Physical Geography Exam #1
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Last updated 12:43 AM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
Geography
Not memorizing place names. It’s about where something is, why it’s there, and what is significant about it. Also concerned with how things differ through time and space.
2
New cards
Immanuel Kant
(1724-1804) placed geography within a contemporary philosophical framework and reasoned that all knowledge can be organized and viewed from 3 points of view.
3
New cards
One of Immanuel Kant’s three points of view
Studies grouped according to specified facts or objects e.g. botany, soils, sociology, psychology
4
New cards
One of Immanuel Kant’s three points of view
Studies of objects and facts through time (historical sciences).
5
New cards
One of Immanuel Kant’s three points of view
Studies of phenomena in space (geographical sciences - spatial context)
6
New cards
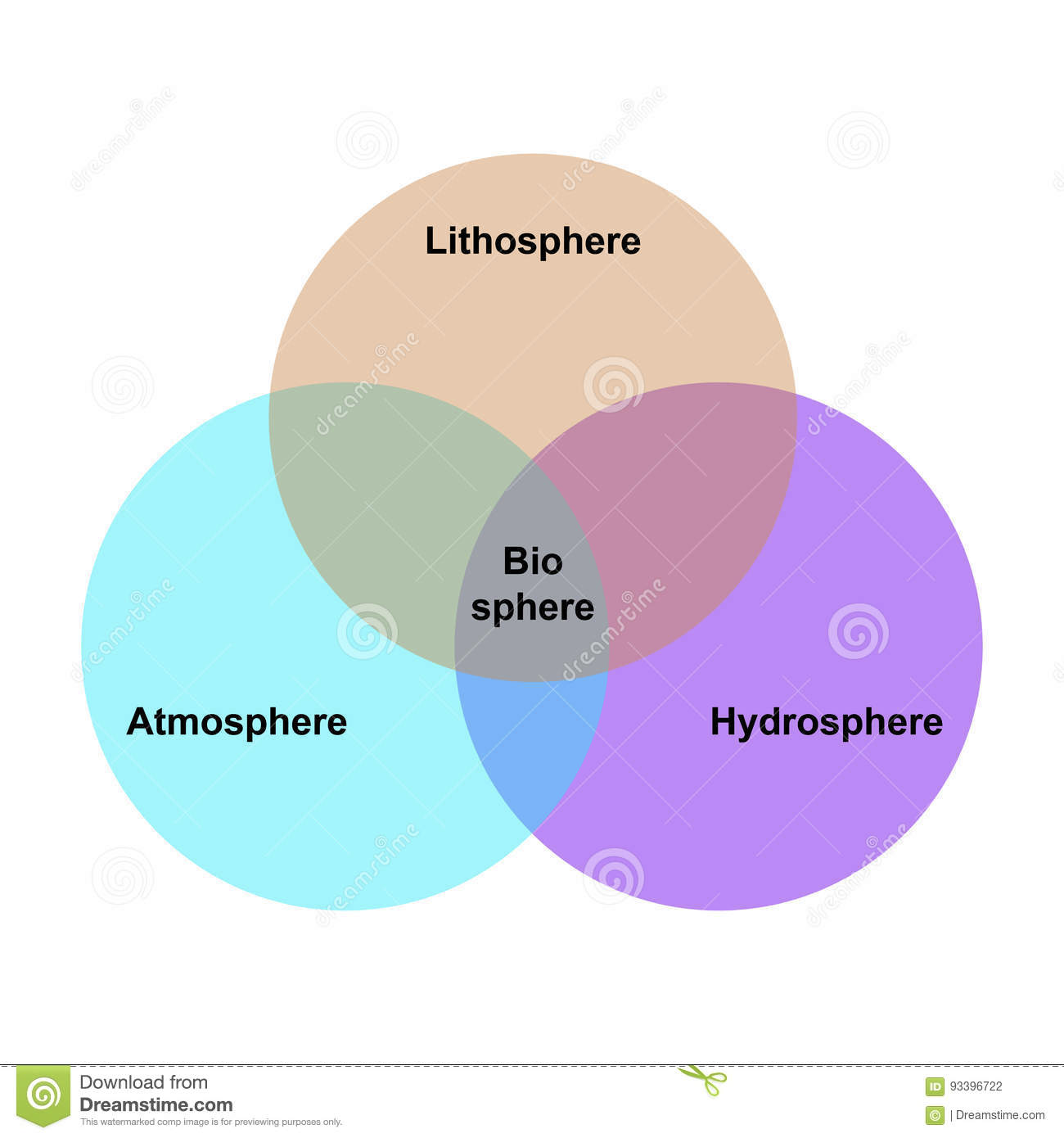
Systematic Approach
Looking at one or more aspects of the human-environmental system in context of spatial dimension. (ex. atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, human dimension)
7
New cards
Regional Approach
Analyze human-physical system in selected setting (e.g. geography of Europe)
8
New cards
Malthus
Focused on unchecked human population versus available resources. Created the J-curve which models exponential population growth.
