Wound management
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
define wound
breakdown in the protective function of the skin
o the loss of continuity of epithelium, with or without loss of underlying connective
tissue (i.e. muscle, bone, nerves) following injury to the skin or underlying
tissues/ organs caused by surgery, a blow, a cut, chemicals, heat/ cold, friction/
shear force, pressure or as a result of disease, such as leg ulcers or carcinomas
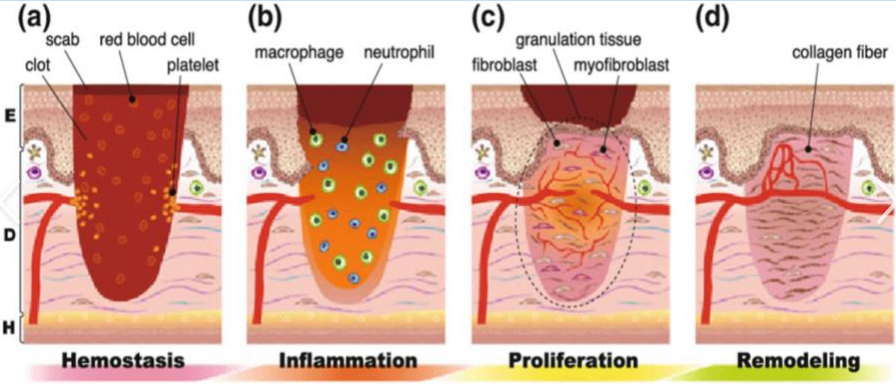
Describe the phases of wound healing: HIPR
Haemostasis / Inflammation / Proliferation / Remodelling
Haemostasis (immediate):
Initial vasoconstriction, release of clotting factors and fibrin clot formation
Inflammation (days 1-4):
Vasodilation, delivery of macrophages, phagocytosis, blood clot formation, loosely united wound edges
Proliferation/Granulation (days 4-21):
Epithelial cells migrate bridging the wound, Angiogenesis-growth of new capillaries, fibroblasts migrate along firbin strands synthesising scar tissue
Remodelling (days 21-2 years):
Develop tensile strength, collagen remodelling, vascular maturation and regression.
Which Factors affect wound healing:
Co-morbidities, Pressure Ulcer Risk, Nutritional status, Mobility status,
Continence status, Vascular supply, Anaemia, Size, sleep, Poverty, Lack of
knowledge, Depression, Advancing age, Cognitive impairment, Patient
What does TIMES mean
Tissue: determine the phase of wound healing, treatment and dressing
Infection: hot, oedema, pus, pain, odor, not healing, redness, pyrexia and more exudate- topical silver, systemic flucloxacillin
Moisture: Heavy exudate is bad, white edge= too much moisture, if its too dry we apply gel OR if too wet then we apply dressing
dressing to reduce it)
Edge of wound: tracking wound edges with sterile cotton tipped swab against a ruler
Surrounding skin: Excess wound exudation is bad, balance is moist is essential
What is a pressure ulcer and how to treat it
A pressure ulcer is localised damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue, usually over a
bony prominence (or related to a medical or other device), resulting from sustained
pressure (including pressure associated with shear). The damage can be present as
intact skin or an open ulcer and may be painful.
Describe the 3 causes of Moisture associated skin damage and their treatment
red diffused, multiple superficial spots aka
kissing lesion in skin folds, natal cleft, under the breasts
Incontinence-associated dermatitis (IAD): exposure to urine or faeces or body fluids, use barrier cream
Intertrigo: Inflammation caused by skin-to-skin friction, groin, bet. folds etc
Fungal: Around legs and bottom-antifungal cream ( avoid soap for washing, use emointment washer to take away moisture)
Describe Peri-Stoma and its treatment
Leakage of stomal effluent onto the peristomal skin
will cause inflammation and even skin erosion
use powder to keep dry
Describe Peri-wound and its treatment
Excess wound exudation may result to the peri-wound skin to become macerated (edges white), excoriated and further skin break down.
Cavilon spray can be applied to peri-wound as skin
protection
What are the functions of the skin
Control of body temperature, Keeping out infection, Monitors pain, A waterproof barrier, Communication, Production of Vitamin D, Protects delicate organs, Mends itself when damaged
What dressing to use for high-exudate dressing
Hydrofibre, foam dressing, Alginate dressing, SurgyHoney RO( reactive o destroys the exudate)m
What dressing to use for infections?
silver dressing, odour absorbing dressing
What to use for peri-wound
cavilon spray, barrier cream
What to use for fungal infection
antifungal cream, clotrimazole, emmointmnet wash ( to reduce moisture)
What to use for incontinence associated dermititis
barrier cream
What dressing to use for pressure ulcer?
Hydrofibre dressing, barrier cream
What to use for viable granulation
non-adherent dressing
What dressing to use for necrotic tissue
Hydrocolloid, Hyrogels - promote moisture