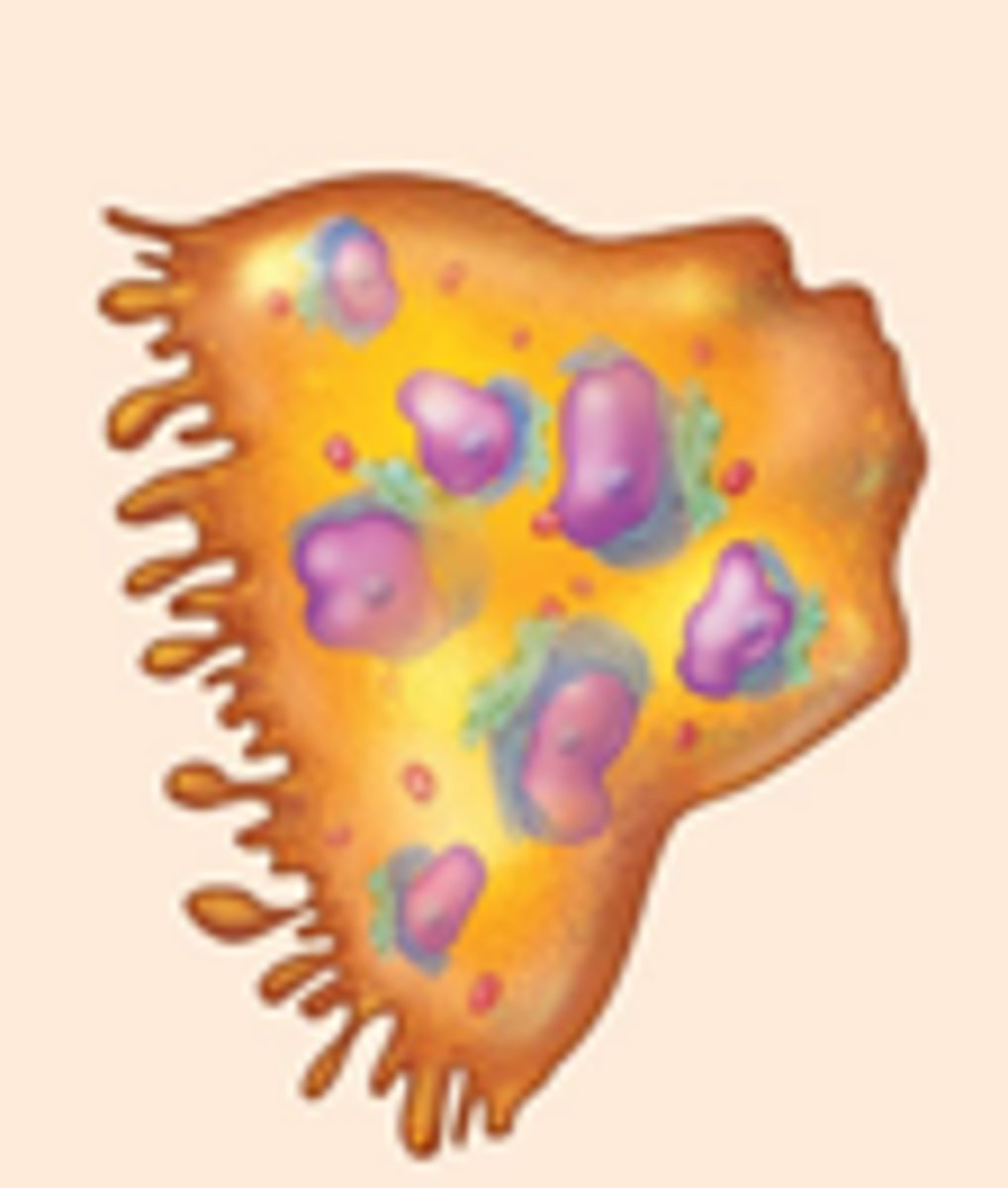
osteoclast
Bones are constantly undergoing resorption (breaking bone down) for various reasons. Which of the following cells accomplishes this process?