9
New cards
Natural Resources
Any natural phenomena that is regarded as useful by humans. (ex. air, water, soil)
10
New cards
Renewable Resources
(AKA “flow resources”) capable of yielding output indefinitely if managed carefully (e.g. air, water, vegetation, soil)
11
New cards
Non-renewable Resources
(AKA “fund resources”) resources that cannot be used without depletion (ex. fossil fuels and metals)
12
New cards
Natural Hazards
Where the humans system is unable to absorb, use, buffer, or control aspects of the natural system. (ex. flooding, earthquakes, wildfires, hurricanes, volcanism, drought, etc.)
13
New cards
Arithmetic Density
Population to total area (e.g. population/square mile or population per square kilometer)
14
New cards
Physiological Density
Population to arable land (land capable of cultivation)
15
New cards
44%
Percent of the world population that lives within 150 km (93 miles) of the ocean.
16
New cards
8 billion
World population today.
17
New cards
10%
Percent of arable land on Earth.
18
New cards
China
Largest country in the world today (population)
19
New cards
24,901 miles
Earth’s circumference (in miles).
20
New cards
Eratosthenes
First to accurately postulate the Earth’s circumference.
21
New cards
Scale
The relation between length measured on a map image to the corresponding distance on the Earth’s surface.
22
New cards
larger, closer
The _____ the scale, the _____ the relation between map distance and ground distance.
23
New cards
smaller, larger
The _____ the denominator, the _____ the map scale.
24
New cards
Geoid
General shape of the Earth.
25
New cards
Latitude
0° to 90° North and South of the equator.
26
New cards
Parallels
Lines of equal latitude.
27
New cards
Longitude
0° to 180° East and West of the Prime Meridian.
28
New cards
Meridians
Lines of equal longitude.
29
New cards
Magnetic Declination
The difference between true north and magnetic north.
