Islamic Art
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
The Islamic Attitude to Images
Aniconism: Avoidance of human/animal imagery in religious contexts.
Rooted in fear of idolatry (worshipping images over God).
Abstract, decorative styles (geometry, calligraphy) replace figural art in religious settings.

Early Islamic Buildings
The Kaaba
Cubic structure in Mecca; most sacred Islamic site.
Dome of the Rock
Islamic shrine on a Christian-Byzantine model.
Features Byzantine mosaics, octagonal plan, central dome.
Site of Muhammad’s Night Journey; first monumental Islamic building.
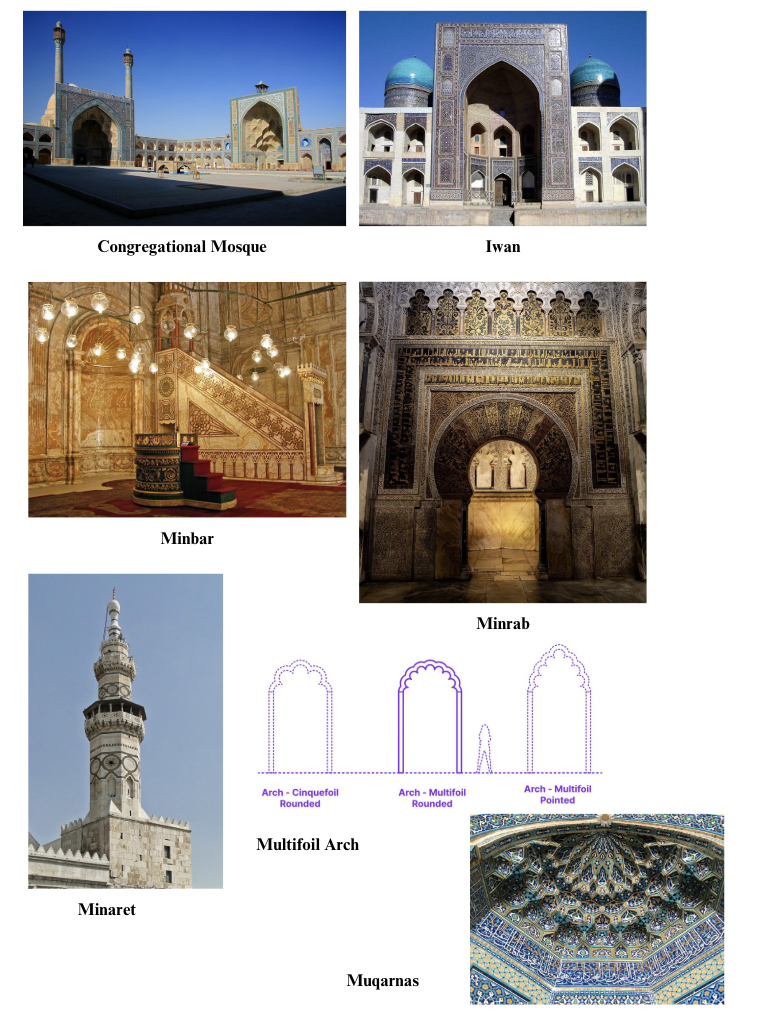
The Mosque
Common Elements:
Congregational Mosque: Main Mosque that hosts prayers
Iwan: A large, vaulted hall or space, walled on three sides and open on one
Minbar: A pulpit from which the imam delivers sermons
Minrab: A niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the direction of Mecca
Minaret: A tall tower is attached to a mosque, from which the call to prayer is announced.
Muqarnas: A type of ornamented vaulting in Islamic architecture. It resembles a honeycomb.
Multifoil Arch: An arch characterized by multiple circular or leaf shapes that are cut into its interior profile.

Type 1: Hypostyle Mosque
Origin: House of the Prophet, Medina (7th century).
Flat roof supported by columns.
Examples:
Great Mosque of Damascus: Byzantine mosaics, Roman plan.
Great Mosque of Córdoba: double-tiered arches, horseshoe arches, ornate mihrab.

Type 2: Four-Iwan Mosque
Iwan = vaulted hall open on one side.
Plan includes four iwans around a central courtyard
Great Mosque of Isfahan : developed over centuries, includes muqarnas and tiles.