thigh bone
Which bone would likely take the longest to heal? (hint: its in an elderly person)
Wolff's law
the thickness and shape of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it
fibrous membranes
Cranial bones develop within
calcitonin
In humans, the effect of what hormone is to temporarily decrease blood calcium levels when administered in large doses
early adulthood
At what age do bones reach their peak density?
appositional growth
the growth pattern of bone in which matrix is laid down on the surface of existing cartilage;
increasing thickness
interstitial growth
what describes Chondrocytes in the lacunae dividing and secreting matrix, allowing the cartilage to grow from within.
Ossification
What is the process of bone formation (Osteogenesis)
sex hormones
Elevated levels of what might cause the epiphyseal plate of the long bones of children closes too early.
calcium and vitamin D
Prevention of osteoporosis includes adequate intake of ________.
fibrocartilage
The pubic symphysis connects the two hip bones anteriorly and provides a little movement during childbirth. Choose the most appropriate tissue for this structure that is subjected to both pressure and stretch.
long
At an archeological site you discover a bone that is cylindrical in shape, about one inch long and a quarter of an inch wide. How would you classify it?
canaliculi
small hairlike channels that radiate through the matrix of bone, connecting lacunae to each other; allow osteocytes to communicate;
most directly provides nutrients and removes wastes from osteocytes in compact bone
18 year old male
Skeletal remains are discovered at an archeological site. X-rays of the femur show evidence of a thin epiphyseal plate. This bone likely belonged to and 18-year old male or a 60-year old female?
osteocyte
When an osteoblast becomes completely surrounded by its own matrix secretions it is referred to as an ________.
hip bone
what is the best location for obtaining a red bone marrow sample from a patient?
increase
the trochanter bone marking would likely (increase/decrease) in size when a weight lifter repeatedly exercises muscles that attach to it
trochanter
Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process
healing stages
In order, the four major ___________ of a simple fracture.
Hematoma formation, fibrocartilaginous callus formation, bony callus formation, and bone remodeling.
hematoma
the formation of what is the first healing stage of a simple fracture (bruise)
fibrocartilaginous callus
the formation of what is the second healing stage of a simple fracture;
Scar tissue of bone; a mass of repair tissue consisting of collagen fibers and cartilage that bridges the broken ends of a bone within 3 weeks after the injury
bony callus
the formation of what is the third healing stage of a simple fracture;
this forms during fracture repair when the fibrocartilage is converted to spongy bone;
lasts 3-4 months
bone remodeling
what is the fourth healing stage of a simple fracture when compact bone replaces spongy bone
flexible
Bones in children are not completely calcified, making them much more ___ than those of the elderly
rigid
Bones in the elderly are completely calcified, making them much more ___ than those of children
Bone
This is an analogy of the chemical compostion of what?
In highway construction metal rebar is used with concrete to form a road that is hard, yet resistant to cracking. Likewise, with this answer, the organic collagen fibers are akin to the metal rebar, providing flexibility, while the inorganic minerals provide the hardness like concrete in a roadway.
organic matrix
What contributes to the bone structure and its tensile strength
inorganic matrix
what contributes to bone hardness and resistance to compression.
Diaphyseal
what bone is composed almost entirely of compact bone; It is the shaft/shank of long bones; has a large medullary cavity, whereas the epiphyses do not.
Epiphyseal
what bones are composed almost entirely of spongy bone?
