PSYCHOLOGY QUIZ 2 COMBINED
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue
Scans show brain anatomy.
EEG (electroencephalogram)
shows brain's electrical activity by positioning electrodes over the scalp
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
A brain-imaging technique that reveals activity in various parts of the brain, based on patterns of blood flow, oxygen use, and glucose consumption.
Neuron
A nerve cell
Sensory system
Gathers sensory information
Interneuron system
Carries information between neutrons in the brain and spinal cord
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Terminal buttons
Ends of axons that secrete neurotransmitters
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. Occurs when excitatory signals outweigh the number of inhibitory signals
all-or-none principle
The principle that when a neuron fires, it fires with the same potency each time; a neuron either fires or not—it cannot partially fire, although the frequency of firing can vary.
Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
lock and key mechanism
Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors of the neuron
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Function: learning, anxiety regulation
Drugs: Valium, Ativan
Dopamine
Mood
Voluntary movement
Reinforcement
Too much (Frontal lobes)- Schizophrenia
Too little (Motor Areas)- Parkinson’s
Serotonin
Function: mood regulation. Drugs: MDMA, LSD, Monamine Oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), SSRIs
Norepinephrine
Function: attention, arousal. Drugs: adderall
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the nervous system to change its activity in response to intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli by reorganizing its structure, functions, or connections after injuries
afferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry impulses towards the central nervous system (CNS) from the PNS
efferent neurons
Nerve cells that conduct impulses away from the central nervous system to the PNS
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Hindbrain
Function and Location: regulates basic life functions, closest to the spinal cord
reticular formation
regulates sleep, wakefulness, and levels of arousal. Main source of serotonin, which is important for mood and activity levels
Pons
Send signals to and from the forebrain and cerebellum. Important for sleep, breathing, swallowing, eye movements, and facial sensation and expression
Medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
substantia nigra (midbrain)
The nucleus from which dopamine neurons send their axons to the striatum(forebrain). Involved in movement control (damaged in Parkinson's disease).
Thalamus (forebrain)
sensory relay station
Hypothalamus (forebrain)
Important for motivation, basic drives, and the control of the endocrine system
pituitary gland
Regulates hormones
limbic system
Involved in the regulation of motivation, emotions, and learning and memory
Amygdala: Emotion/fear-
Hippocampus: Memory
Amydala
This structure is located on the ends of the hippocampus and is related to the emotions of fear and anger.
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
nucleus accumbens
important for experiencing reward and motivating behaviour and addiction
Structure of the Cerebrum
Is composed of 2 cerebral hemispheres: Left and Right
Like mirror images of each other
Comprised of 4 lobes:
Frontal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
Parietal lobe
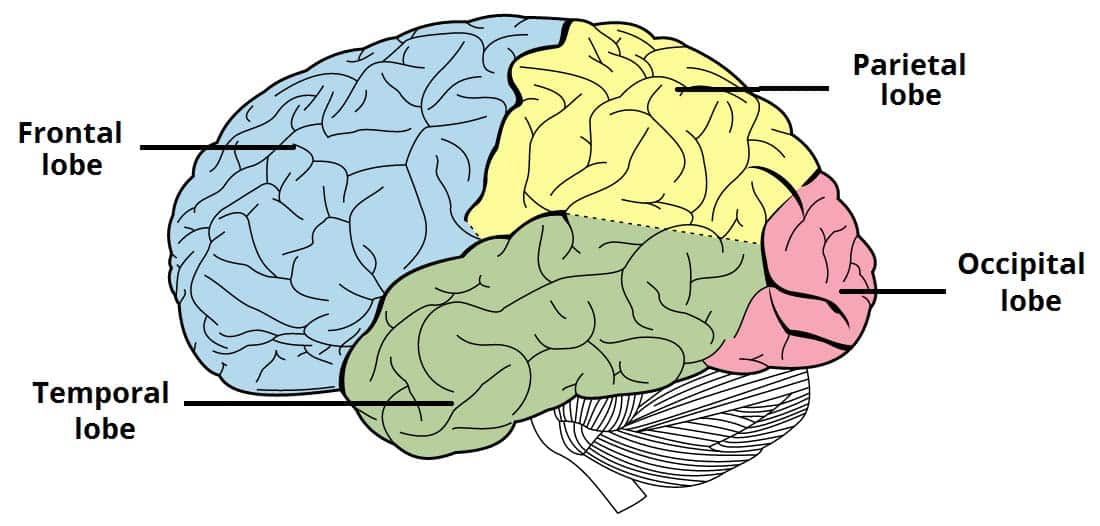
frontal lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving. Right side controls left side of body
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and languages
occipital lobe
visual processing
sensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
Motor cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
association cortex
regions of the cerebral cortex that integrate simpler functions to perform more complex functions
Parallel processing
Brain's ability to process multiple pieces of information or tasks simultaneously rather than one at a time
EX.