30
New cards
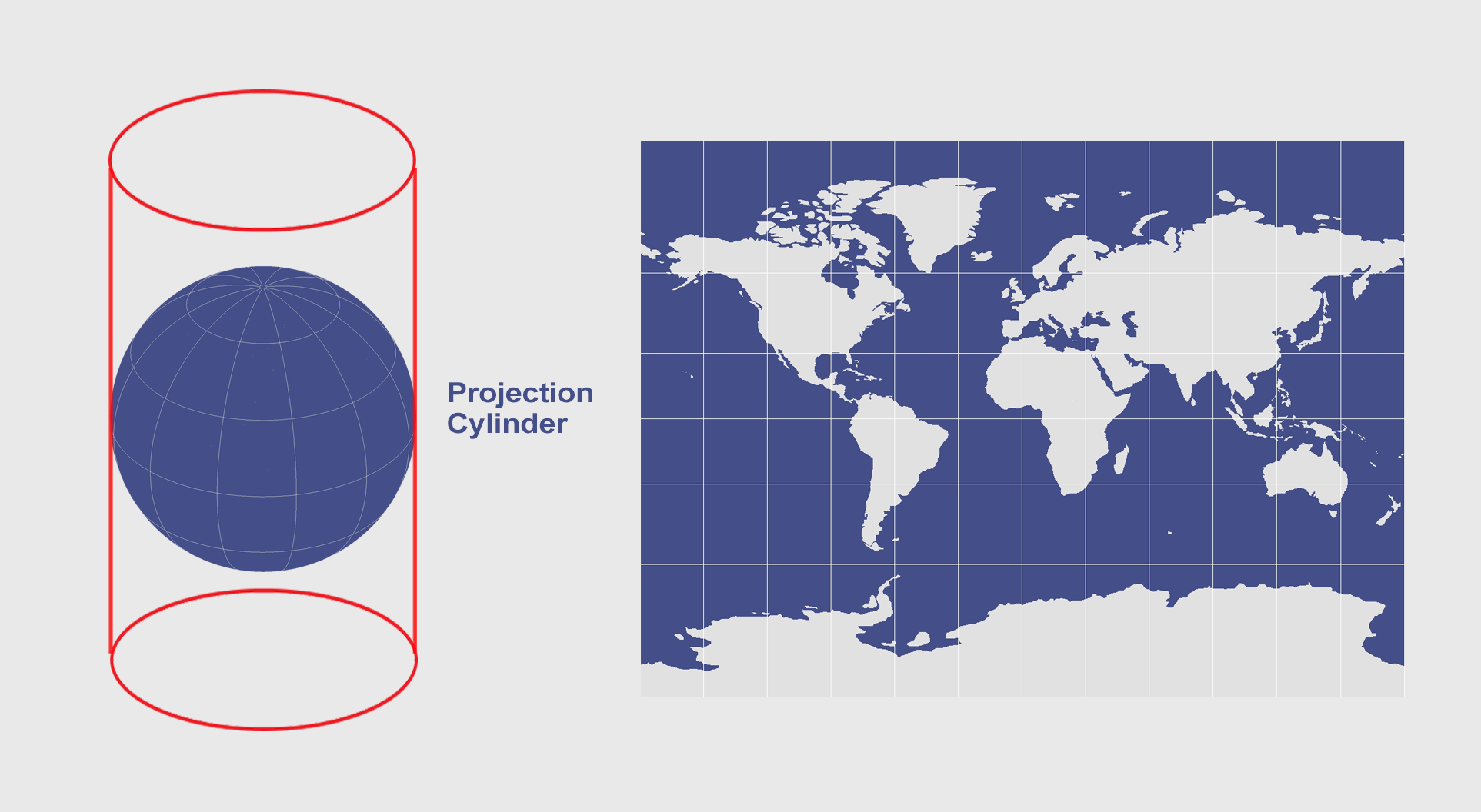
Cylindrical Map Projection
Map projection formed by placing a cylinder over a globe and transferring points, then unfolding (ex. Mercator projection -- distortions poleward)
31
New cards
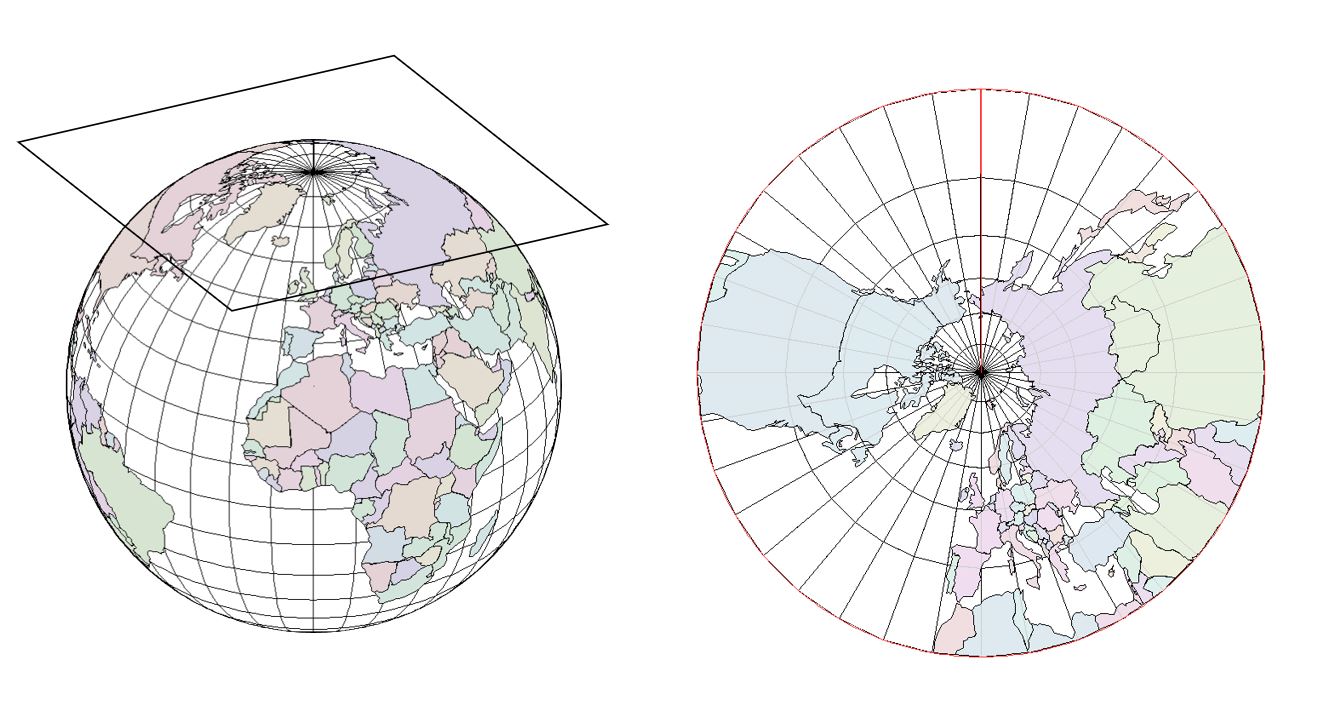
Plane or Azimuthal Projection
Map projection formed by placing a flat surface next to a globe -- distortions form away from the point of contact.
32
New cards
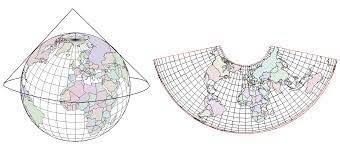
