5 Cardiac Output & Atherosclerosis
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what is cardiac ouput?
volume of blood each ventricle pumps out in liters per one minute
what is the formula for cardiac output?
CO = SV (stroke volume) x HR (heart rate)
what is stroke volume?
volume ejected by each ventricle with each beat
how do you measure stroke volume?
EDV-ESV
what are the three factors influencing cardiac output?
preload
afterload
myocardial contractility
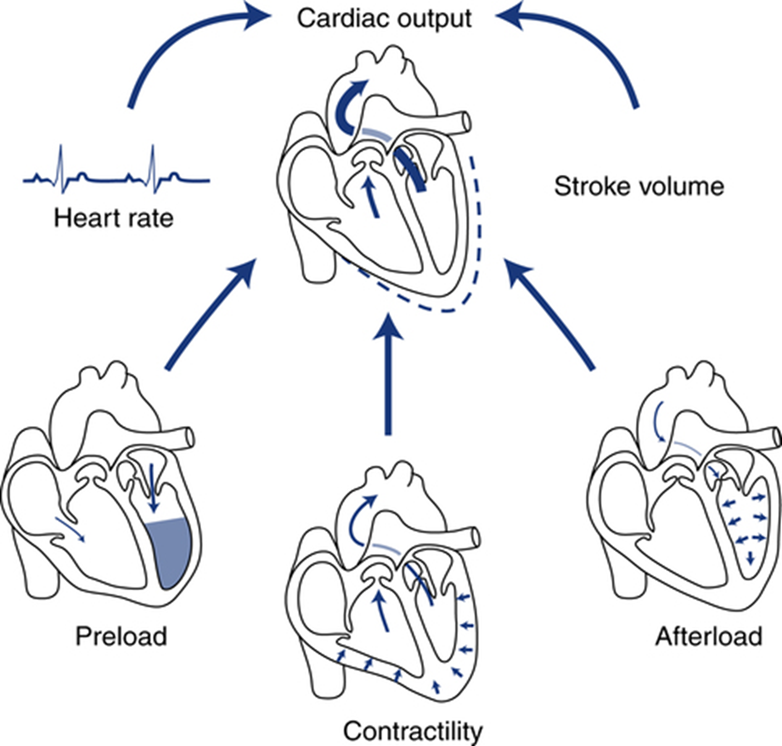
the frank starling law is best related to which of the 3 influencing factors of cardiac output?
preload
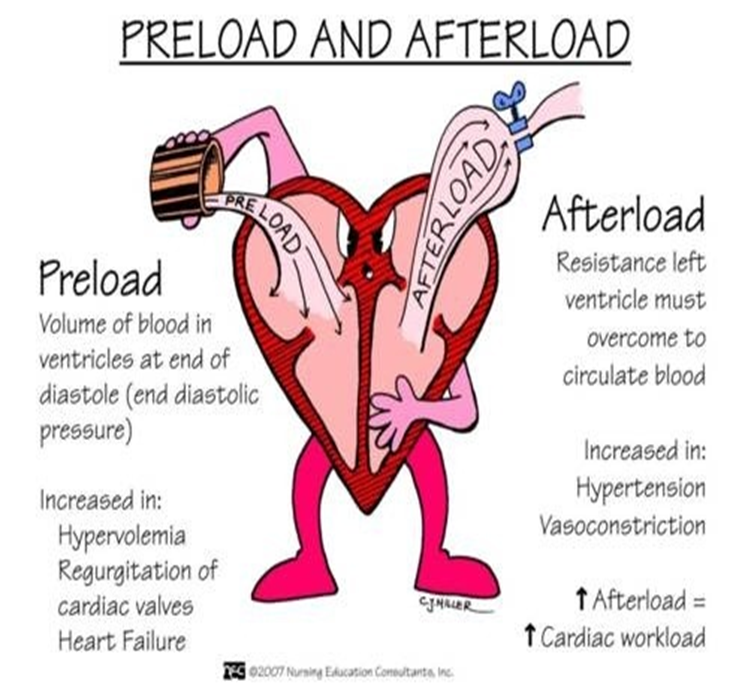
what is preload?
the amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole (heart’s filling phase) ; initial stretching of cardiac myocytes prior to contraction
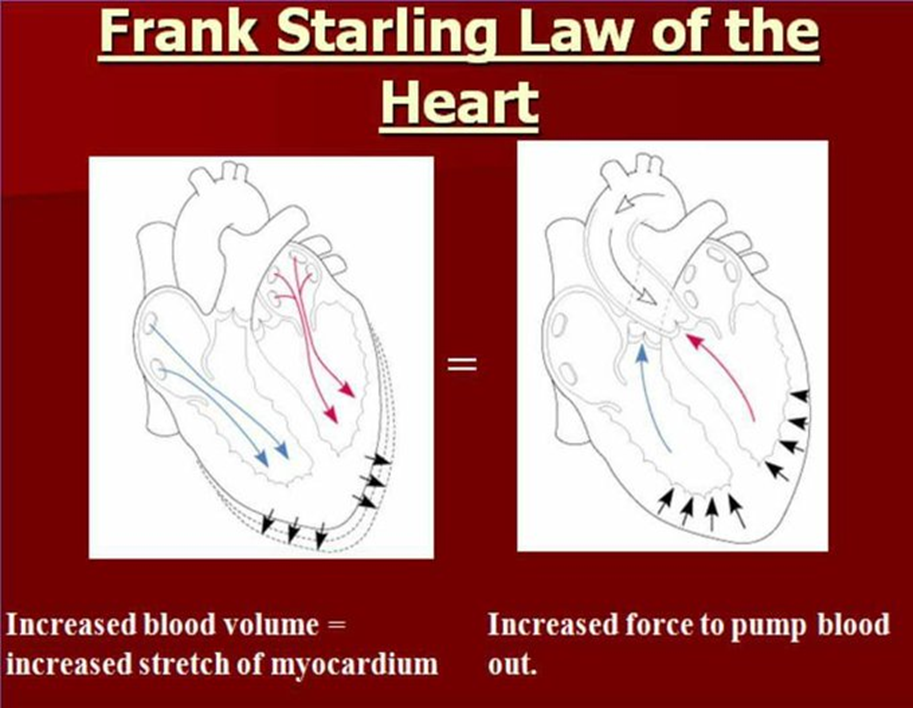
what does the frank starling law state?
as the EDV increases, the greater the ventricular sarcomeres are stretched causing a more forceful contraction
what is the sliding filament theory
energy released during contraction depends on initial fiber length (increased EDV → increased length → more cross bridges)
what factors affect preload?
venous return
total blood volme
ventricular compliance
heart rate
atrial contraction
valvular disease
what is afterload?
force that must be overcome for the ventricle to eject its contents ; pressure in wall of LV during ventricular ejection
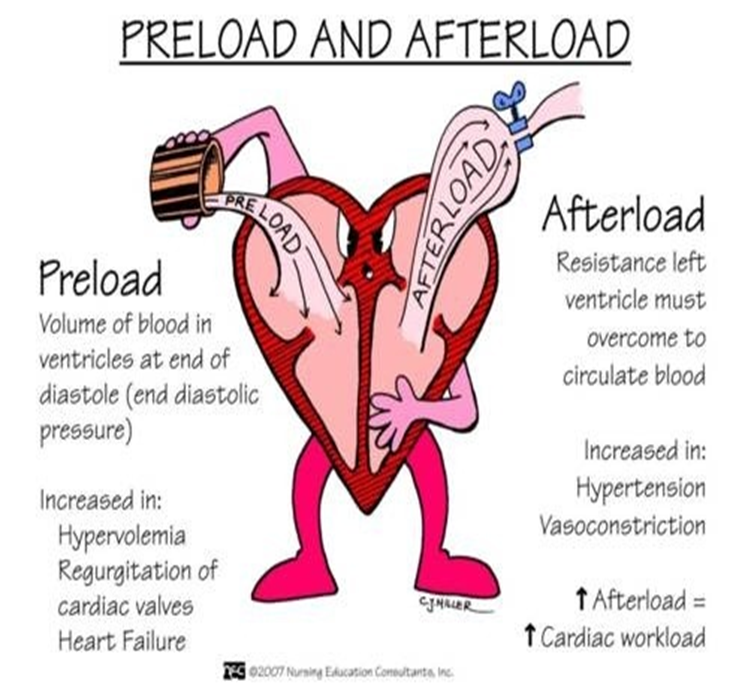
what are the most common pathologic processes that increase afterload?
systemic hypertension
aortic stenosis
how does the heart respond to persistent increased afterload?
the cardiac cells begin to hypertrophy (thickens)
what is contractility?
force of contraction
contractility is aka?
inotropic state
what affects contractility?
chemical hormonal influences
how does increased contractility affect force?
increased force for the same fiber length ; heart is squeezing harder
how does contracility affect stroke volume and ESV?
increases stroke volume
smaller than normal ESV (typically not all blood gets ejected after contraction but with higher contractility, more blood gets ejected out)
what is compliance?