They're on the ends of the bone.
skeletal cartilage
Water lends streanth; no blood vessels or nerves
perichondrium
Surrounds the bone with dense connective tissue; contains blood vessels; resists outward expansion; protects cartilage
Lacunae
Tiny spaces between lamellae that house the osteocytes of the osteon
hyaline
cartilage made of Collagen fibers only; covers articulated surfaces of bones
Elastic
cartilage with the most elastic fibers
fibrocartilage
cartilage that's mostly Thick collagen fibers
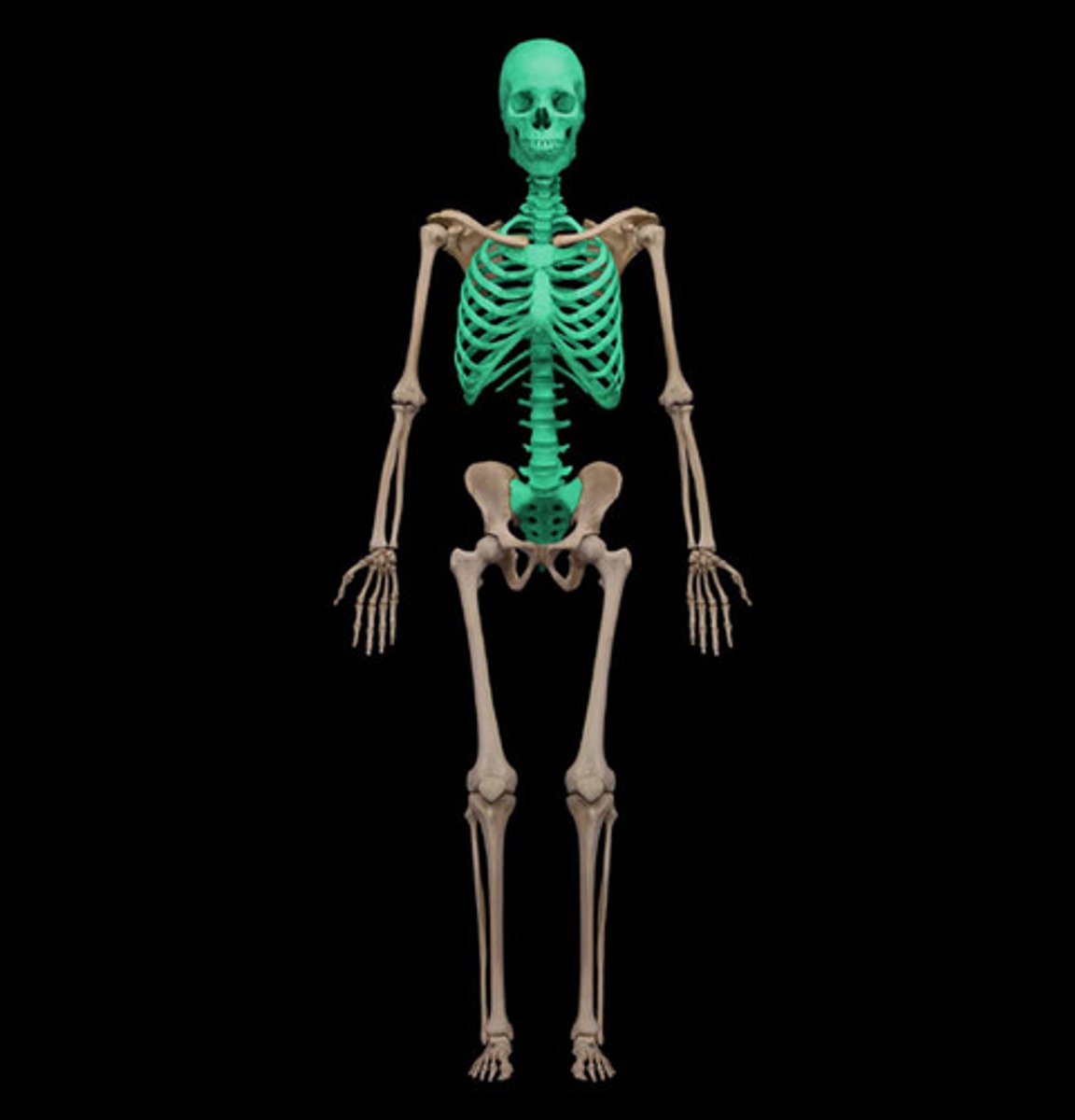
axial skeleton
skull
vertebral column
rib cage
protect support, carrying other body parts
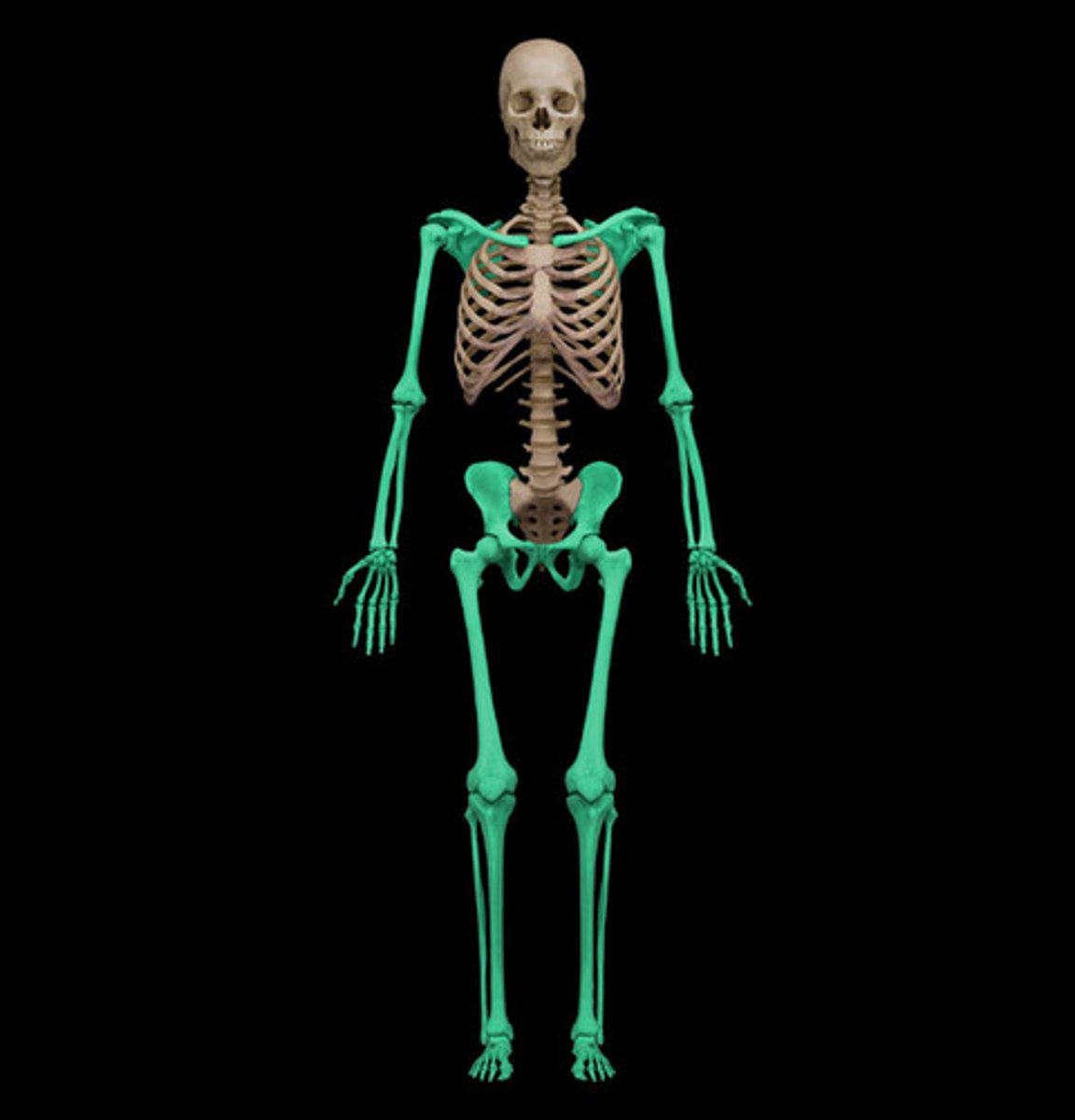
appendicular skeleton
Girdles; shoulder bones and hip bones-attach limbs to axial skeleton
locomotion
manipulate environnment
spongy bone
honeycomb needle like or flat pieces called trabeculae easy to crack;
contains irregularly arranged lamellae and osteocytes interconnected by canaliculi
metaphysis