Conical Map Projection
Map projection formed by placing a cone on a globe. It helps converge the lines of longitude but has the issue of globe coverage.
33
New cards
Remote Sensing
Detecting the nature of an object while at some distance. Requires some type of detector/sensor. (often uses electromagnetic energy)
34
New cards
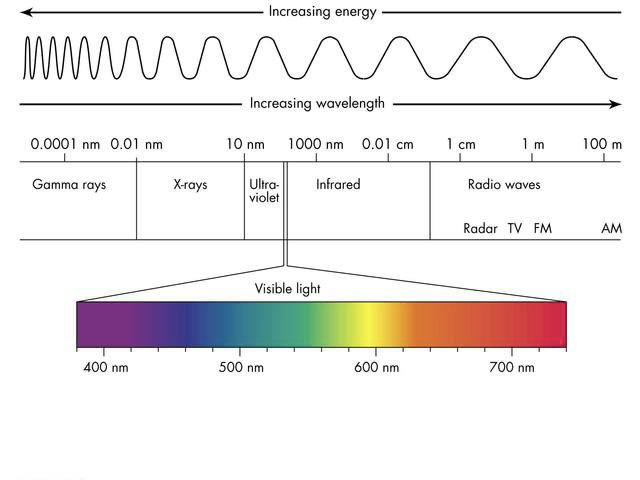
Electromagnetic Energy
Radiant energy traveling at the speed of light in harmonic wave patterns.