ease by which ventricle expands with as filling pressure increases
compliance relates to
structural properties of the cardiac muscle and the state of ventricular contraction and relaxation
compliance is the ratio of
change in volume / change in pressure
know this
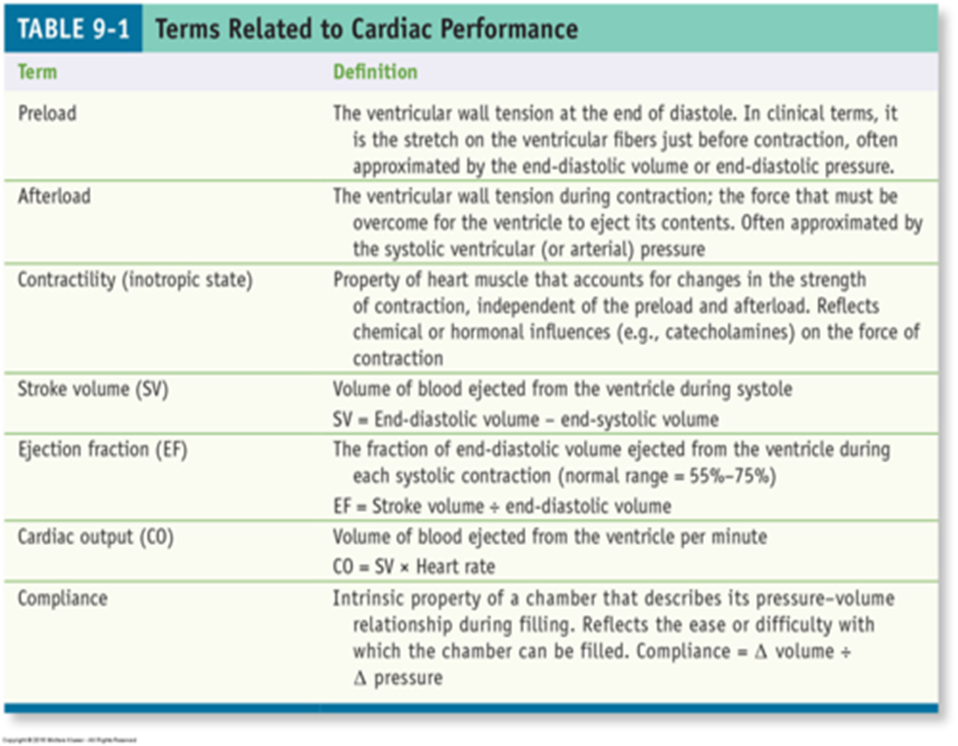
know this
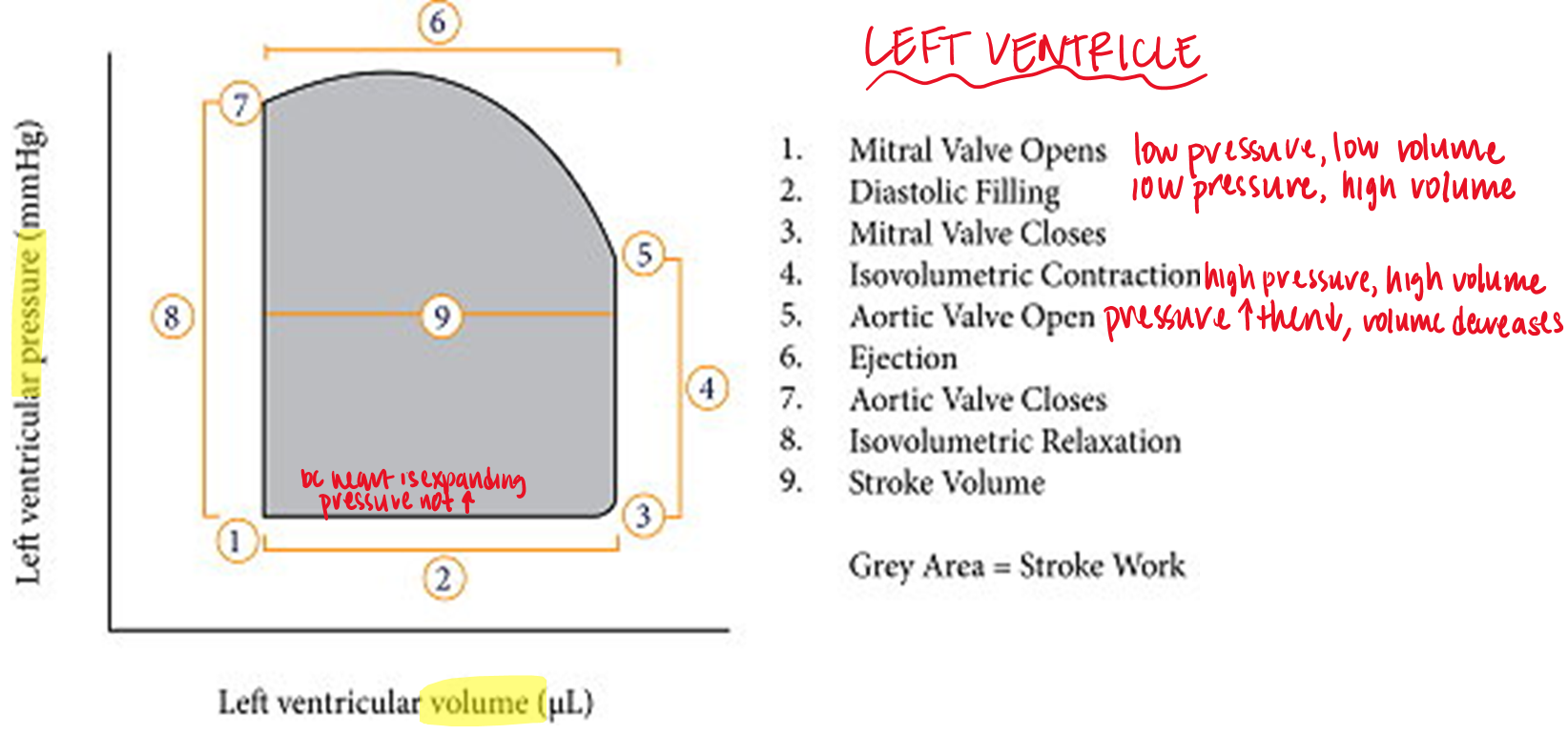
if afterload and contractility are constant and preload increases what happens to stroke volume?
increased preload → LV EDV rises → LV can adjust its SV to effectively empty its contents to match diastolic filling volume
if preload and contractility are constant and afterload increases what occurs?