the growing part of a long bone in children between the diaphysis and the epiphysis
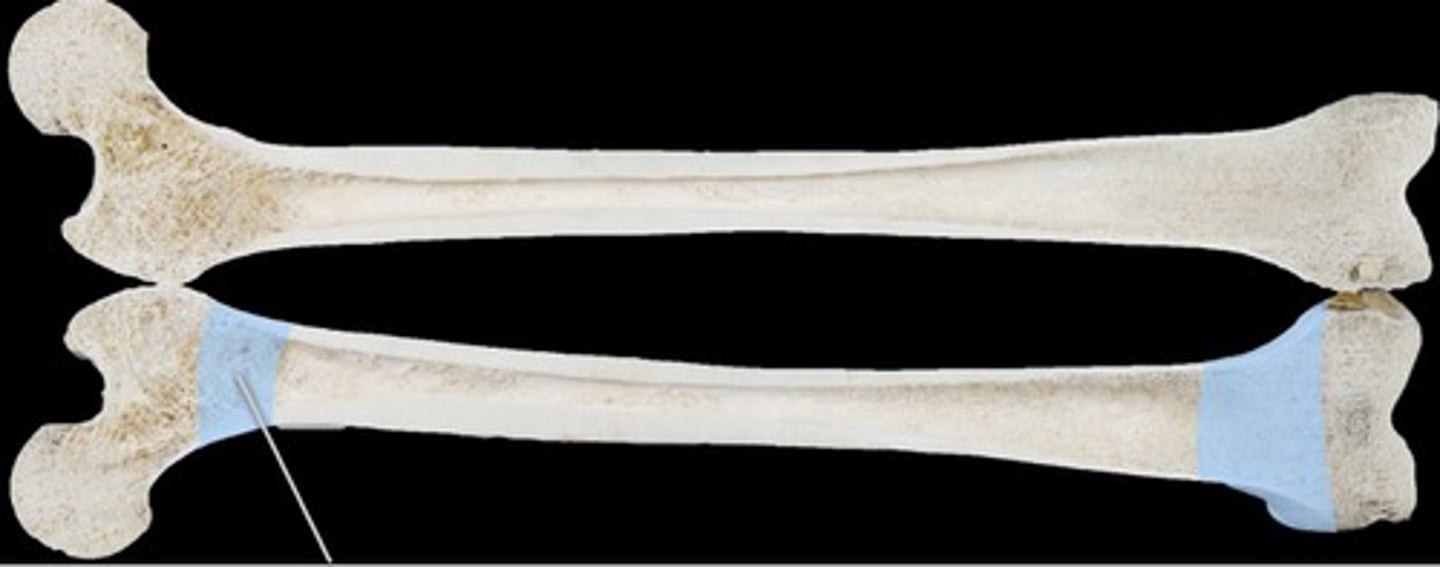

fibrous layer
dense irregular connective tissue layer of joint capsule that limits motion
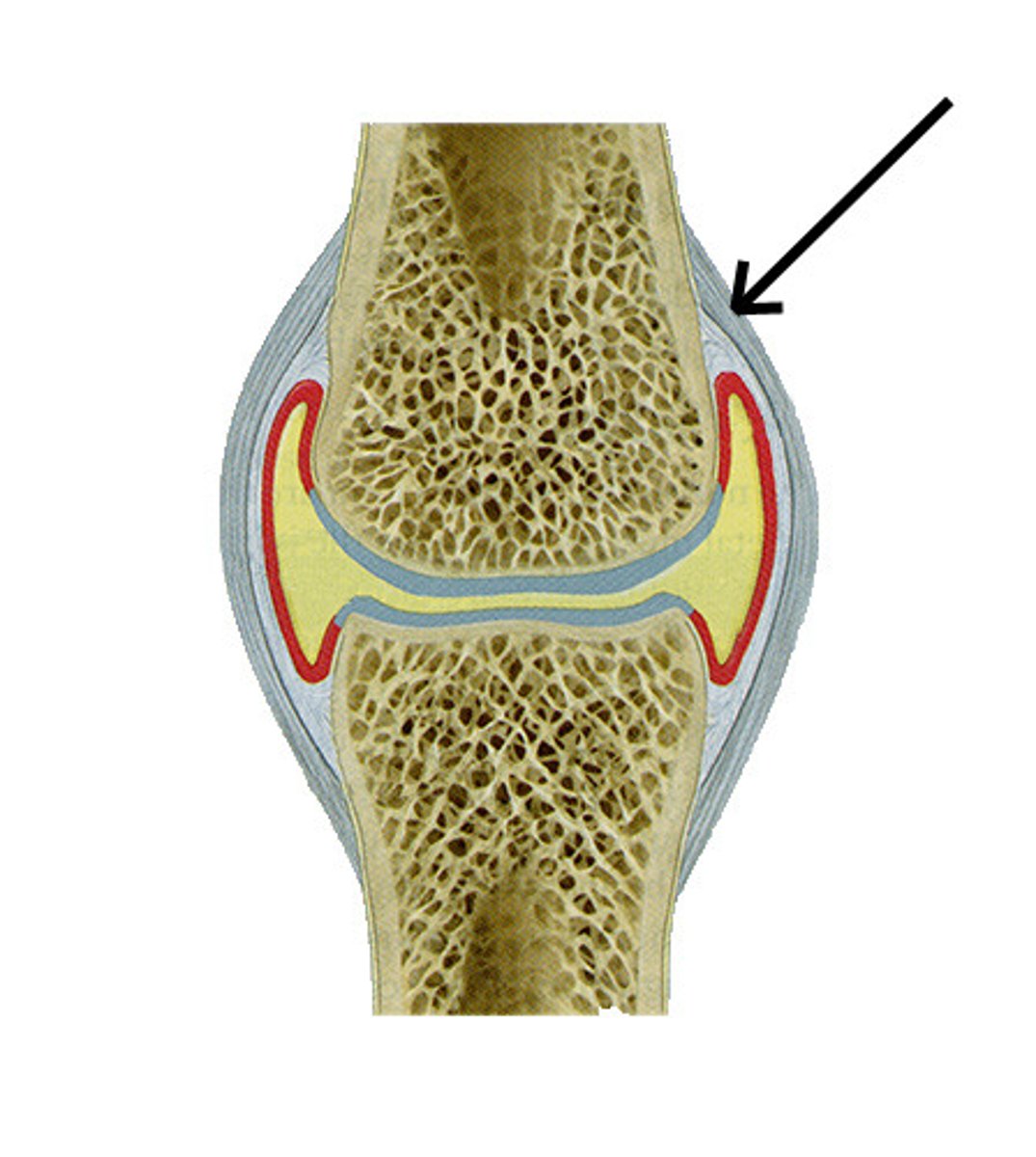
osteogenic layer
This is the inner layer of the periosteum and consits of differentiating osteoblast that are laying down new bone. Has stem cells
osteogenic cells
stem cells that develop in osteoblasts-- found inside of the periosteum and endosteum
red marrow
