5.1+5.2 Rotational Kinematics + Dynamics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Rigid Object
An object with a definite shape that doesn't change, so that the particles composing it stay in fixed positions relative to another.
Axis of Rotation
An imaginary line around which rotation occurs.
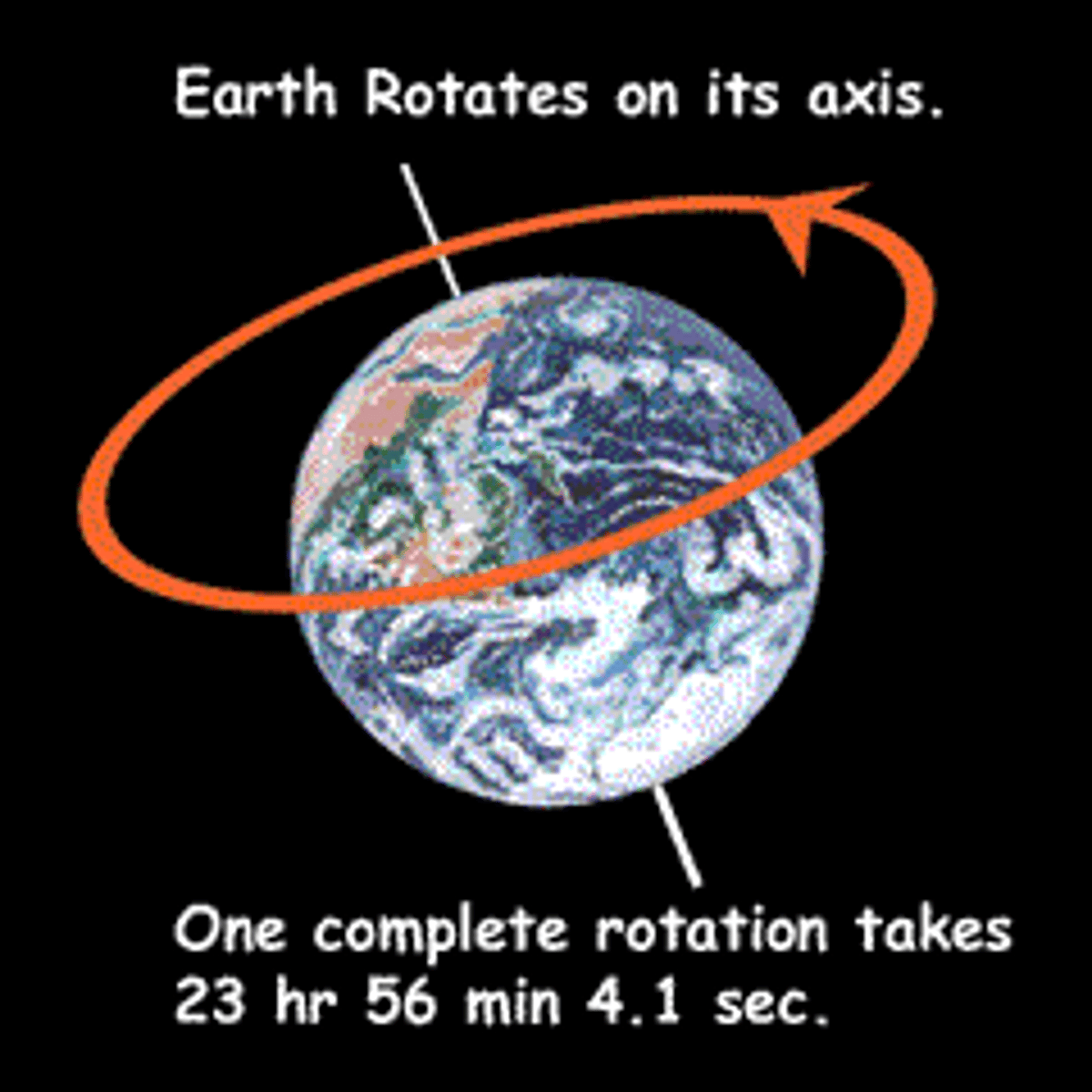
Angular Position
The position, , of an object according to a co-ordinate system measured in s of the angle of the object from a certain origin axis. Conventionally, this origin axis is the positive x-axis.