pressure in LV increases → higher ventricular systolic pressure → reduced stroke volume → greater than normal LV ESV
SV rises when (preload, afterload, contractility)
increased preload
decreased afterload
increased contractility
preload is representative of
ventricular EDV
EDV is influenced by the chamber’s
compliance
ventricular ESV depends on
afterload and contractility (NOT PRELOAD)
what is atherosclerosis?
disease in which plaque builds up inside the arteries ; hardening of arteries
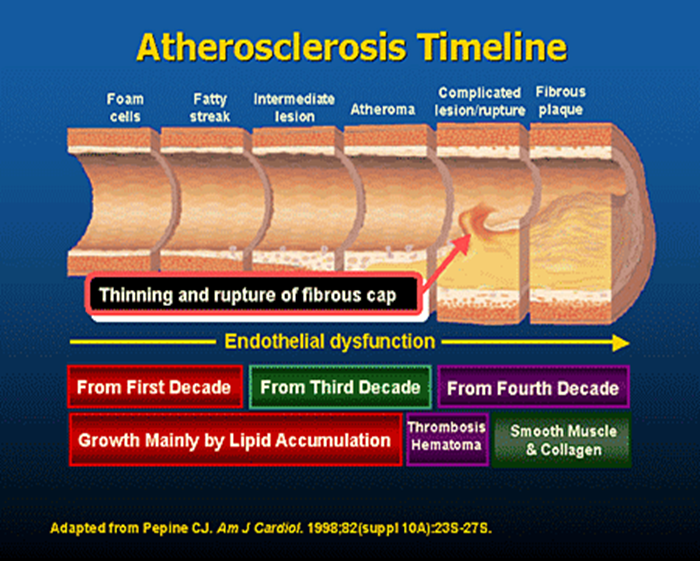
what are the two components of atherosclerosis?
