Brain
1/94
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
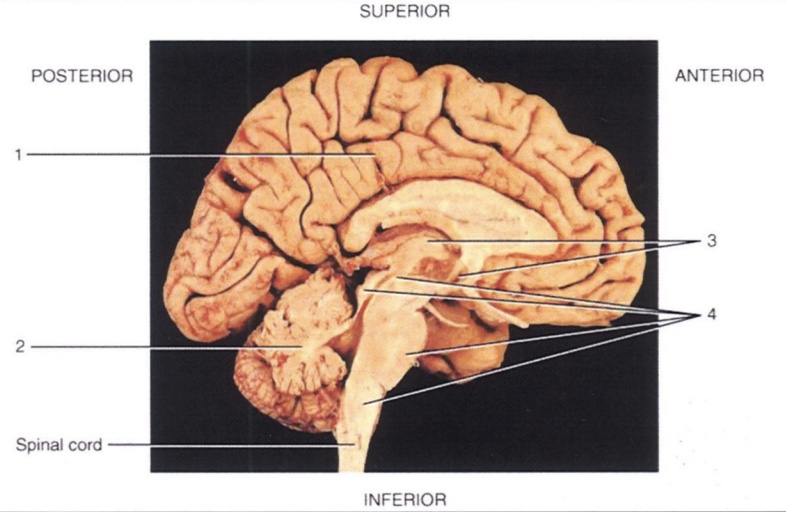
1
Cerebrum
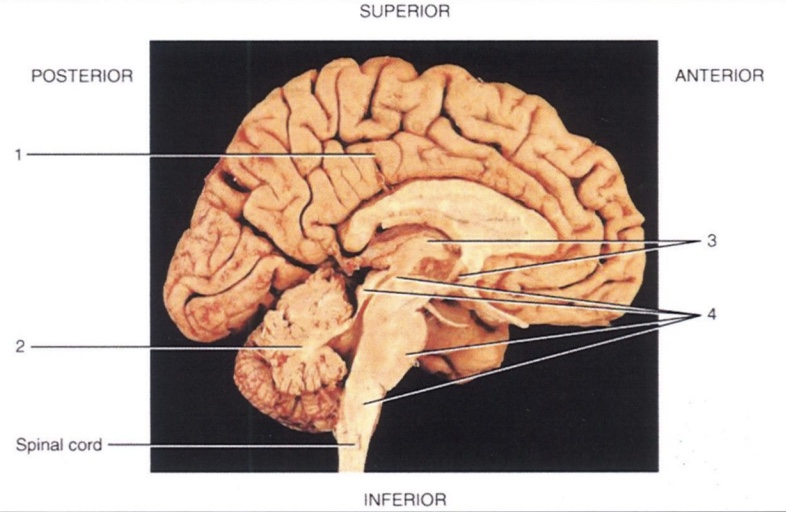
2
Cerebellum
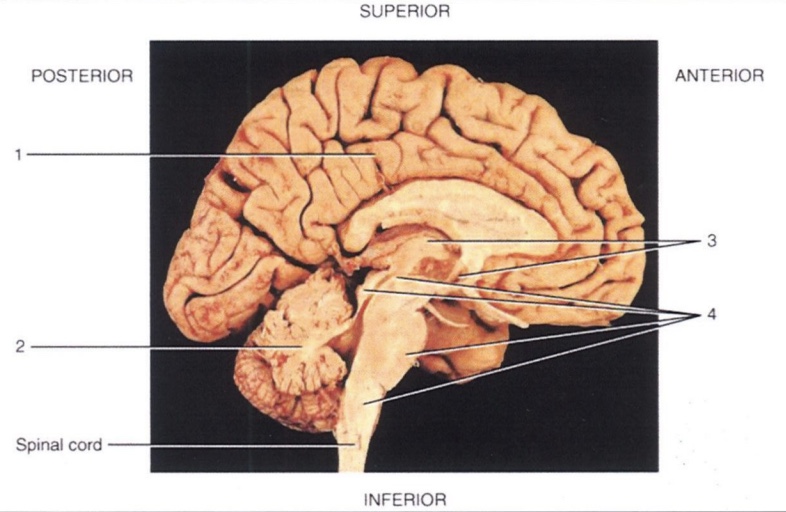
3
Diencephalon
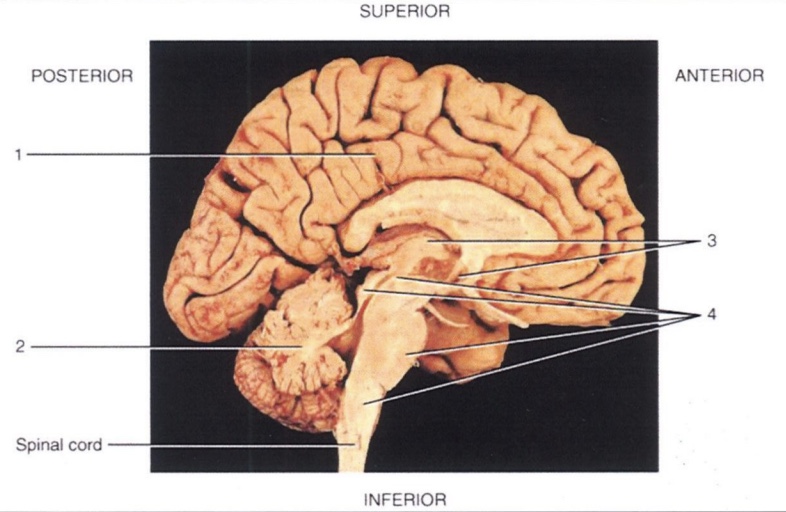
4
Brain Stem
What lobe involves taste (gustatory), memory, integrates roles of other lobes
Insula Lobe
What lobe involves the basic functions?
Cerebral Lobe
What lobe involves voluntary motor movement, personality decision making?
Frontal Lobe
What lobe involves vision?
Occipital Lobe
What lobe involves hearing and smell?
Temporal Lobe
What lobe involves general senses?
Parietal Lobe
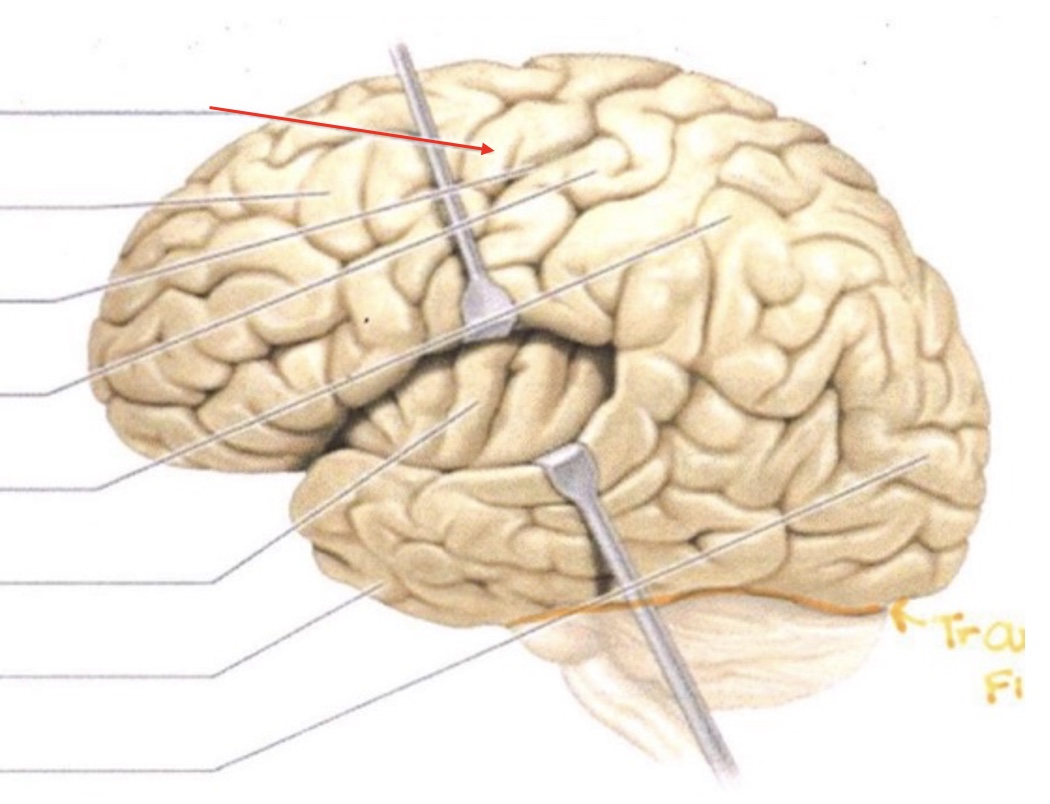
Precentral Gyrus
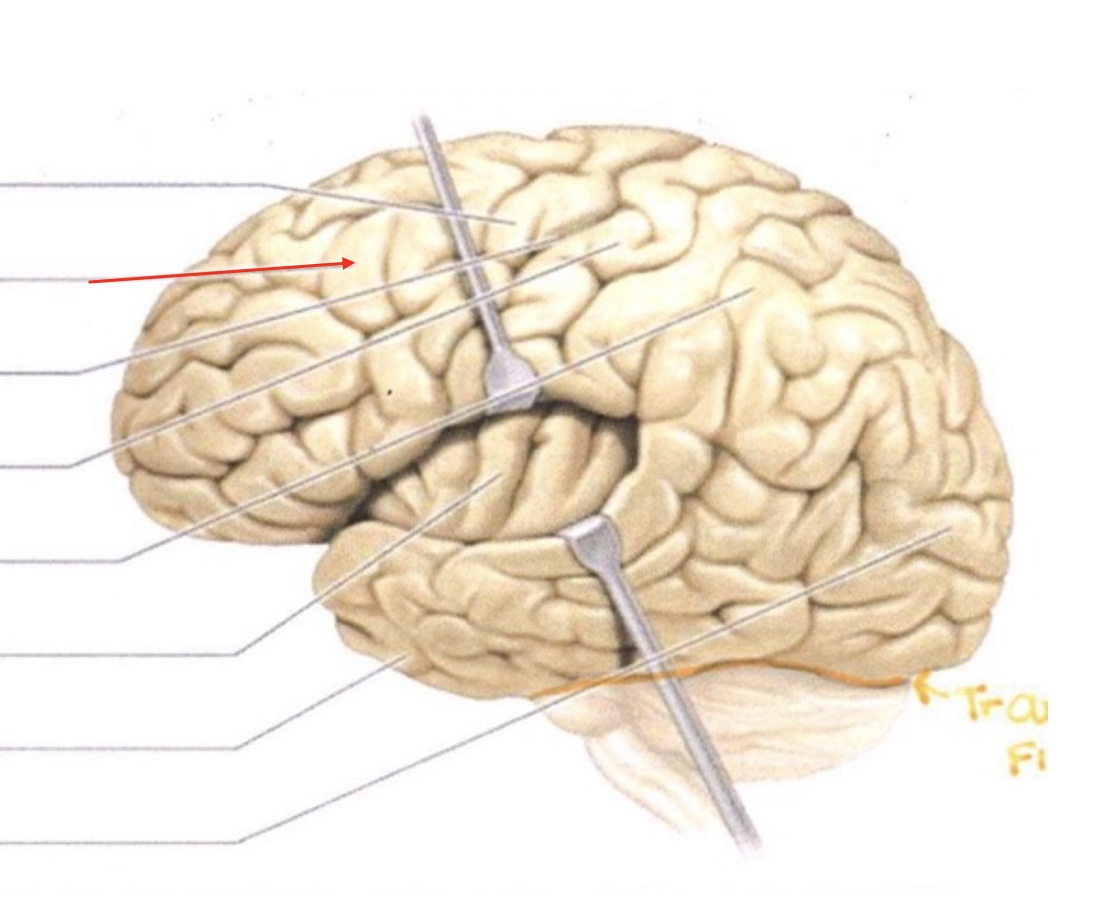
Frontal Lobe