Type 3: Centrally-Planned Mosque
Dome-covered main space, often with surrounding semi-domes.
Influenced from Hagia Sophia from Early Christian Art
Example: Blue Mosque: large central dome, six minarets, interior tilework.
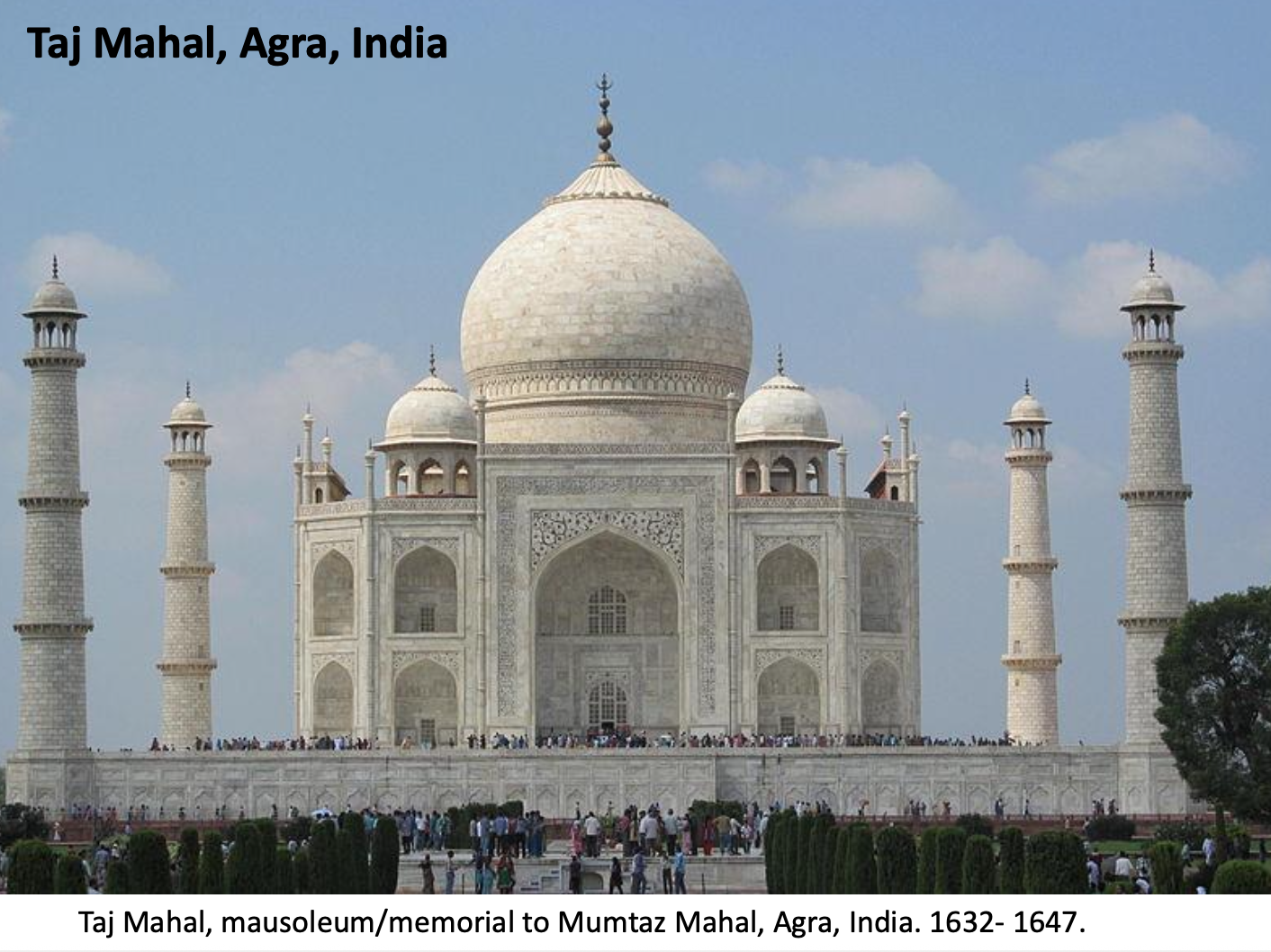