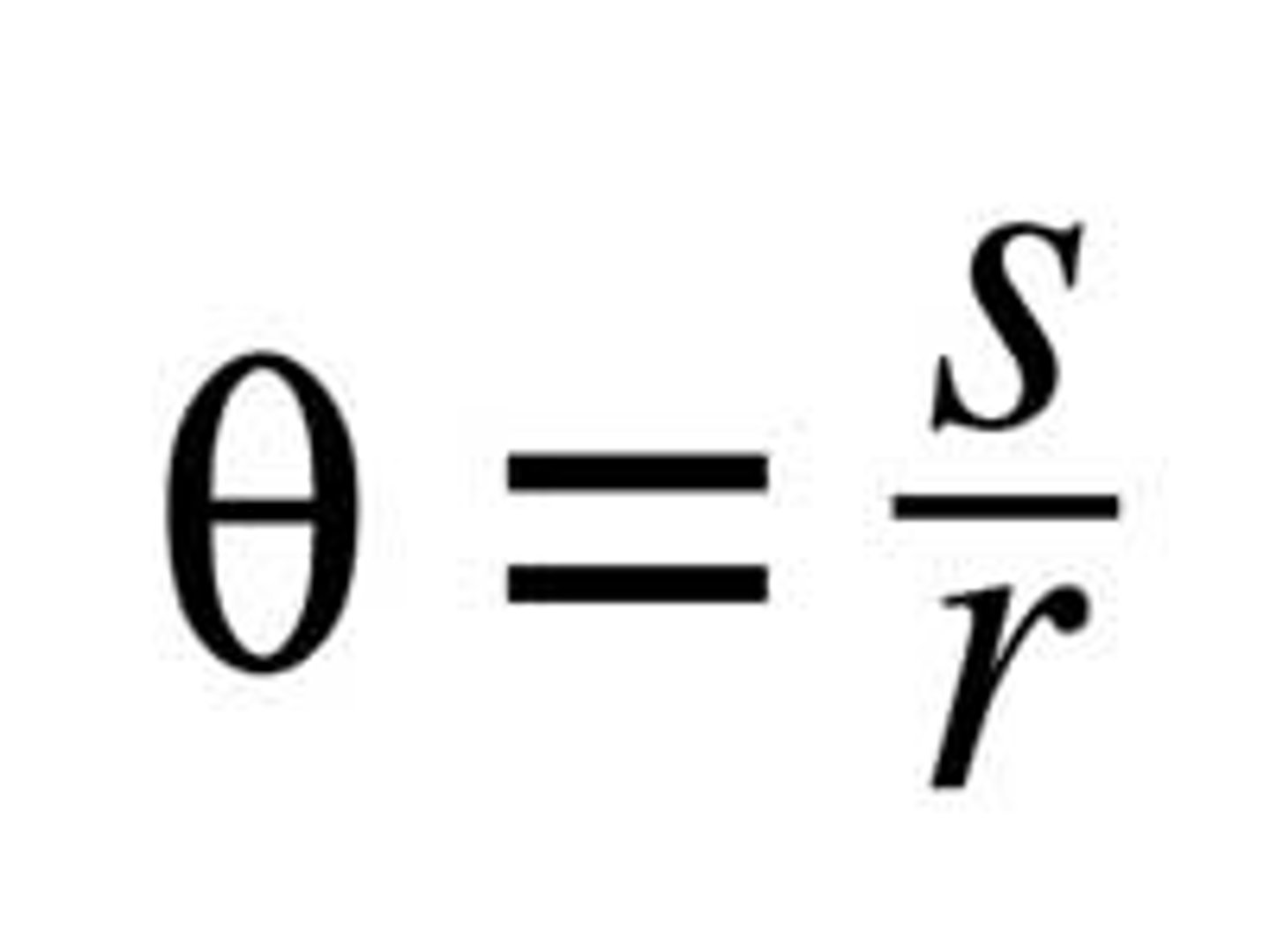
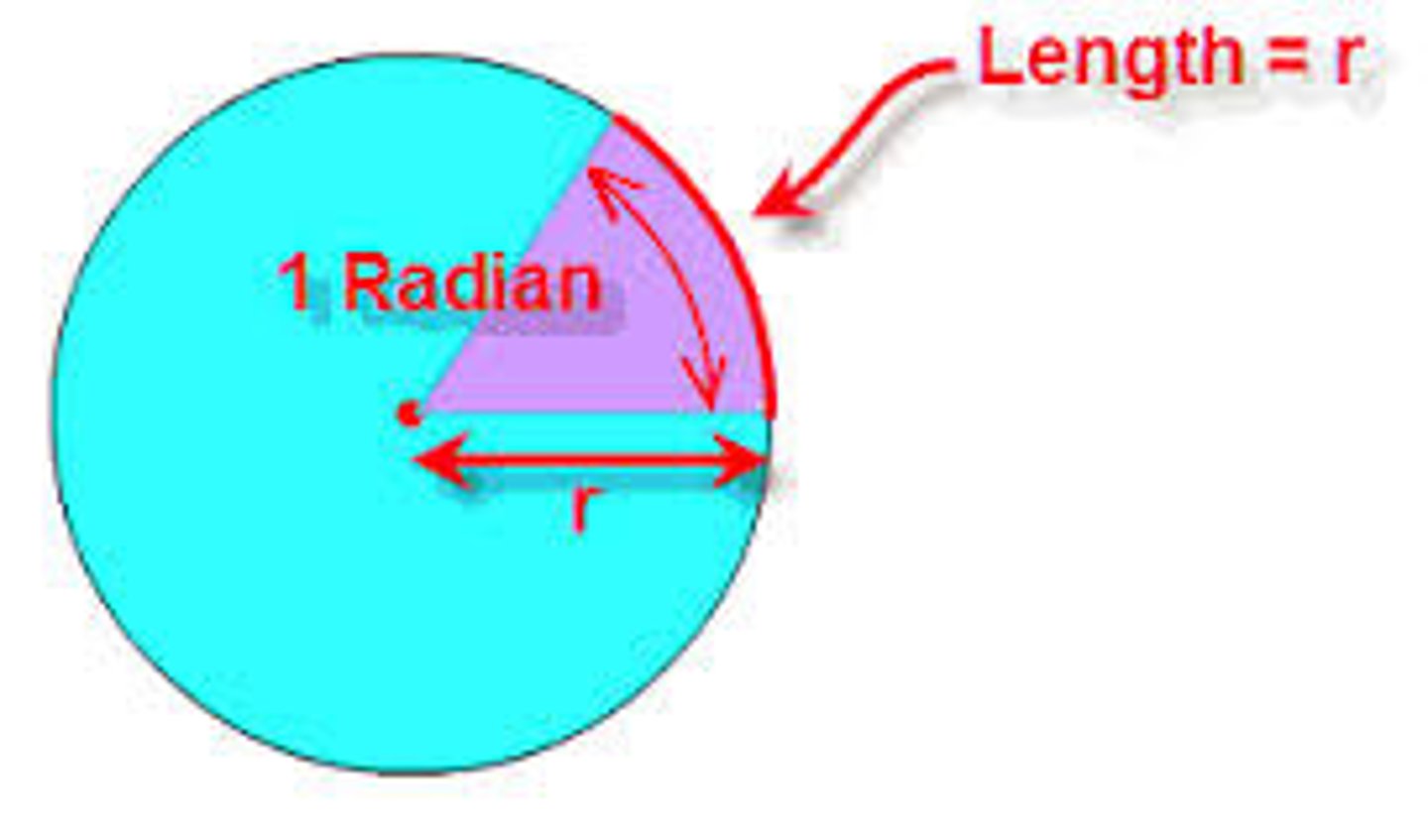
Radian
The angle subtended by an arc who's length is equal to the radius.