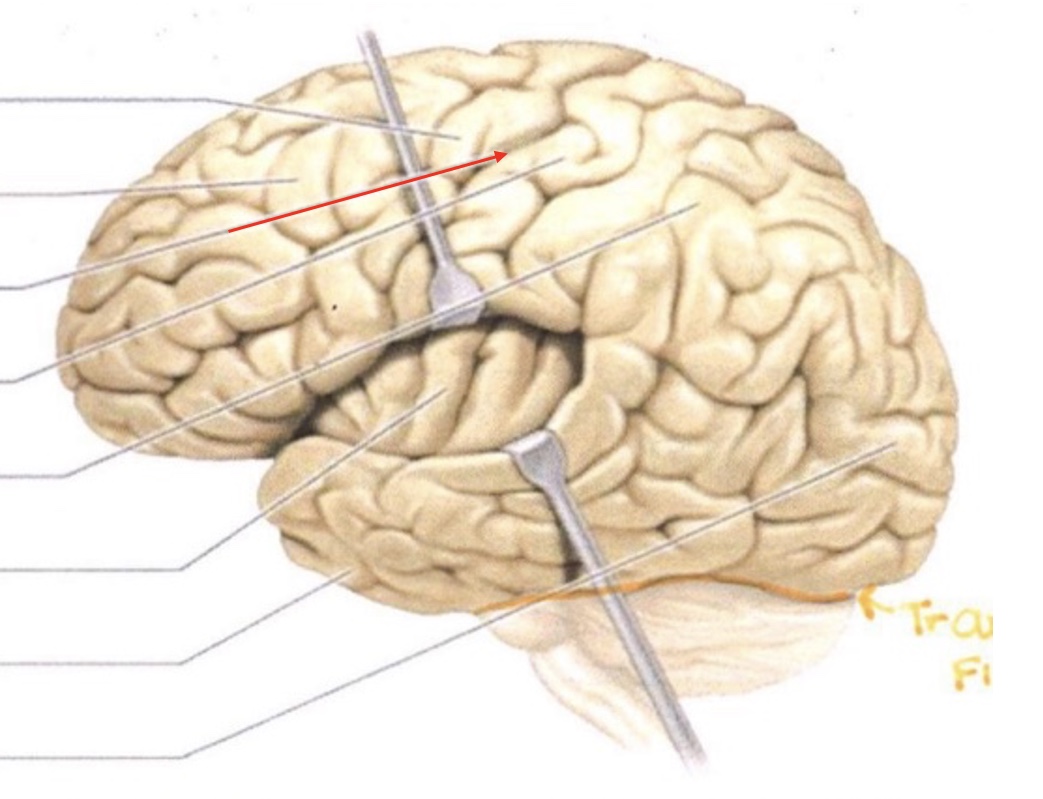
Central Sulcus
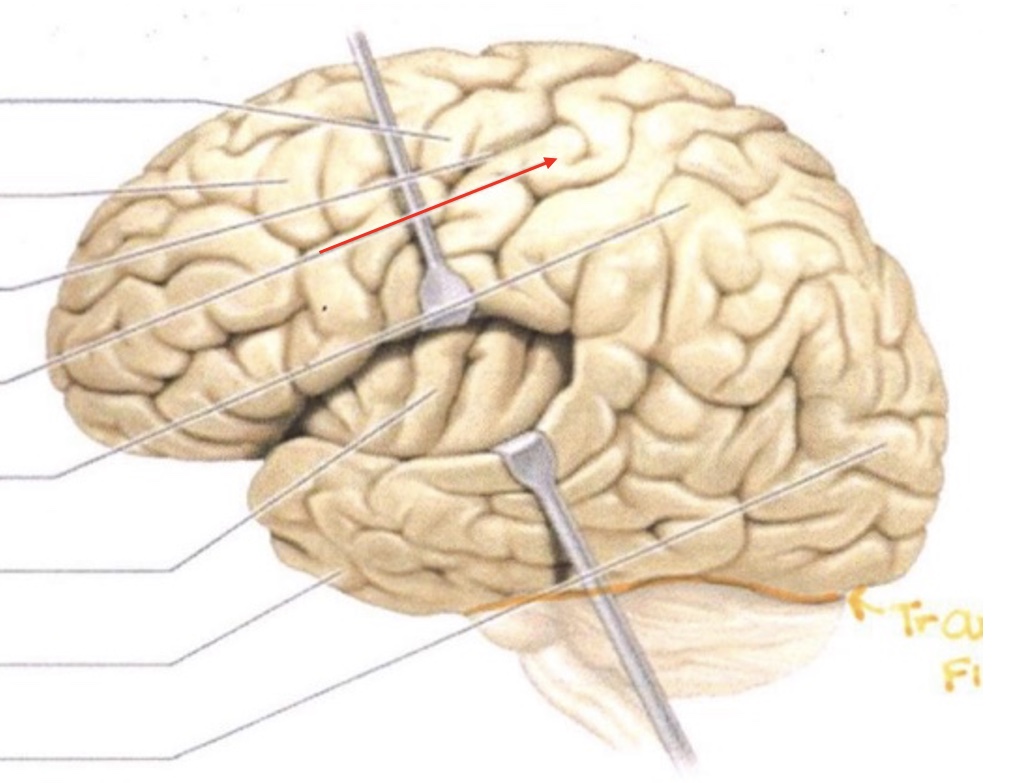
Postcentral Gyrus
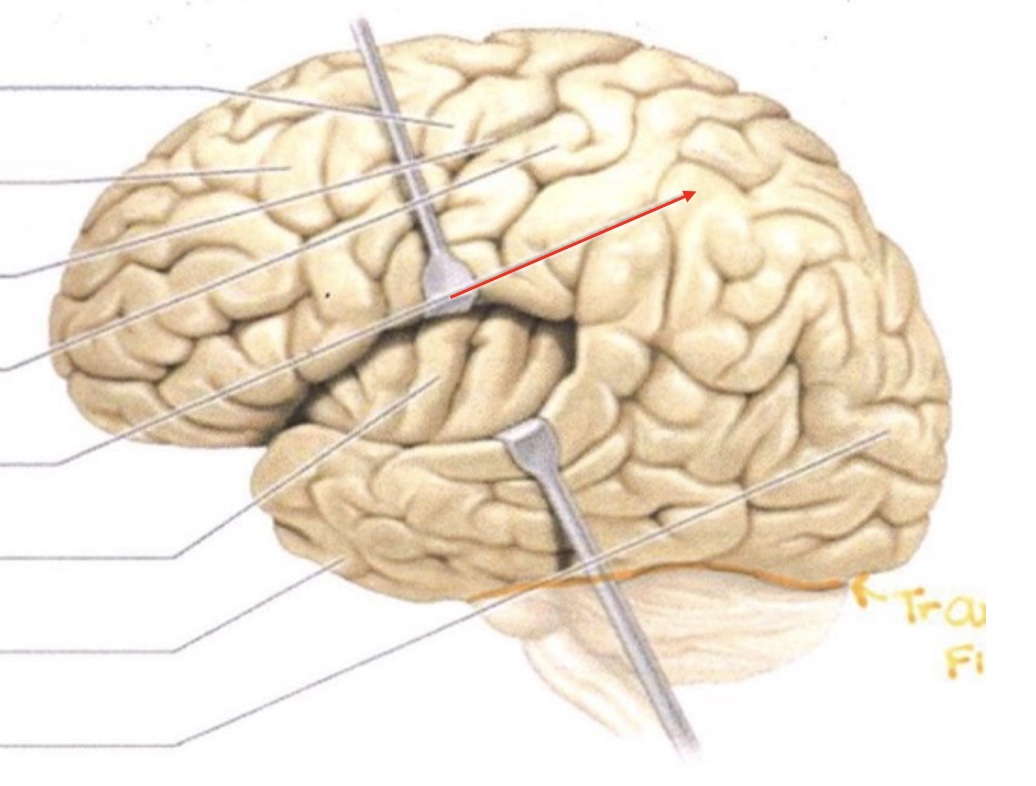
Parietal Lobe
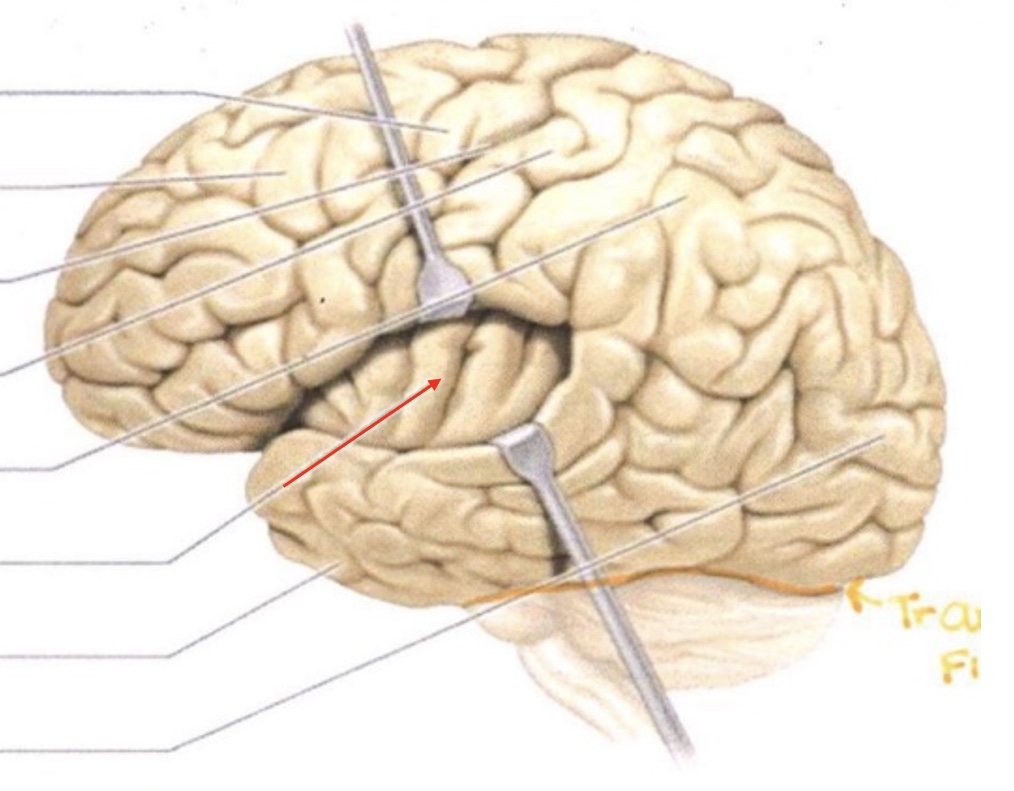
Insula
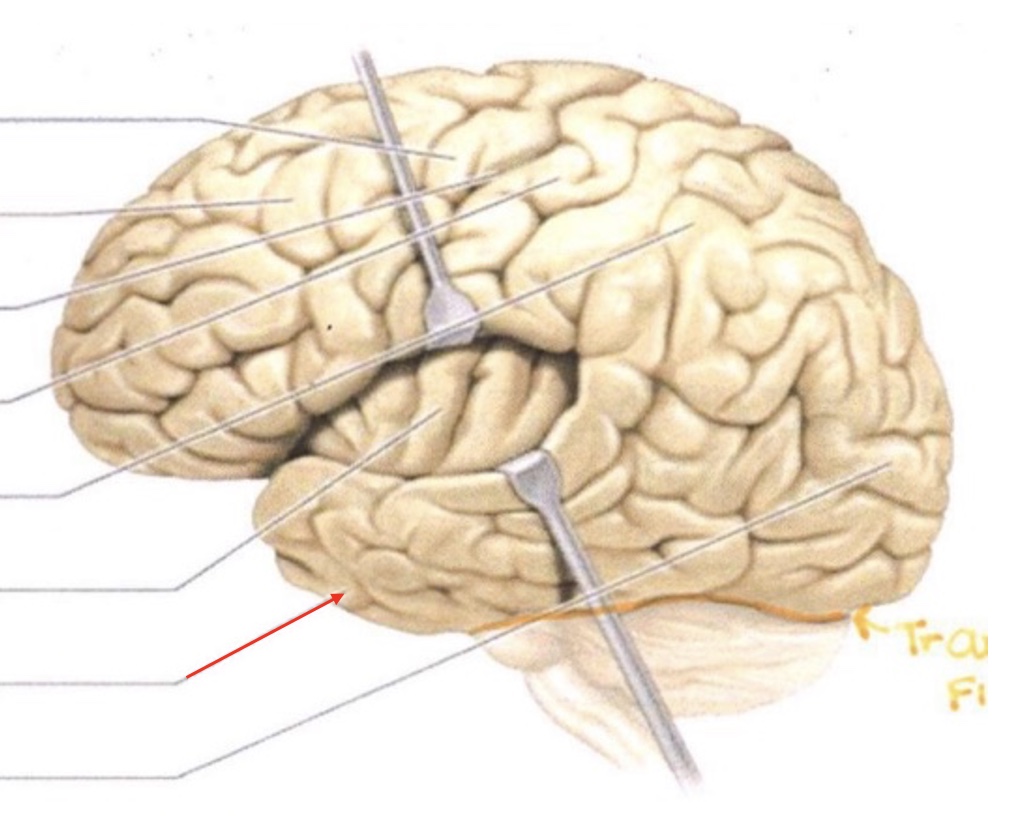
Temporal Lobe
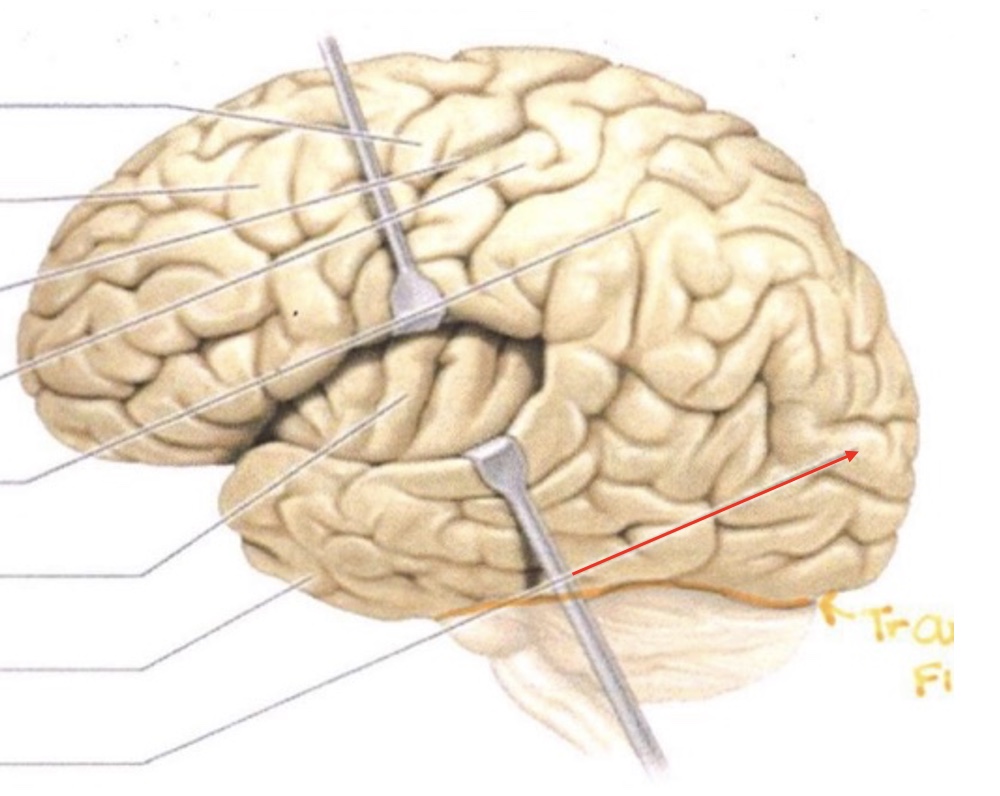
Occipital Lobe
Fissure
Deep Groove
Gyri/Gyrus
Elevated ridges (write singular & plural versions of the term)
Sulci/Sulcus
Shallow grooves (write singular & plural versions of the term)
Longitudinal Fissure
Fissure that separates cerebrum into R & L hemispheres
Transverse Fissure
Fissure that separates cerebrum from cerebellum
Corpus Callosum
White matter tract that connects the R & L hemispheres
Cerebral Cortex