While watching a movie your brain is processing the images and scenes on the screen, recognizing shapes, colors, and movements
corpus callosum
Connects the two brain hemispheres. Dense bundles of neural fibres (axons) that allow communication of information from one side of the brain to the other
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
the WAIS is the most widely used intelligence test; contains verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging)
An imaging method that uses a modified MRI scanner to reveal bundles of myelinated axons in the living human brain
astroglial cells
Regulate brain blood flow, as needed
4 main types of ions that contribute to the resting potential
Positive sodium
Positive potassium
Negative chloride
Negative proteins (anions)
Myelin
fatty white substance that surrounds the axon of some nerve cells, forming an electrically insulating layer. Formed from glial
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Active during restful times
Often used in digestion (Urination, etc)
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Activated under conditions of stress.
Sympathetic division arouses
Parasympathetic division calms
peripheral nervous system
Made up of the somatic nervous system and the autonomic system
sympathetic nervous system
Part of autonomic nervous system that is activated under stress.
endocrine system
The system that controls levels of hormones throughout the body
Broca's area
A brain region located in the frontal lobe that is important for speech production
reticular formation
A complex neural network extending from the hindbrain into the midbrain that plays a central role in regulating consciousness and arousal
The basal ganglia
a group of structures linked to the thalamus in the base of the brain and involved in coordination of movement.
Psychoanalytic theory
A theory developed by Freud that attempts to explain personality, motivation, and mental disorders by focusing on unconscious determinants of behavior
Behaviorism
All behaviors are acquired through conditioning
Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment
Behaviorists believe that our actions are shaped by environmental stimuli
information processing
humans accomplish this either in parallel (unconsciously) or in serial fashion (consciously)
cognitive neuroscience
study of the physical changes in the brain and nervous system during thinking
Conscious
personal awareness of an ongoing mental processes, behaviours & environmental events
Unconscious
Hypothesized repositions of thoughts, feelings, & sensations outside human awareness
Some theories to have a strong bearing on human behaviour
What is neuroscience?
the study of the brain & the nervous system
Neurons
- Specialized cells that carry messages throughout the nervous system
- Electrochemical exchange-both electrical and chemical
- Differ in shape and size and function
What are the parts of a neuron?
Cell body
Dendrites
Axon
Myelin sheath
Nodes of ranvier
Terminal buttons
What is a glial cell?
Make up the nervous system
Are like glue that hold neurons together
What is a synapse?
junction between two neurons
What is the synaptic cleft?
gap between the terminal button of one neuron
What are neurotransmitters?
chemical messengers - transmit information between neurons
What are axons?
a long thin fibre that transmits signals way from the soma to other neurons or to muscles or glans
What are myelin sheaths?
axon coverings that help speed up transmission signals that move along axon
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
-70 millivolts, negative charge when the cell is inactive
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Black window
the venom causes you to produce too much acetylcholine so you suffocate
Curare
stops the production of acetylcholine from you body so you die
Monoamines 3 neurotransmitters
Dopamine
Norepinephrine
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Affects eating habits, alertness, and wakefulness, leads into depression
Predominant in fear/angry
Serotonin
play roles in regulating mood, eating, sleeping, and dreaming
Oversupply of _______ produce manic states while undersupply is thought to produce depression
Epinephrine
Causes surges of energy, predominant energy
Endorphins
Relieve pain and produce feelings of pleasure and well-being;
Runner's high
Resemble opilate drugs
Anti-depressants/Anxiety
(1) MAO inhibiters - monoamine oxidase inhibitors
(2) SSRIs - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Imprinting
Process in which young animals form strong and rapid attachments to the first moving object they see, typically their parent or caregiver
Konrad Lorenz duckling experiment
UCS- Unconditioned stimulus
Stimulus that elicits a reflexive or innate unconditioned response (UCR) without prior learning:
Sour lemon candy to a kid
UCR-Unconditioned Response
An automatic response to a stimulus
Pucker up the lips
CS- Conditioned Stimulus
Learned
“Ding”--> Here's a lemon, suck on it
Stimulus Generalization
When you react in the same way to a similar but different stimulus than your originally conditioned to.
Ex. Applied in Ads, prejudices, and phobias
Phobias
Irrational fear attached to specific situation or stimulus
Need to change the association to fix it
Contingency
The sense that what is happening is connected to what has just happened and what is about to happen
Dependency or relationship between two events or variables
(IF, THEN, if=behavior, then=consequence)
Skinner Box
A small enclosure in which an animal can make a specific response that is systematically recorded while the consequences of the response are controlled
Operant Conditioning
Positive Reinforcement
Anything that follows a behavior and increases the probability that the behavior will occur again; something that's desired gets added
EX.
A child cleans their room (behavior), and in return, they receive a sticker (positive stimulus)
Punishment
Anything that follows a behavior and decreases the probability that the behavior will occur again.
Extinction
Withholding reinforcement, eventually causes the behavior to weaken and stop.
Negative Reinforcement
Behaviour is strengthened or increased by the removal or avoidance of an aversive or unpleasant stimulus immediately following that behaviour.
Ex. Wearing a seatbelt to stop the annoying car alarm
Primary Reinforcement
Occurs naturally and doesn't require learning; often aids in survival of species, ex. food, water, sex...
Secondary Reinforcement
Stimuli that have become rewarding by being paired with another reinforcing stimulus; values learned