Average Angular Velocity
rate of change of angular position, rad/s
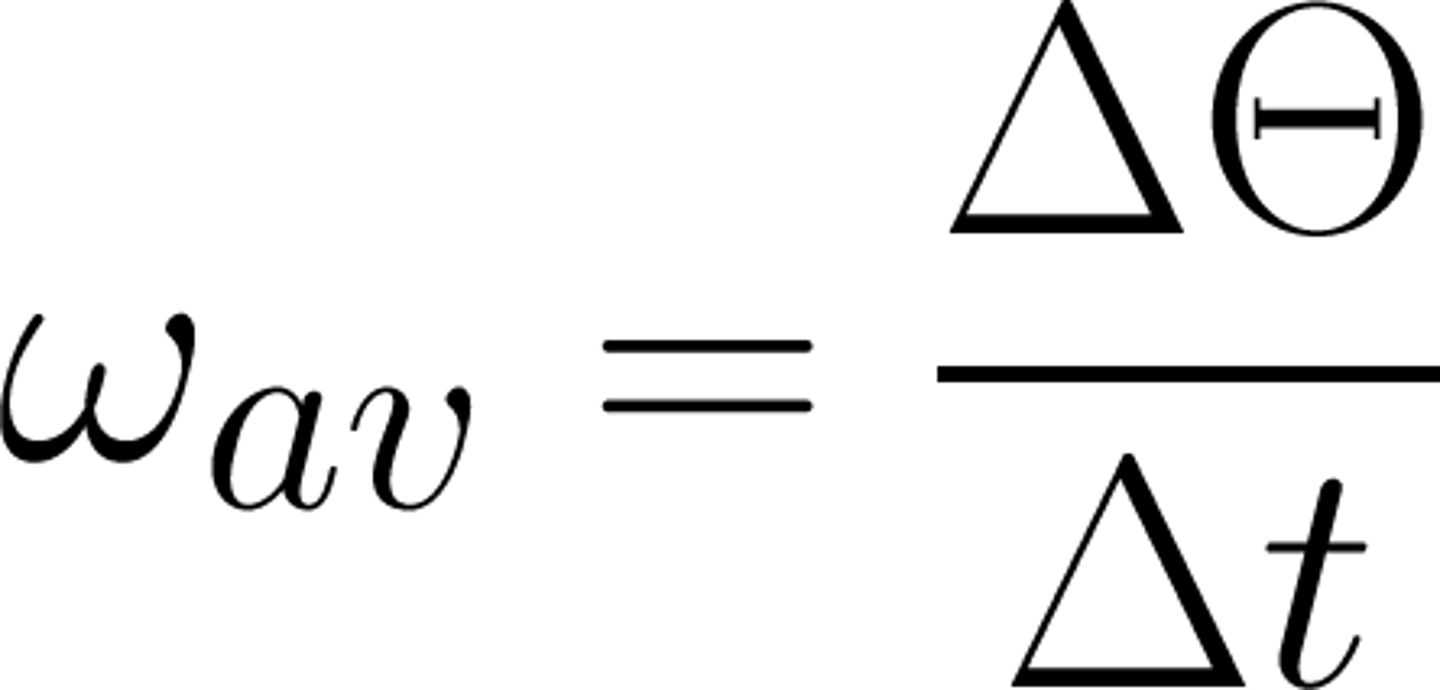
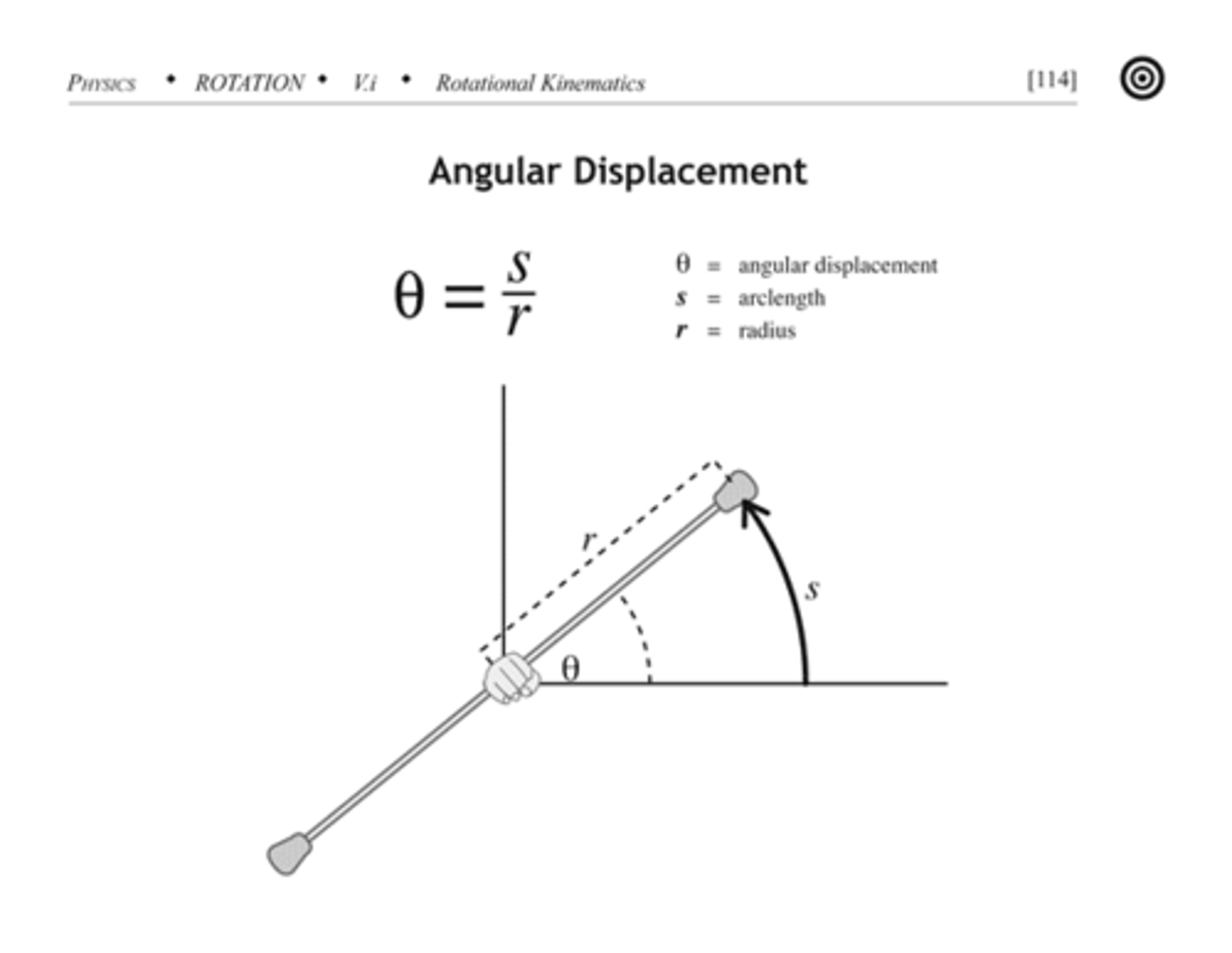
Angular Displacement
The change in angular position or the radian measure of the angle through which the body turns.
Period
In physics, the time that it takes a complete cycle or wave oscillation or for an object to make a complete circle.