The surface of the cerebrum is made up of a thin layer of gray matter known as the ________ . Deep to that laver is underlying white matter.
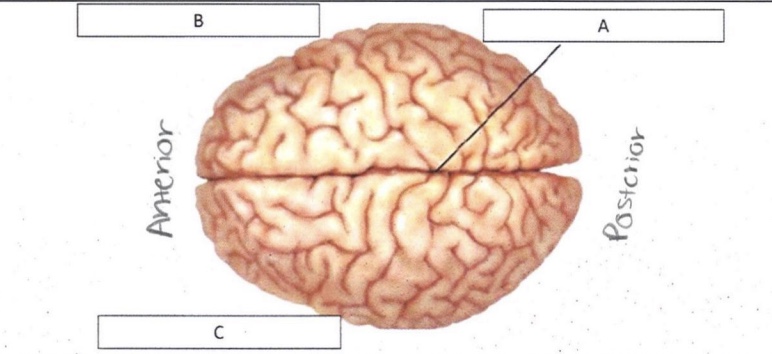
A
Longitudinal Fissure
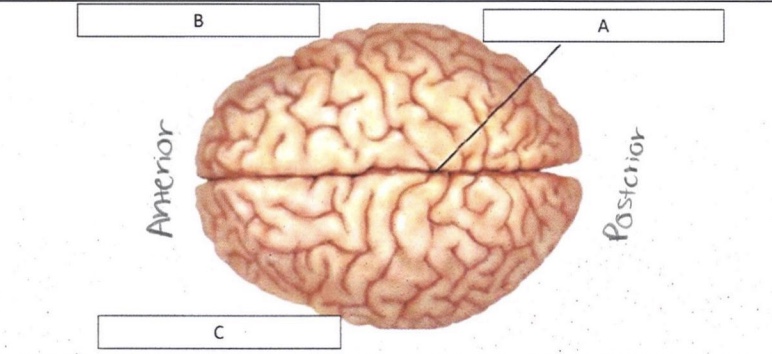
B
Right Hemisphere
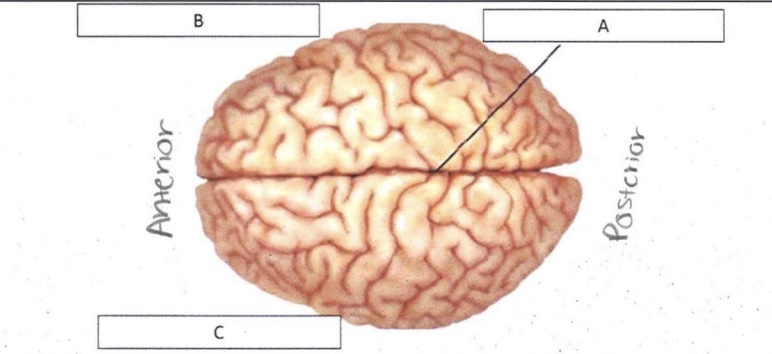
C
Left Hemisphere
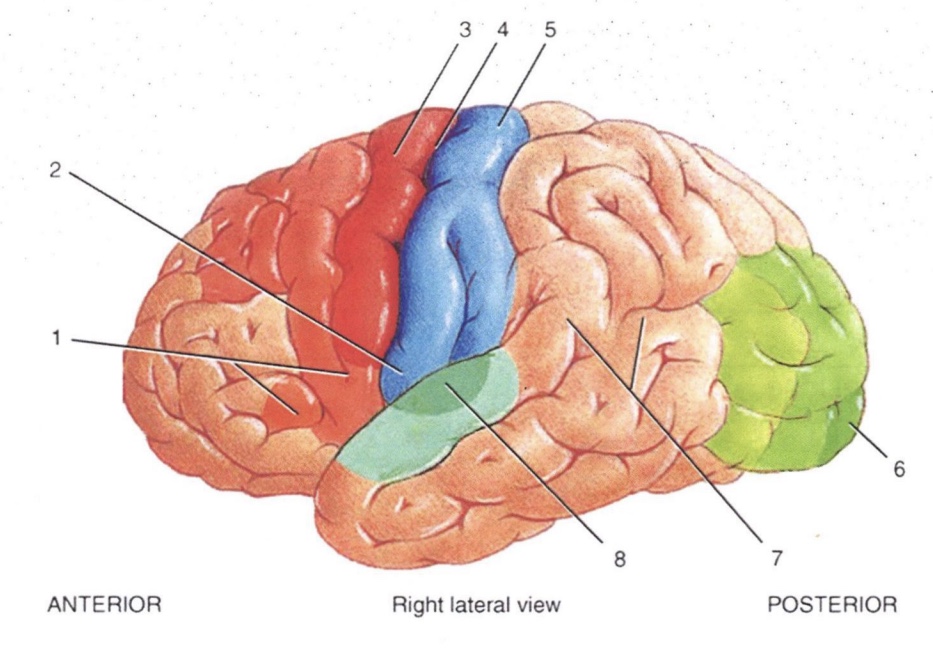
1
Broca’s Speech Area
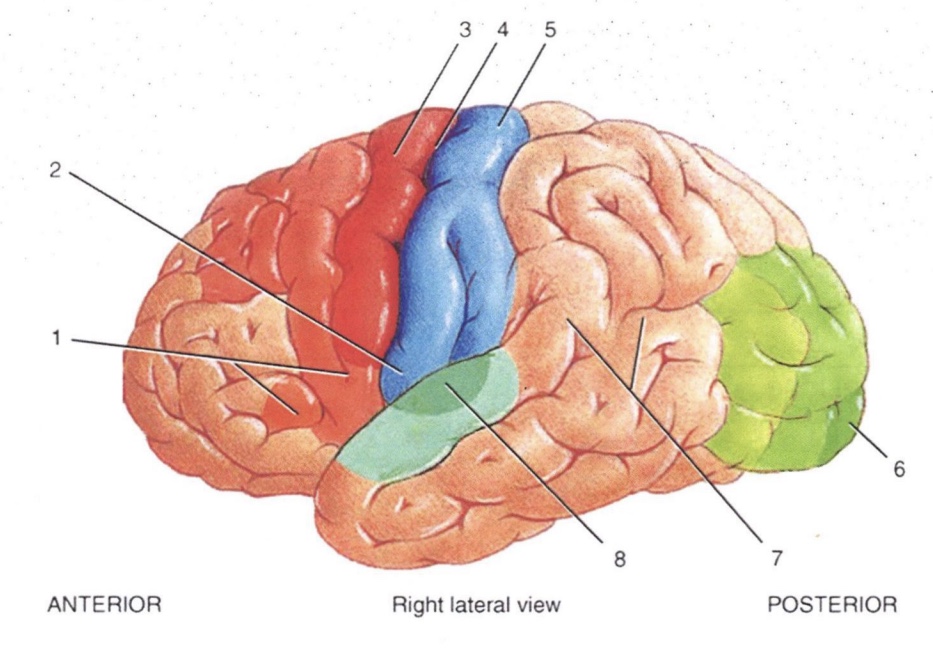
2
Primary Gustatory Area
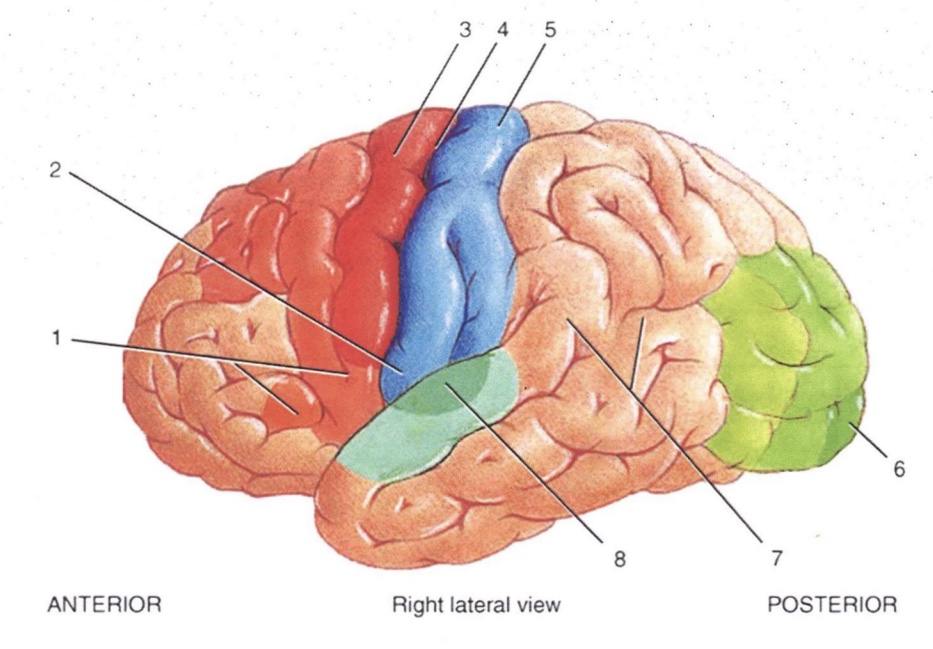
3
Primary Motor Area
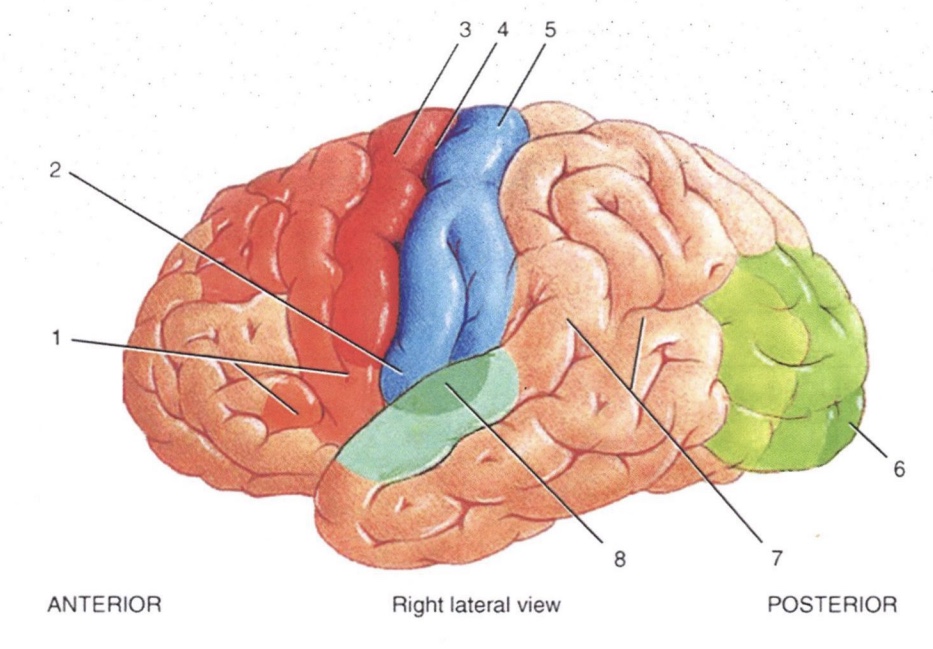
4
Central Sulcus
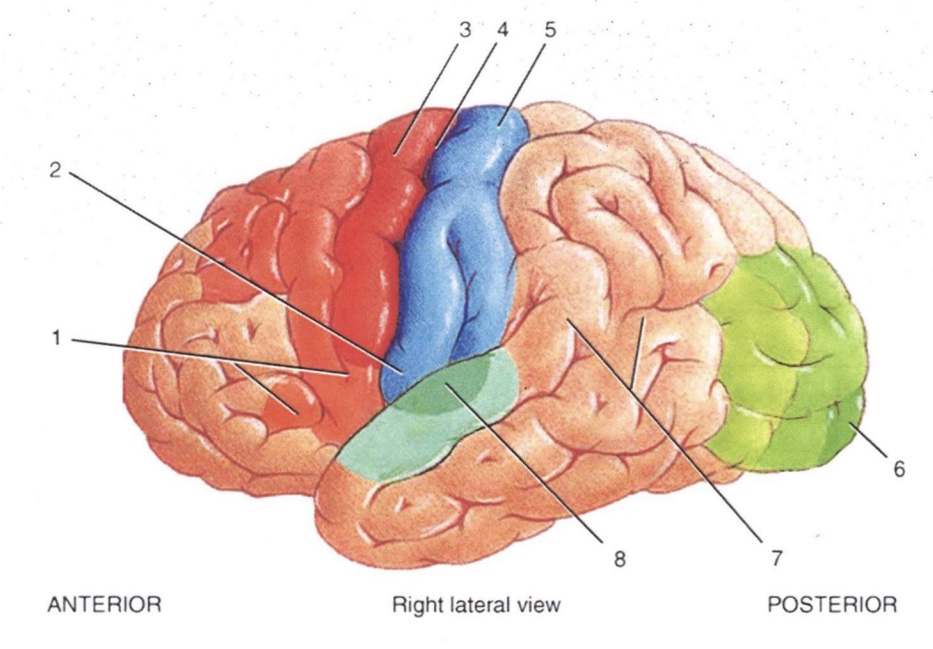
5
Primary Somatosensory Area
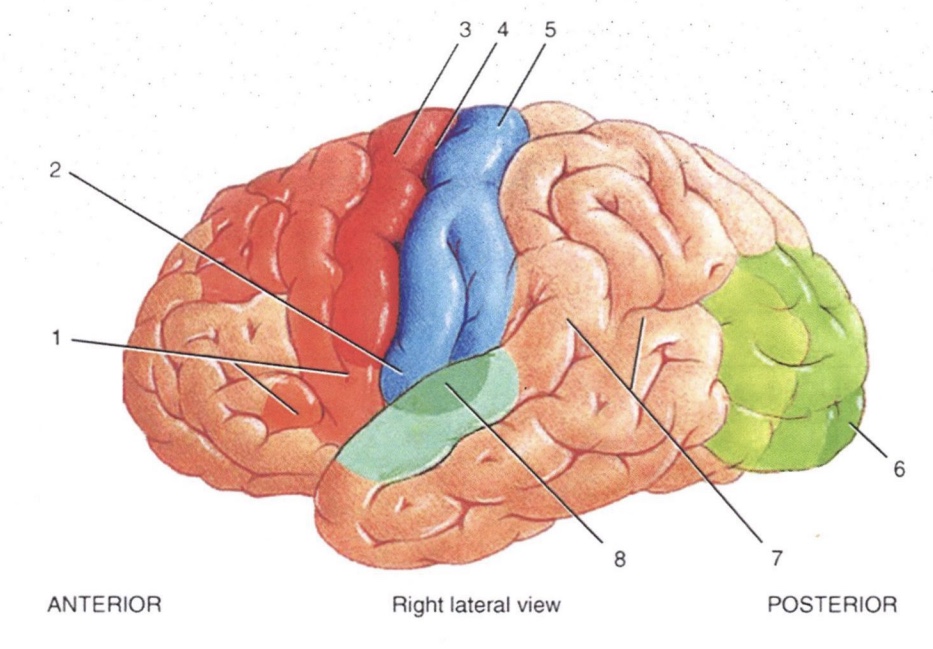
6
Primary Visual Area
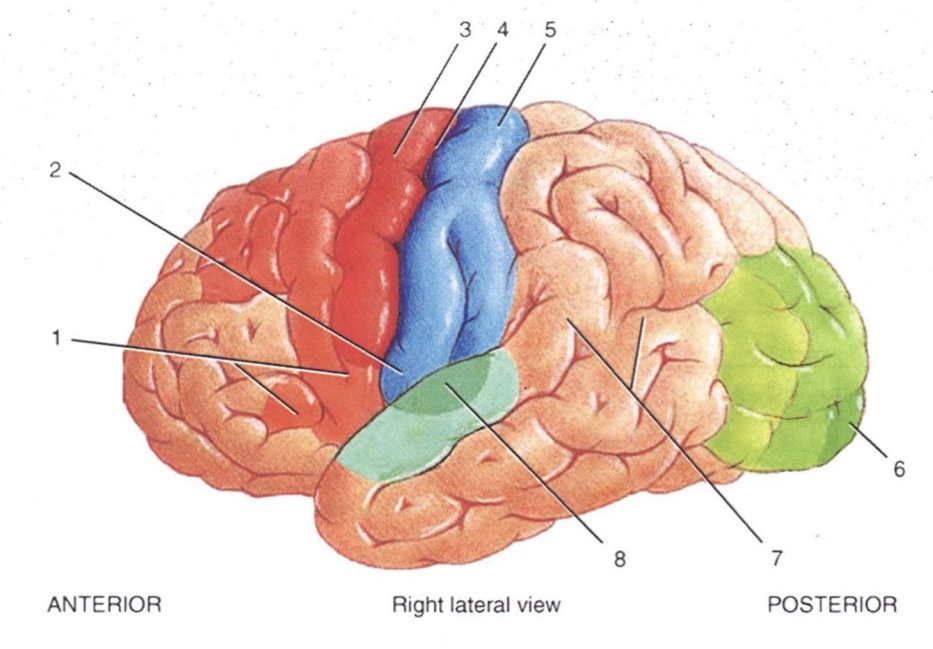
7
Wernicke’s Area
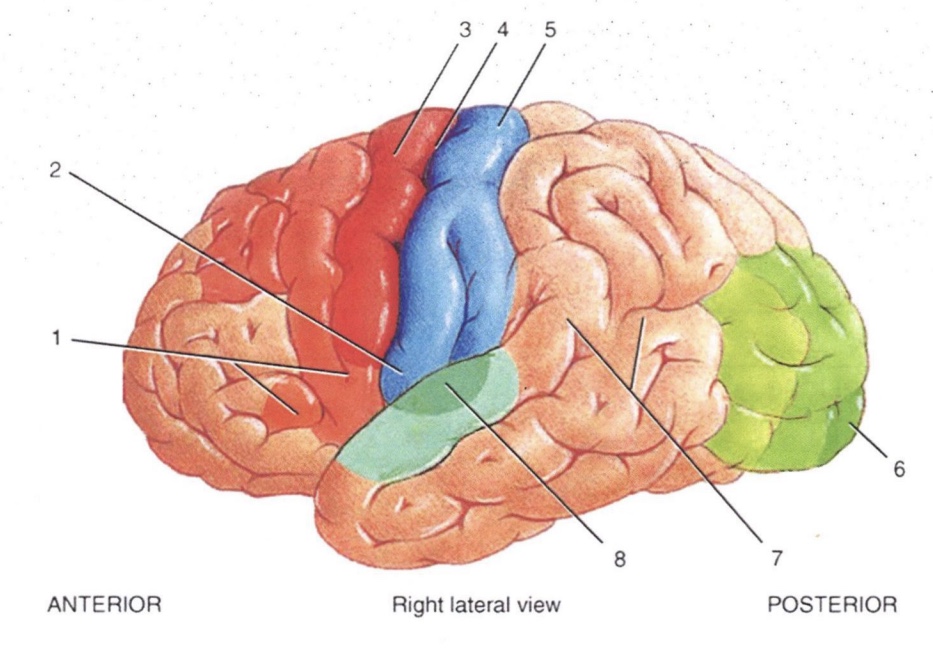
8
Primary Auditory Area