plaque buildup
inflammatory response (to chronic injury of arteries → cells accumulate at site of injury )
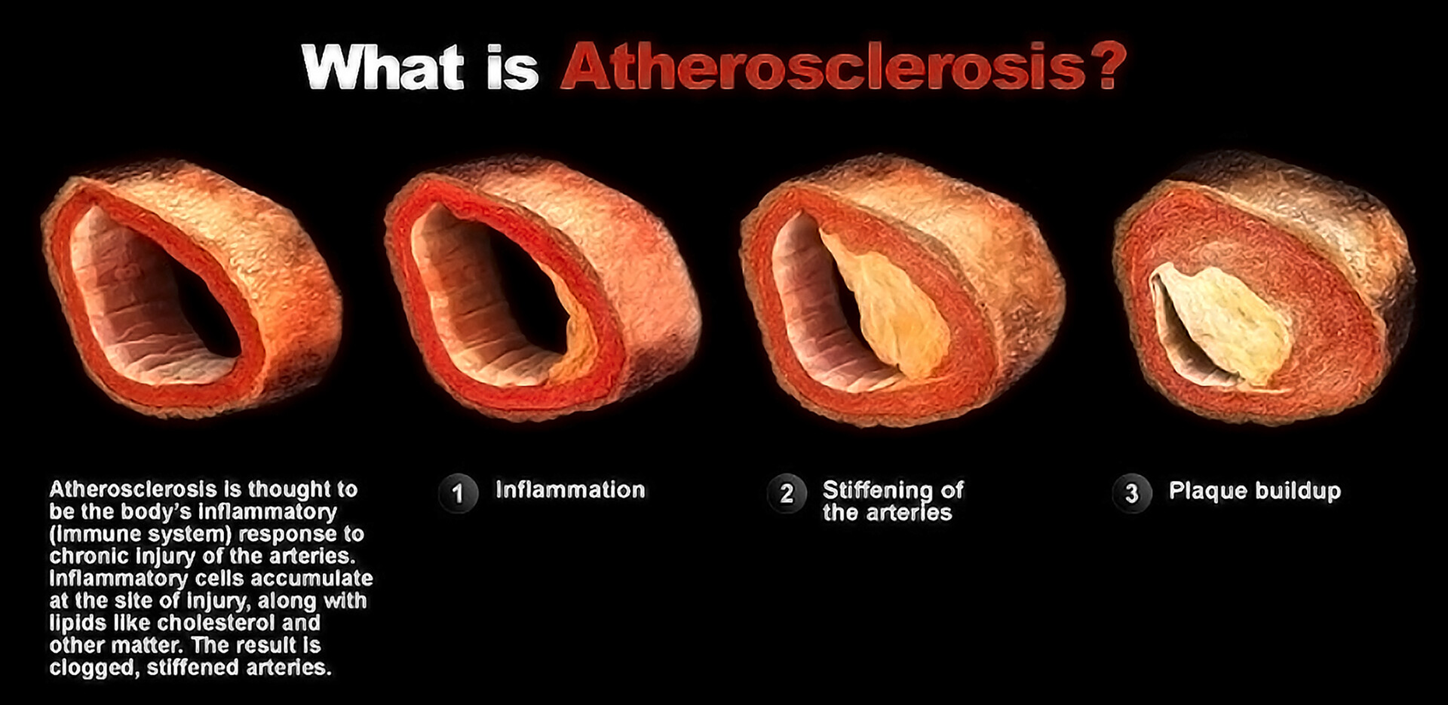
what are the risk factors for atherosclerosis?
diabetes
obesity
poor diet
physical inactivity
excessive alcohol use
what is the endothelium of an artery & its purpose?
one cell layer thick that lines inside of vascular system
regulates permeability, clotting, immune function
name the 3 basic wall layers from inner to outer
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
what is the earliest visible lesion of atherosclerosis?
fatty streak
what are fatty streaks caused by?
endothelial dysfunction ; genetic or chronic exposure to inflammatory markers
what promotes plaque progression?
smooth muscle cell in intima
what is an embolism?
detached thrombus
what is plaque disruption?
when fibrous cap covering atherosclerotic plaque breaks down and exposes the underlying thrombus core
what is plaque rupture determined by?
fibrous cap stability
what increases liklihood of plaque rupture?
localized inflammation
greater LDL cholesterol depositions
what are the complications of atherosclerosis?
calcification of atherosclerotic plaque (increases fragility of vessel wall)
rupture of ulceration (procoagulants in circulation → clots)
heorrhage into plaque
embolization
what are the major targets of atherosclerosis?
large elastic arteries (aorta, carotid, iliac) & large and medium sized muscular arteries
what are the modifiable risk factors of atherosclerosis?
high BP
smoking
lack of physical activity
excess stress
alcohol onsumption
what are the non modifiable risk factors of atherosclerosis?
gender (more common in males)
family hx
advancing age
sleep apnea
pt has a resting heart rate of 100 bpm with EDV of 150ml and ESV of 75 ml. What is the cardiac output?
7500 → 7.5L/min
atherosclerosis of coronary arteries can cause
heart attack