Upper and Lower Motor Neurons
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
2 descending/efferent nerve cells
How many efferent neurons are required to get a signal from the brain to skeletal muscles?
1st: UMN
2nd: LMN
2 nerves cells required to get a signal from the brain to the skeletal muscle
brain/brainstem
Location of cell bodies of UMN
axons synapse with LWM in the SC
Location of axons of UMN
Influence LMN activity including reflexes by transmitting signals from the brian to the SC
Function of UMN
cell bodies in SC
Location of cell bodies in LMN
transmit signals from the SC to the motor unit (muscles)
Function of LMN
ventral horn (red)
What horn of the SC are LMN cell bodies found
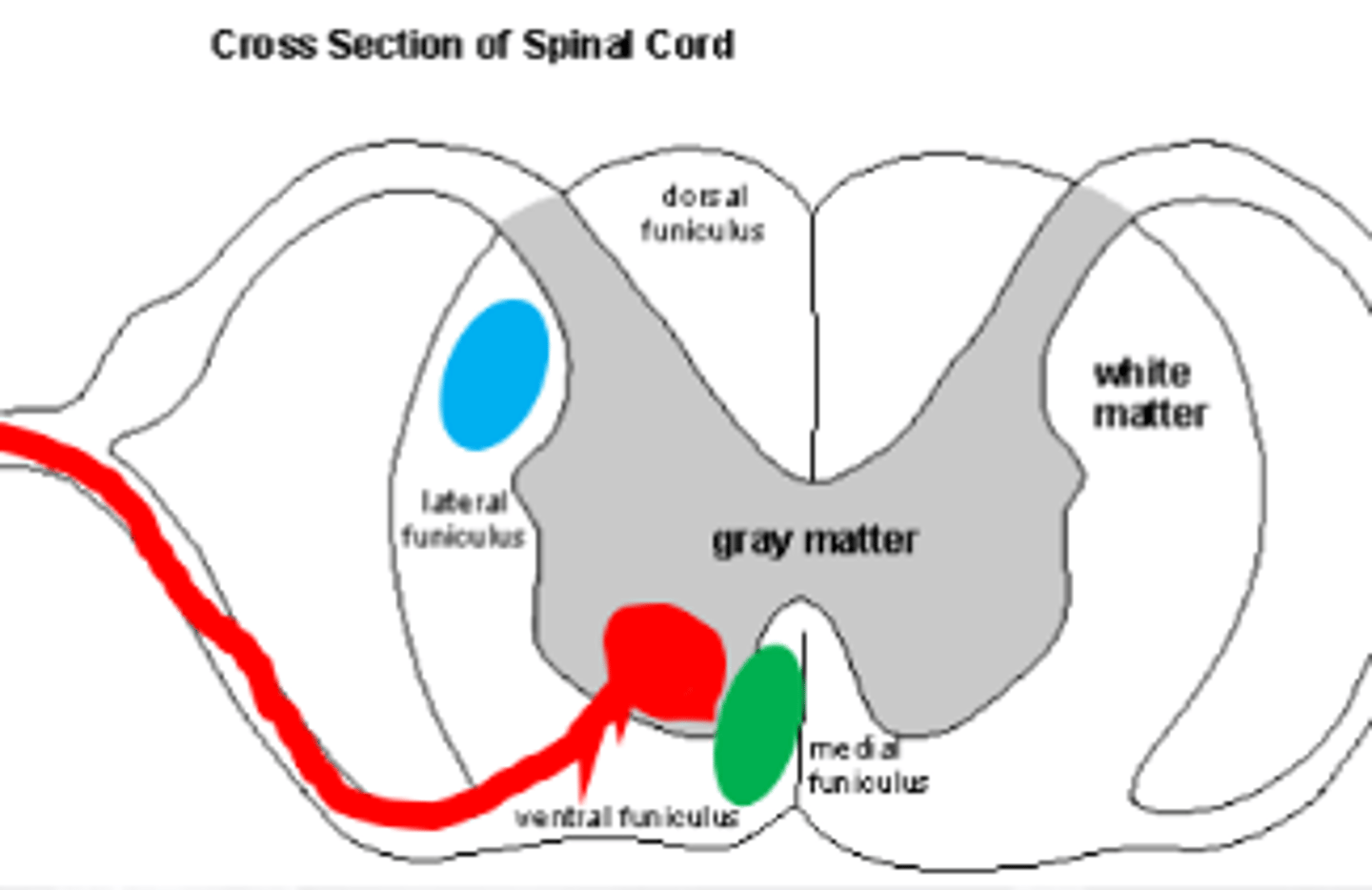
1. dorsolateral motor system (blue)
2. ventromedial motor system (green)