Infundibulum
'Stalk' that connect pituitary gland to hypothalamus
Thalamus
2-lobed region connected by intermediate mass (AKA interthalamic adhesion). Serves as a relay for all sensory impulses (except smell)
Epithalamus
Area above thalamus; houses a choroid plexus
Optic Chiasma
Cross-over point for optic nerves
Pituitary Gland
Endocrine gland that secretes many & varied hormones
Pineal Gland
Endocrine gland that secretes melatonin
Hypothalamus
Major homeostatic center; regulates hunger/thirst, blood pressure and body temperature
Mammillary Bodies
Pea-shaped bodies that serve as relay for olfactory pathways
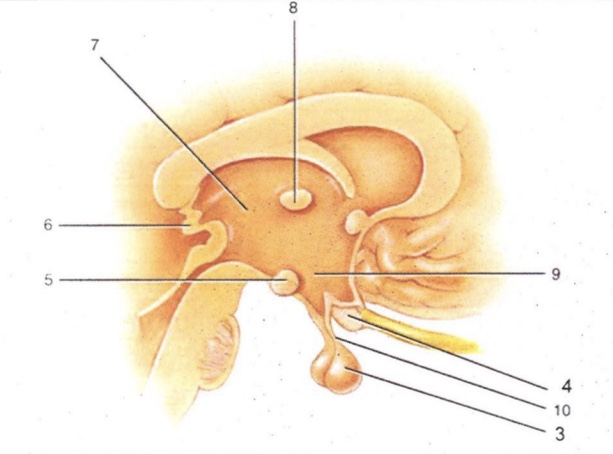
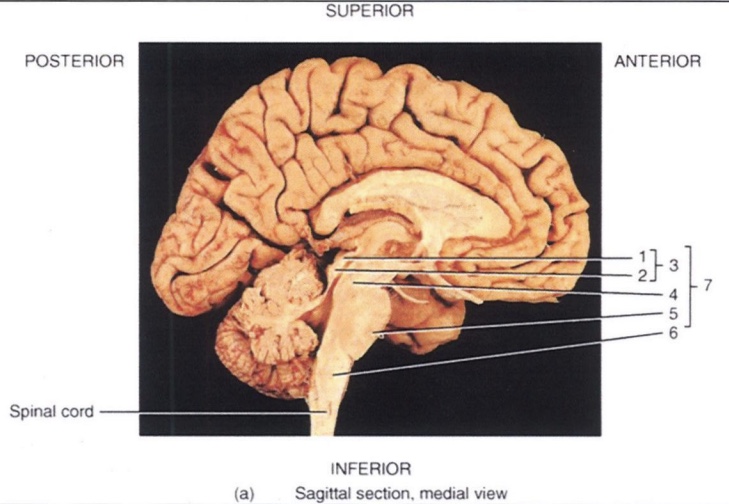
3
Pituitary Gland
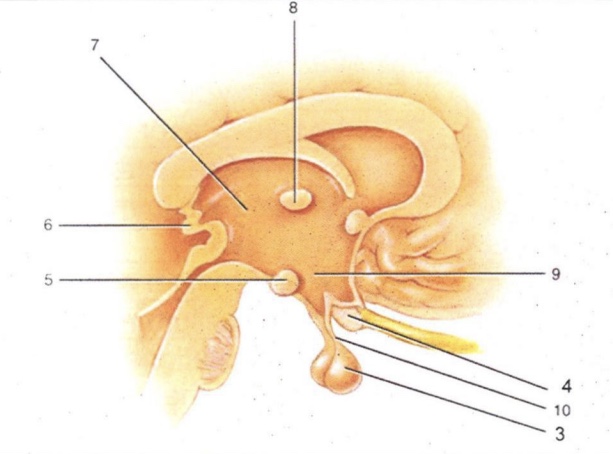
4
Optic Chiasm