Gives rise to blood cells
yellow marrow
fat stored in bones
bone markings
Projections, depressions, and openings; important for blood vessels and nerves to get into the bone
lamellae
Rings of the osteon; layers of bone matrix
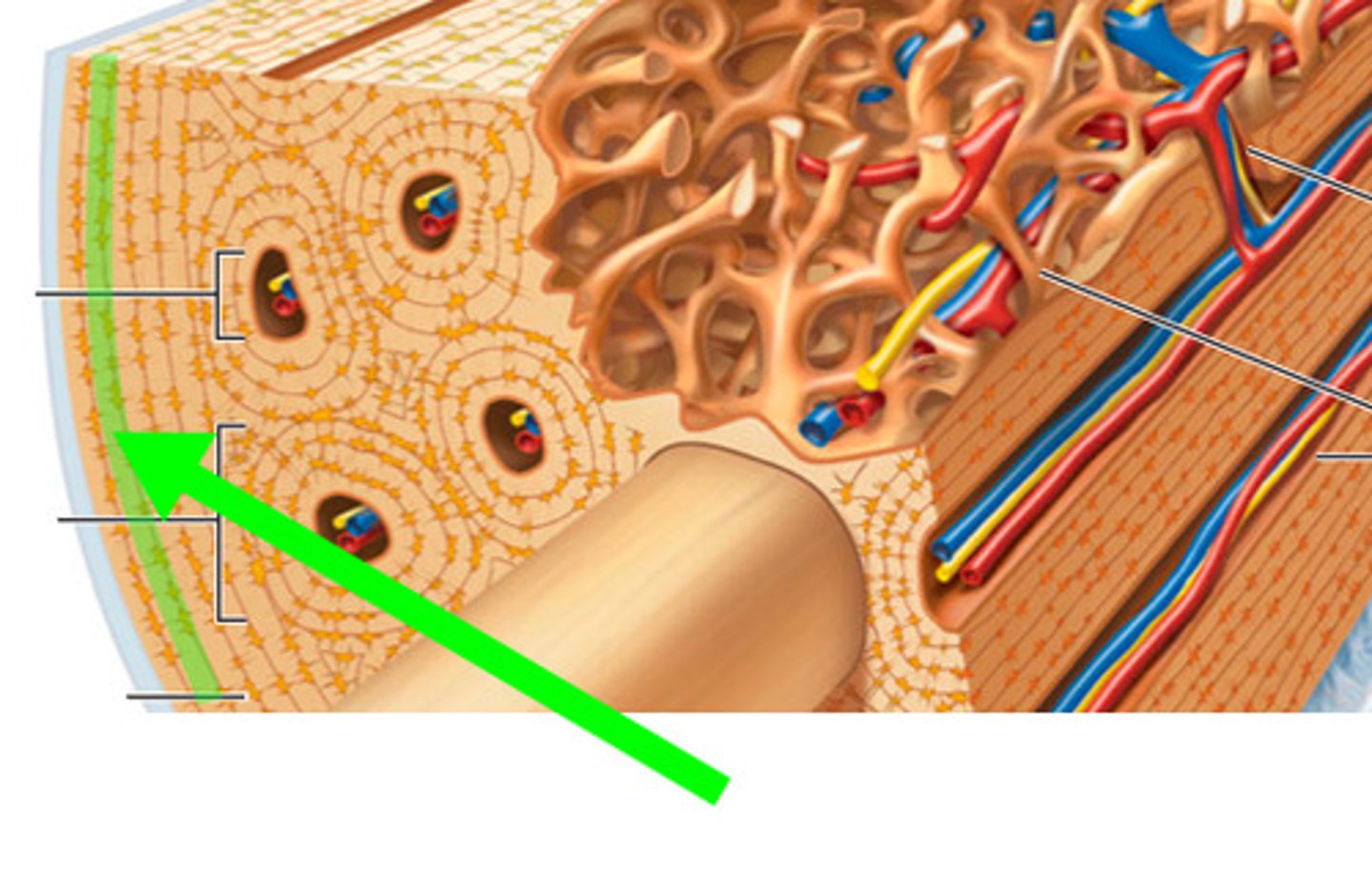
Volkmann canals
channels lying at right angles to the central canal, connecting other osteions together
ossification
Formation of bony skeleton begins in second month of development and in postnatal growth until early adulthood; Continues as bone remodeling and repair lifelong
endochondral ossification
the most common bone formation process, which involves the replacement of hyaline cartilage with bone; late second month of development
endochondral bone
what begins as hyaline cartilage that is subsequently replaced by bone tissue
bone growth
These hormones are involved in what?
Growth hormone
Thyroid hormone
Sex hormone
Dwarfism
Achondroplasima and achondroplasia; defective cartilage formation that affects bone growth