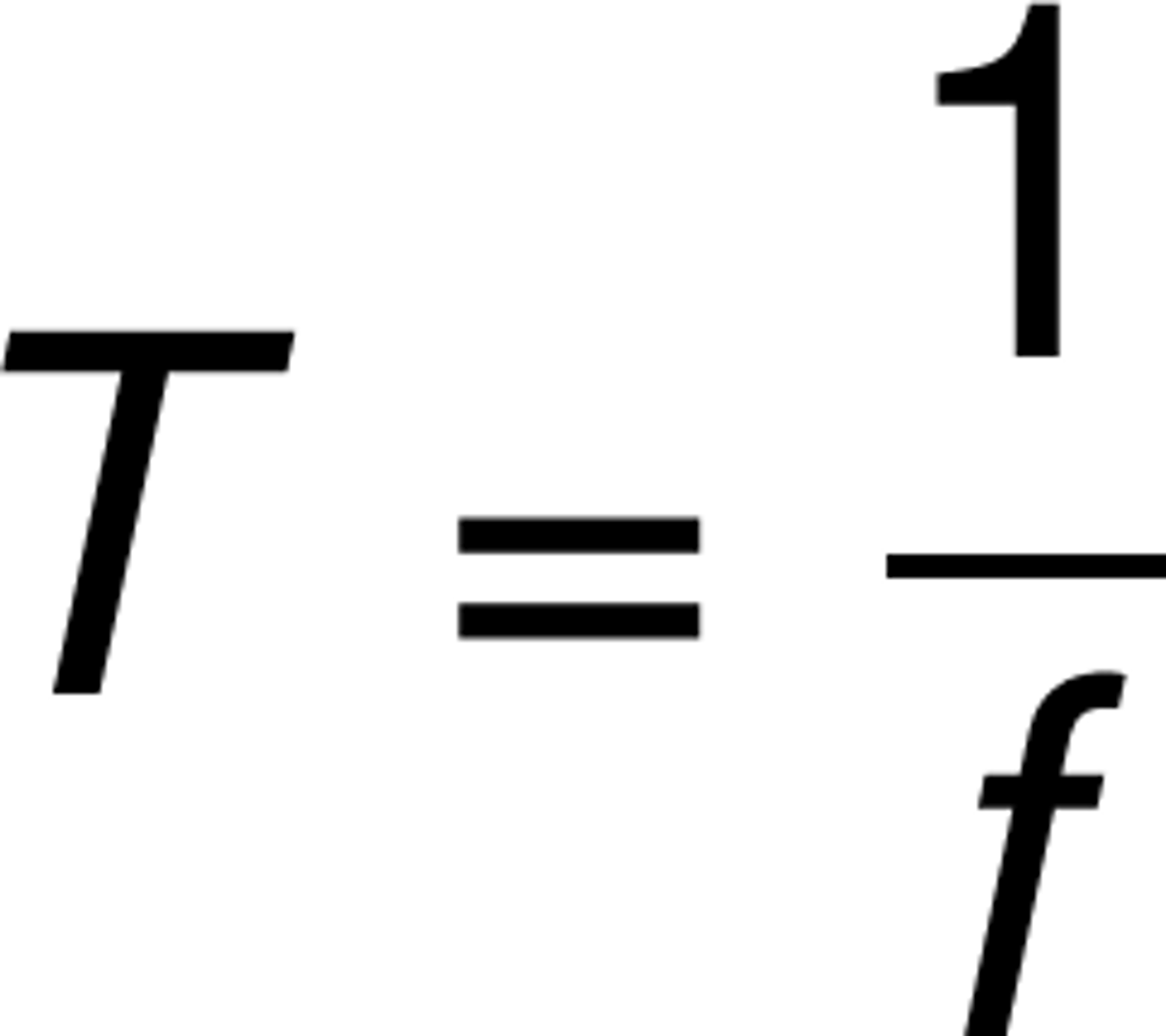
Frequency
Number of complete cycles in a given time.