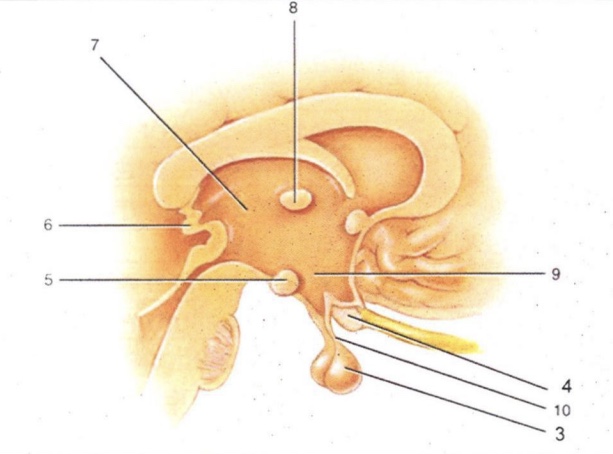
5
Mammillary Body
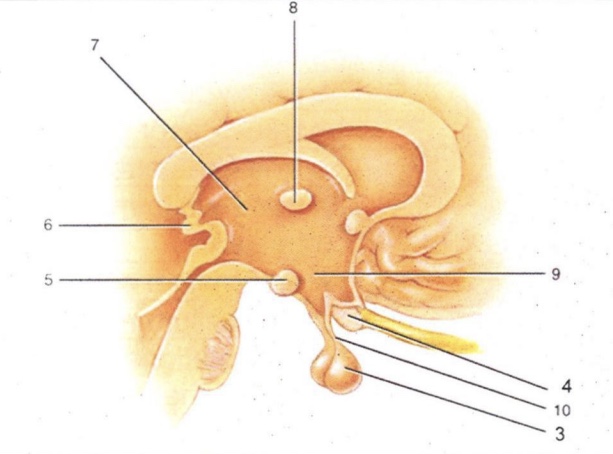
6
Pineal Gland (Epithalamus)
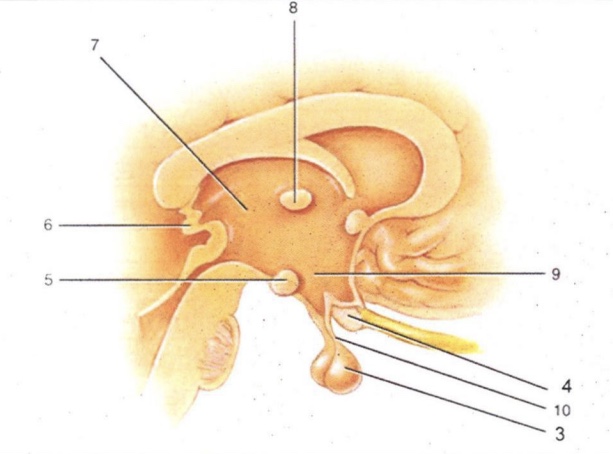
7
Thalamus
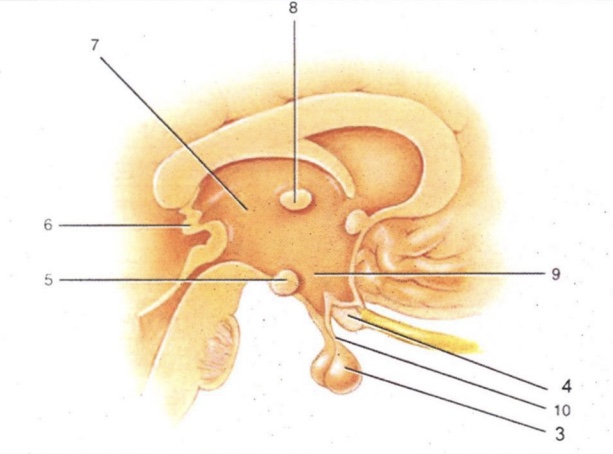
8
Intermediate Mass
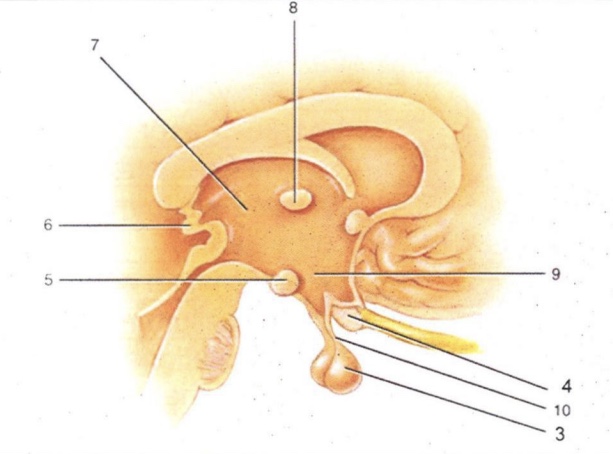
9
Hypothalamus (hunger and thirst center)
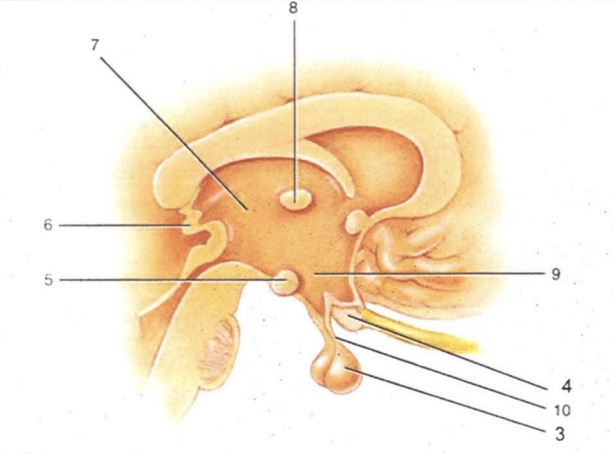
10
Infundibulum
Medulla Oblongata
The most inferior section of the brainstem, vital centers
Medullary Pyramids
Motor fiber cross-over point found in the medulla oblongata
Pons
Middle section of the brainstem; its name means 'bridge'
Midbrain
Most superior section of the brainstem
Inferior Colliculi
The two inferior 'bumps' on the midbrain that serve as an auditory relay
Superior Colliculi