35
New cards
Passive Systems
Sensors that acquire images without providing a source of energy. (most common = the camera)
36
New cards
Gamma Rays
Electromagnetic energy with the shortest wavelength (and therefore the most energy).
37
New cards
Radio Waves
Electromagnetic energy with the longest wavelength (and therefore the least energy).
38
New cards
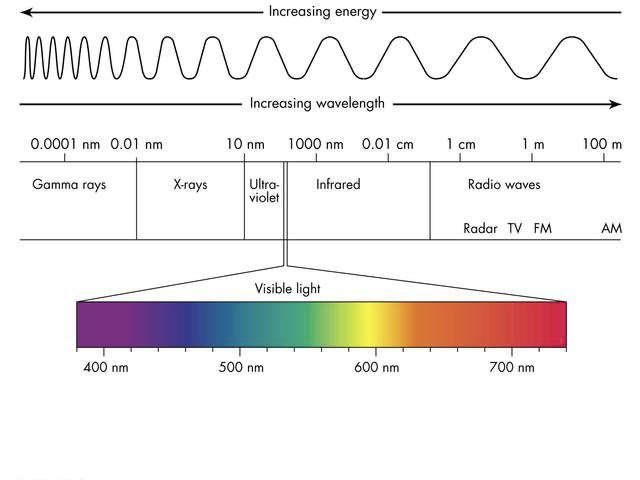
Radio waves, Microwaves, Infrared, Near Infrared, Visible light, Ultra-violet, X-rays, and Gamma Rays
Electromagnetic spectrum from longest to shortest wavelength (increasing energy).
39
New cards
Active Systems
Sensors that use a beam of wave energy as a source and send the beam toward an object. Part of the energy is reflected back to the source and is recorded by a detector. (ex. radar, lidar)
40
New cards
Sun-Synchronous satellites
In sync with the sun -- orbits near polar and completes one circle of the Earth every 90 to 100 minutes. Designed to pass a set point at approximately the same time.
41
New cards
Geo-Synchronous satellites
Satellites that move at the same rate as the Earth’s rotation. Fixed on one part of the globe and see one part of the globe constantly (used as weather satellites, tv satellites, communication satellites).
42
New cards
Radar
Uses short pulses of microwave radiation directed towards an object and detects the return echo of the microwave response. The strength of each return pulse and time received allows an image to be created of the object.
43
New cards
Frequency
Measures of waves in circles per second or Hertz (Hz).
44
New cards
Landsat
One of primary Earth sensing satellites (sun-synchronous orbit).
45
New cards
Counterclockwise
Direction of the Earth’s rotation (reference: looking down on the North Pole).
46
New cards
Diverts them to the right
Coriolis effect on winds and ocean currents in the Northern Hemisphere.
47
New cards
Diverts them to the left.
Coriolis effect on winds and ocean currents in the Southern Hemisphere.
48
New cards
Aphelion
When Earth is at its greatest distance from the sun.
49
New cards
Perihelion
When Earth is at its closest distance to the sun.
50
New cards
Tropic of Cancer
When the sun is at this position (23.5°N latitude) the Earth experiences the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere (Summer Solstice). (Same time, winter solstice in Southern Hemisphere).
51
New cards
Tropic of Capricorn
When the sun is at this position (23.5°S latitude) the Earth experiences the shortest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere (Winter Solstice). (Same time, summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere).
52
New cards
Subsolar Point
The point at which the sun is directly overhead.
53
New cards
Weather
Atmospheric conditions at any given time and place.
54
New cards
Climate
Weather conditions over time for a particular area or region of the Earth.
55
New cards
Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma
The states of matter are…
56
New cards
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, and Carbon Dioxide
Prominent gases in the atmosphere.
57
New cards
Nitrogen
Most prominent gas in the atmosphere (78%).
58
New cards
Albedo
The reflectivity of anything.
59
New cards
32%
The albedo of Earth is…
60
New cards
Barometer
Instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure.
61
New cards
About 0.2% to about 4%
Water vapor variation in the atmosphere.