2 regions of the SC the axons of UMNs travel down
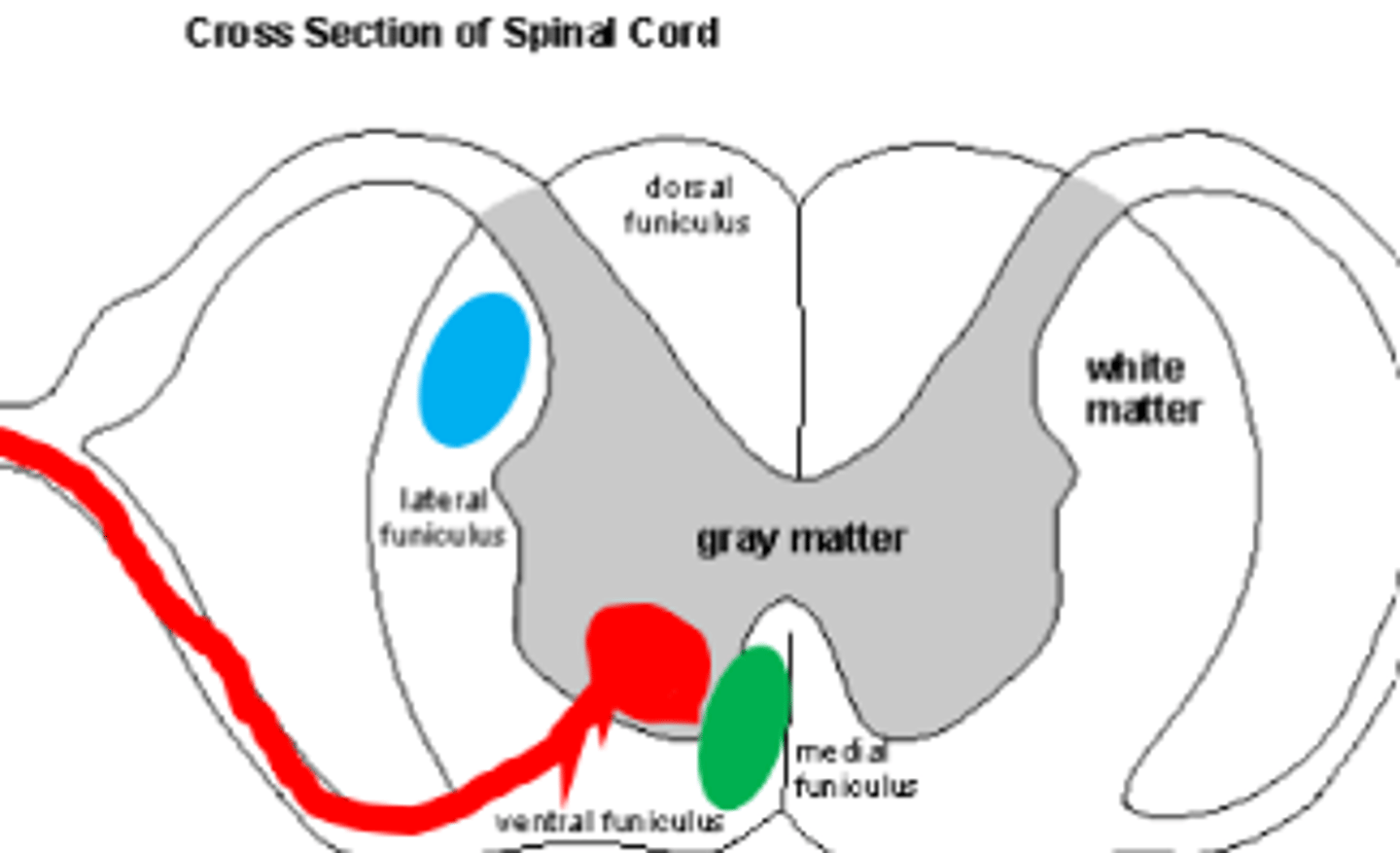
1. conscious efferent (UMN)
2. Reflexes (interneuron)
2 stimuli of LMN
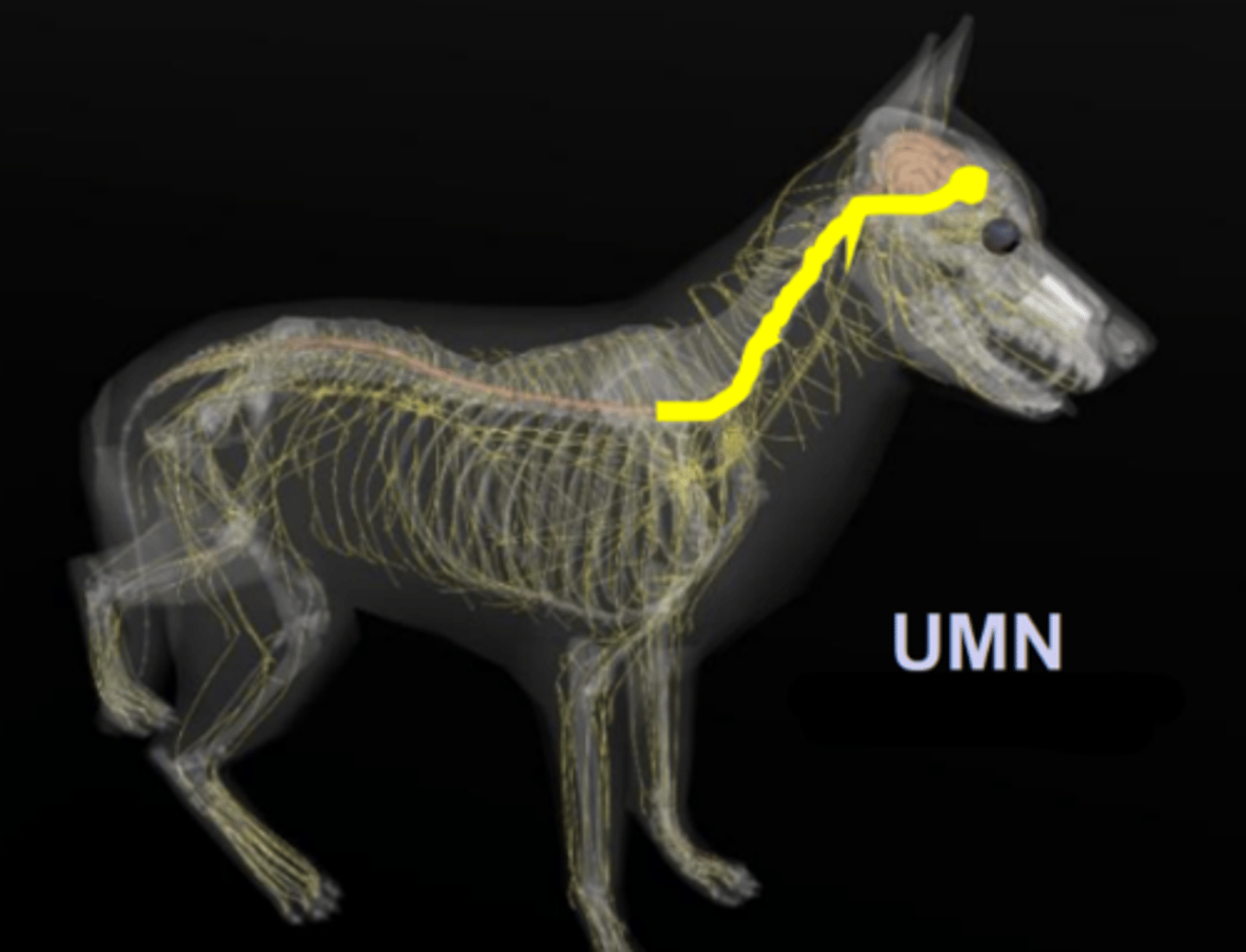
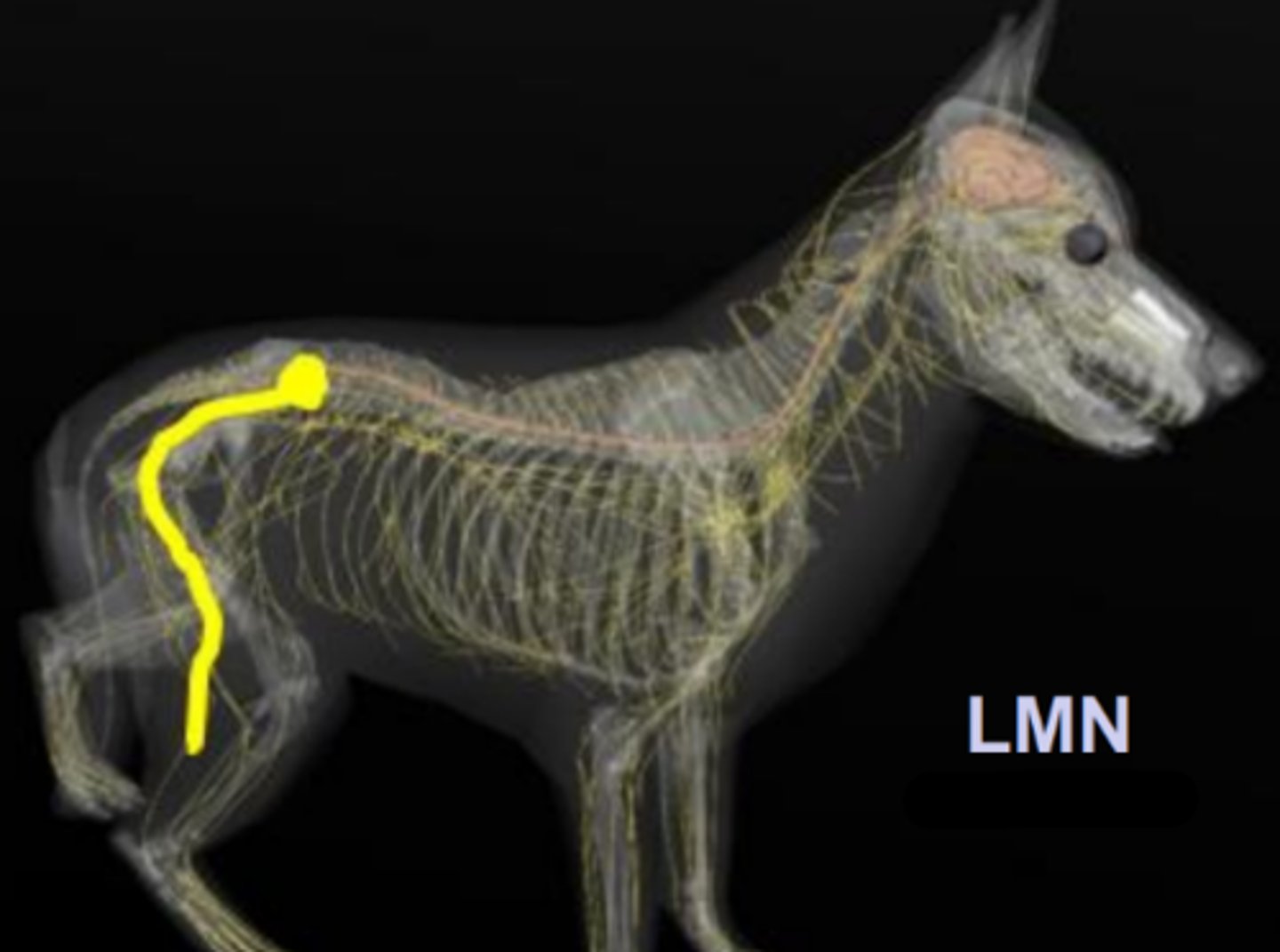
thoracic limb
UMN of the _______
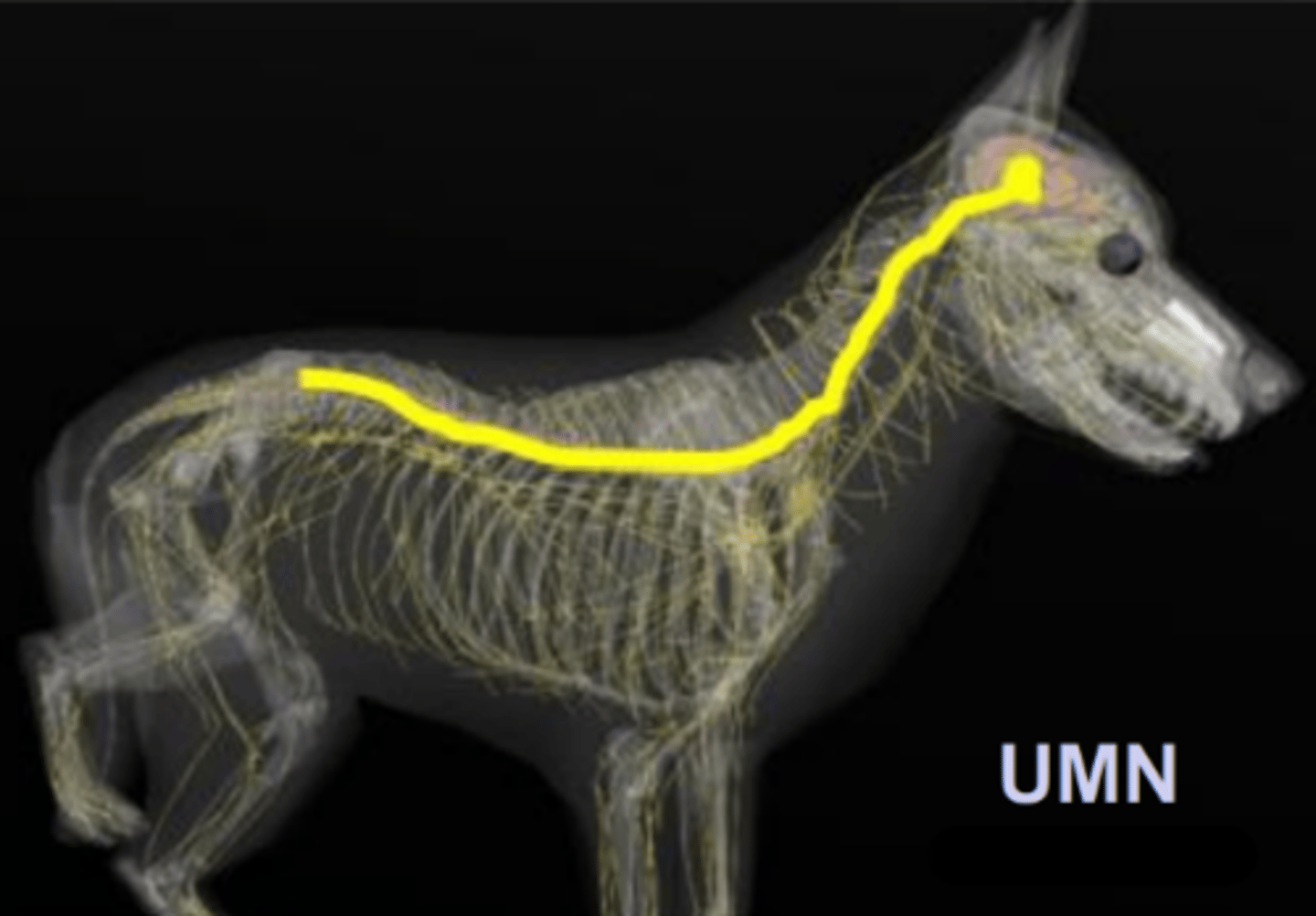
pelvic limb
UMN of the __________
thoracic limb
LMN of the _________
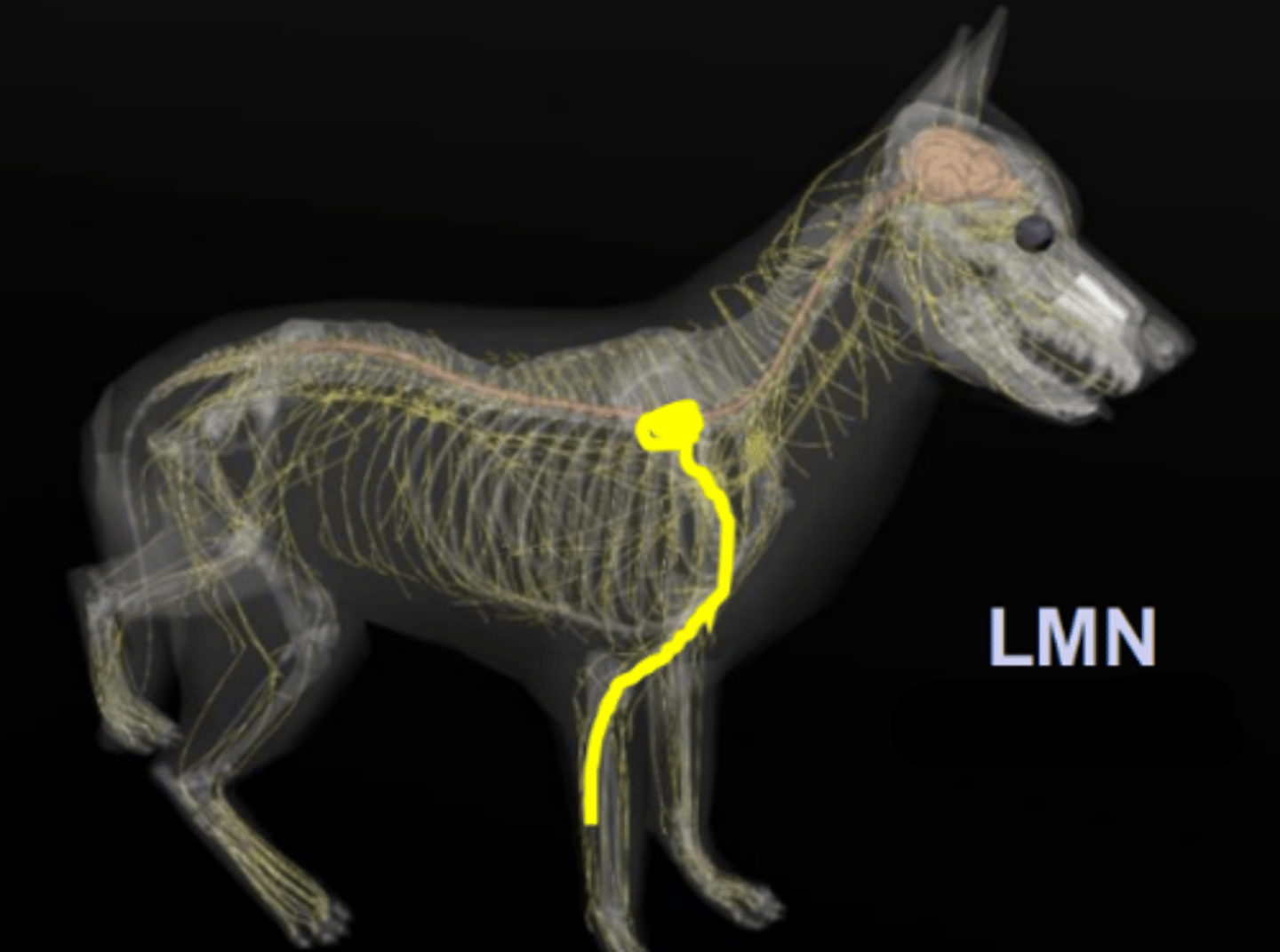
pelvic limb
LMN of the _________
1. conscious motor function
2. muscle tone
3. reflexes
4. muscle atrophy
5. proprioception
6. sensation
Lesions to UMN and LMN cause 6 different outcome
somatotopy
UMN pathways have __________
point for point correspondence of function to location of CNS
Somatotopy
1. proximal muscles "whole limb movement"/posture and balance
2. extension