The two superior 'bumps' on the midbrain that serve as a visual relay
Corpora Quadrigemina
4 colliculi are collectively known as the ________
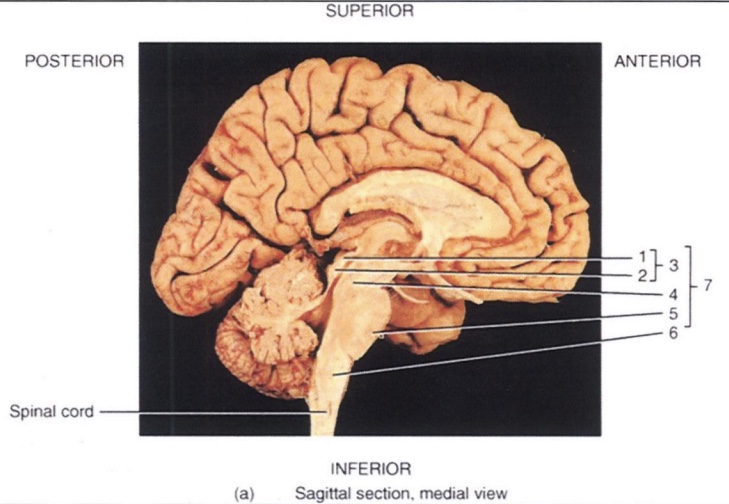
1
Superior Colliculus
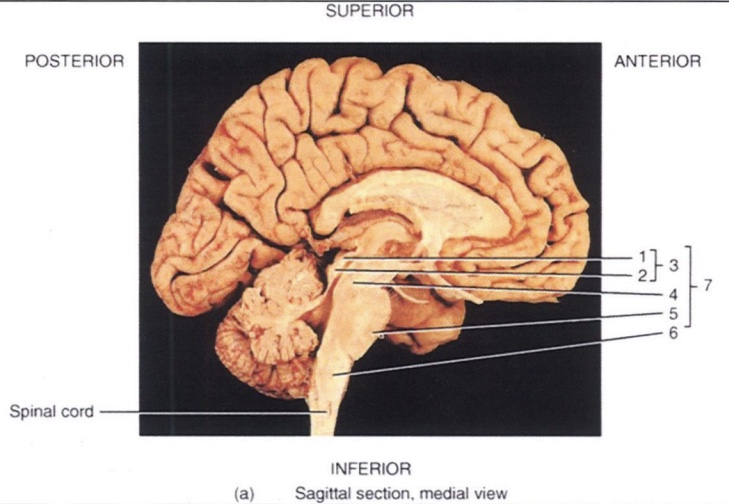
2
Inferior Colliculus
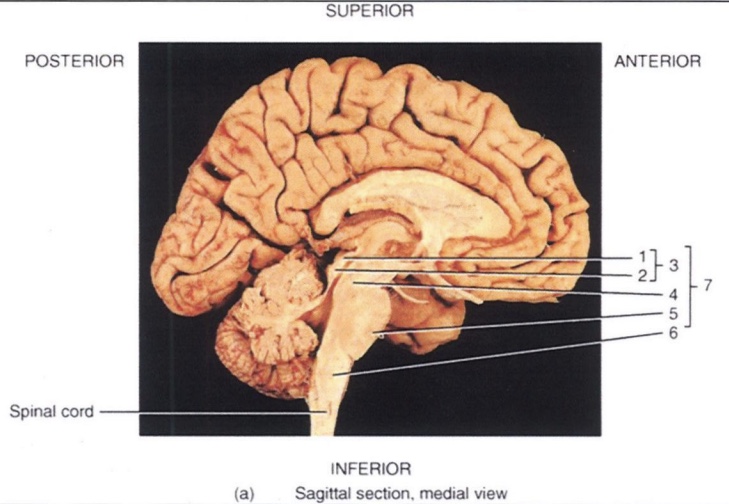
3
Corpora Quadrigemina
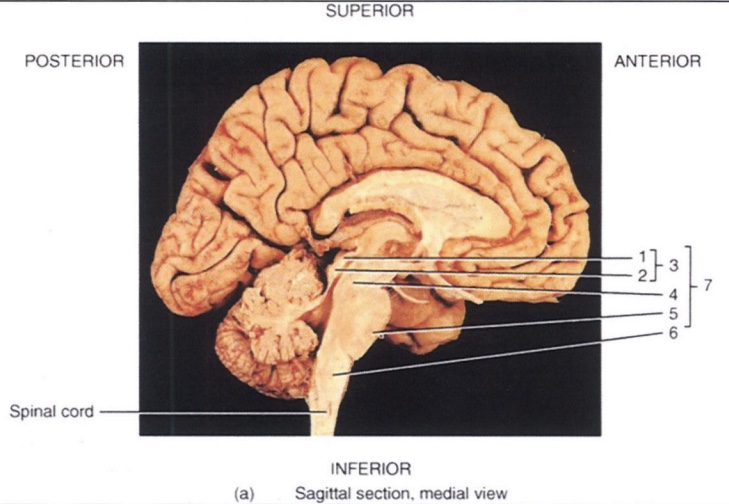
4
Midbrain
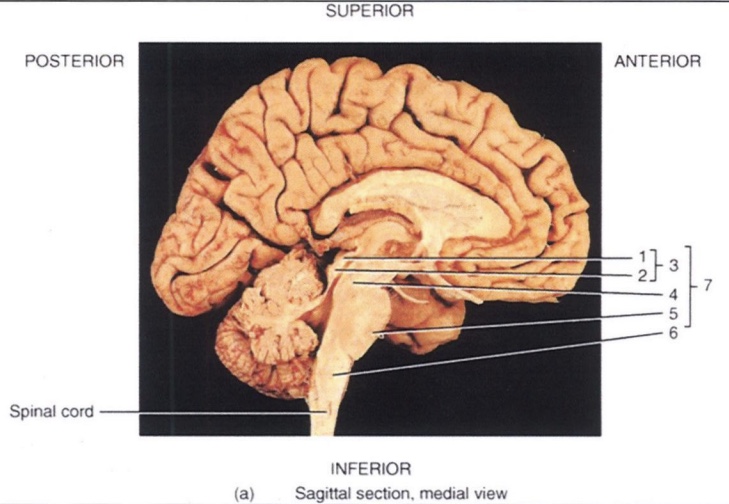
5
Pons
6
Medulla Oblongata
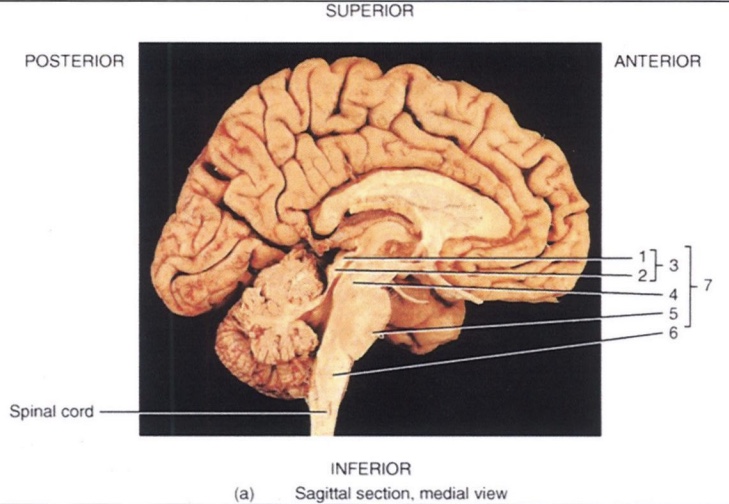
7
Brain Stem
Hemispheres
The cerebellum is divided into right and left ______
Vermis
The structure that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
Cerebral Cortex
Superficial layer of gray matter in the cerebellum
Arbor Vitae
The tree-like pattern of underlying white matter in the cerebellum