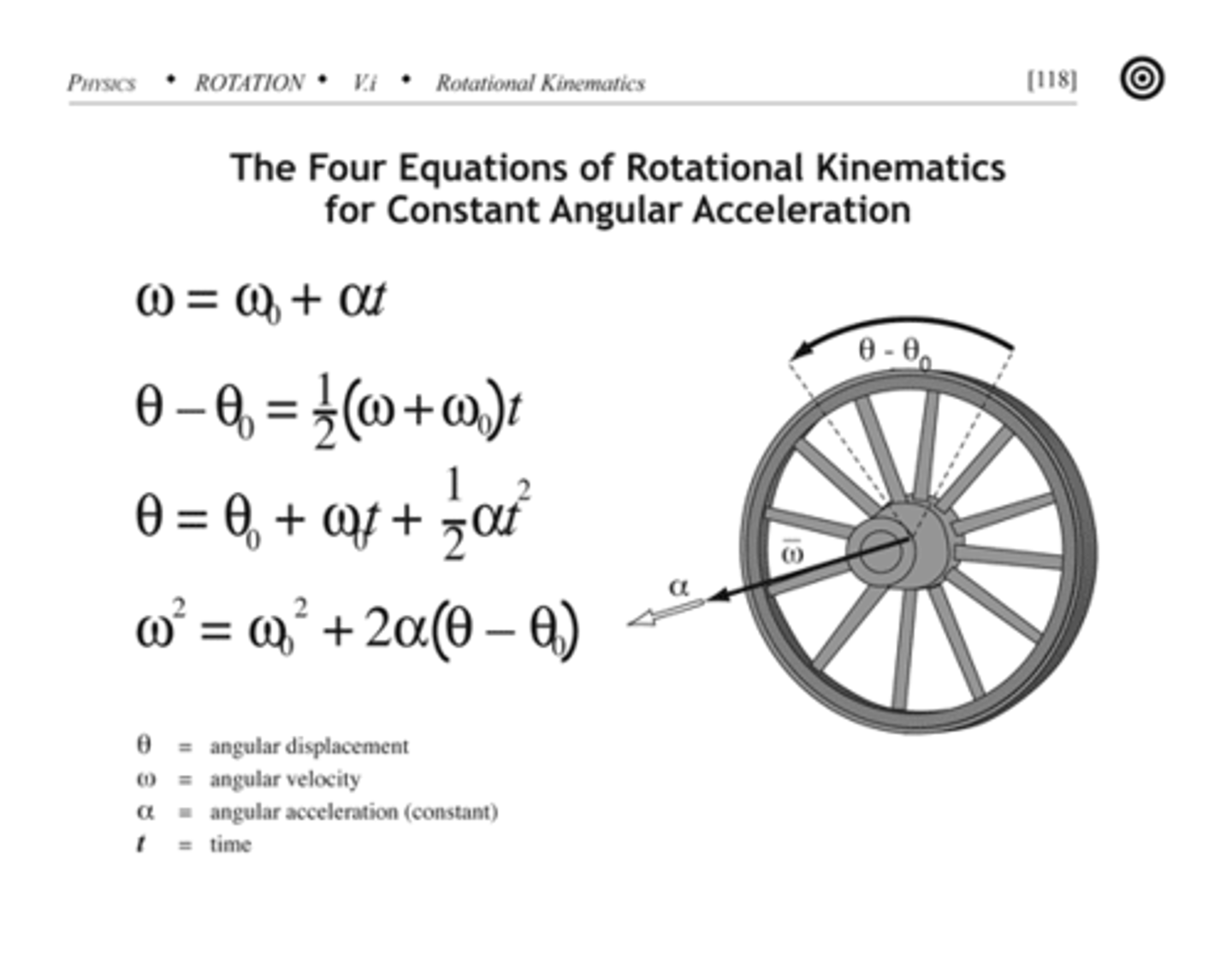
Constant Angular Acceleration
When an object traveling in a circular motion changes its angular velocity at a steady rate.