62
New cards
Troposphere
The layer of atmosphere closest to the Earth’s surface. (main focus of geographers -- up to 9 miles thick)
63
New cards
Stratosphere
Second closest atmospheric layer to the Earth’s surface. (extends to about 31 miles above the surface)
64
New cards
Mesosphere
Layer of atmosphere between the stratosphere and the thermosphere. (third closest to the Earth’s surface -- up to 53 miles above)
65
New cards
Thermosphere
Atmospheric layer located between the mesosphere and the ionosphere (fourth closest layer to the surface -- between 53 and 372 miles above the ground)
66
New cards
Ionosphere
Atmospheric layer located between the thermosphere and the magnetosphere (fifth closest layer to the surface -- between 50 and 600 miles above the ground)
67
New cards
Magnetosphere
Atmospheric layer furthest from the surface and the outer edge of the Earth’s magnetic field (Van Allen Radiation Belt).
68
New cards
Solar Constant
The amount of incoming radiation from the sun (approx. 2 calories/centimeter squared/minute)
69
New cards
Isotherms
Lines of equal temperature.
70
New cards
Conduction
The process by which heat is directly transmitted to a substance when there is a difference in temperature between adjoining substances.
71
New cards
Convection
The transfer of heat by circulation or movement of the heated parts of liquid and gas -- where hotter, less dense material will rise; colder, dense material will sink.
72
New cards
Thermometer
Instrument that measures temperature.
73
New cards
Anemometer
Instrument that measures wind direction and speeds.
74
New cards
Psychrometer
Instrument that measures relative and specific humidity.
75
New cards
Pyranometer
Instrument that measures solar radiation.
76
New cards
Evaporation Pan
Instrument that measures evaporation rates.
77
New cards
Fahrenheit scale
Water boils at 212° and water freezes at 32°.
78
New cards
Celsius scale
Water boils at 100° and water freezes at 0°.
79
New cards
mid-afternoon
The maximum temperature generally occurs around…
80
New cards
just before sunrise
The coolest temperature (in general) recorded in a 24 hour period occurs…
81
New cards
Isobars
Lines of equal atmospheric pressure.
82
New cards
more, stronger
The _____ pressure variation, the _____ the wind.
83
New cards
high, low
Air moves from _____, to _____ pressure.
84
New cards
source
Winds are named after the…
85
New cards
Local winds
Winds driven by local effects (ex. sea and land breezes, mountain and valley breezes)
86
New cards
Santa Ana Winds
Strong, extremely dry downslope winds that originate inland and affect coastal Southern California.
87
New cards
Nor’easters (Northeasterlies)
Storms along the east coast of North America where the winds are strong from the northeast. (may occur at anytime, but most often from September to April)
88
New cards
Chinook Wind
Warming dry wind off the leeward side of a mountain range that can cause a rapid rise in temperature.
89
New cards
Cyclone
A low pressure cell → air converges and rises from the center.
90
New cards
Anticyclone
A high pressure cell → air descends to the center and diverges.