Cerebral Peduncles
The three white matter tracts that connect the brainstem to the cerebellum
Skeletal Muscle Activity
The cerebellum coordinates ________
The cerebellum regulates ________ and ________
Balance and posture
Folia
The convolutions on the surface of the cerebellum
Meninges/Menix
The connective tissue wrappings that surround both the brain & spinal cord
Pia Mater
The innermost menix
Arachnoid Mater
The middle menix
Dura Mater
Outermost menix
Falx Cerebri
The extension of the dura mater that folds into the longitudinal fissure
Falx Cerebelli
The extension of the dura mater that separates the R/L hemispheres of the cerebellum
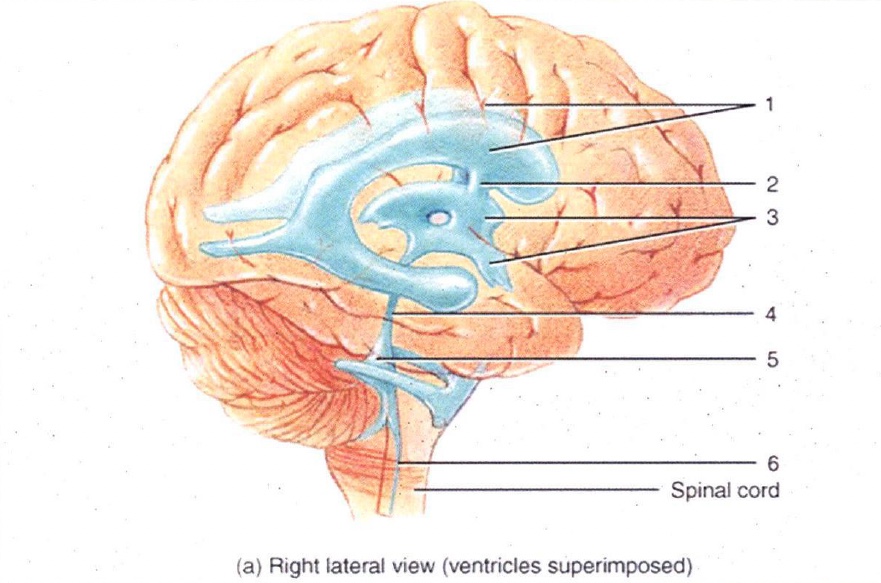
1
Lateral Ventricles
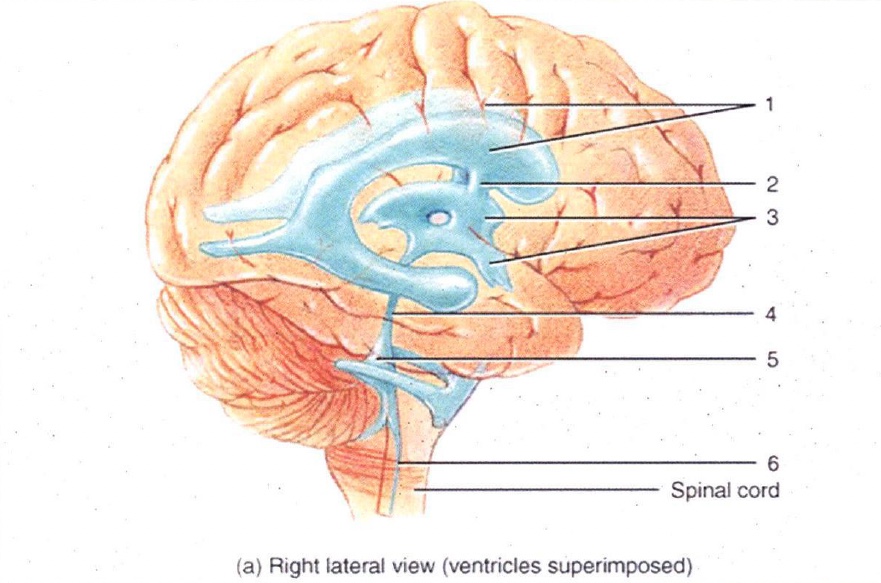
2
Interventricular Foramen