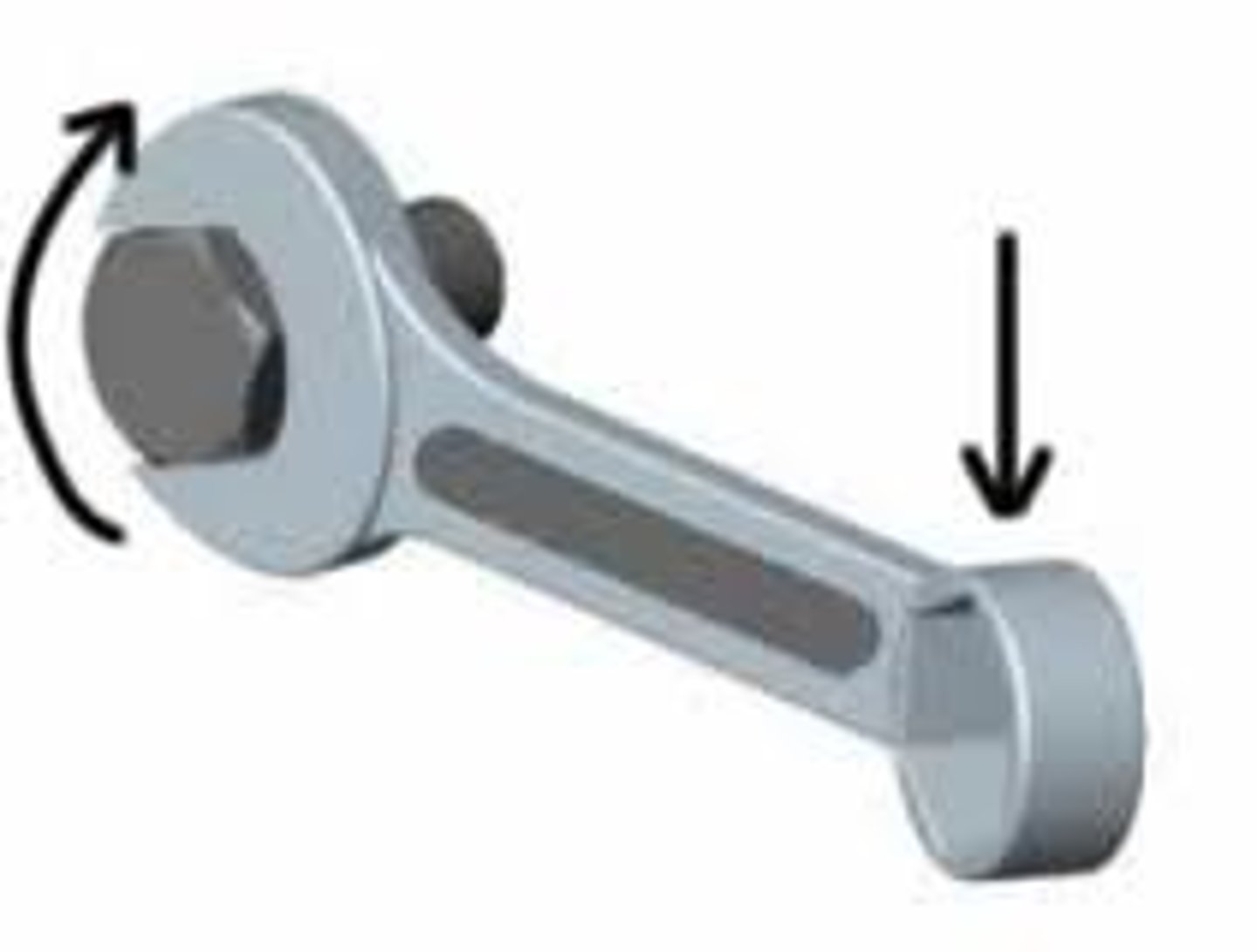
Torque
Force that causes rotation that is perpendicular to the distance the force is from the axis of rotation.

translational position to angular position
x = θ r
translational velocity to angular velocity
v = ω r
translational acceleration to angular acceleration
a = α r
centripetal acceleration and angular speed
a(sub)c = ω²r