Fiber functions of the ventromedial system
1. distal muscle fine motor movement
2. flexion
Fiber functions of the dorsolateral system
decreased/absent voluntary movement of the fine motor/flexor systems caudal to the site of damage
Signs of dorsolateral motor systems
decreased/absent voluntary movement of the whole limb/extensors caudal to the site of damage
Signs of ventromedial motor systems
1. trauma
2. localized/diffuse infection
3. space-occupying lesions
4. intervertebral disk disease
4 examples of local pathology
1. muscle tone
2. muscle atrophy
3. reflexes
4. sensation
4 signs to observe when diagnosing a SC lesions
-thoracic limb deficit: UMN
-pelvic limb deficit: UMN
C1-C5 injury
-thoracic limb deficit
-pelvic limb deficit
-thoracic limb deficit: LMN
-pelvic limb deficit: UMN
C6-T2 injury
-thoracic limb deficit
-pelvic limb deficit
-thoracic limb deficit: normal
-pelvic limb deficit: UMN
T3-L3 injury
-thoracic limb deficit
-pelvic limb deficit
-thoracic limb deficit: normal
-pelvic limb deficit: LMN
L4-S2
-thoracic limb deficit
-pelvic limb deficit
1. paresis/paralysis
2. decreased to absent muscle tone
3. decreased to absent reflexes
4. rapid-onset muscle atrophy
4 LMN signs
1. paresis/paralysis
2. normal to increase muscle tone
3. normal to increased reflexes
4. slow muscle atrophy
4 UMN signs
both UMN and LMB damage
Transverse damage to the spine causes
caudal to the spinal lesion
Where will you see UMN signs
at the site of the spinal lesion
Where will you see LMN signs
pudendal n. (S1-S3)
What nerve supplies somatic innervation to the urethralis m.
efferent n. to the reflex closure of the urethral m.