Islamic Mausolea
Cemetery House
Taj Mahal
White marble mausoleum
Features: symmetrical plan, iwan, central dome, garden symbolizing paradise.
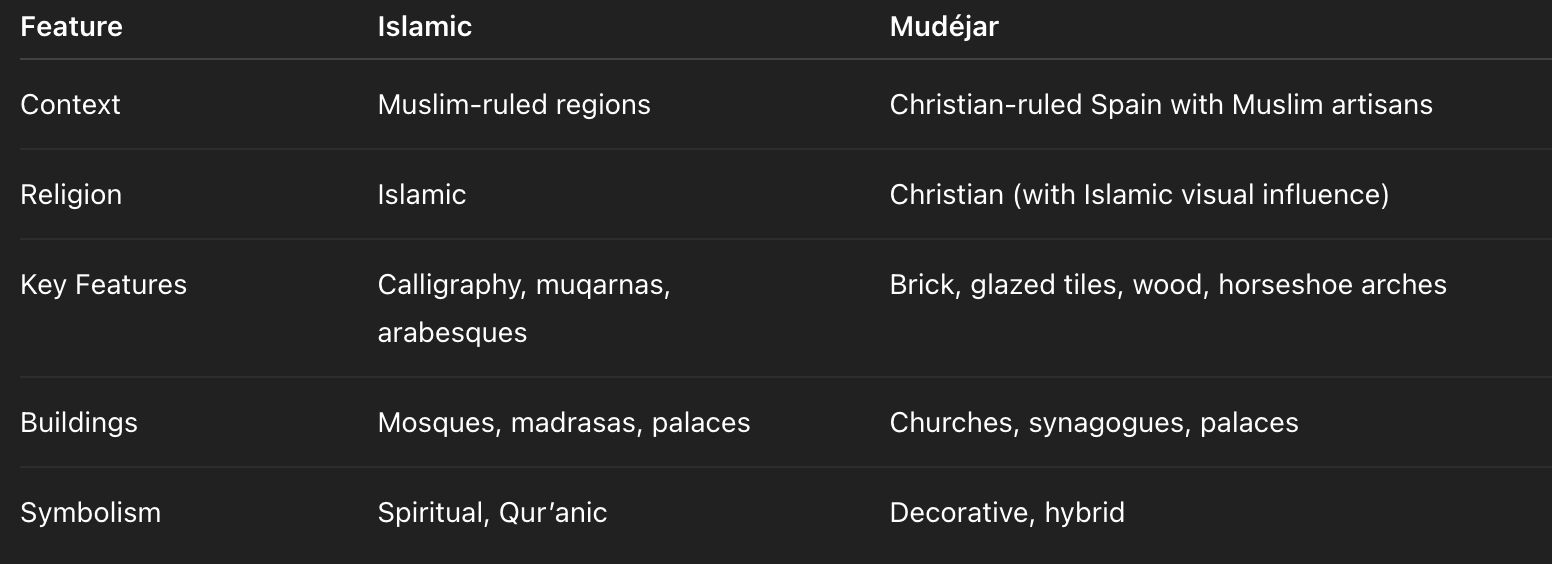
Mudejar vs Islamic
Islamic Art
Origin: Islamic world
Religious: Built for Muslim worship and rule
Key features: Calligraphy, geometry, arabesques, muqarnas
Common structures: Mosques, palaces, mausolea
Avoids human figures in religious spaces (aniconism)
Mudejar Art
Origin: Christian Spain
Cultural mix: Christian buildings made by Muslim artisans
Combines: Islamic motifs + Christian forms
Key features: Brickwork, horseshoe arches, tilework, wooden ceilings
Found in: Churches, synagogues, palaces
Decorative, not religiously Islamic

Key Characteristics of Islamic Ornament: Secular Art
Geometry: Infinite, complex patterns reflecting unity and divine perfection.
Arabesque: Flowing, vegetal patterns symbolizing paradise and growth.
Calligraphy: The highest art form; often quotes from the Qur’an in Arabic script.
Carpets/Rugs: The Ardabil Carpet, huge, symmetrical, spiritual in function.
Tiles: Glazed ceramics for decoration in mosques and palaces.
Muqarnas: Stalactite-like vaulting in domes and niches; architectural ornament that plays with light and shadow.

Secular Art: Illuminated Manuscripts
Art that is not based on religious themes
Bahram Gur in a Peasant's House: Narrative scene from Persian epic.
Bahram Gur Fights the Karg: Heroic Persian king battles a horned wolf; dynamic and richly colored.
Reflects royal ideals, Persian influence, and secular storytelling.

Palaces
The idea of paradise garden
The Alhambra (Spain)
Three Nasrid (the last Islamic dynasty to rule) palaces: Court of the Lions, Comares Palace, Mexuar.
Features: intricate stucco work, muqarnas, calligraphy, and light/water reflections.
Topkapi Palace (Istanbul)
Seat of Ottoman sultans; includes courtyards, pavilions, tiles, and gardens.
Chehel Sotoun (Iran)
17th-century palace with garden pavilion, mirrored hall, and reflecting pool.

Gardens
Role of Landscape and Water
Water = spiritual purity and paradise.
Gardens mirror Qur’anic descriptions of heaven.
Paradise Gardens
Alhambra: enclosed, symmetrical, quadripartite garden.
Chahar Bagh (Iran): cross-axial plan with water channels.
Taj Mahal Gardens: integrates Chahar Bagh concept, frames mausoleum.