91
New cards
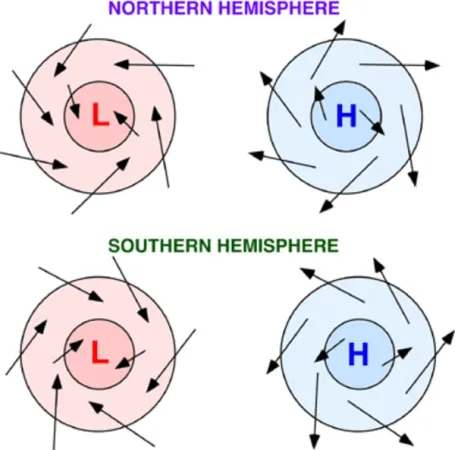
clockwise outspiral
In the Northern Hemisphere, anticyclones form winds moving in a…
92
New cards
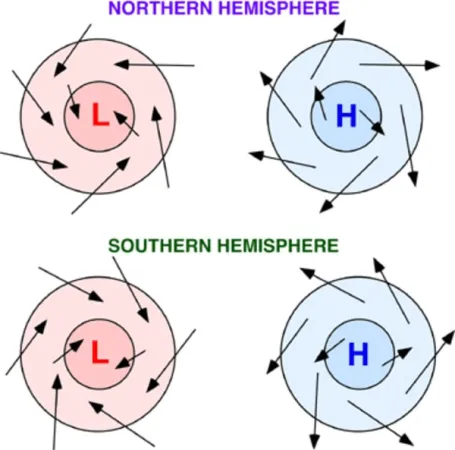
counterclockwise inspiral
In the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones form winds moving in a…
93
New cards
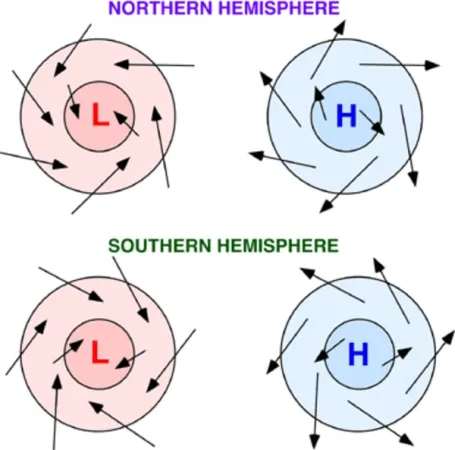
counterclockwise outspiral
In the Southern Hemisphere, anticyclones form winds moving in a…
94
New cards
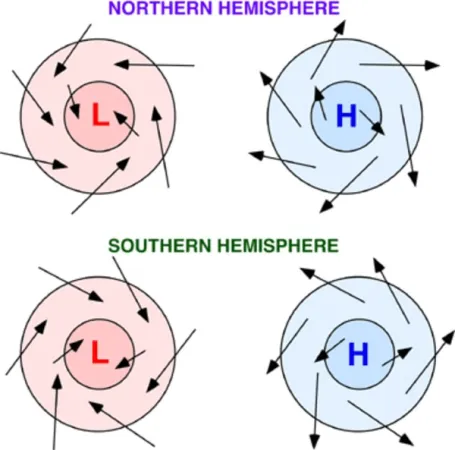
clockwise inspiral
In the Southern Hemisphere, cyclones form winds moving in a…
95
New cards
Air mass
A body of air in which upward gradients of temperature and moisture are relatively uniform for large areas.
96
New cards
A front
Surface of contact between two unlike air masses.
97
New cards
The Jet Stream
The core of the upper air westerlies.
98
New cards
Rossby Wave
Undulations in the jet stream.
99
New cards
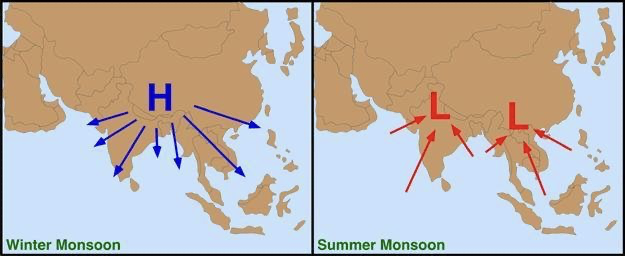
Winter Monsoon
Dry weather caused by high pressure cells and seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation. (very dry)
100
New cards
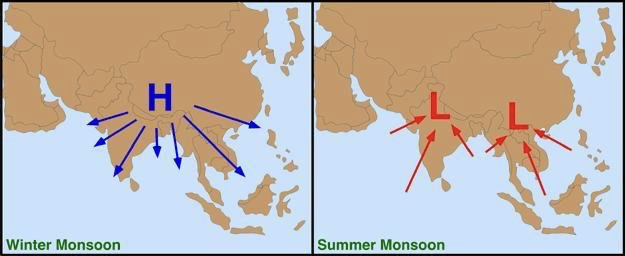
Summer Monsoon
Wet weather caused by low pressure cells and seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation. (lots of moisture)