What does voluntary control of the urethralis m. supply
pelvic n. (S1-S3)
Parasympathetic innervation to the urinary bladder
involuntary SM contraction of the bladder wall (detrussor m.)
Function of the pelvic n. on the urinary bladder
visceral afferent -> stretch of the bladder
Sensory afferent innervation provided by the pelvic n.
hypogastric n. (lumbar nn.)
Sympathetic innervation to the urinary bladder
inhibitory action (relaxation)
Action of the hypogastric n. on the detrussor m.
stimulatory/contraction
Action of the hypogastric n. on the SM of the neck of the bladder
pelvic n.
When the bladder fills, what n is going to send afferents to the cortex to make the animal aware of the need to urinate
stimulates somatic afferent neurons via the pudendal n -> will also inform the animal that they need to urinate
When the bladder fills a small amount of urine will enter the proximal urethra, what will this trigger
1. reflex contraction of urethralis m. via efferent pudendal n.
2. somatic voluntary control of urethralis m via efferent pudendal n.
3. sympathetic fibers via hypogastric n inhibit contraction of detrussor m.
3 things that need to happen during storage of urine in the urinary bladder
1. conscious awareness of needing to urinate via pudendal and pelvic nn.
2. conscious voluntary motor and relaxation of urethralis m via pudendal n
3. parasympathetic fibers via pelvic n. induce contraction of detrussor m.
3 things that need to happen during micturition
urinary incontinence
What can a spinal cord injury cause in terms of the urinary bladder
result from lesions cranial to sacral spinal
When would UMN lesion signs of the urinary bladder occur
result from lesions of S1-S3
When would LMN lesion signs of the urinary bladder occur
1. bladder is turgid
2. inconsistent urine leakage (incontinent)
3. resistance to manual expression
UMN lesion signs in the urinary bladder
no somatic control of the urethralis m but continual contraction from the reflex
Why is the bladder turgid and resistant to expression during an UMN lesion
continuous leakage!
-no voluntary control
-no tone
-no reflex
-minimal resistance to urine flow from bladder through urethra
-small and flaccid bladder during palpation
LMN lesion signs in the urinary bladder
lack afferent and efferent fibers for conscious control while also lacking the reflex to keep the urethralis m. contracted involuntarily
Why are we seeing continuous leakage with a LMN lesion