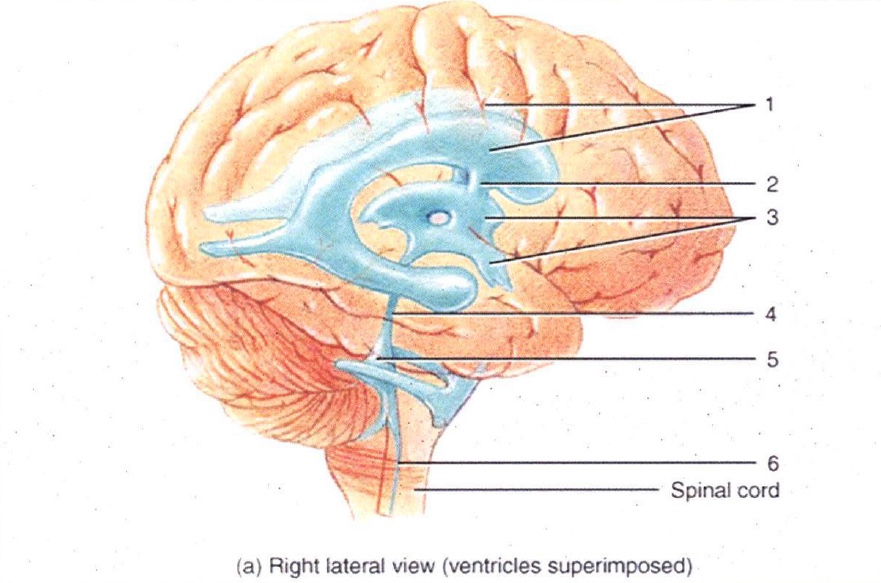
3
3rd Ventricle
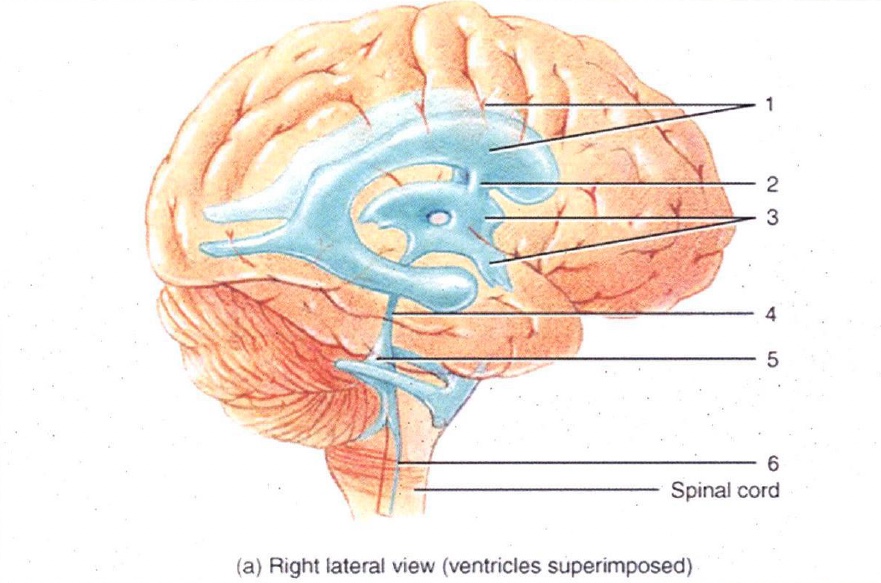
4
Cerebral Aqueduct
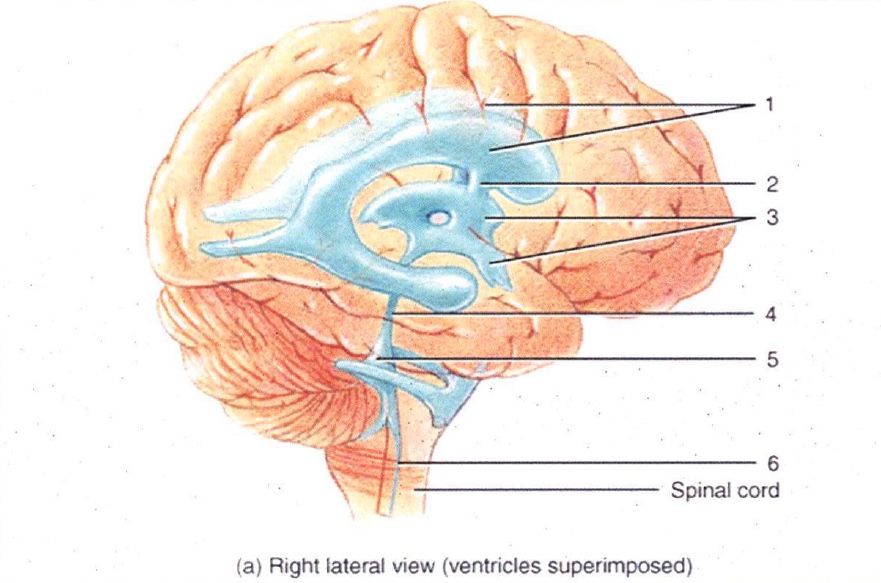
5
4th Ventricle
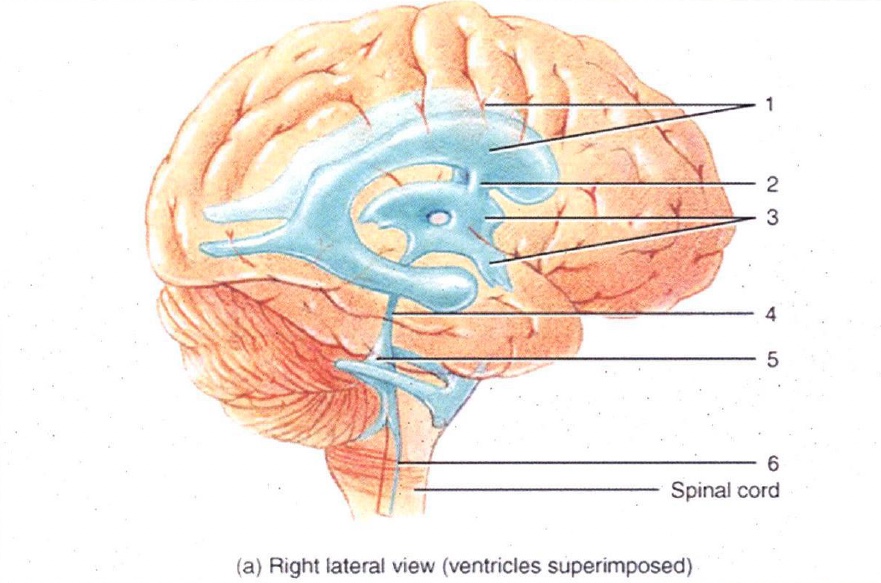
6
Central Canal
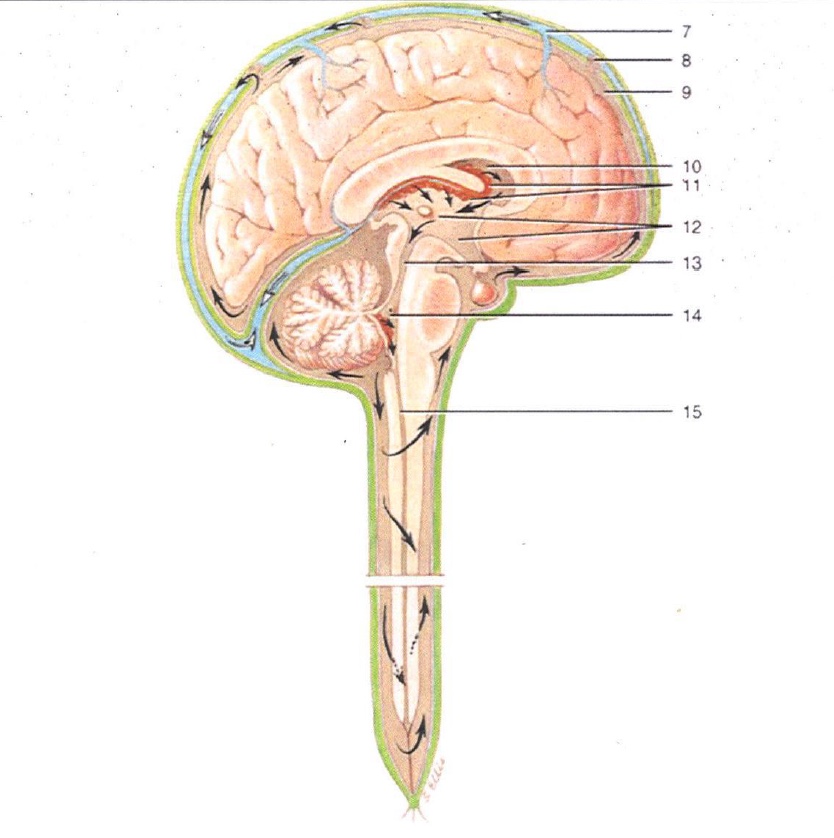
7
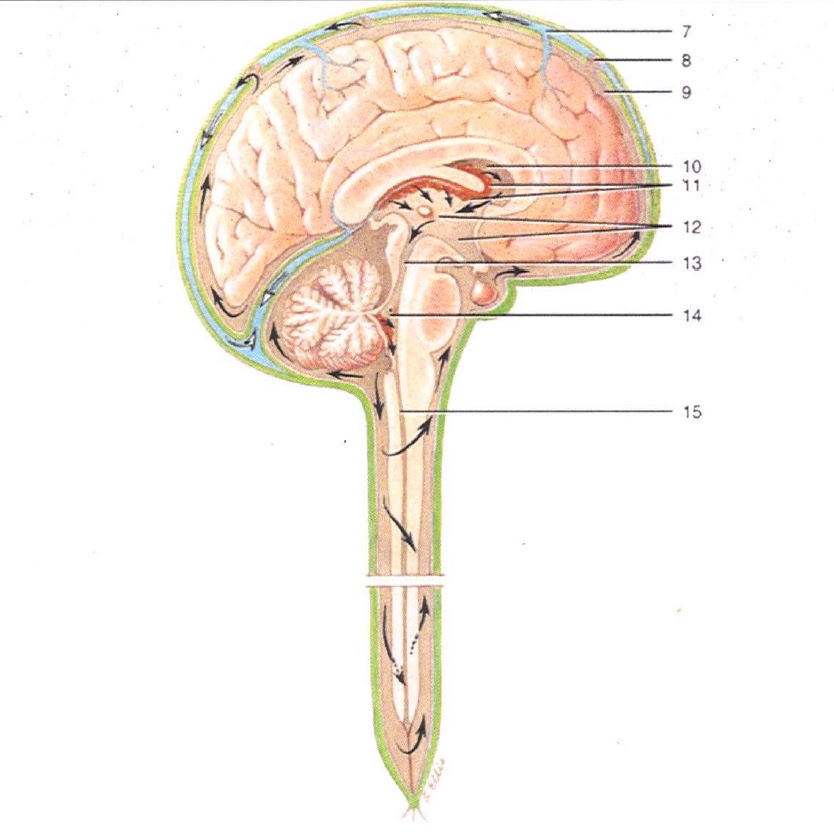
Superior Sagittal Sinus
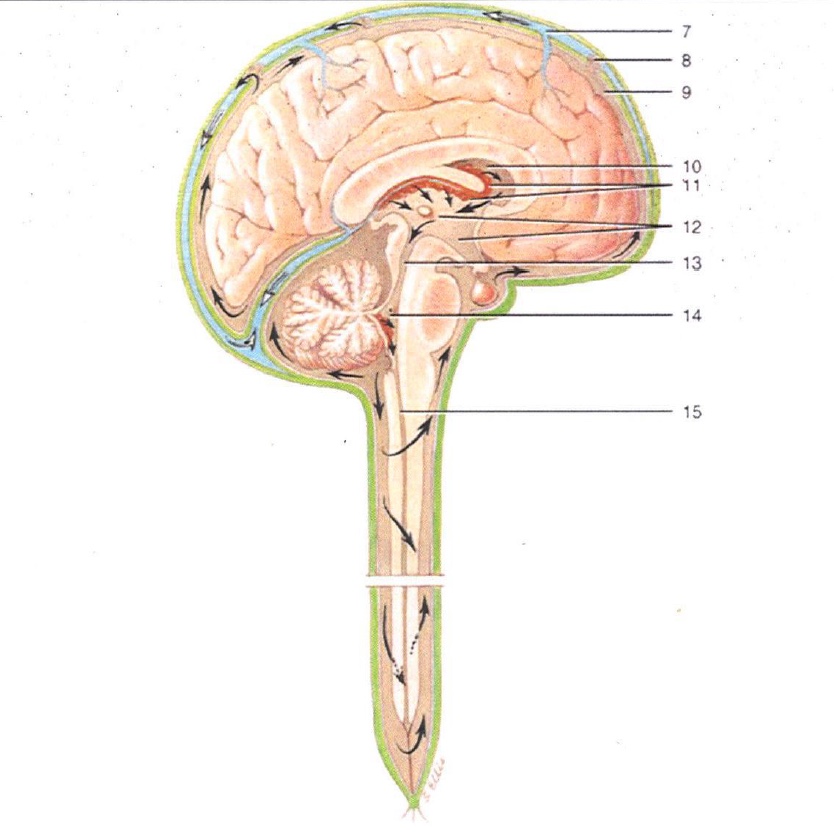
8
Arachnoid Villus
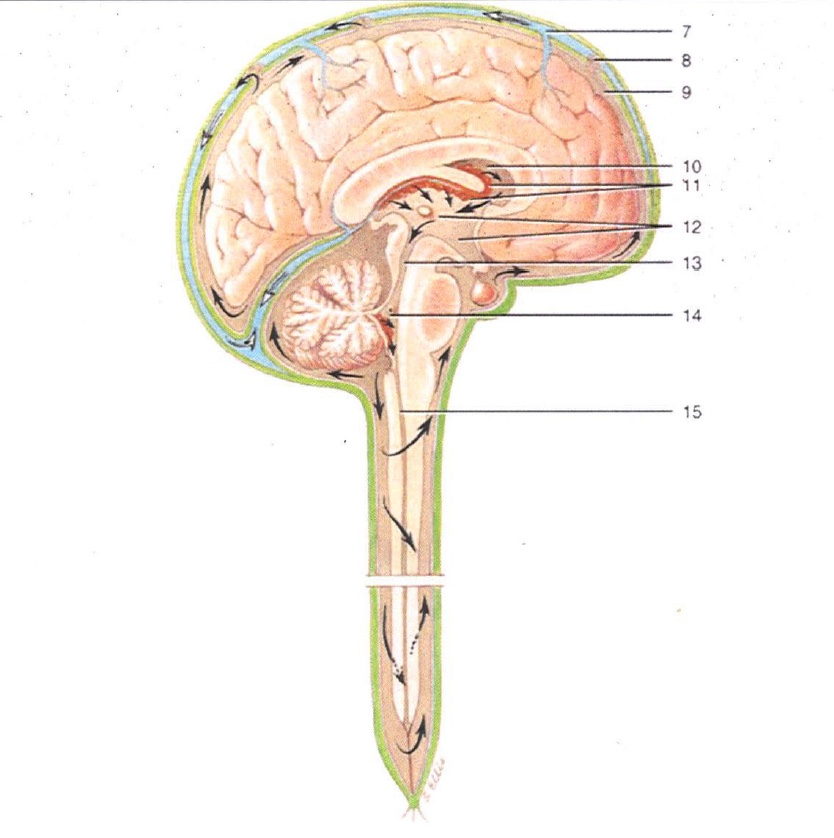
9
Subarachnoid Space
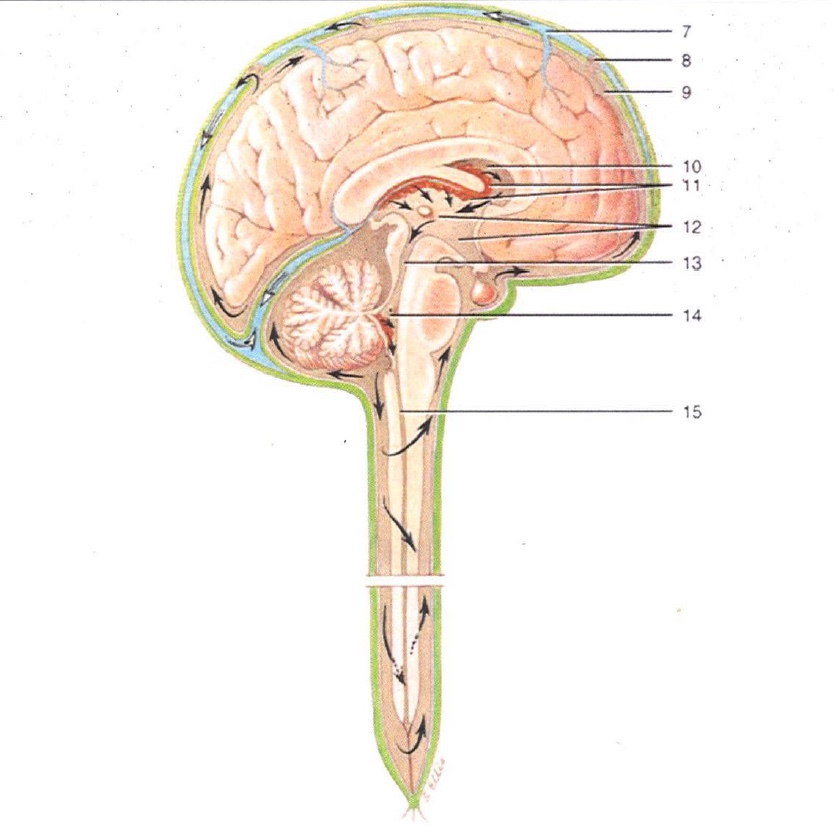
10
Lateral Ventricle
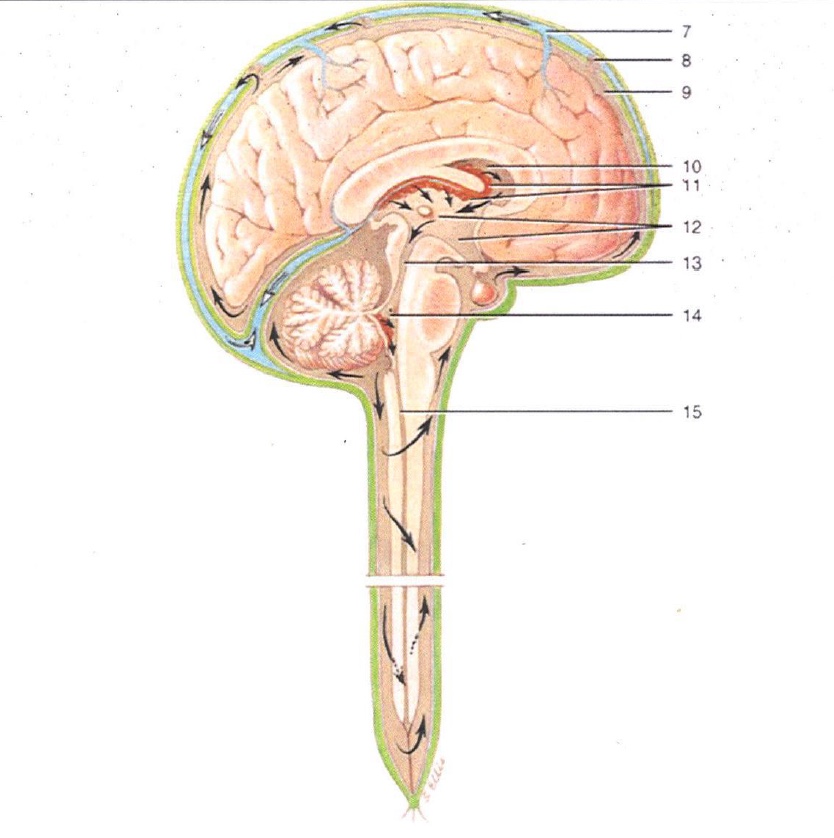
11
Choroid Plexus
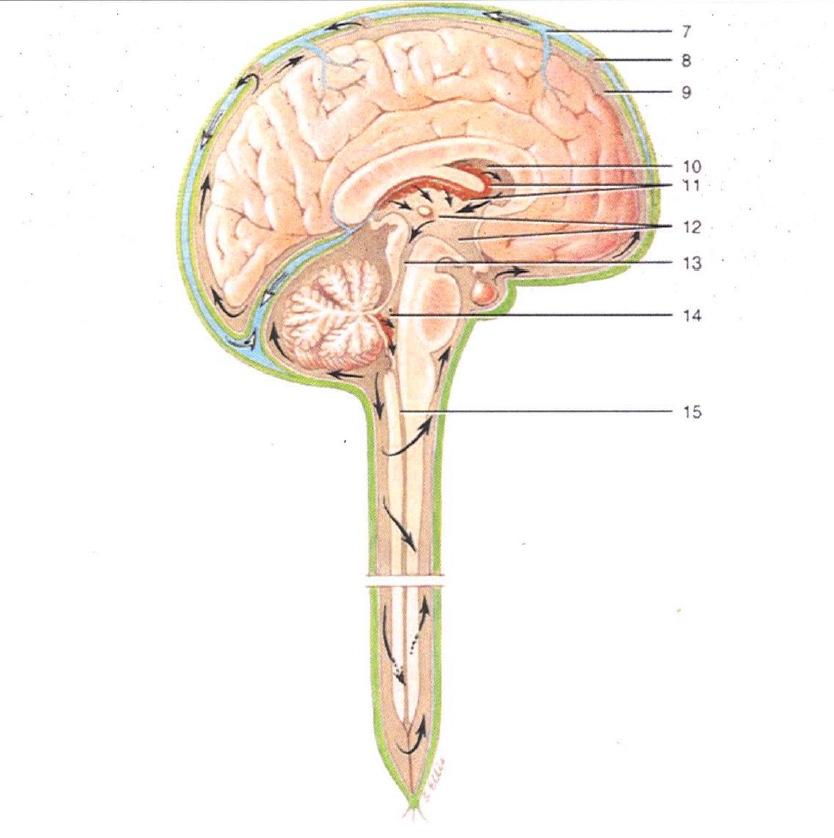
12
3rd Ventricle
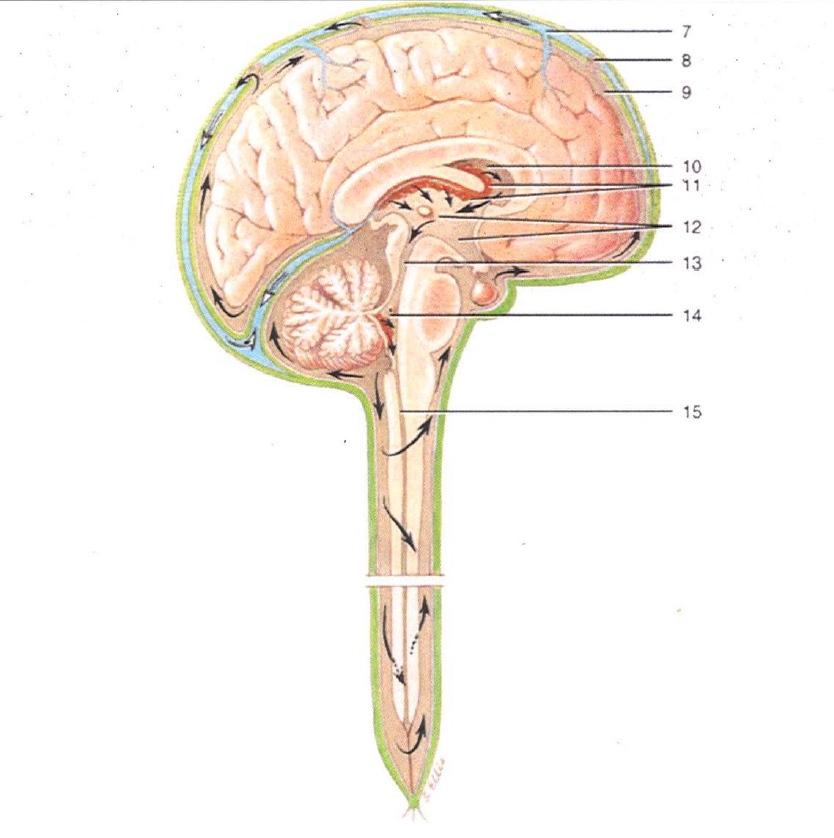
13
Cerebral Aqueduct
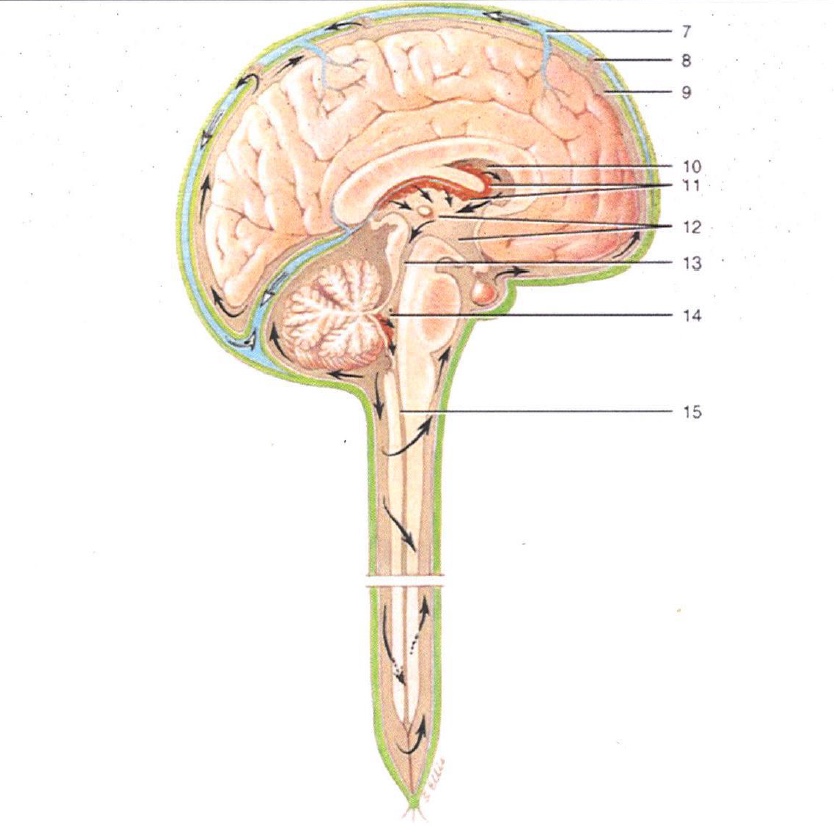
14
4th Ventricle
15
Central Canal